Similar presentations:
Venture capital
1. Venture capital
Prof. R. Aernoudt1
2. Content
I. Not all the money is the sameII. Credits
III. Formal and informal vc
III. Formal VC
IV. Informal BA
2
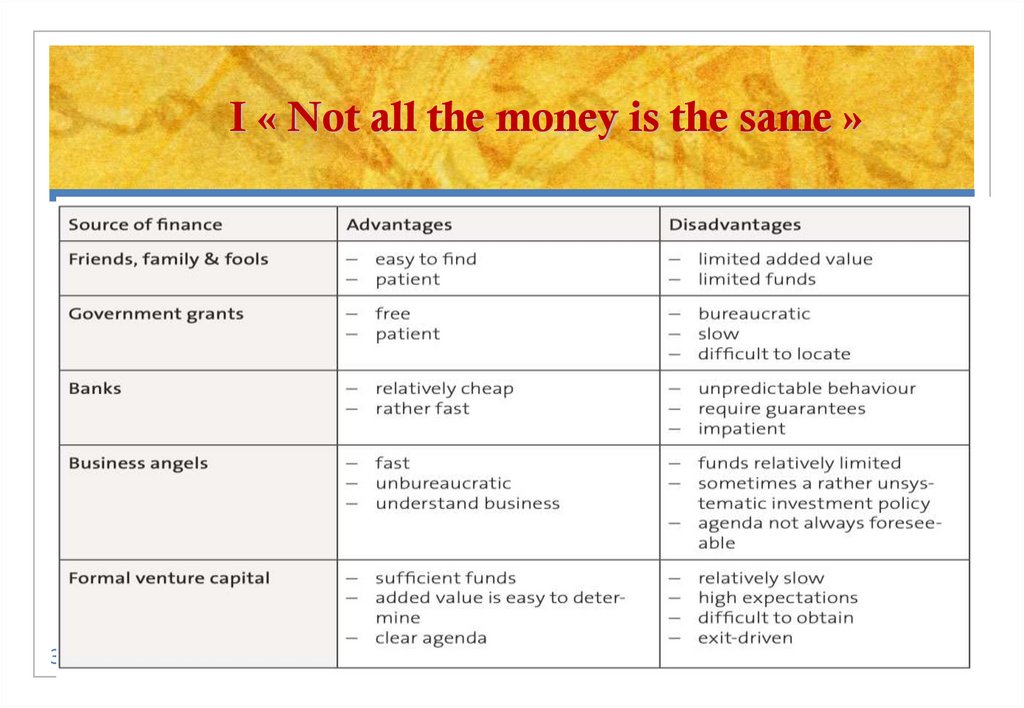
3. I « Not all the money is the same »
I « Not all the money is the same »3
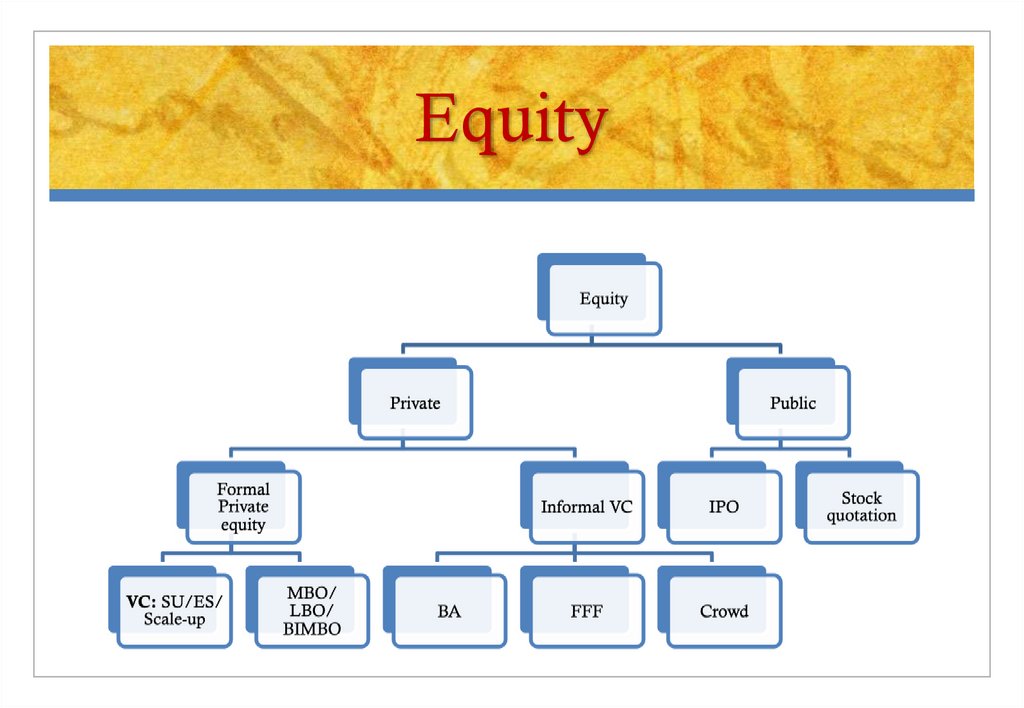
4. Equity
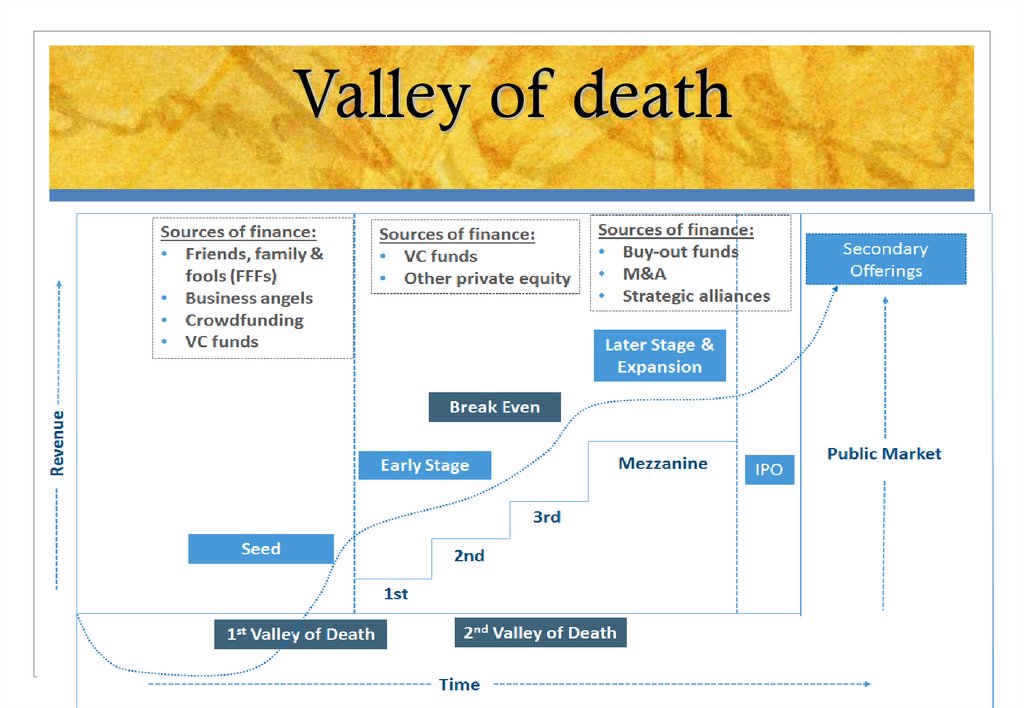
5. Valley of death
56. Definitions
6Private equity = equity capital to enterprises not quoted on a
stock market
Venture capital = equity investments made for the launch, early
development or expansion of a business
Seed money = financing provided to research, assess and develop
an initial concept before a business has reached the start-up
phase
Start-up = financing provided for product development and initial
marketing
7. Definitions
Expansion= financing provided for the growth and
expansion of a company which is breaking even or
trading profitably
Replacement
capital = purchase of existing shares in a
company from another private equity investment
organization, or from (an)other shareholder(s)
Buy-out
= management buy-out/-in : financing to enable
current operating management and investors to acquire
an existing product line or business
7
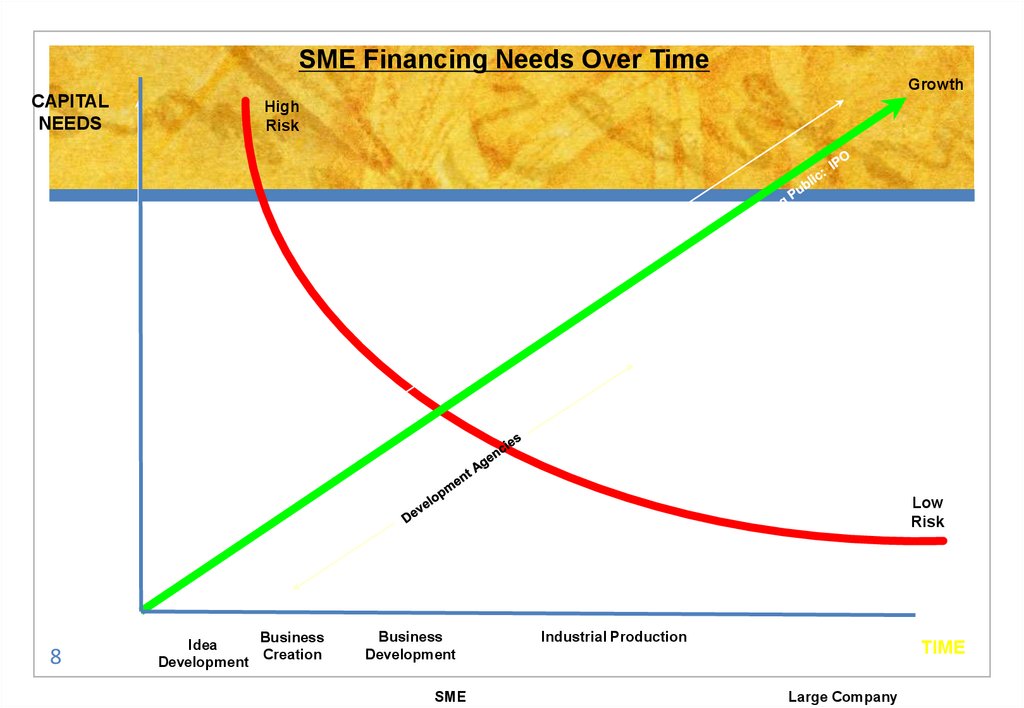
8.
SME Financing Needs Over TimeGrowth
CAPITAL
NEEDS
High
Risk
Low
Risk
8
Business
Idea
Creation
Development
Business
Development
SME
Industrial Production
TIME
Large Company
9. Marktstandaarden
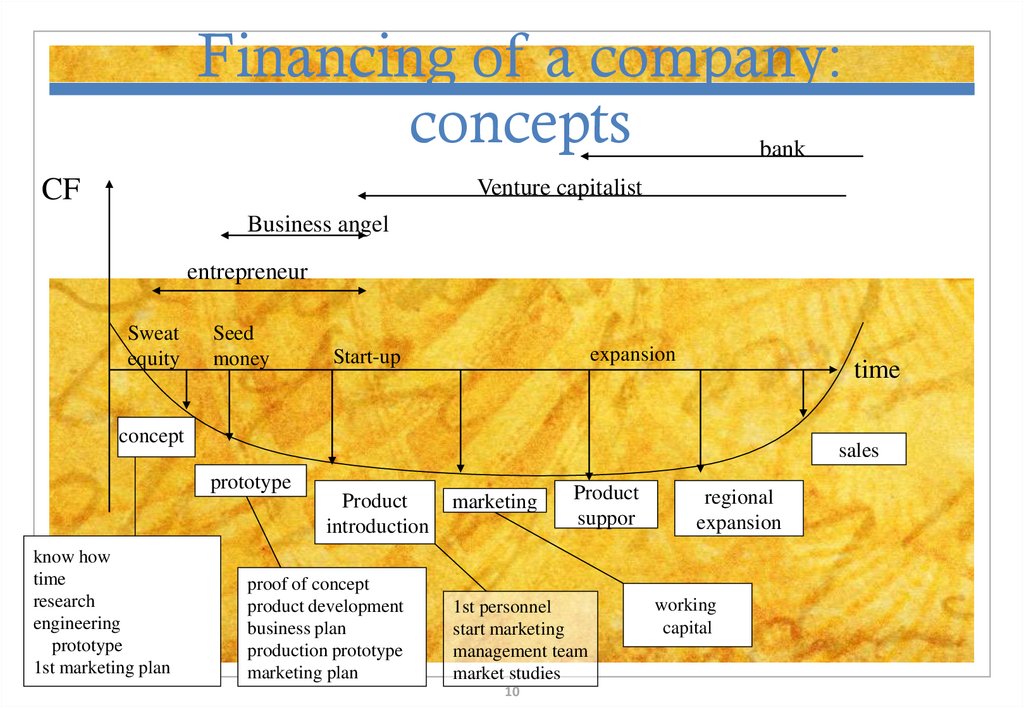
10. Financing of a company: concepts
bankCF
Venture capitalist
Business angel
entrepreneur
Sweat
equity
Seed
money
expansion
Start-up
time
concept
sales
prototype
Product
introduction
know how
time
research
engineering
prototype
1st marketing plan
proof of concept
product development
business plan
production prototype
marketing plan
marketing
Product
suppor
1st personnel
start marketing
management team
market studies
10
regional
expansion
working
capital
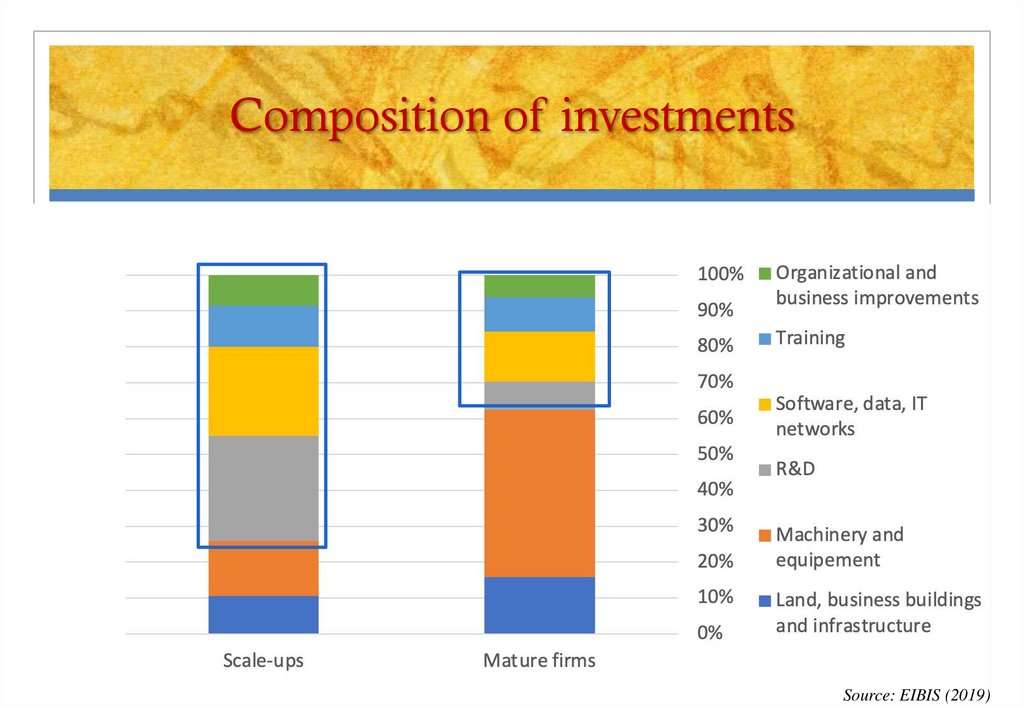
11. Composition of investments
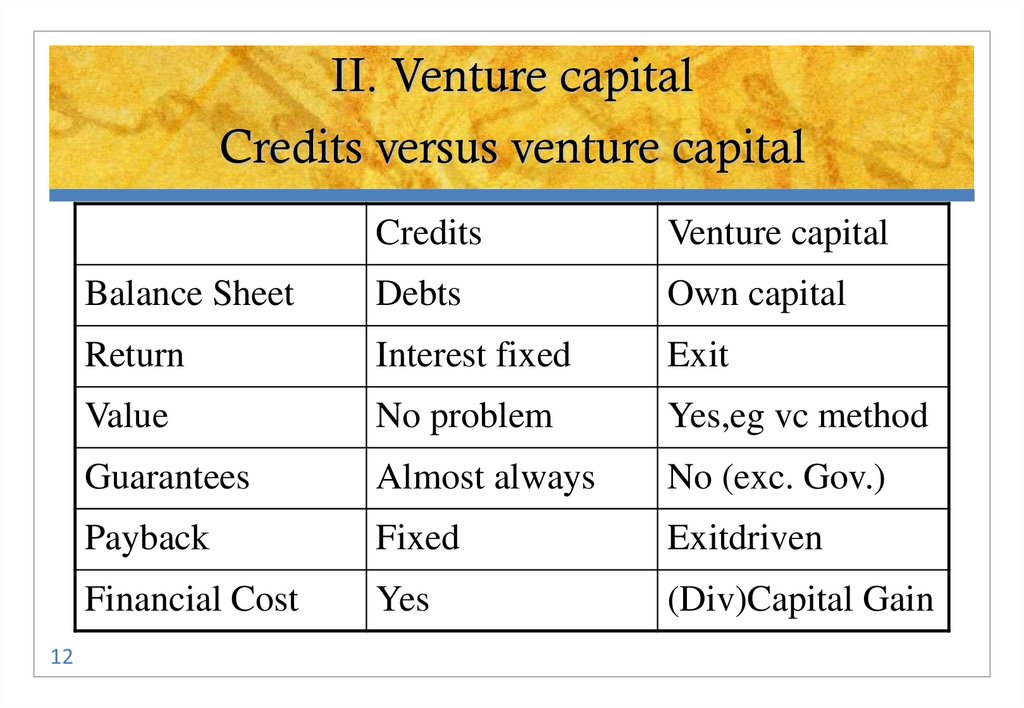
Source: EIBIS (2019)12. II. Venture capital Credits versus venture capital
12Credits
Venture capital
Balance Sheet
Debts
Own capital
Return
Interest fixed
Exit
Value
No problem
Yes,eg vc method
Guarantees
Almost always
No (exc. Gov.)
Payback
Fixed
Exitdriven
Financial Cost
Yes
(Div)Capital Gain
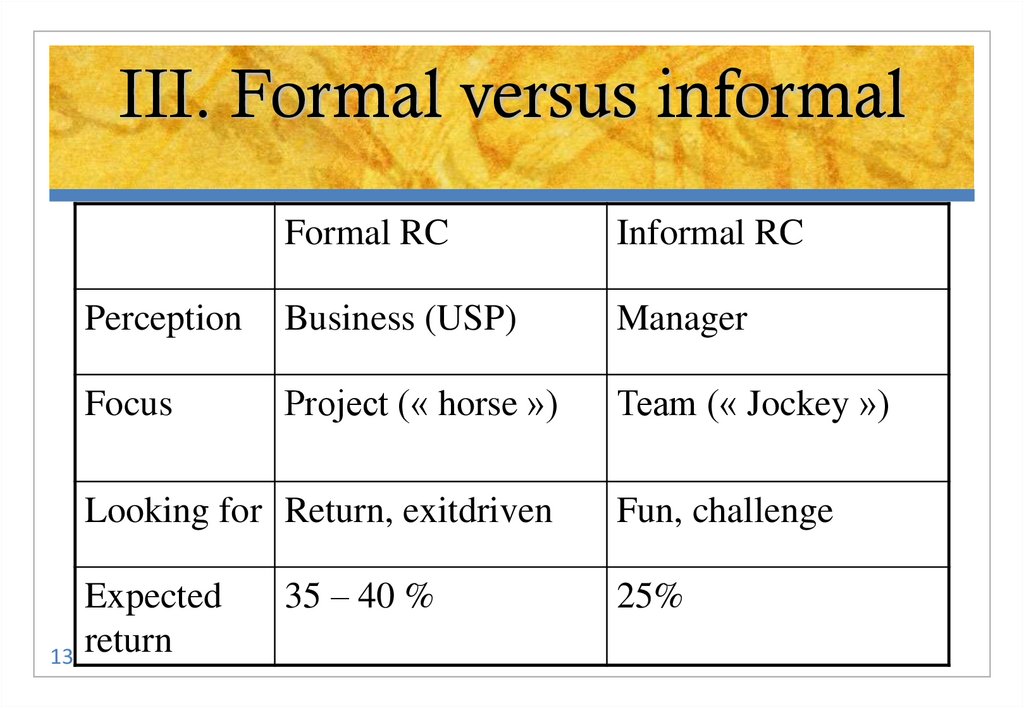
13. III. Formal versus informal
Formal RCInformal RC
Perception
Business (USP)
Manager
Focus
Project (« horse »)
Team (« Jockey »)
Looking for Return, exitdriven
Expected
13 return
35 – 40 %
Fun, challenge
25%
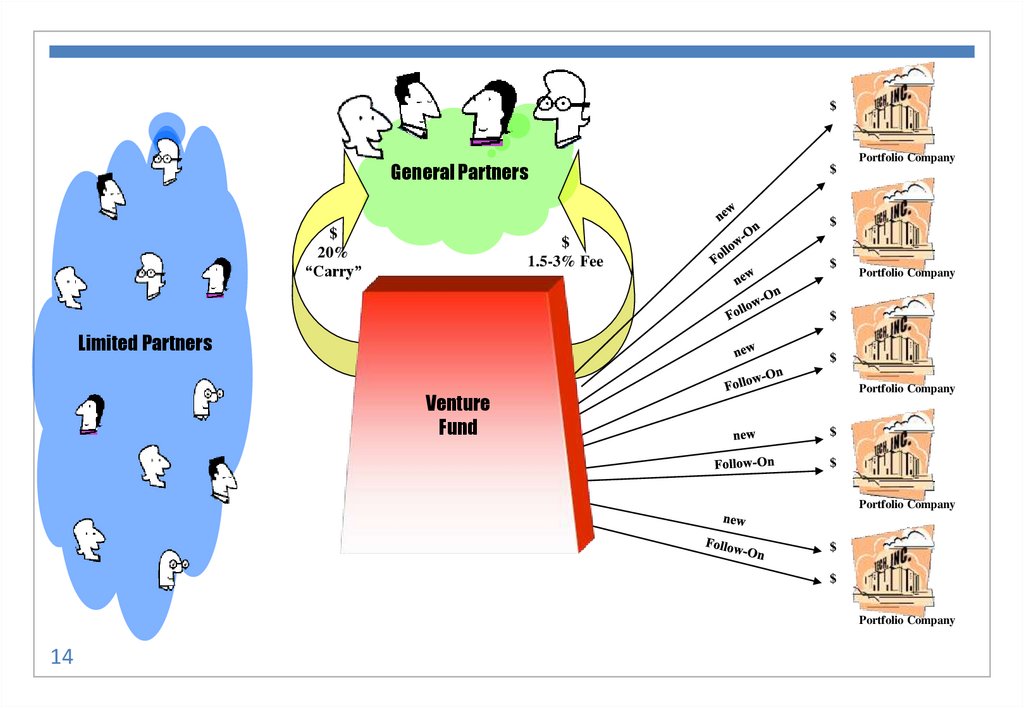
14.
$General Partners
Portfolio Company
$
$
$
20%
“Carry”
$
1.5-3% Fee
$
Portfolio Company
$
Limited Partners
$
Venture
Fund
Portfolio Company
$
$
Portfolio Company
$
$
Portfolio Company
14
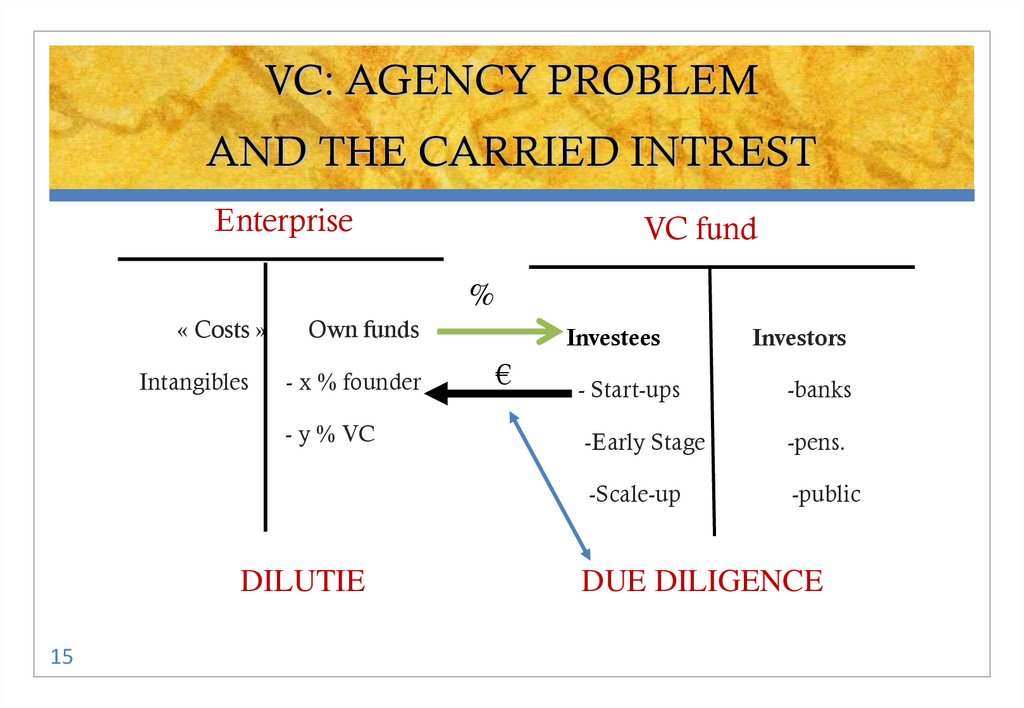
15. VC: AGENCY PROBLEM AND THE CARRIED INTREST
EnterpriseVC fund
%
« Costs »
Intangibles
Own funds
- x % founder
- y % VC
DILUTIE
15
Investees
€
Investors
- Start-ups
-banks
-Early Stage
-pens.
-Scale-up
-public
DUE DILIGENCE
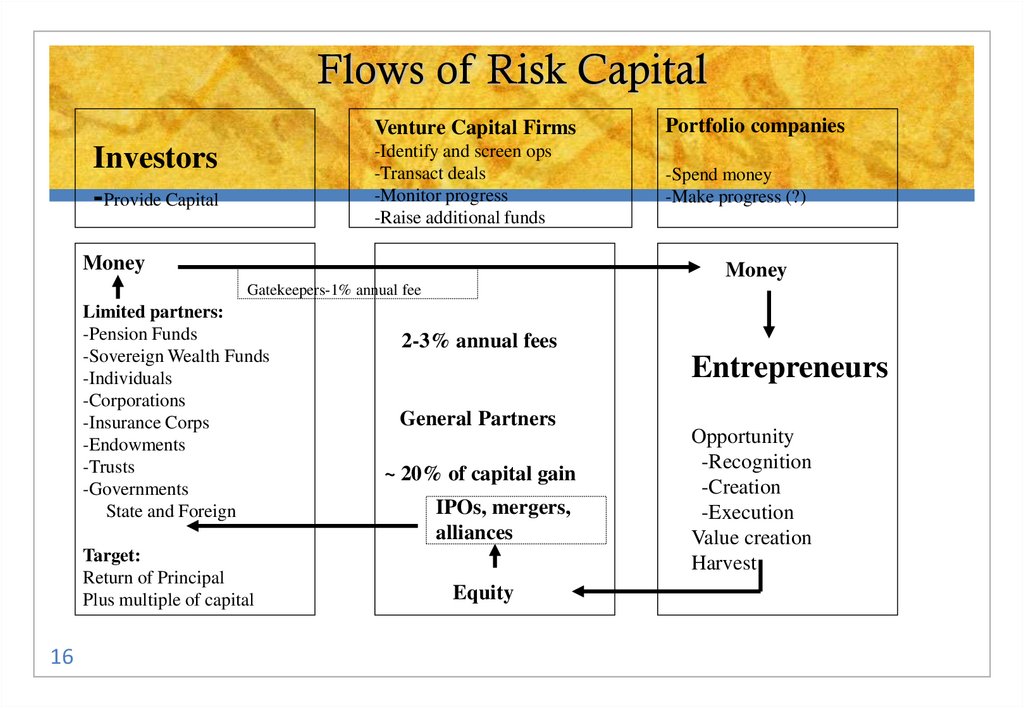
16. Flows of Risk Capital
Investors-Provide Capital
Venture Capital Firms
Portfolio companies
-Identify and screen ops
-Transact deals
-Monitor progress
-Raise additional funds
-Spend money
-Make progress (?)
Money
Money
Gatekeepers-1% annual fee
Limited partners:
-Pension Funds
-Sovereign Wealth Funds
-Individuals
-Corporations
-Insurance Corps
-Endowments
-Trusts
-Governments
State and Foreign
Target:
Return of Principal
Plus multiple of capital
16
2-3% annual fees
Entrepreneurs
General Partners
~ 20% of capital gain
IPOs, mergers,
alliances
Equity
Opportunity
-Recognition
-Creation
-Execution
Value creation
Harvest
17.
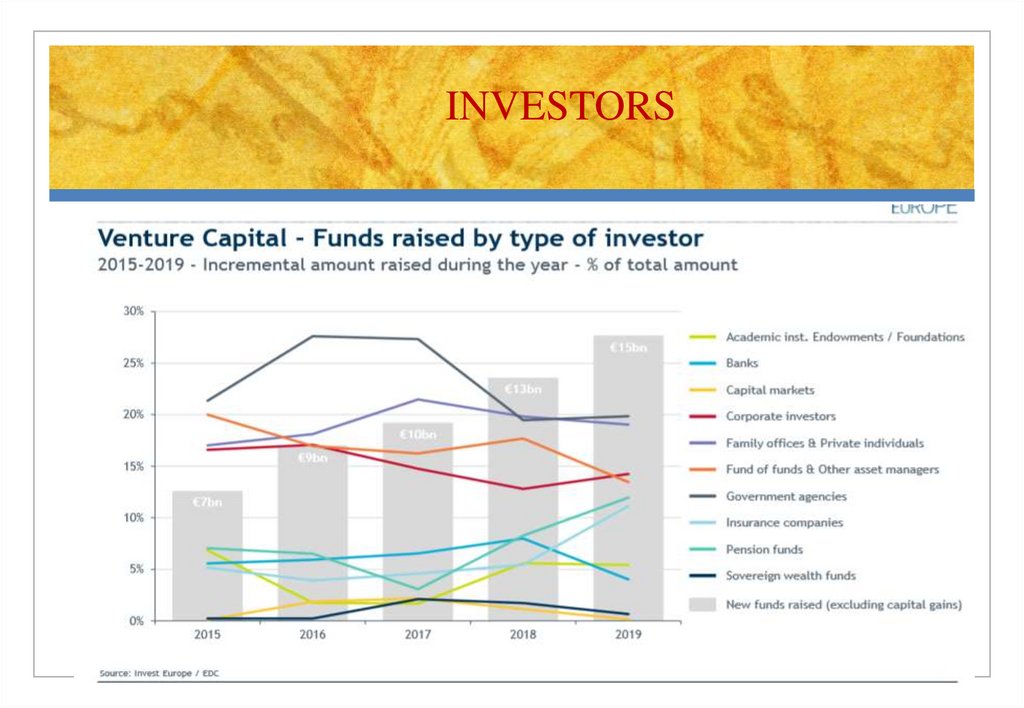
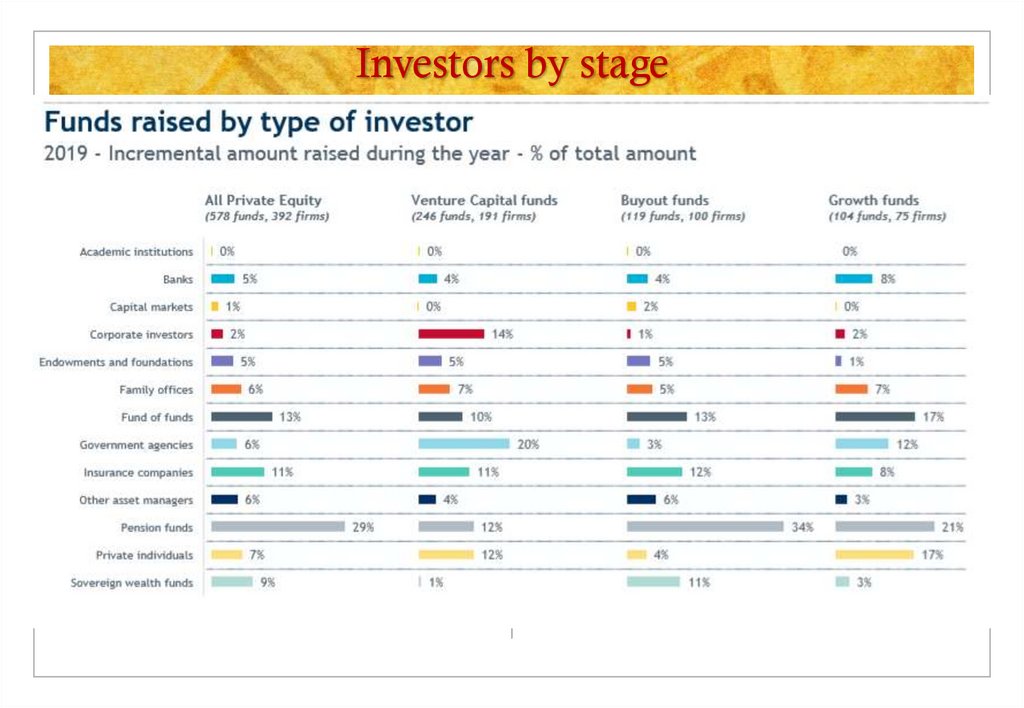
INVESTORS18. Investors by stage
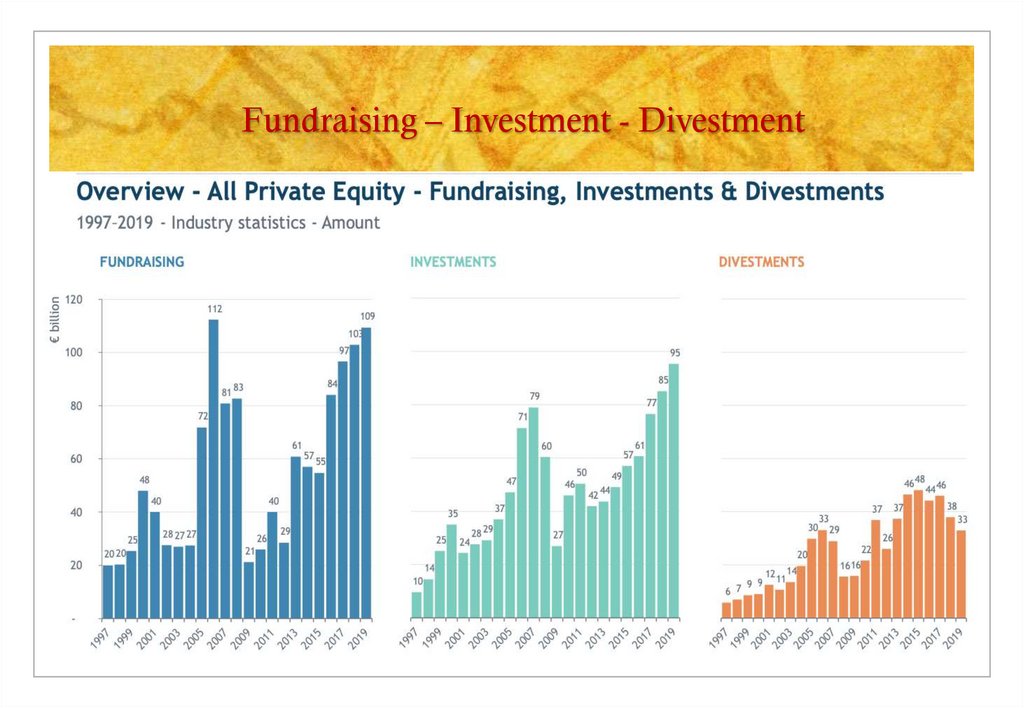
19. Fundraising – Investment - Divestment
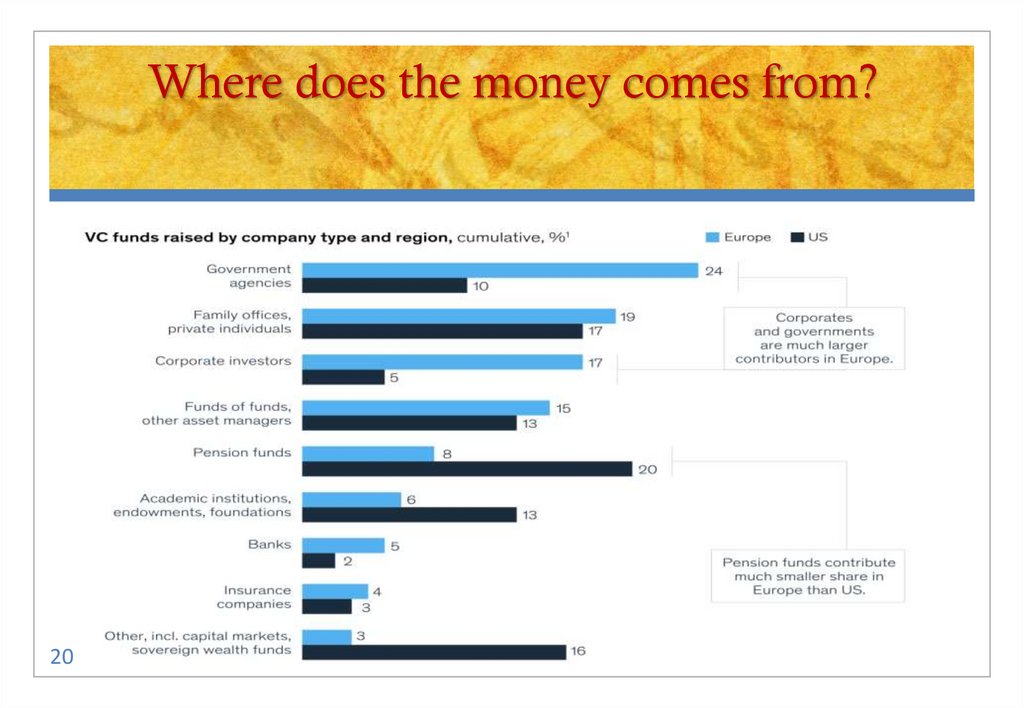
20. Where does the money comes from?
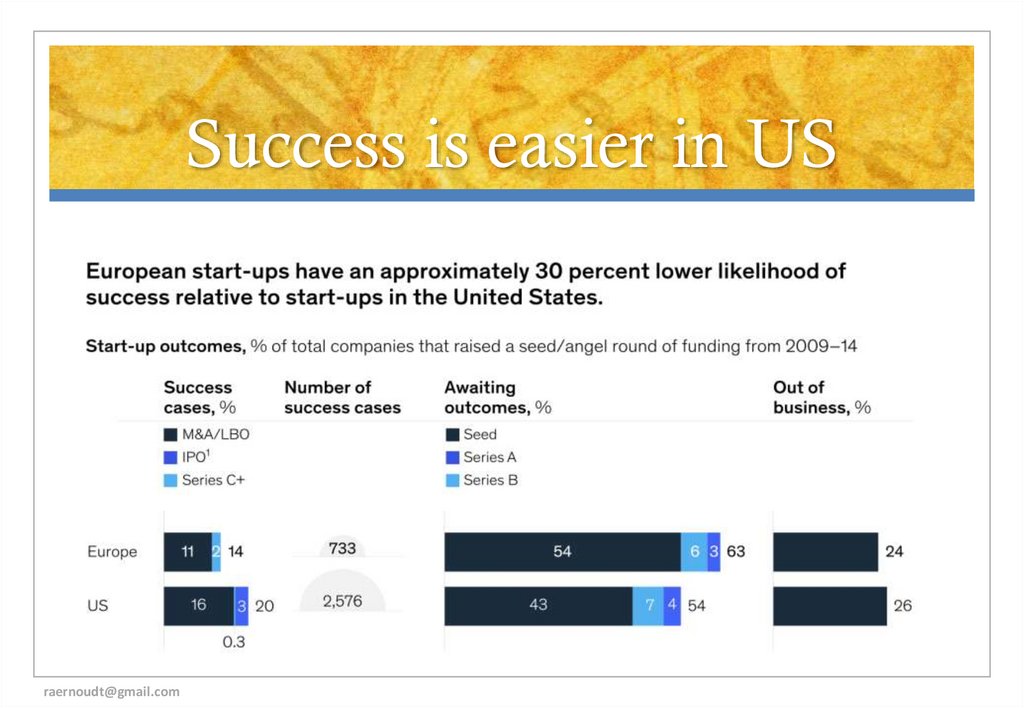
2021. Success is easier in US
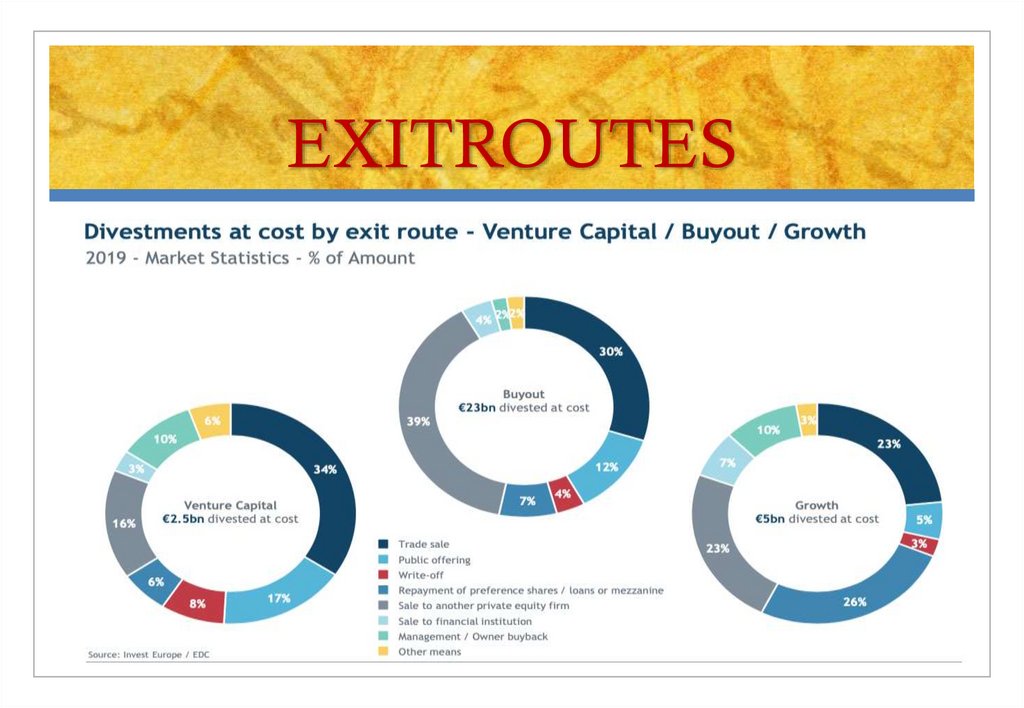
raernoudt@gmail.com22. EXITROUTES
23. What does a vc want?
231.
Management capacity and track record
2.
Market and growth potential
3.
Market niche
4.
Return (liquidity/exit)
5.
Market is more important than technology
24.
What does a VC offersbefore investment?
24
1.
Due diligence (analysis of business
plan/market/technology/competition/...)
2.
Analysis of gaps
3.
Optimal financial structure
4.
Valuation
5.
Stock option plan (milestones)
25.
What does VC offersduring investment?
choice
of distribution channels
product/marketing strategy
fixing priorities
networks:
financial advice (next rounds)
25
26. What does VC offers after the investment??
R&D,fiscal advice
M&A
Exit
Organisation (IPO, trade sale, …)
International
26
experience
Smart money
27. VC Market
27Supply
Venture capitalist avoid risk (MBO preference)
Pervert risk – return relation
Demand
Lack of investment readiness (pecking order
theory)
Market lacks transparancy
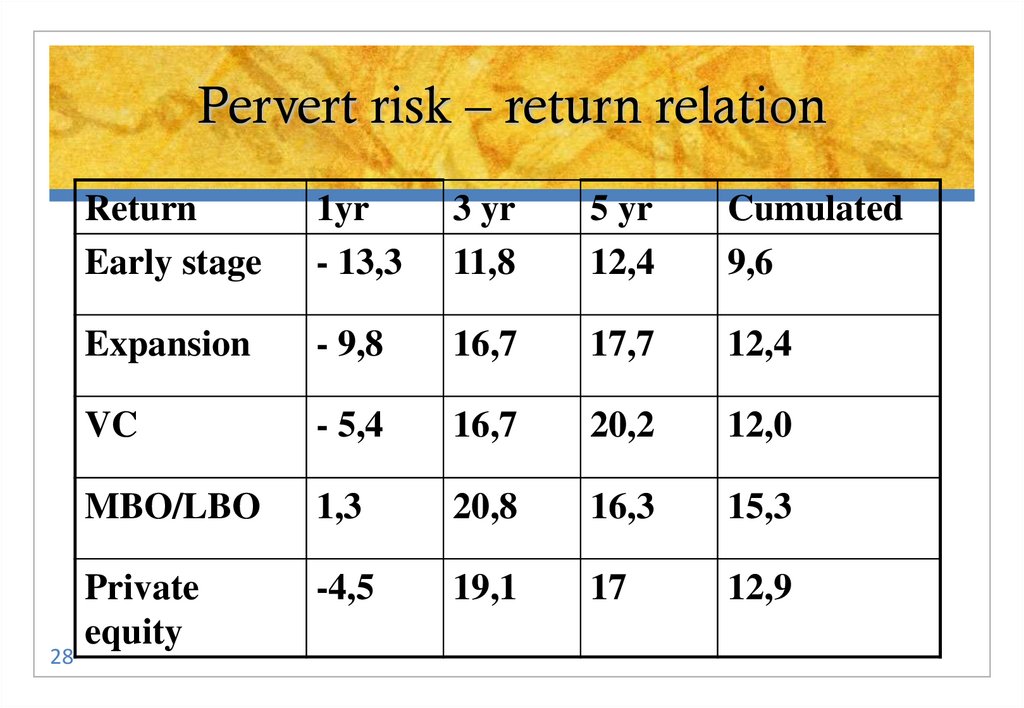
28. Pervert risk – return relation
28Return
Early stage
1yr
- 13,3
3 yr
11,8
5 yr
12,4
Cumulated
9,6
Expansion
- 9,8
16,7
17,7
12,4
VC
- 5,4
16,7
20,2
12,0
MBO/LBO
1,3
20,8
16,3
15,3
Private
equity
-4,5
19,1
17
12,9
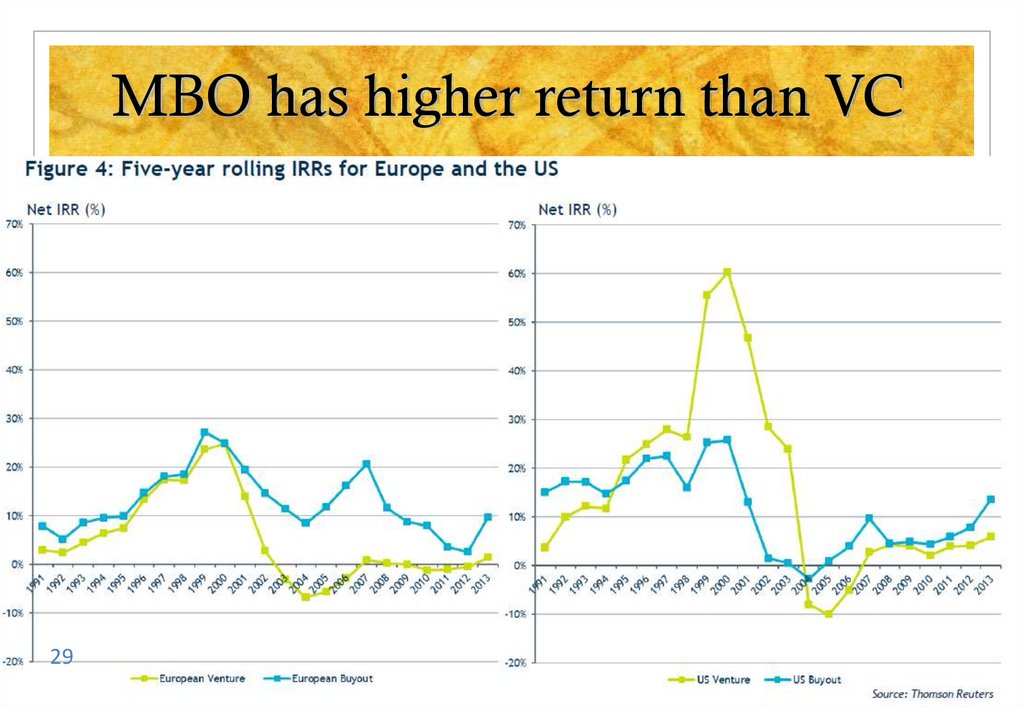
29. MBO has higher return than VC
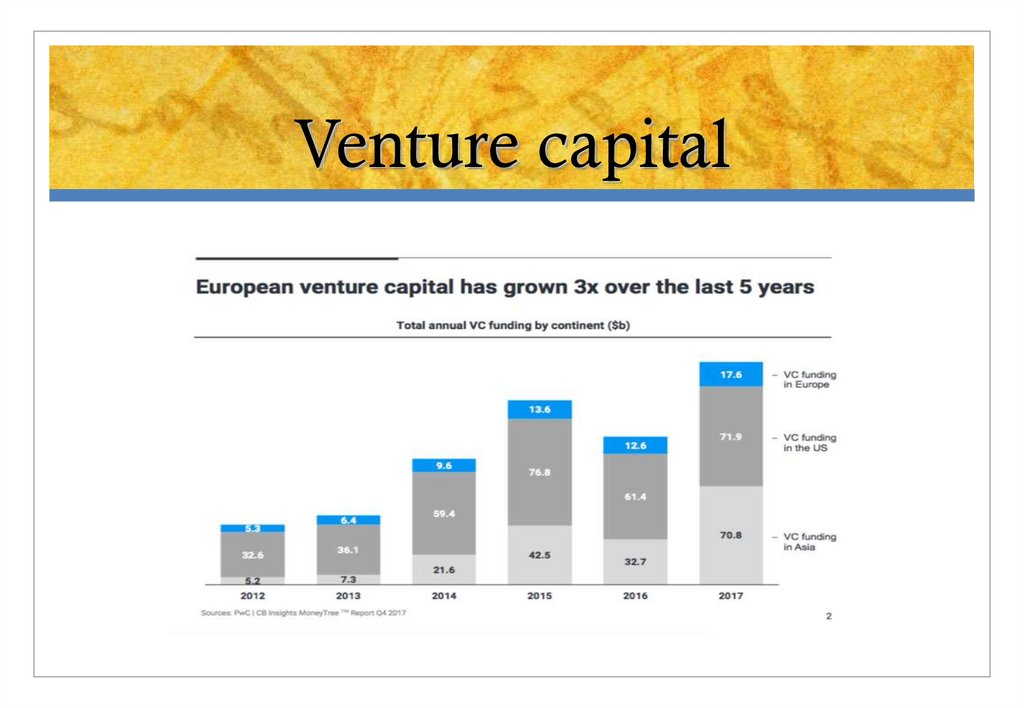
2930. Venture capital
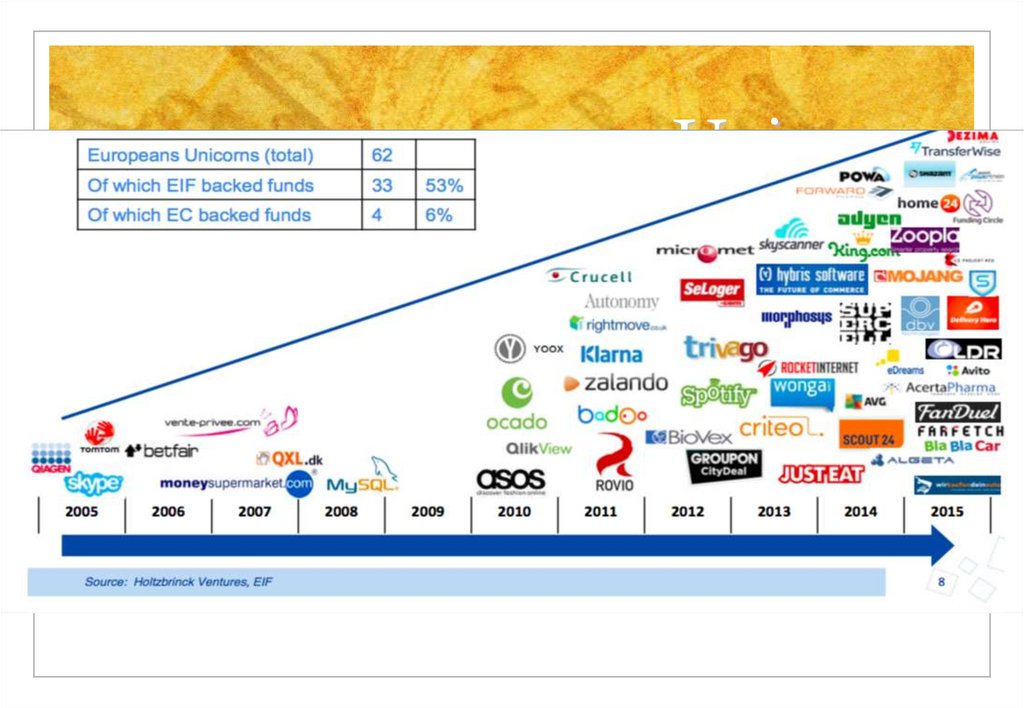
31. Unicorns
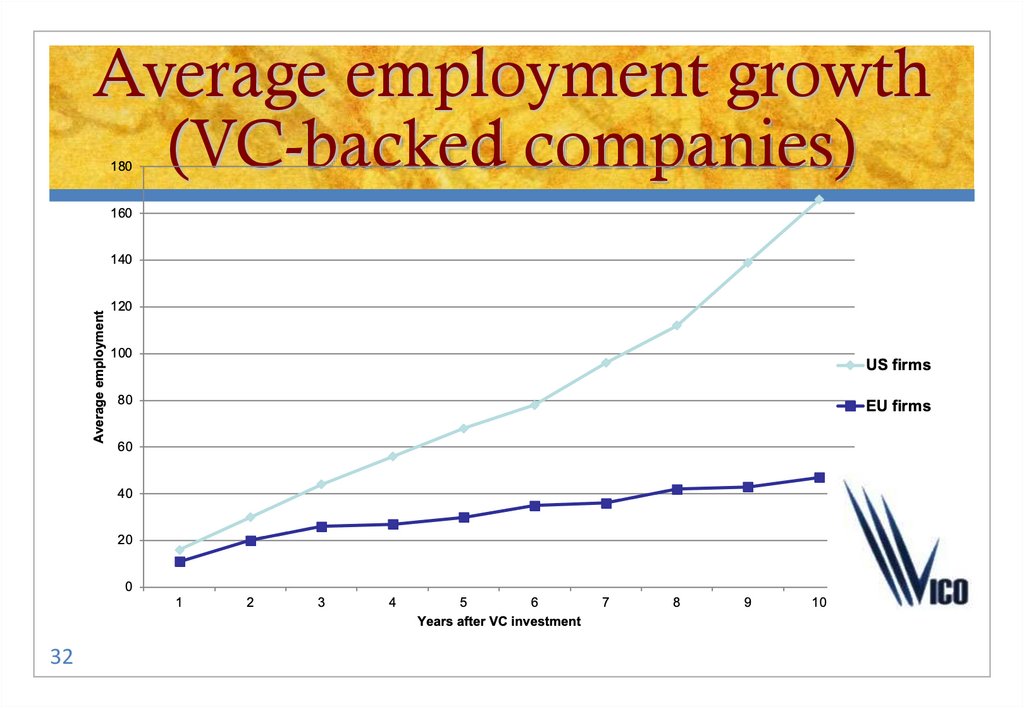
32. Average employment growth (VC-backed companies)
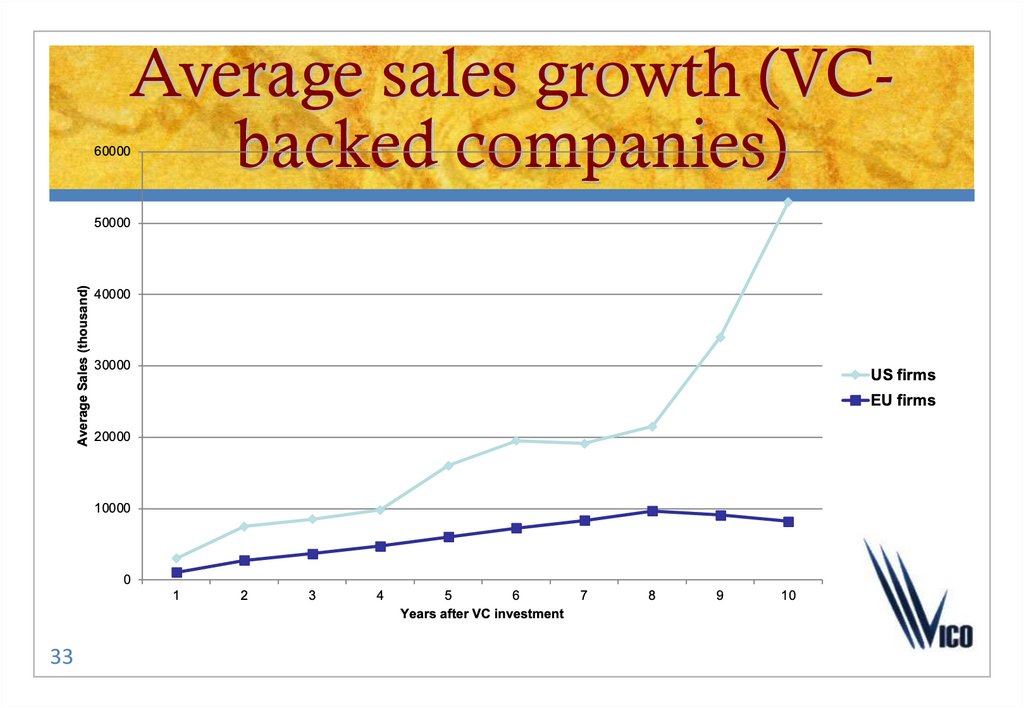
3233. Average sales growth (VC-backed companies)
Average sales growth (VCbacked companies)33
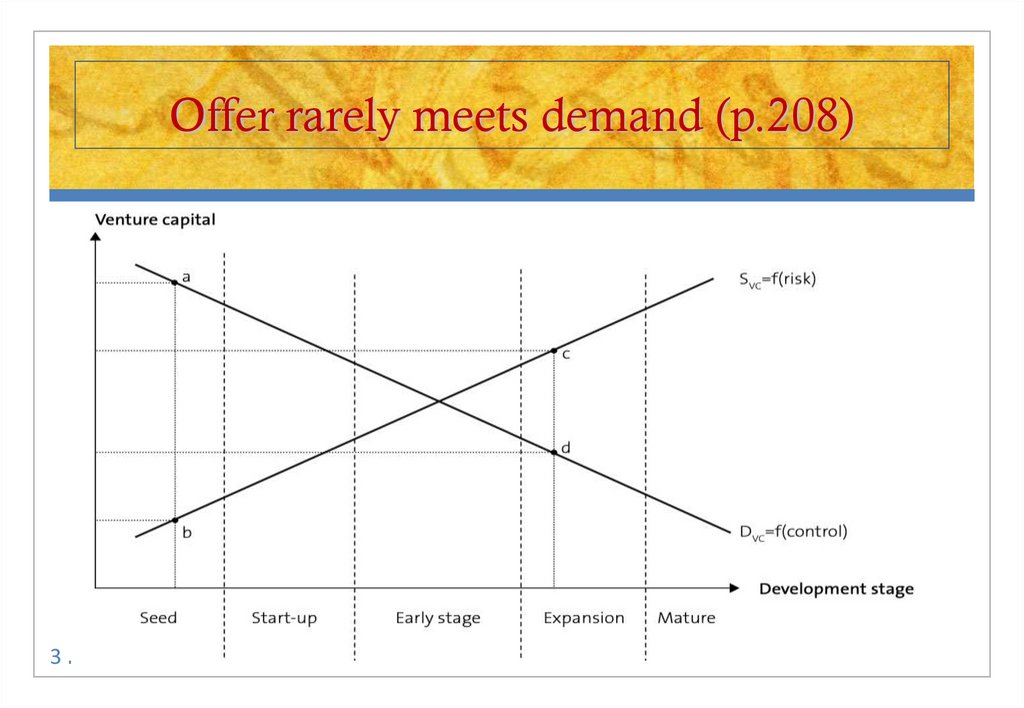
34. Offer rarely meets demand (p.208)
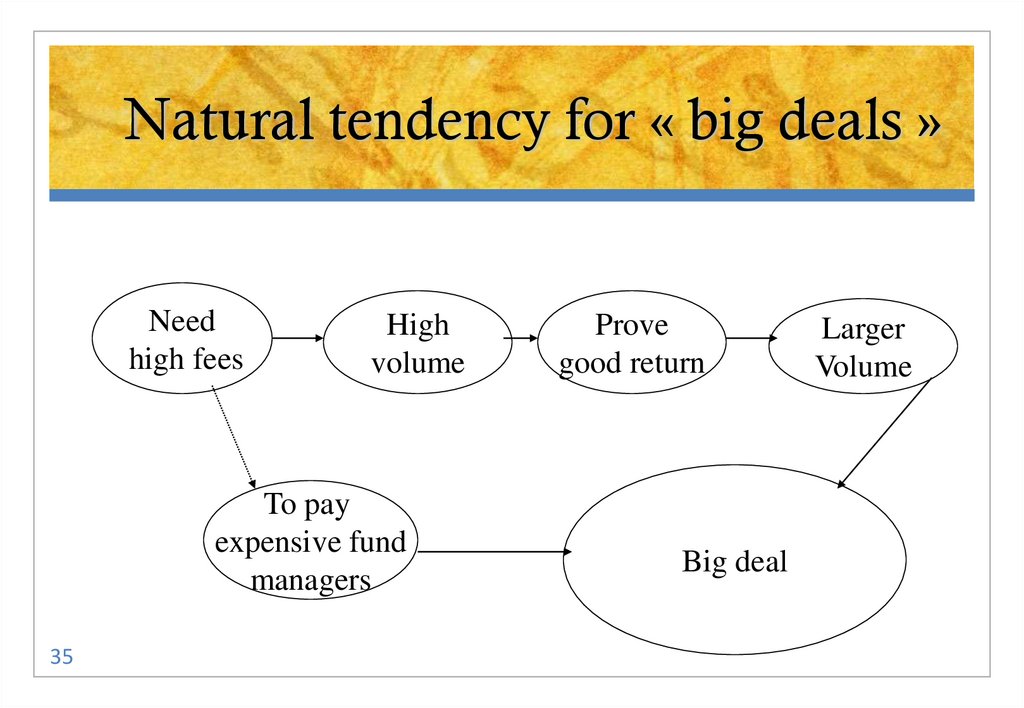
3435. Natural tendency for « big deals »
Natural tendency for « big deals »Need
high fees
High
volume
To pay
expensive fund
managers
35
Prove
good return
Big deal
Larger
Volume
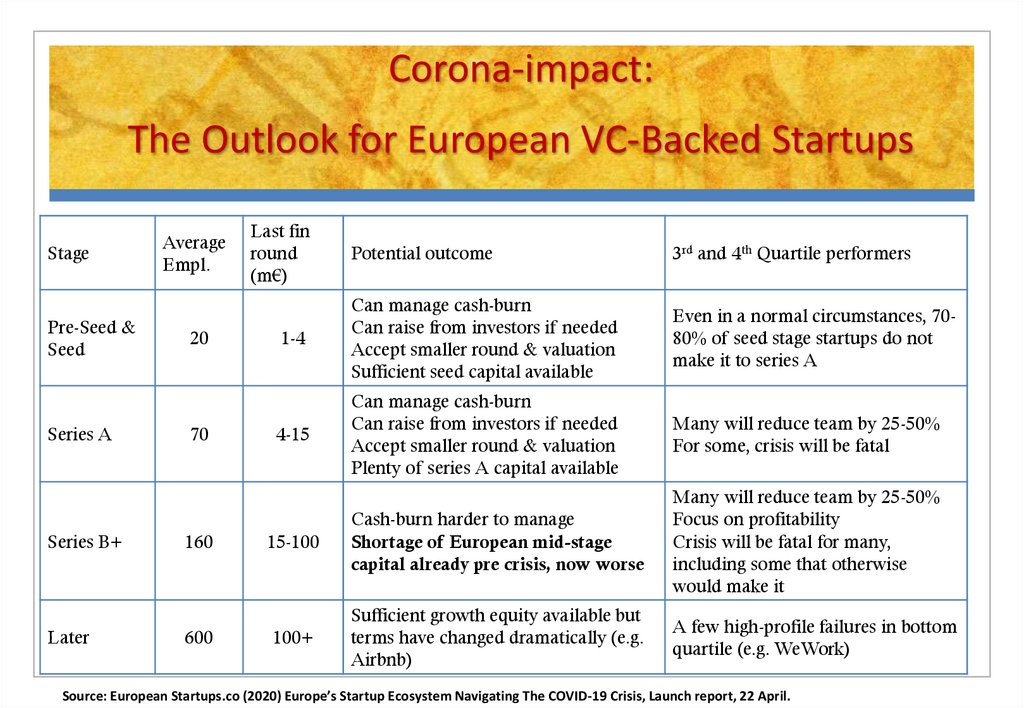
36. Corona-impact: The Outlook for European VC-Backed Startups
StagePre-Seed &
Seed
Series A
Series B+
Later
Average
Empl.
20
70
160
600
Last fin
round
(m€)
Potential outcome
3rd and 4th Quartile performers
1-4
Can manage cash-burn
Can raise from investors if needed
Accept smaller round & valuation
Sufficient seed capital available
Even in a normal circumstances, 7080% of seed stage startups do not
make it to series A
4-15
Can manage cash-burn
Can raise from investors if needed
Accept smaller round & valuation
Plenty of series A capital available
Many will reduce team by 25-50%
For some, crisis will be fatal
15-100
Cash-burn harder to manage
Shortage of European mid-stage
capital already pre crisis, now worse
Many will reduce team by 25-50%
Focus on profitability
Crisis will be fatal for many,
including some that otherwise
would make it
100+
Sufficient growth equity available but
terms have changed dramatically (e.g.
Airbnb)
A few high-profile failures in bottom
quartile (e.g. WeWork)
Source: European Startups.co (2020) Europe’s Startup Ecosystem Navigating The COVID-19 Crisis, Launch report, 22 April.
37. Conclusion on formal VC
Forthe « happy few »
Big
deals
Smart
money versus investment readiness
Exitdriven
Hard
37
versus (family) continuity
for starters











 finance
finance








