Similar presentations:
Disturbances of emotions
1. DISTURBANCES OF EMOTIONS
2. Emotions
- are responses in the form of subjectivelytinctured feelings of an individual which
reflect significance of an acting stimulus or
a result of his own act for him
3. FUNCTION OF EMOTIONS
Reflective functiontarget function
Information function
Enabling function
regulatory function
reinforces the function
4. FUNCTION OF EMOTIONS
Switchingfunction
Adaptive function
Communicative
function
Protective function
5. STAGES OF DEVELOPMENT OF EMOTIONS
Stage1 - the newborn
- the predominance of
the instincts and
especially selfpreservation instinct
6. STAGES OF DEVELOPMENT OF EMOTIONS
2STAGES OF DEVELOPMENT OF
EMOTIONS
stage - the stage of the
organic feeling - processing
information from the extraand interceptors, the
emergence of unstable
figurative representations of
reality to the experience of
meeting a child /
dissatisfaction, pleasant /
unpleasant, etc.
7. STAGES OF DEVELOPMENT OF EMOTIONS
Stage3–
3 - 4 years to 12 - 14
years old - a stage
epikricheskih emotions
and organic needs - the
coupling of developing
emotions with organic
needs
8. STAGES OF DEVELOPMENT OF EMOTIONS
4 STAGE –from 10 - 12 years
old to 22 years old a stage of mental
self-expression "cortical emotion"
9. COMPONENTS emotional functioning
INTENSITYTHE
(Strength, depth)
BASIC BACKGROUND
positive
negative
10. CLASSIFICATION OF EMOTIONS
STHENIC- Increase
the functioning of
the organism
ASTHENIC
- Reducing
the vital functions of
the body
11. CLASSIFICATION OF EMOTIONS
EMOTIONALSTATE
(mood)
EMOTIONAL
EMOTIONAL
REACTIONS
(affect)
RELATIONS
(feelings)
12. CLASSIFICATION OF EMOTIONS
AFFECT- a special
emotional state, which is a
very strong short-term
excitement, flash emotions
(fear, anger, rage, despair,
and so forth.), Rapidly
flowing and characterized by
sudden onset, short
duration, pronounced
changes of consciousness,
disturbance of volitional
control over the actions.
13. CLASSIFICATION OF EMOTIONS
Atphysiological affect
arisen state is the
intense emotion that
dominates the mind of
man, reduces his
control over his actions,
is characterized by a
narrowing of
consciousness, specific
inhibition of intellectual
activity.
14. CLASSIFICATION OF EMOTIONS
Pathological affect ischaracterized by full
dimming of
consciousness and
uncontrollable impulsive
action, more aggressive
and destructive nature.
15. DISORDERS OF EMOTIONS
QUANTITATIVE VIOLATIONHyperthymia
- painful
emotions increase...
Gipotimiа - painful emotions
reduction
Apathy - lack of higher emotions
- Emotional stupidity (emotional
-
Mania
persistent
painful mood
enhancement
Depression
-a
persistent painful
depressed mood
Moria
Euphoria
-
persistent
painful mood
enhancement +
motor
retardation
persistent
painful mood
enhancement +
motor excitation
+ silliness
impoverishment) - the absence of higher
and lower emotions
- Emotional monotony - the
weakening of expression of emotional
reactions
- Emotional coldness - indifference,
indifference to loved ones
- Emotional brutalization - loss of
thin differentiated emotions (tact,
empathy, etc.)
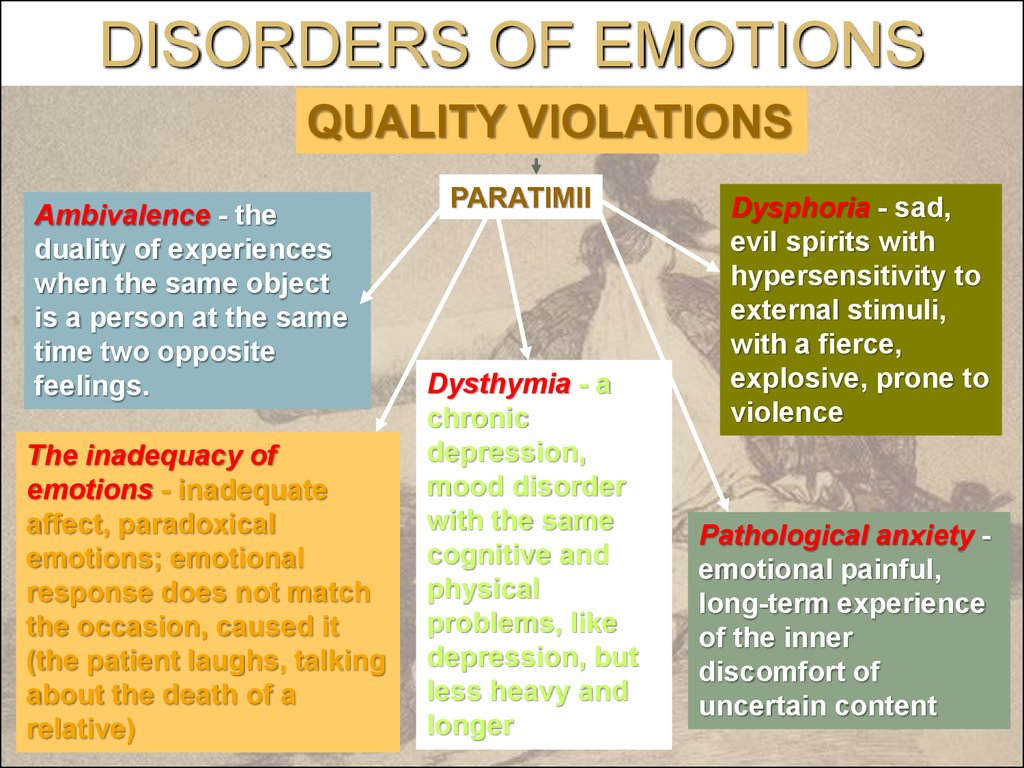
16. РАССТРОЙСТВА ЭМОЦИЙ
DISORDERSOF EMOTIONS
КОЛИЧЕСТВЕННЫЕ
НАРУШЕНИЕ
QUALITY VIOLATIONS
ГИПЕРТИМИЯ
ГИПОТИМИЯ
PARATIMII
Dysphoria - эмоций
sad,
– болезненное
увеличение эмоций
– болезненное уменьшение
Ambivalence
- the
evil spirits with
duality of experiences
– апатия – отсутствие высших
hypersensitivity to
when
the same object
мания
эмоций
депрессия
external stimuli,
is
a
person
at
the
same
– стойкое
– эмоциональная тупость
– стойкое
with a fierce,
болезненное
time two opposite
(эмоциональное
оскудение)
–
болезненное
explosive,
prone to
повышение
Dysthymia
-a
feelings.
отсутствие
высших
и низших эмоций
понижение
violence
настроения
chronic – эмоциональная
монотонность –
настроения
depression,
The inadequacy of
ослабление выразительности
mood disorder
эмоциональных реакций
emotions - inadequate
мория
with the –same
affect,
paradoxical
эмоциональная
холодность
–
эйфория
Pathological
anxiety
- стойкое
cognitive
and
равнодушие,
безразличие к близким
emotions;
emotional
болезненное
emotional painful,
- стойкое
physical
– эмоциональное огрубение –
response
does not повышение
match
болезненное
long-term experience
утрата
problems,
likeтонких дифференцированных
the
occasion, caused
it
настроения
+
повышение
of the inner
эмоций
(деликатность,
сопереживание
(the
patient+laughs,двигательное
talking depression, but
настроения
discomfort
of
и
т.п.)
less
+ heavy and
двигательная
about
the death of возбуждение
a
uncertain content
дурашливость
заторможенность
longer
relative)
17. РАССТРОЙСТВА ЭМОЦИЙ
SPHEREPATHOLOGY
EMOTIONAL
РАССТРОЙСТВА
ЭМОЦИЙ
КОЛИЧЕСТВЕННЫЕ
НАРУШЕНИЕ
КАЧЕСТВЕННЫЕ
НАРУШЕНИЯ
AFFECTIVE
SYNDROMES
ГИПЕРТИМИЯ
–
ГИПОТИМИЯ
ПАРАТИМИИ
болезненное увеличение эмоций
– болезненное уменьшение эмоций
–
апатия – отсутствие высших
мания
эмоций
depressive депрессия
– стойкое
– эмоциональная тупость
– стойкое
экстаз
дисфория
болезненное
(эмоциональное оскудение)
–
амбивалентность болезненное
повышение
отсутствие высших и низших эмоций
понижение
настроения
– эмоциональная монотонность –
настроения
ослабление выразительности
manic
эмоциональных реакций
дистимия
мория
– эмоциональная холодность –
эйфория
- стойкое
равнодушие, безразличие к близким
болезненное
- стойкое
– эмоциональное огрубение –
повышение
болезненное
утрата тонких дифференцированных
dysphoric
настроения +
повышение
неадекватность
патологическая
эмоций (деликатность, сопереживание
двигательное
настроения
+
эмоций
тревога
и т.п.)
возбуждение +
двигательная
заторможенность
дурашливость
18.
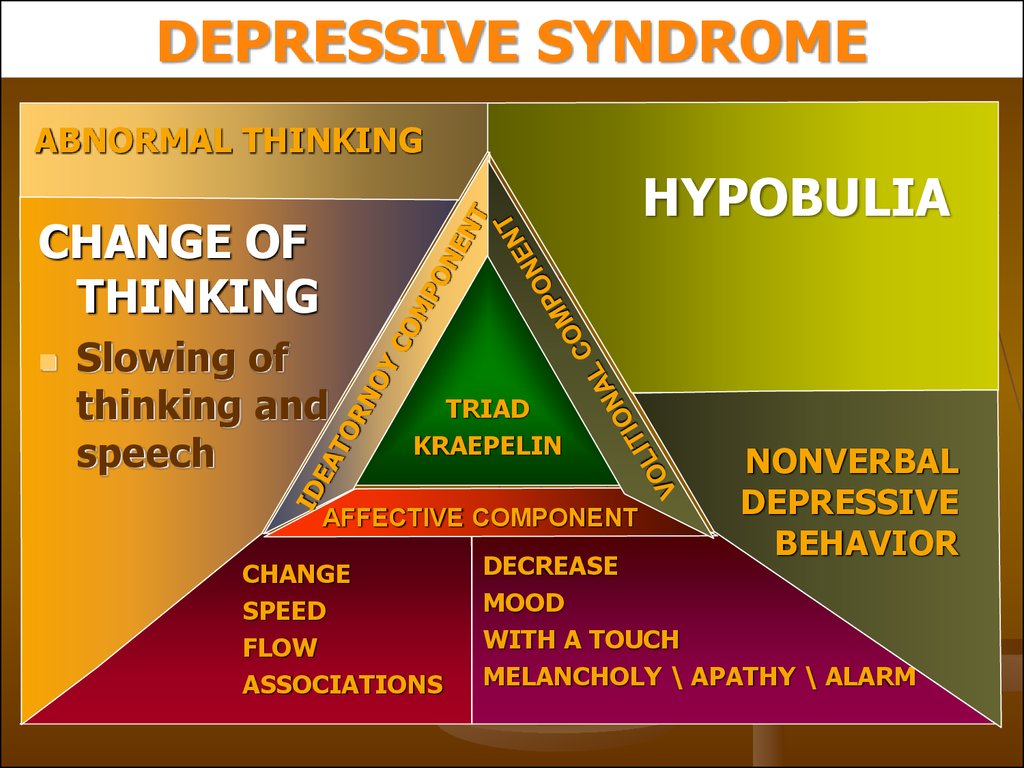
DEPRESSIVE SYNDROMEABNORMAL THINKING
HYPOBULIA
CHANGE OF
THINKING
Slowing of
thinking and
speech
TRIAD
KRAEPELIN
AFFECTIVE COMPONENT
CHANGE
SPEED
FLOW
ASSOCIATIONS
NONVERBAL
DEPRESSIVE
BEHAVIOR
DECREASE
MOOD
WITH A TOUCH
MELANCHOLY \ APATHY \ ALARM
19.
DEPRESSIVE SYNDROMECOMPLEX SYMPATHETIC-TONIC SYMPTOMS
PROTOPOPOV
TRIAD
CONSTIPATION
20. Depressive syndrome
Clinical variants of depression :- anaesthetic
- with phobias
- with anxiety
- agitated depression
- depressive stupor
- psychotic depression
- “mask” depression
- subdepression
21. MANIC SYNDROME
Painfullyelevated
mood
Motor
Increasing
excitation, instincts
giperbuliya (food, sex )
Violation
of thinking:
acceleration of associative
processes tahipsihiya
delusions of grandeur
(sometimes)
Shortening
the
duration of sleep
22. MANIC SYNDROME
Clinical variants :-
with euphoria
with moria
with irritability
unproductive
psychotic
23. DYSPHORIA
- irritability, maliciousness, dissatisfactionaccompanied by aggression and
destructive actions
1) dysphoric
reaction
2) dysphoric
background
24.
WILLWill
- the mental process of
deliberate and targeted regulation
of human activities and their
behavior in order to achieve this
goal
25. Stages of volitional process and his violation
Attraction - primary, instinctive, emotionalmanifestation of human needs, unawareness
motivation
Lucid
attraction - wish
26. Stages of volitional process and his violation
origin of motive -incentive to action;
psycho-physiological
process that controls
human behavior,
defining its direction,
organization, activity
and stability
27. Stages of volitional process and his violation
fight of reasonsThe process of
analyzing the
ways and
possibilities of
satisfying the
desire
28. Stages of volitional process and his violation
decision-choicemaking -
a route and method of
satisfying the desire
29. Stages of volitional process and his violation
choice of ways of realization30. Stages of volitional process and his violation
execution of decision31. Violation of volitional process
DISORDERS DESIRE (INSTINCT)Violation of volitional process
EATING DISORDERS ATTRACTION
GAIN
Quantitative :
BULIMIA
POLYPHAGIA
- hypobulia
- hyperbulia
- abulia
High-quality :
- parabulias
WEAKENING
ANOREXIA
PERVERSION
EATING INEDIBLE
32. Sickly strengthening of food instinct
Bulimia -uncontrolled food
intake in a large
amount
Polyphagia increased appetite
and voracity. The
constant need for
food
33. Sickly weakening of food instinct
Anorexia –a syndrome
consisting in the
complete absence
of appetite with
the objective needs
of the body in the
diet
34. Sickly weakening of food instinct
EATINGINEDIBLE
Sickly
weakening
of food
instinct
Sustainable
Anorexia –
a syndrome
craving
for eating
consisting in the
non-food
complete absence
products
(such
of appetite
with as
the objective
needs
land,
paint chips,
of the body in the
etc.)
diet
35. Violation of volitional process
DISORDERS DESIRE (INSTINCT)Violation of volitional process
DISORDER SURVIVAL INSTINCT
GAIN
Quantitative :
ACTIVE
PASSIVE
DEFENSIVE
- hypobulia DEFENSIVE
POSITION
POSITION
- hyperbulia
(FEAR, PANIC)
(AGGRESSI
ON)
- abulia
High-quality :
- parabulias
WEAKENING
PERVERSION
SELF-TORTURE
SUICIDE
36. Sickly strengthening of self-preservation instinct
Sickly strengthening of selfpreservation instinctAggression - motivated
destructive behavior that is
contrary to the norms of
coexistence of the people,
causing damage to their targets
Panic - adversely affect
painted caused by a real or
imaginary danger.
37. Sickly weakening self-preservation instinct
Sickly weakening selfpreservation instinctSuicide -
deliberate
deprivation of
life itself
independent
and voluntary
38. Perversion of instincts
Auto aggression -intentional infliction ofphysical damage itself
39. Violation of volitional process
DISORDERS DESIRE (INSTINCT)Violation of volitional process
DISORDERS OF SEXUAL ATTRACTION
WEAKENING
GAIN
Quantitative :
OVERSEXED
HYPOSEXUALITY
- hypobulia
(SATIRIAZIS,NYMPHOMANIA)
(FRIGIDITY)
- hyperbulia
- abulia
PERVERSION
High-quality :
- parabulias
SEXUAL
DEVIANCY
40. Sickly weakening of sexual instinct
impotencefrigidity
41. Sickly strengthening of sexual instinct
SatyriasisNymphomania
42. Classification of instinctive drives
Self-preservation43. Perversion of instincts
Sexualnarcissism
sadism
masochism
exhibitionism
voyeurism
44. PARABULIAS ambitendenc
theexistence of antagonistic emotions,
ideas or desires in relation to one and the
same person, the subject or the situation










































 medicine
medicine








