Similar presentations:
Biological mutagens factors
1.
BIOLOGICAL MUTAGENS FACTORS2.
WHATS IS BIOLOGICAL MUTAGENS ?A mutation is a change in a DNA sequence. Mutations can result
from DNA copying mistakes made during cell division, exposure to
ionizing radiation, exposure to chemicals called mutagens, or
infection by viruses.
3.
COMMON EXAMPLES OF BIOLOGICAL MUTAGENS:TRANSPOSABLE ELEMENTSBACTERIA
VIRUSES
4.
TRANSPOSABLE ELEMENTS•Transposons and IS elements are small sequence of DNA that
moves from one site to another along DNA strand and causes
mutation. Transposons and insertion sequences are also known
as jumping gene. These sequence contains gene which codes
the enzyme transposase which helps in transposition of these
sequence from one site to other.
5.
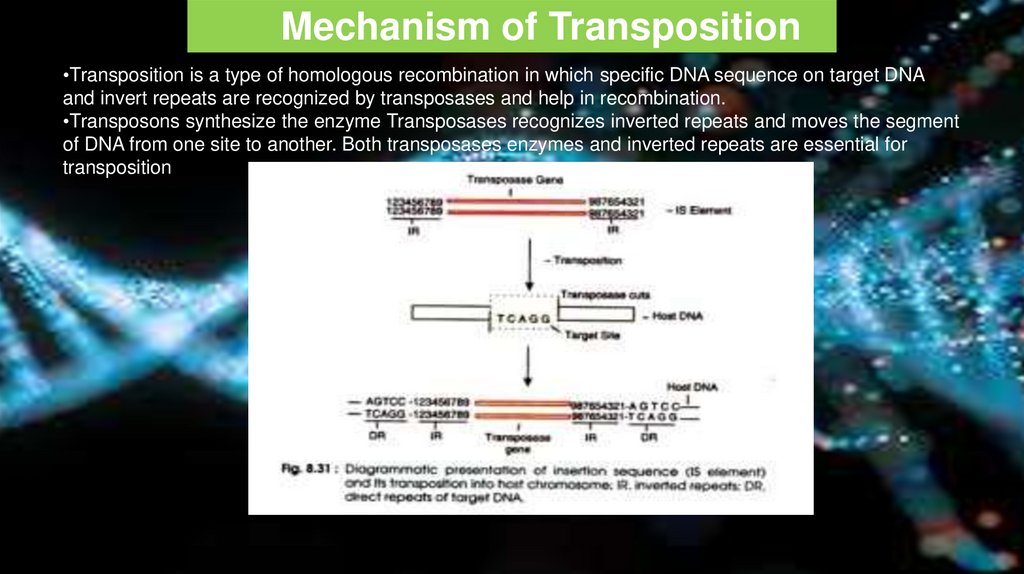
Mechanism of Transposition•Transposition is a type of homologous recombination in which specific DNA sequence on target DNA
and invert repeats are recognized by transposases and help in recombination.
•Transposons synthesize the enzyme Transposases recognizes inverted repeats and moves the segment
of DNA from one site to another. Both transposases enzymes and inverted repeats are essential for
transposition
6.
BACTERIASome bacteria such as Helicobacter pylori cause inflammation during
which oxidative species are produced, causing DNA damage and
reducing efficiency of DNA repair systems, thereby increasing mutation.
7.
VIRUSVirus causes insertion of their DNA into the
genome of host organism and disrupts genetic
function.
Some viruses causes the cancer
e.g. Rous sarcoma virus
SOME OTHER MUTAGENIC VIRUSES:RUBELLA VIRUS
CYTOMEGALOVIRUS
HEPATITIS B VIRUS
8.
Mutagen test systems• Ames test – This is the most commonly used test, and
Salmonella typhimurium strains deficient in histidine biosynthesis
are used in this test. The test checks for mutants that can revert to
wild-type.
• Resistance to 8-azaguanine in S. typhimurium – Similar to Ames
test, but instead of reverse mutation, it checks for forward mutation
that confer resistance to 8-Azaguanine in a histidine revertant
strain.
9.
EFFECTS OF MUTAGENSMutagens can cause changes to the DNA and are therefore genotoxic . They can affect the transcription and replication of the DNA, which in severe
cases can lead to cell death. The mutagen produces mutations in the DNA, and deleterious mutation can result in aberrant, impaired or loss of function
for a particular gene, and accumulation of mutations may lead to cancer. Mutagens may therefore be also carcinogens. However, some mutagens exert
their mutagenic effect through their metabolites, and therefore whether such mutagens actually become carcinogenic may be dependent on the
metabolic processes of an organism, and a compound shown to be mutagenic in one organism may not necessarily be carcinogenic in another.
Different mutagens act on the DNA differently. Powerful mutagens may result in chromosomal instability,causing chromosomal breakages and
rearrangement of the chromosomes such as translocation, deletion, and inversion. Such mutagens are called clastogens.
Mutagens may also modify the DNA sequence; the changes in nucleic acid sequences by mutations include substitution of nucleotide basepairs and insertions and deletions of one or more nucleotides in DNA sequences. Although some of these mutations are lethal or cause serious disease,
many have minor effects as they do not result in residue changes that have significant effect on the structure and function of the proteins. Many
mutations are silent mutations, causing no visible effects at all, either because they occur in non-coding or non-functional sequences, or they do not
change the amino-acid sequence due to the redundancy of codons.
10.
PRESENTED BY:- LA2 207(1)(1) AFSHEEN SHAMSI
(2) RAVI SUGISENAN
(3) NAIDU NALINAKSHI SREE GOUD





 biology
biology








