Similar presentations:
Thermodynamics of biological systems
1.
THERMODYNAMICSOF BIOLOGICAL SYSTEMS
2.
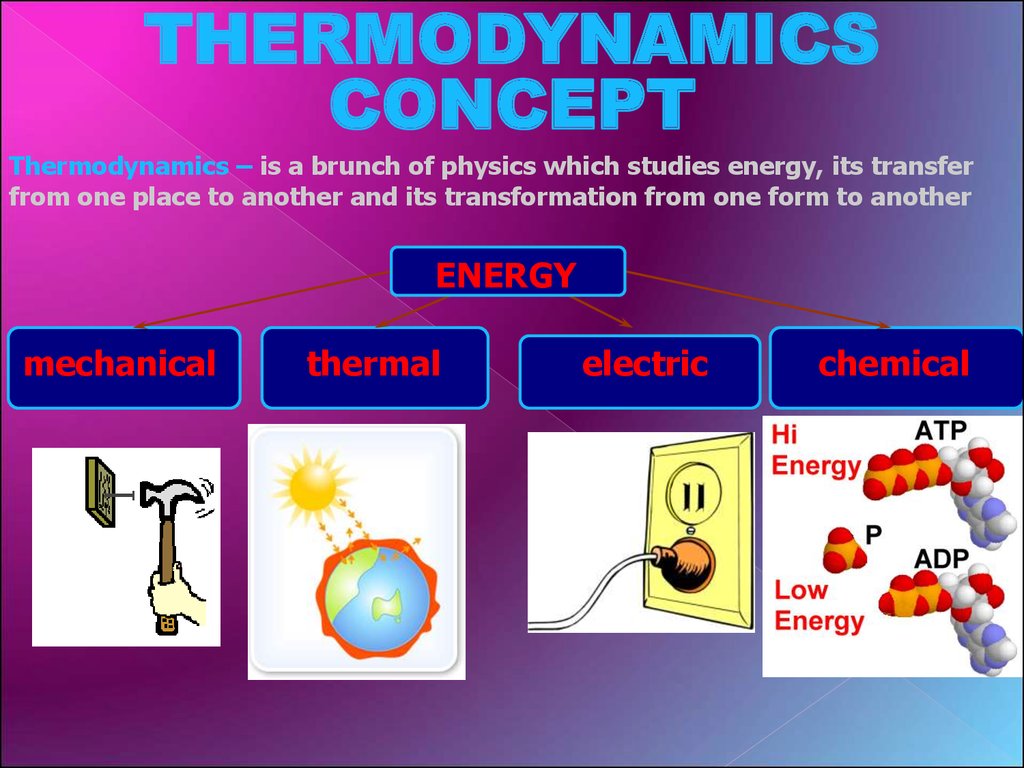
THERMODYNAMICSCONCEPT
Thermodynamics – is a brunch of physics which studies energy, its transfer
from one place to another and its transformation from one form to another
ENERGY
mechanical
thermal
electric
chemical
3.
THERMODYNAMIC SYSTEMenergy
energy
closed
system
open
system
х
energy
Isolated
system
х
х
matter
matter
matter
4.
ISOLATED SYSTEMThis system doesn’t exchange energy or matter with the surroundings.
Universe is considered to be an
isolated system
5.
CLOSED SYSTEMA system, that doesn’t exchange matter but exchanges
energy with the surroundings.
6.
OPENED SYSTEMA system, that exchanges both matter and energy with surroundings.
All living organisms are opened systems.
7.
WORK & HEAT EXCHANGEsurrounding
ΔU
system
Q>0
A>0
Q=0
Q
8.
THE FIRST LAW OFTHERMODYNAMICS
ΔU = Q – A.
heat Q
work А
U1
U2
state 1
ΔU
=Q–A
state 2
9.
THE SECOND LAW OFTHERMODYNAMICS
Heat flow direction
Heat equilibrium
Impossible heat
flow direction
10.
IRREVERSIBILITY OF THERMALPROCESSES
11.
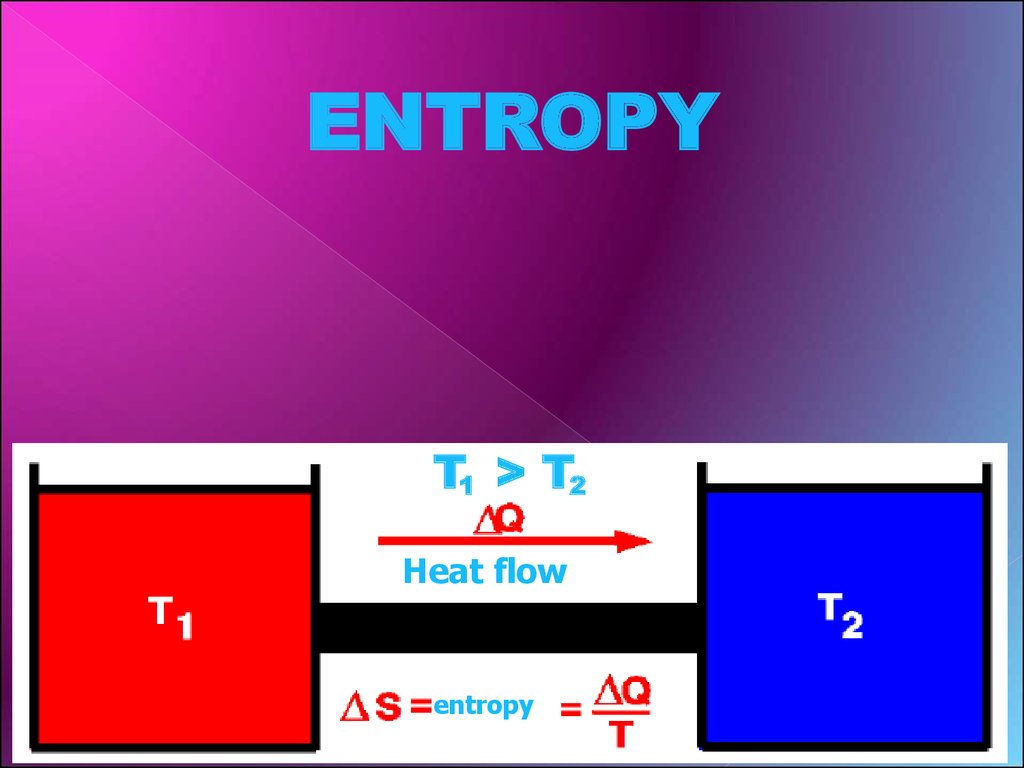
ENTROPYT1 > T2
Heat flow
entropy
12.
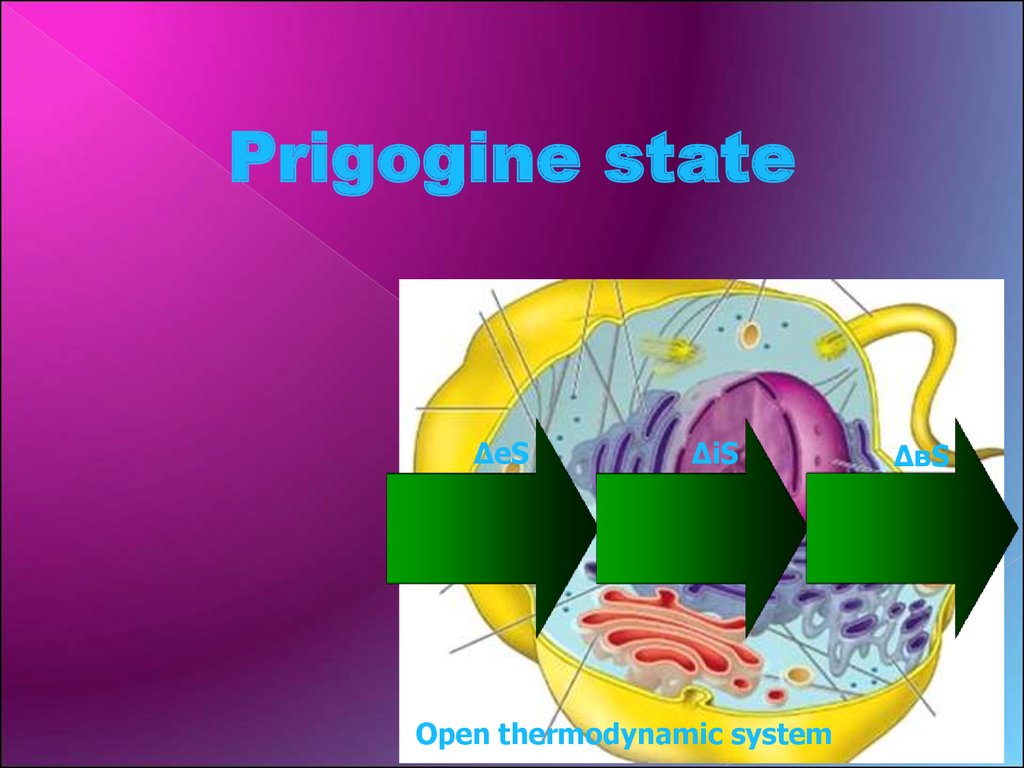
Prigogine stateΔeS
ΔiS
Open thermodynamic system
ΔвS
13.
BIOCALORYMETRYBiocalorymetry – is a measurement of the energetics of biological
processes such as biochemical reactions, association of ligands to
biological macromolecules, folding of proteins into their native
conformations, phase transitions in biomembranes, and enzymatic
reactions, among others.
14.
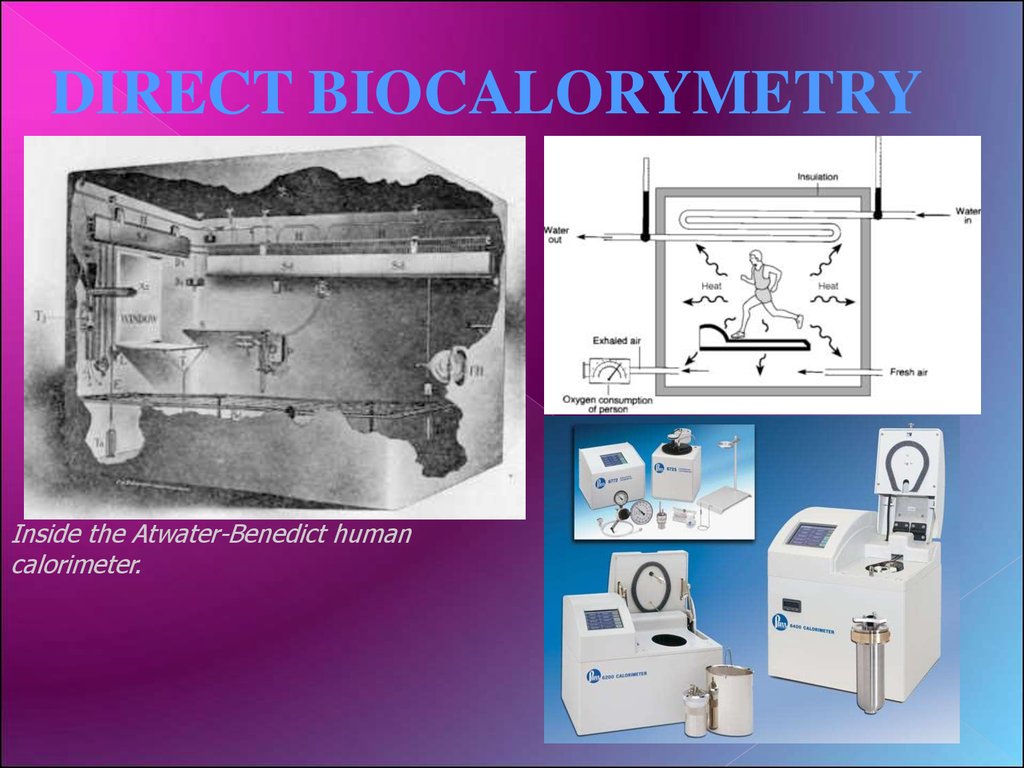
DIRECT BIOCALORYMETRYInside the Atwater-Benedict human
calorimeter.
15.
DIRECT BIOCALORYMETRY16.
INDIRECT BIOCALORYMETRYCALORIMETER
17.
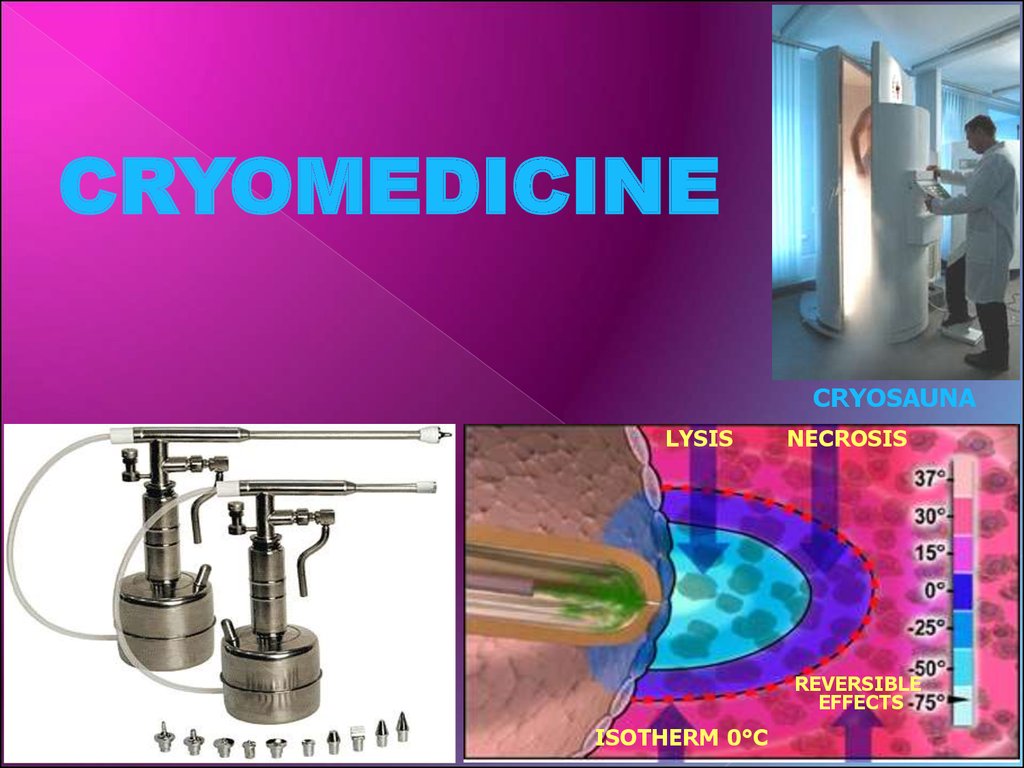
CRYOMEDICINECRYOSAUNA
LYSIS
NECROSIS
REVERSIBLE
EFFECTS
ISOTHERM 0°С












 biology
biology physics
physics








