Similar presentations:
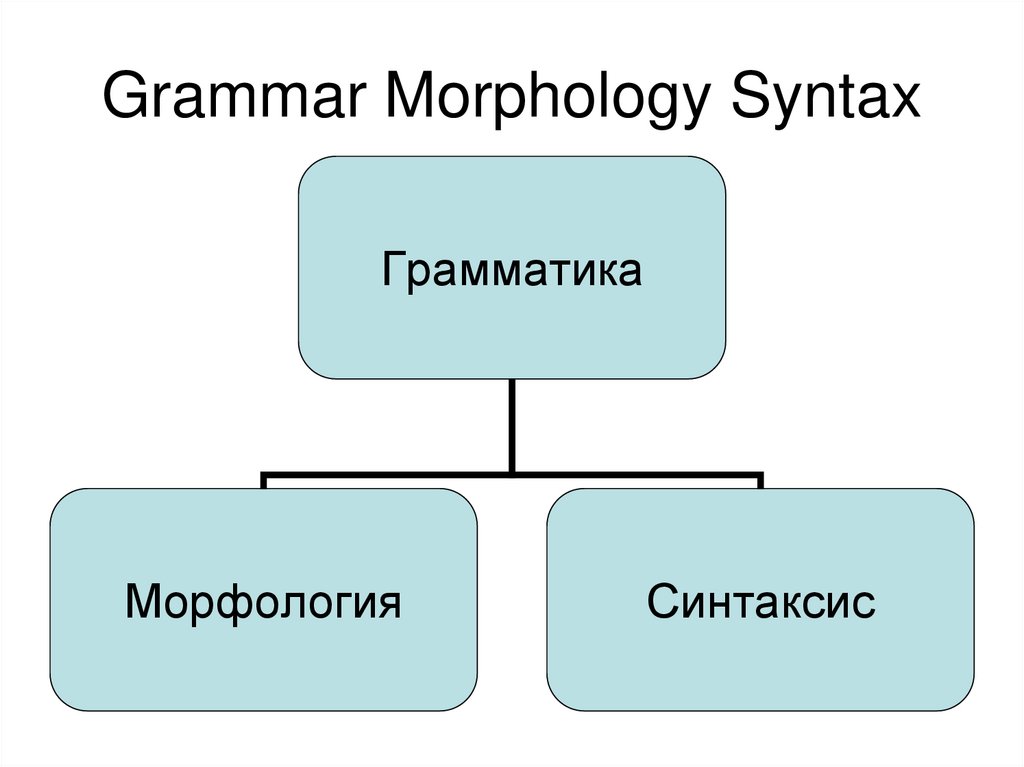
Грамматика Морфология Синтаксис
1. Grammar Morphology Syntax
ГрамматикаМорфология
Синтаксис
2. Грамматическое и лексическое значение
• Гло́кая ку́здра ште́ко будлану́ла бо́кра икурдя́чит бокрёнка
• The iggle squiggs trazed wombly in the
harlish hoop
• fox, foxes, fox’s, foxes’
• I have translated the text
3. Виды языков в зависимости от грамматического строя
• флективные - словоизменение при помощи флексий –формантов (сочетающих несколько значений (немецкий,
русский, латынь)
• агглютинативные – словоизменение при помощи
агглюцинации, где каждый формант имеет одно значение
(тюркские, эсперанто)
• изолирующие – языки, где в слове мало морфем, а часто –
одна (английский)
• синтетические – грамматическое значение передается
формой слова/словоизменением (порядок слов может быть
свободным) (русский, древнеанглийский)
• аналитические – грамматическое значение передается
служебными/ грамматикализованными словами и порядком
слов (в основном) (английский, французский, африкаанс)
4. Особенности английского языка как языка аналитического строя
• The hunter killed the bear• The bear killed the hunter
The bear was killed by the hunter
The bear killed by the hunter was dead
5. Means of expressing Grammatical Meaning
What is most popular in English?• Word Order
• Auxiliary words
• Flection (endings etc.)
What is most popular in Russian?
6. Грамматические категории
Всякая грамматическая форма входит в ту илииную грамматическую категорию
Всякая категория представлена минимум двумя
категориальными формами (принцип
оппозиций)
• Именные категории (падеж, род/
согласовательный класс, определенность,
одушевленность)
• Глагольные (вид, лицо, наклонение, залог,
время, аспект)
7. Парадигматические и синтагматические отношения в языке
• «Парадигма – вместо» (стол, столу,столу, столом, столе, столы…)
• «Синтагма – вместе» (большой стол,
накрытый стол)
8. Способы образования форм слова в английском языке
• Синтетический – образование форм словапосредством его изменения с сохранением
корня (I go, he goes) или супплетивно (I go, I
went). Изменение при помощи аффиксации (I
work I worked) или при помощи изменения
корневого гласного и аффиксации (childchildren)
• Аналитический – образование форм слова
посредством использование служебных
(грамматикализованных) слов
9. Parts of Speech
Noun (n) (inflection)
Verb (v) (conjugation)
Adjective (adj) (attached to noun)
Adverb (adv) (adheres to verb)
Pronoun (pron)
Numeral (num)
Preposition (prep)
Conjunction (cj)
10. Parts of Speech +
Interjection (int)
Category of state (afloat, apart, alike)
Modal words (sentence adverbs)
Particles (just, only)
Article (a/an, the)
11. How do you identify parts of speech?
12. Части речи Критерии выделения
• По смыслу (абстрактное, самое общеезначение всего класса)
• По форме (способность к изменению по
лицу и числу, времени, наклонению…
или неизменяемость)
• По функции (способ связи с другими
словами, функция в предложении)
13. Часть речи
• Лексико-грамматический класс слов,характеризуемый общим абстрактным
грамматическим значением,
выражаемым определенными
маркерами
14. Charles Fries (1887-1967) 15 groups of words
• A. Determiners(position of the
definite article – your,
both, John’s, four, no,
most…)
• B. Modal, auxiliary
verbs (may in “may
be good’)
• D. very in “very good”
15. Grammar in Rhyme
Three little words you often see,Are articles — a, an, and the.
A Noun’s the name of any thing,
As school, or garden, hoop, or
swing,
Adjectives tell the kind of Noun,
As great, small, pretty, white, or
brown.
Instead of Nouns the Pronouns
stand–
Her head, his face, your arm, my
hand.
Verbs tell of something to be
done–
To read, count, sing, laugh,
jump, or run.
How things are done, the
adverbs tell,
As slowly, quickly, ill, or well.
Conjunctions join the words
together–
As men and women, wind or
weather.
The Preposition stands before
A Noun, as in, or through a door.
The Interjection shows surprise,
As oh! how pretty–ah! how wise.
The whole are called Nine Parts
of Speech,
Which reading, writing,
speaking, teach.
Source: Dr. Chase’s Recipes,
1863
16. Имя существительное
Noun/ substantive17. Значение Meaning
• thingness. Thus, nouns include notonly chair and iron, etc., but also
beauty, peace, necessity, journey,
and everything else presented as a
thing, or object.
18. Форма Form
Nouns have the categories1) of number (singular and plural).
2) case (common and genitive/ possessive);
19. Функция Function
(a) A noun combines with1) a preceding adjective (large room),
2) occasionally with a following adjective (times immemorial),
3) a preceding noun in either the common case (iron bar) or the genitive case (father's
room),
4) a verb following it (children play) or preceding it (play games).
5) Occasionally with a following or a preceding adverb (the man there; the then
president).
6) with prepositions (in a house; house of rest).
7) It is typical of a noun to be preceded by the definite or indefinite article (the room, a
room).
(b) Function in the sentence.
1) subject
2) predicative
3) object,
4) attribute,
5) adverbial modifier.
6) part of each of these when preceded by a preposition.
20. Способы образования множественного числа Plural of Nouns
• Путем прибавления окончания: -(e)s• Путем изменения корневой гласной и
прибавления окончания (исконные слова)
Man-men, woman-women;Child-children, oxoxen; Goose-goose, tooth-teeth; Mouse-mice
• Прибавлением тех же окончаний, что в языкеисточнике (заимствования из греч. и латыни)
phenomenon-phenomena, datum-data…
• Без изменений (a sheep-many sheep, deer)
21.
22. Существительные, не изменяющиеся по числам
• Согласующиеся с формой глаголамножественного числа
Police, staff, stairs, scissors, wages, …
• Согласующиеся с формой глагола
единственного числа
News, money, means, …
23.
24. Nouns with 2 plurals (continued)
25. Падеж существительного
• General/ Common case(-) - possessivecase (‘s/’)
26. Some examples of Possessive Case
Today’s newspaperEarth’s satellite
Have you been to the doctor’s?
my father's room,
my father's arrival,
my father's willingness,
the young man's friends,
nothing could console Mrs Birch for her daughter's loss,
Smith and Brown's office,
Oxford professor of poetry's lecture,
the Duke of Edinburgh's speech,
the King of England's residence,
somebody else's child,
nobody else's business,
This girl in my class's mother took us,
The blonde I had been dancing with's name was Bernice.
My father was a happy man and My father's was a happy life
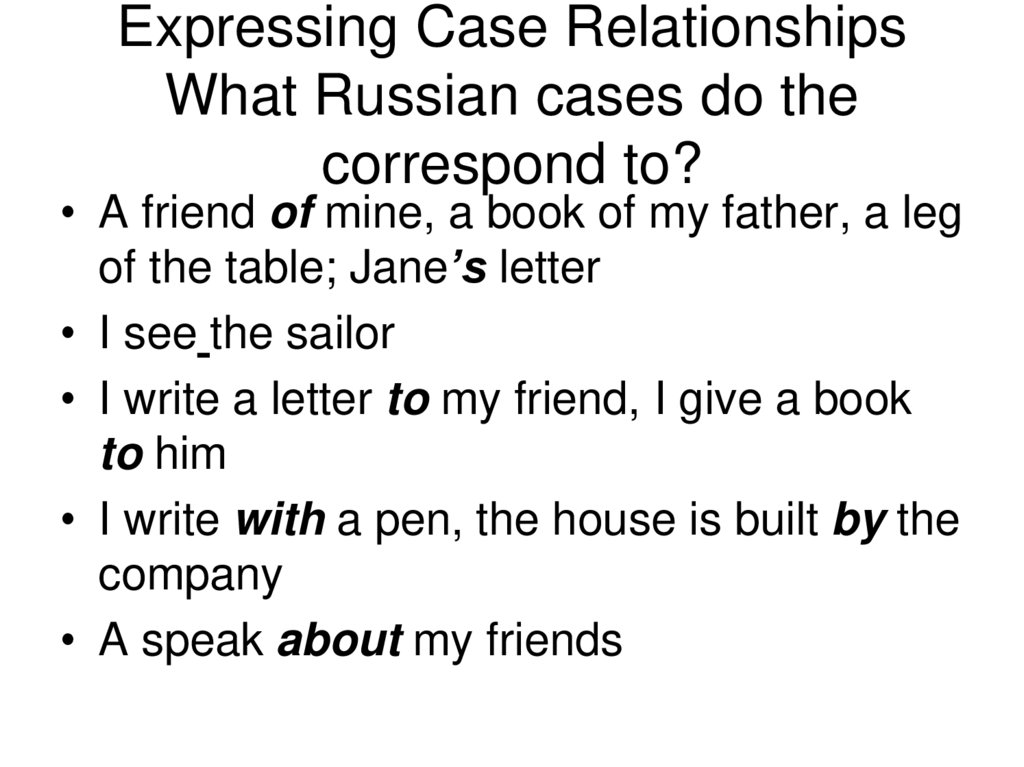
27. Expressing Case Relationships What Russian cases do the correspond to?
• A friend of mine, a book of my father, a legof the table; Jane’s letter
• I see the sailor
• I write a letter to my friend, I give a book
to him
• I write with a pen, the house is built by the
company
• A speak about my friends
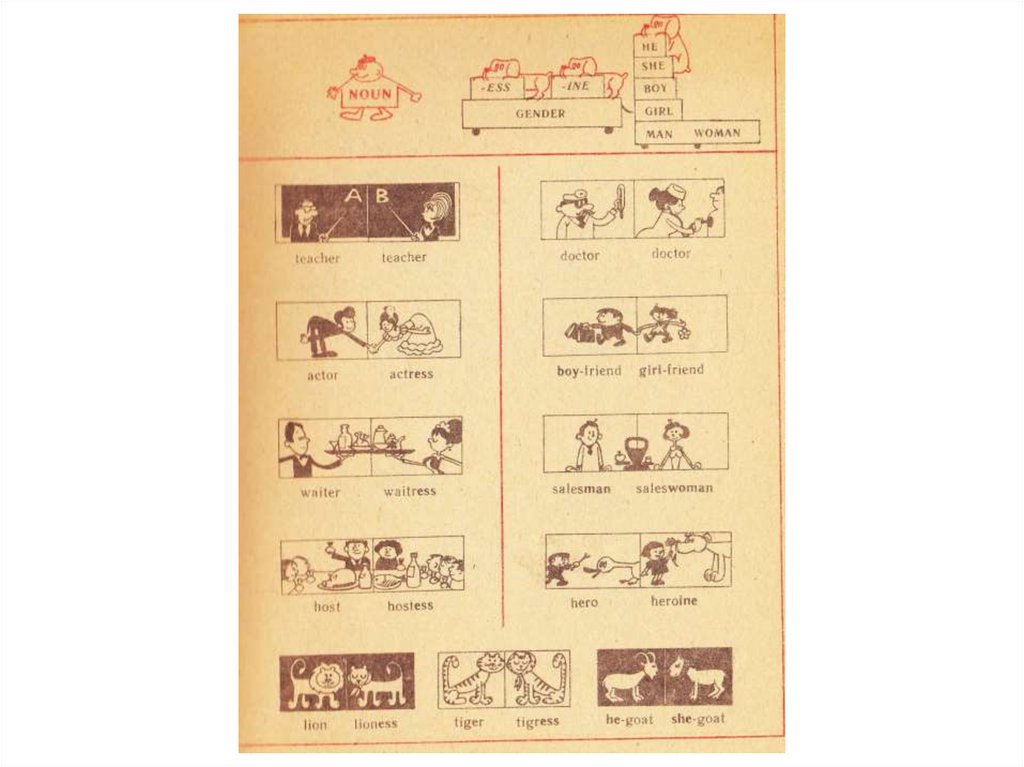
28. Род Gender
• Есть ли у английскогосуществительного категория рода?
• А у русского?
• Есть ли категория рода у русского/
английского прилагательного?
• For this topic read the file about genderbenders
29.
30. What do these words mean?
• Chairman – chairperson-chair• Saleswoman – salesman – salesassistant
31. How many nouns are there?
32. Артикль
Article33. Виды артикля
• Определенный Definite (the [ðǝ]/ [ði:])denotes individual object (from the wordthat/this)
• Неопределенный Indefinite (a [æ]/ [ǝ]/
[ei], an [æn]/ [ǝn]) – Classifying, denotes
any object of a class (from the word one)
• Нулевой Zero article/ Omission of the
article(-)
34. What articles do we need to use?
There is… fly in my lemonade
I want to buy … smartphone
Close… door, please!
Show me… way to … station
He is fond of lying in … sun
…Moon orbits round… Earth
35. What articles do we need to use?
• Before:• …same, …next, …previous, …last,
…very, …only, …following
• 1) We’ll take …next bus. That was… last!
… next will be tomorrow morning.
• 2) speaking about time:
• …last week, …next day, …next year.
• Will you come…next week?
36. Articles before names of
• Seas, oceans, rivers: …Black Sea,…Atlantic Ocean, …Thames
• Mountain Chains:…Alps, …Caucasus
• Mountain peaks: …Ben Nevis
• Cardinal points: …east, …west, …south,
…north
• Deserts, Channels and Canals: …Sahara,
…English Channel, …Suez Canal
37. Articles before names of
• Ships, whole families: …Queen Mary,…Browns
• Abbreviated names of countries: …USA,
…United Kingdom.
38. Set expressions
Be in … hurry
Be at…loss
Have .. headache
In… low voice
Tell… truth
On…one hand, on …other hand
Play…piano
Read in …original
At…home
At…work
39. Прилагательное
Adjective40. Значение Meaning
• The adjective expresses propertyGreen, grey, blue, greenish, nice, fine,
awful, Chinese, French, dangerous,
careless, loud, clean, empty
The property may be either permanent or
temporary; cf. a red tie and a face red with
excitement
41.
42.
43.
44.
45.
46. Форма Form
• invariable.• Some adjectives form degrees of
comparison (long, longer, longest).
47. Функция Function
(a) combine with1) nouns both preceding (large room), and (occasionally)
following them (times immemorial).
2) They also combine with a preceding adverb (very large).
3) can be followed by the phrase "preposition + noun" (free
from danger).
4) Occasionally with a preceding verb (married young).
(b) In the sentence, an adjective can be
1) an attribute (large room) or
2) a predicative (is large).
3) objective predicative (painted the door green).
48. What are the Comparative and Superlative degrees of these adjectives
• Loud, fat, pale, big, foggy, clever• Convenient, interesting
• Good, bad, little, many/ much, far,
49.
50.
51.
52. Order of adjectives according to their meaning
• A valuable large old oval brownVictorian handmade table
















































 english
english








