Similar presentations:
Capturing Light… in man and machine
1. Capturing Light… in man and machine
15-463: Computational PhotographyAlexei Efros, CMU, Fall 2012
2. PHOTOGRAPHY
EtymologyPHOTOGRAPHY
light
drawing
/ writing
3. Image Formation
Digital CameraFilm
The Eye
4. Sensor Array
CMOS sensor5. Sampling and Quantization
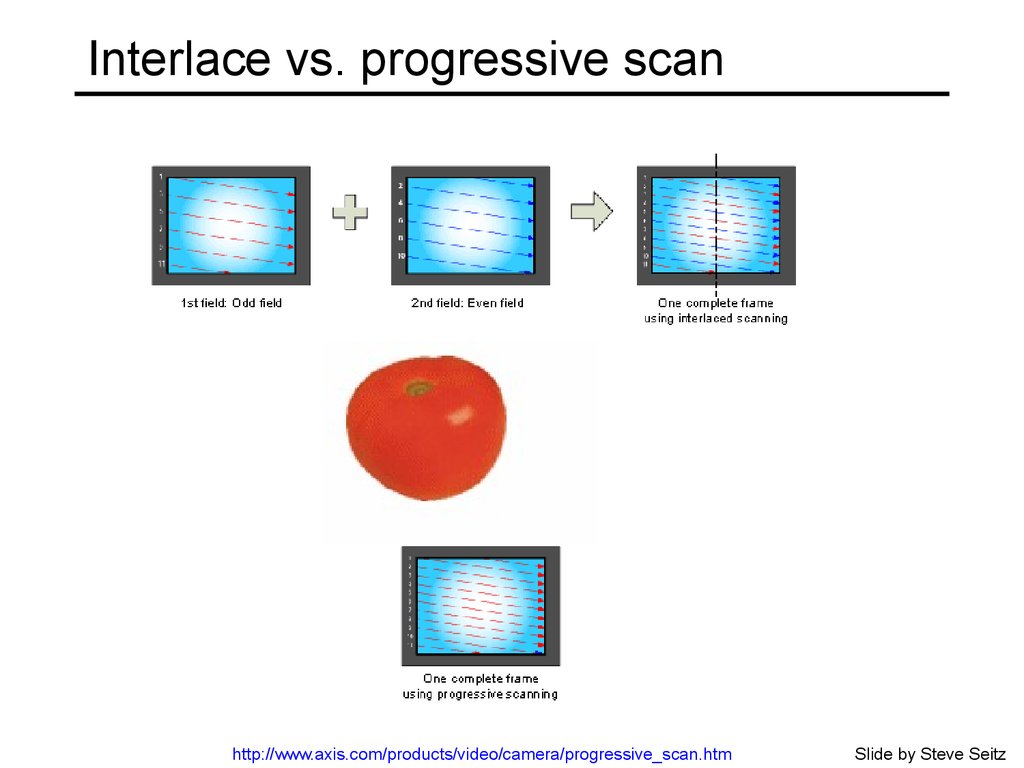
6. Interlace vs. progressive scan
http://www.axis.com/products/video/camera/progressive_scan.htmSlide by Steve Seitz
7. Progressive scan
http://www.axis.com/products/video/camera/progressive_scan.htmSlide by Steve Seitz
8. Interlace
http://www.axis.com/products/video/camera/progressive_scan.htmSlide by Steve Seitz
9. The Eye
The human eye is a camera!• Iris - colored annulus with radial muscles
• Pupil - the hole (aperture) whose size is controlled by the iris
• What’s the “film”?
– photoreceptor cells (rods and cones) in the retina
Slide by Steve Seitz
10. The Retina
Crosssection of eyeGanglion axons
Ganglion cell layer
Bipolar cell layer
Receptor layer
Cross section of retina
Pigmented
epithelium
11. Retina up-close
Light12.
Two types of lightsensitive receptorsCones
coneshaped
less sensitive
operate in high light
color vision
Rods
rodshaped
highly sensitive
operate at night
grayscale vision
cone
rod
© Stephen E. Palmer, 2002
13. Rod / Cone sensitivity
The famous sock-matching problem…14.
Distribution of Rods and Cones# Receptors/mm2
.
lin
d
Fovea B
Spot
150,000 Rods
Rods
100,000
50,000 Cones
Cones
080 60 40 20 0 20406080
Visual Angle (degrees from fovea)
Night Sky: why are there more stars off-center?
© Stephen E. Palmer, 2002
15.
Foundations of Vision, by Brian Wandell, Sinauer Assoc., 199516. Electromagnetic Spectrum
Human Luminance Sensitivity Functionhttp://www.yorku.ca/eye/photopik.htm
17.
Visible LightWhy do we see light of these wavelengths?
10000 C
.
Energy
…because that’s where the
Sun radiates EM energy
5000 C
2000 C
700 C
0
400 700 1000
Visible
Region
2000
Wavelength (nm)
3000
© Stephen E. Palmer, 2002
18.
The Physics of LightAny patch of light can be completely described
physically by its spectrum: the number of photons
(per time unit) at each wavelength 400 700 nm.
# Photons
(per ms.)
400 500 600 700
Wavelength (nm.)
© Stephen E. Palmer, 2002
19.
The Physics of LightSome examples of the spectra of light sources
# Photons
B. Gallium Phosphide Crystal
# Photons
A. Ruby Laser
.
400 500 600 700
400 500 600 700
Wavelength (nm.)
Wavelength (nm.)
D. Normal Daylight
# Photons
# Photons
C. Tungsten Lightbulb
400 500 600 700
400 500 600 700
© Stephen E. Palmer, 2002
20.
The Physics of Light% Photons Reflected
Some examples of the reflectance spectra of surfaces
Red
Yellow
Blue
Purple
400 700 400 700 400 700 400 700
Wavelength (nm)
© Stephen E. Palmer, 2002
21.
The Psychophysical CorrespondenceThere is no simple functional description for the perceived
color of all lights under all viewing conditions, but …...
A helpful constraint:
Consider only physical spectra with normal distributions
mean
area
# Photons
400
500
variance
600
700
Wavelength (nm.)
© Stephen E. Palmer, 2002
22.
The Psychophysical Correspondence# Photons
Mean
blue
Hue
green yellow
Wavelength
© Stephen E. Palmer, 2002
23.
The Psychophysical Correspondence# Photons
Variance
Saturation
hi. high
med. medium
low
low
Wavelength
© Stephen E. Palmer, 2002
24.
The Psychophysical CorrespondenceArea
Brightness
# Photons
B. Area Lightness
bright
dark
Wavelength
© Stephen E. Palmer, 2002
25.
Physiology of Color VisionThree kinds of cones:
440
RELATIVE ABSORBANCE (%)
.
530 560 nm.
100
S
M
L
50
400 450 500 550 600 650
WAVELENGTH (nm.)
• Why are M and L cones so close?
• Why are there 3?
© Stephen E. Palmer, 2002
26. More Spectra
metamers27.
Color ConstancyThe “photometer metaphor” of color perception:
Color perception is determined by the spectrum of light
on each retinal receptor (as measured by a photometer).
© Stephen E. Palmer, 2002
28.
Color ConstancyThe “photometer metaphor” of color perception:
Color perception is determined by the spectrum of light
on each retinal receptor (as measured by a photometer).
© Stephen E. Palmer, 2002
29.
Color ConstancyThe “photometer metaphor” of color perception:
Color perception is determined by the spectrum of light
on each retinal receptor (as measured by a photometer).
© Stephen E. Palmer, 2002
30.
Color ConstancyDo we have constancy over
all global color transformations?
60% blue filter
Complete inversion
© Stephen E. Palmer, 2002
31.
Color ConstancyColor Constancy: the ability to perceive the
invariant color of a surface despite ecological
Variations in the conditions of observation.
Another of these hard inverse problems:
Physics of light emission and surface reflection
underdetermine perception of surface color
© Stephen E. Palmer, 2002
32. Camera White Balancing
• Manual• Choose color-neutral object in the photos and normalize
• Automatic (AWB)
• Grey World: force average color of scene to grey
• White World: force brightest object to white
33. Color Sensing in Camera (RGB)
3-chip vs. 1-chip: quality vs. costWhy more green?
Why 3 colors?
http://www.cooldic
http://www.cooldi tionary.com/words/Bayer-filter.wikipedia
Slide by Steve Seitz
34. Practical Color Sensing: Bayer Grid
Estimate RGBat ‘G’ cels from
neighboring
values
http://www.cooldictionary.com/
words/Bayer-filter.wikipedia
Slide by Steve Seitz
35. RGB color space
RGB cubeEasy for devices
But not perceptual
Where do the grays live?
Where is hue and saturation?
Slide by Steve Seitz
36. HSV
Hue, Saturation, Value (Intensity)• RGB cube on its vertex
Decouples the three components (a bit)
Use rgb2hsv() and hsv2rgb() in Matlab
Slide by Steve Seitz
37. Programming Project #1
Prokudin-Gorskii’s Color Photography (1907)38. Programming Project #1
• How to compare R,G,B channels?• No right answer
• Sum of Squared Differences (SSD):
• Normalized Correlation (NCC):





































 informatics
informatics








