Similar presentations:
Conditional sentences
1.
Conditional sentences:3 types
Principal clause
Check how much you
remember!
If-clause
I. I will go for a walk
if the weather is fine.
II. I would go for a walk
if the weather were fine.
III. I would have gone for
a walk
if the weather had been
fine.
2.
The Use of Forms ExpressingUnreality (the Oblique Moods) in
COMPLEX SENTENCES with a
SUBORDINATE CLAUSE of
CONDITION
3.
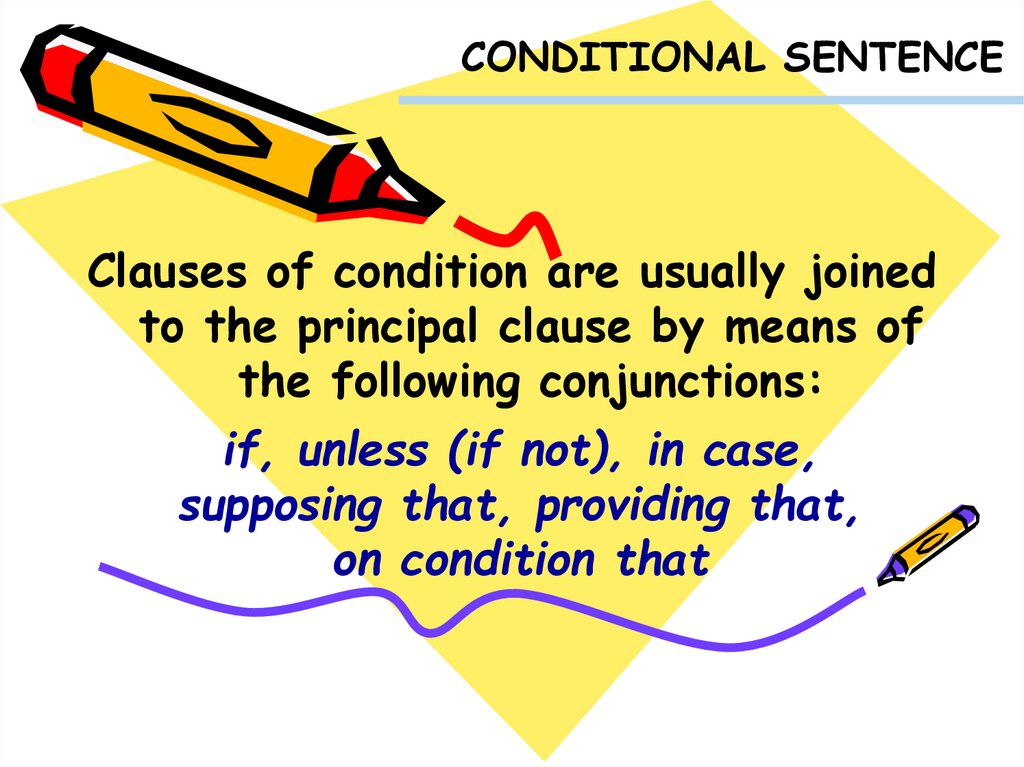
CONDITIONAL SENTENCEClauses of condition are usually joined
to the principal clause by means of
the following conjunctions:
if, unless (if not), in case,
supposing that, providing that,
on condition that
4.
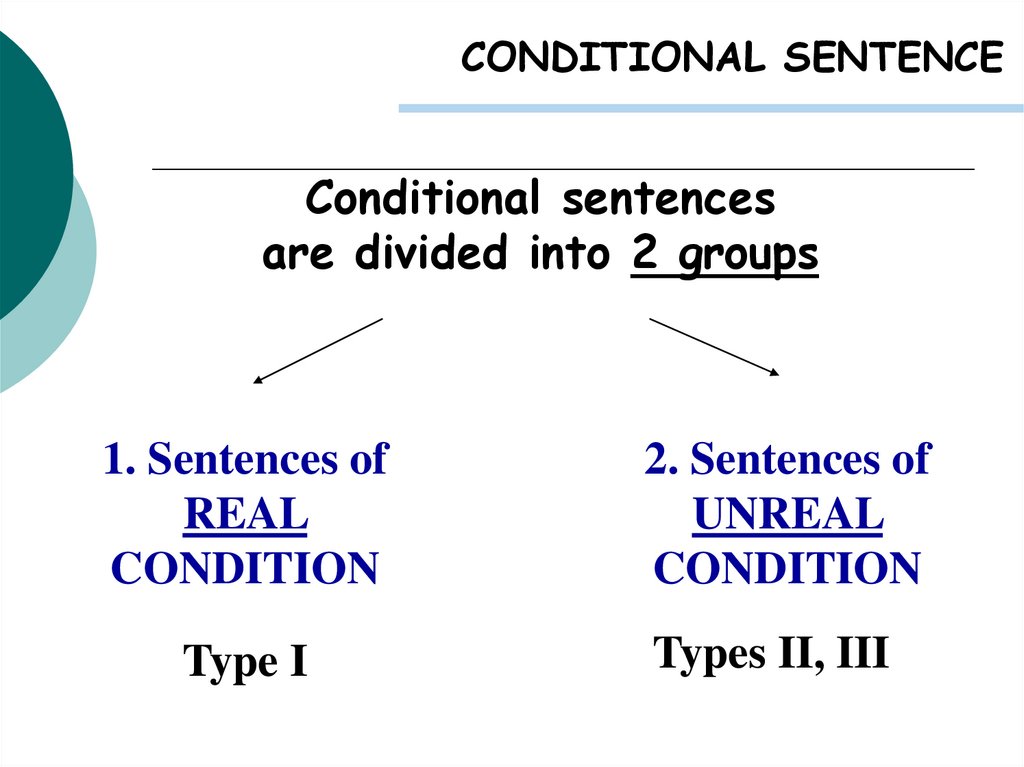
CONDITIONAL SENTENCEConditional sentences
are divided into 2 groups
1. Sentences of
REAL
CONDITION
Type I
2. Sentences of
UNREAL
CONDITION
Types II, III
5.
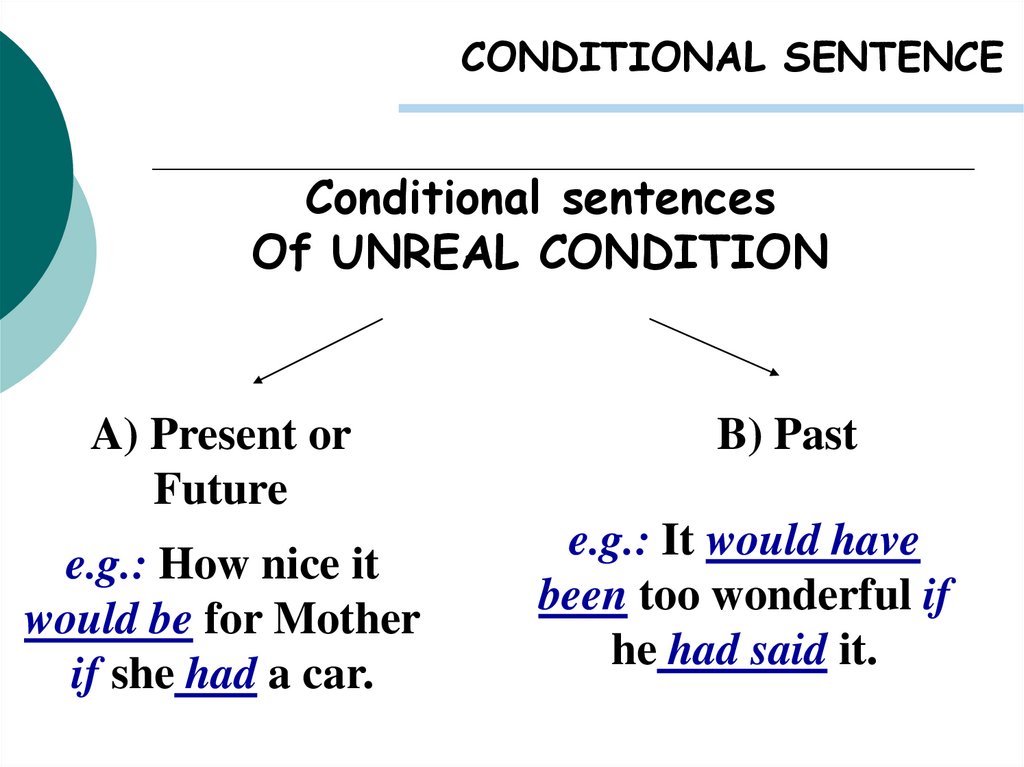
CONDITIONAL SENTENCEConditional sentences
Of UNREAL CONDITION
A) Present or
Future
e.g.: How nice it
would be for Mother
if she had a car.
B) Past
e.g.: It would have
been too wonderful if
he had said it.
6.
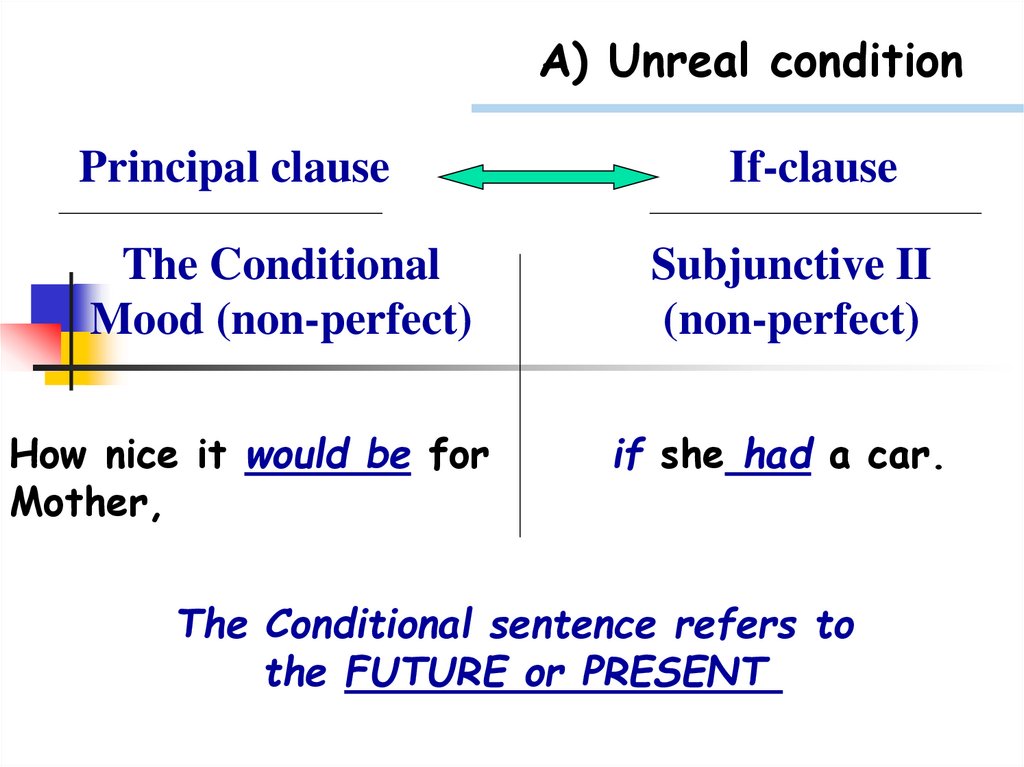
A) Unreal conditionPrincipal clause
The Conditional
Mood (non-perfect)
How nice it would be for
Mother,
If-clause
Subjunctive II
(non-perfect)
if she had a car.
The Conditional sentence refers to
the FUTURE or PRESENT
7.
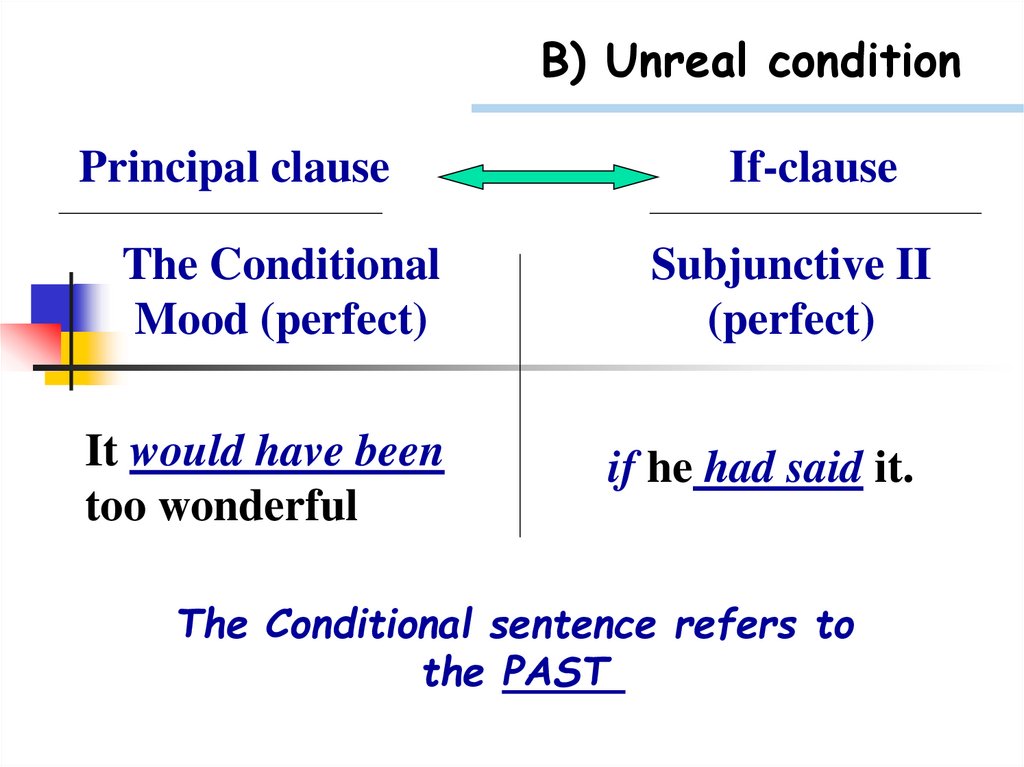
B) Unreal conditionPrincipal clause
The Conditional
Mood (perfect)
It would have been
too wonderful
If-clause
Subjunctive II
(perfect)
if he had said it.
The Conditional sentence refers to
the PAST
8.
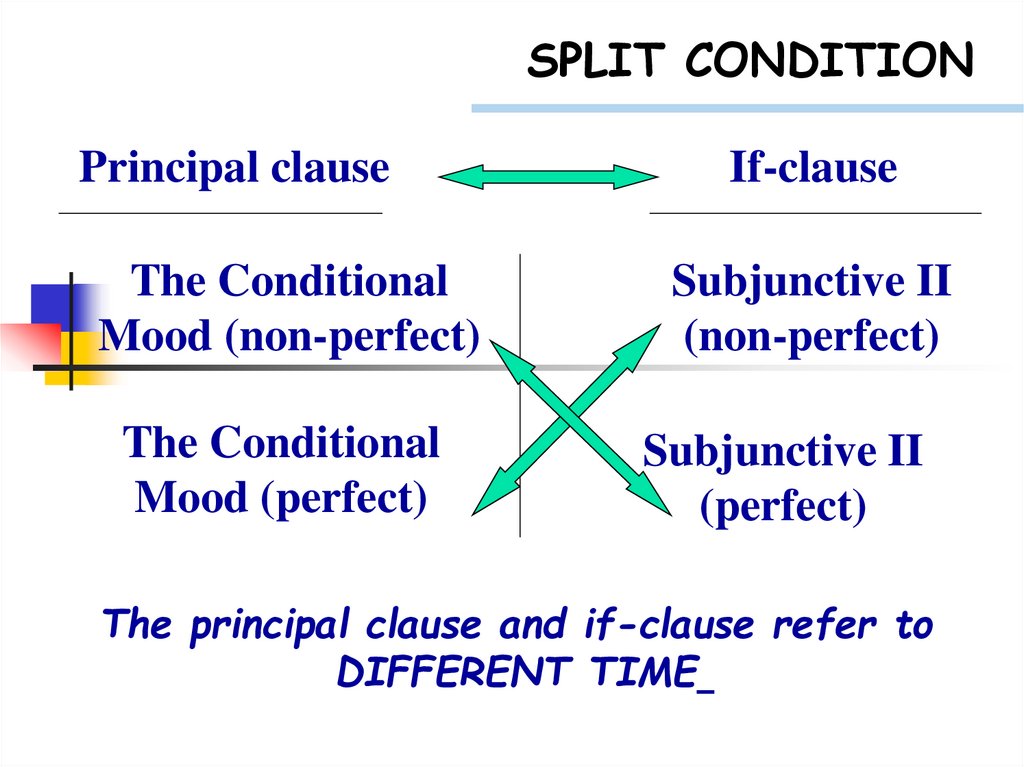
SPLIT CONDITIONPrincipal clause
The Conditional
Mood (non-perfect)
The Conditional
Mood (perfect)
If-clause
Subjunctive II
(non-perfect)
Subjunctive II
(perfect)
The principal clause and if-clause refer to
DIFFERENT TIME
9.
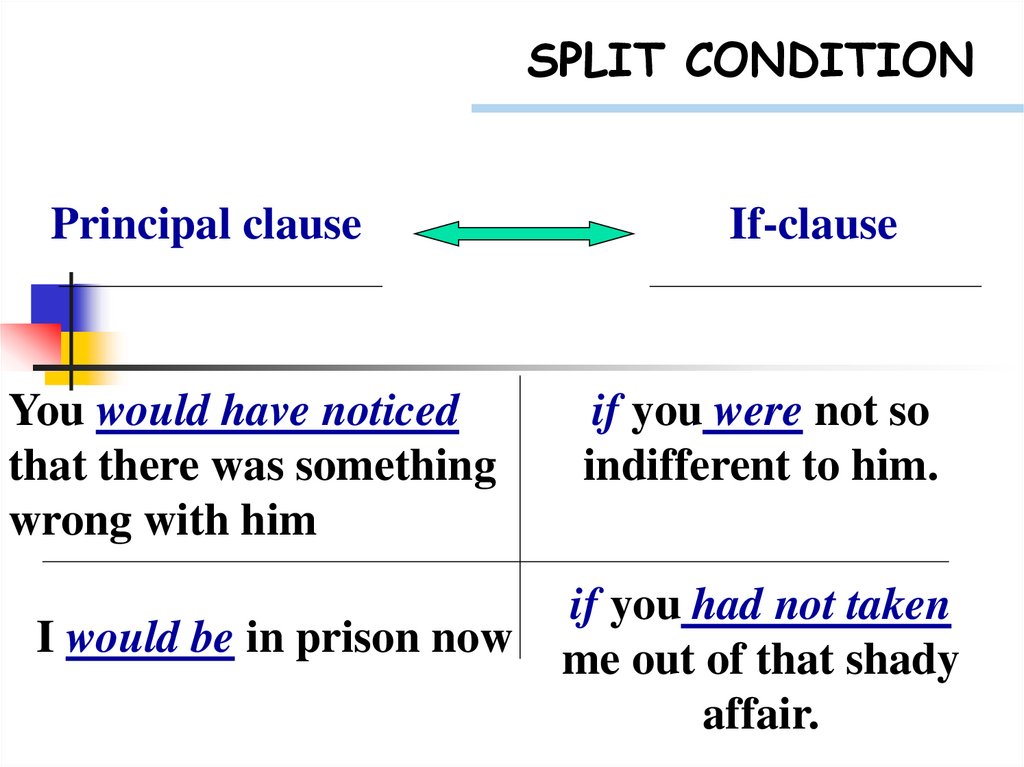
SPLIT CONDITIONPrincipal clause
You would have noticed
that there was something
wrong with him
I would be in prison now
If-clause
if you were not so
indifferent to him.
if you had not taken
me out of that shady
affair.

 english
english








