Similar presentations:
Spring teplates. Thymeleaf & spring framework
1. Spring Teplates
Thymeleaf & Springframework
2. History
3. Servlets
public class HelloWorldServlet extends HttpServlet {protected void doGet(request, response) {
response.setContentType("text/html");
PrintWriter out = response.getWriter();
out.println("<html>"); out.println("<head>");
out.println("<title>Hello!</title>");
out.println("</head>");
out.println("<body bgcolor=\"white\">");
out.println("</body>");
out.println("</html>");
}
Hello!
}
Html symbols are writing directly to the browser from java code.
4. Servlets
<html><head>
<title>Hello!</title>
</head>
<body bgcolor=“gray">
<h1>Hello!</h1>
</body>");
</html>
Hello!
public class HelloWorldServlet extends HttpServlet {
protected void doGet(request, response) {
request.getRequestDispatcher("/login.jsp").
forward(request, response);
}
}
Html code saved separately from java code
and can be dynamically changed before sending to browser . It’s good.
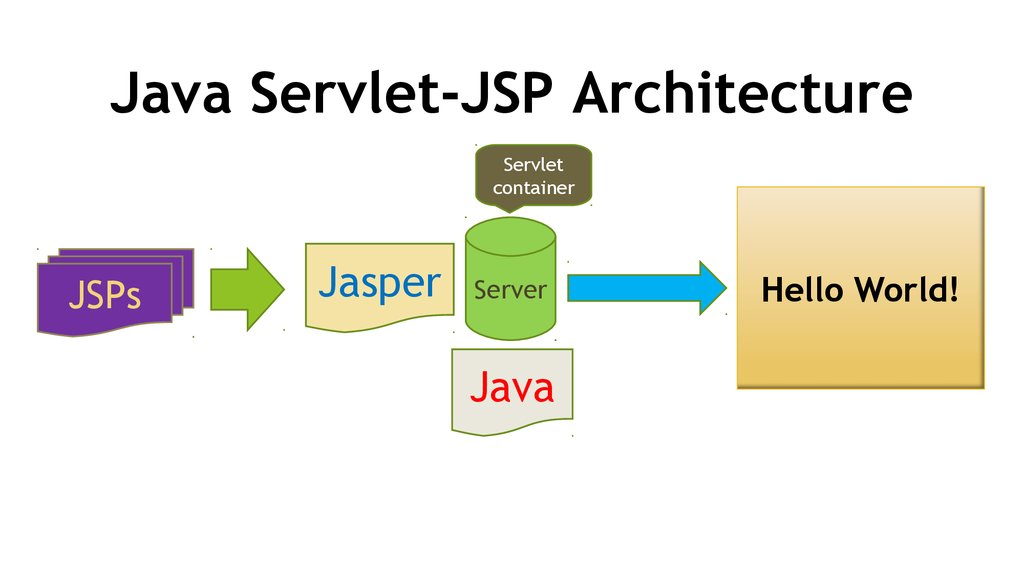
5. Java Servlet-JSP Architecture
Servletcontainer
JSPs
Jasper
Server
Java
Hello World!
6. Templates
7. Template – document or parts of document with basic configuration.
HeaderLeft
menu
Table
with dynamic
content
Footer
Spam
8. Spring templates.
ApacheVelocity
FreeMarker
Rythm
Thymeleaf
3.8
seconds
4.8 seconds
3 seconds
43.2 seconds
Results obtained after testing with
benchmarking tool
for 10000 requests.
9. Thymeleaf. Thymeleaf integration with Spring framework.
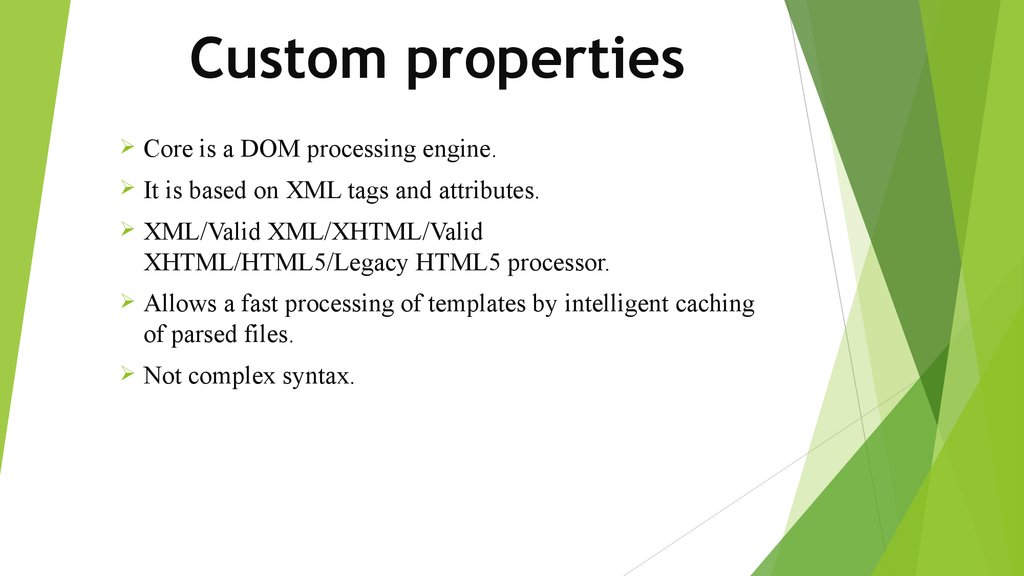
10. Custom properties
Core is a DOM processing engine.It is based on XML tags and attributes.
XML/Valid XML/XHTML/Valid
XHTML/HTML5/Legacy HTML5 processor.
Allows a fast processing of templates by intelligent caching
of parsed files.
Not complex syntax.
11. Syntax compare
FreeMarker syntax:ApacheVelocity syntax:
<table>
<#list animals as animal>
<#if animals.python.price != 0>
<tr> <td>${animal.name}<td>$
{animal.price}
</tr>
</#if>
</#list>
</table>
<table>
#foreach($mud in $mudsOnSpecial)
#if($customer.hasPurchased($mud))
<tr>
<td>$flogger.getPromo($mud)</td>
</tr>
#end
#end
</table>
12. Syntax compare
Thymeleaf syntax:<table>
<tr>
<th>NAME</th>
<th>PRICE</th>
<th>IN STOCK</th>
</tr>
<tr th:each="prod : ${prods}">
<td th:text="${prod.name}">Onions</td>
<td th:text="${prod.price}">2.41</td>
<td th:text="${prod.inStock}? #{true} : #{false}">yes</td>
</tr>
</table>
13. Integration with Spring framework
Spring application context:<bean id="templateResolver"
class="org.thymeleaf.templateresolver.ServletContextTemplateResolver">
<property name="prefix" value="/WEB-INF/templates/" />
<property name="suffix" value=".html" />
<property name="templateMode" value="HTML5" />
</bean>
<bean id="templateEngine"
class="org.thymeleaf.spring4.SpringTemplateEngine">
<property name="templateResolver" ref="templateResolver" />
</bean>
Html file template:
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml"
xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
14. Standard dialect
Expressions:Using with basic objects:
Variable Expressions: ${...}
#ctx : the context object.
Selection Variable Expressions: *{...}
#vars: the context variables.
Message Expressions: #{...}
#locale : the context locale.
Link URL Expressions: @{...}
#httpServletRequest : (only in Web Contexts) the
If-then: (if) ? (then)
HttpServletRequest object.
If-then-else: (if) ? (then) : (else)
#httpSession : (only in Web Contexts) the
Default: (value) ?: (defaultvalue)
HttpSession object.
15.
Expression Utility Objects:#dates : utility methods for java.util.Date objects: formatting, component extraction, etc.
#calendars : analogous to #dates , but for java.util.Calendar objects.
#numbers : utility methods for formatting numeric objects.
#strings : utility methods for String objects: contains, startsWith, prepending/appending, etc.
#objects : utility methods for objects in general.
#bools : utility methods for boolean evaluation.
#arrays : utility methods for arrays.
#lists : utility methods for lists.
#sets : utility methods for sets.
#maps : utility methods for maps.
#aggregates : utility methods for creating aggregates on arrays or collections.
#messages : utility methods for obtaining externalized messages inside variables expressions, in the
same way as they would be obtained using #{…} syntax.
#ids : utility methods for dealing with id attributes that might be repeated.
16.
Dialect extension:<bean id="templateEngine"
class="org.thymeleaf.spring4.SpringTemplateEngine">
<property name="templateResolver" ref="templateResolver" />
<property name="additionalDialects">
<set>
<bean class="org.thymeleaf.extras.springsecurity4.dialect.SpringSecurityDialect"/>
</set>
</property>
</bean>
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml"
xmlns:sec=“http://www.thymeleaf.org/thymeleaf-extras-springsecurity4”
xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
17. Messages internationalization
Application context:<bean id="messageSource“
class="org.springframework.context.support.ResourceBundleMessageSource">
<property name="basename" value=“classpath:messages" />
</bean>
Class path:
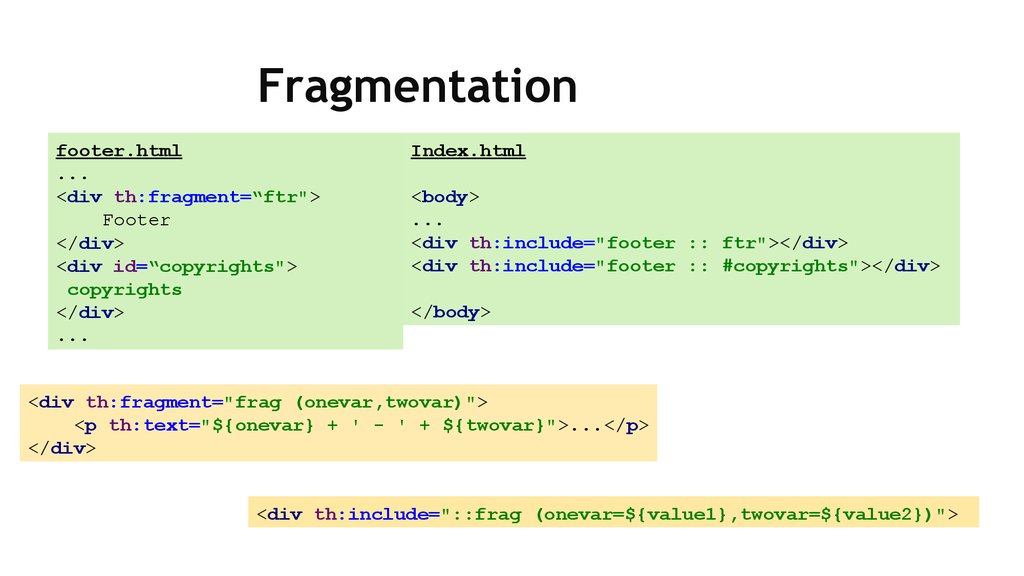
18. Fragmentation
footer.html...
<div th:fragment=“ftr">
Footer
</div>
<div id=“copyrights">
copyrights
</div>
...
Index.html
<body>
...
<div th:include="footer :: ftr"></div>
<div th:include="footer :: #copyrights"></div>
</body>
<div th:fragment="frag (onevar,twovar)">
<p th:text="${onevar} + ' - ' + ${twovar}">...</p>
</div>
<div th:include="::frag (onevar=${value1},twovar=${value2})">
19. Usage Examples
Object expression:Today is: <span th:text="${#calendars.format(today,'dd MMMM yyyy')}">11 March
2016</span>
Links usage:
<a href="details.html" th:href="@{/order/details(orderId=${o.id})}">view</a>
<a th:href="@{'/details/'+${user.login}(orderId=${o.id})}">view</a>
Conditions usage:
<div th:if="${user.isAdmin()} == false"> ...<div th:if="${user.isAdmin() == false}> ... - Spring EL
<tr th:class="${row.even}? 'class-name'"> ...
<tr th:class="${1 > 0}? 'Yes' : 'No'"> ...
20.
Default expression:<span th:text=“${value}?: 'no value specified'">Some value</span>
Setting attribute:
<input type="submit" value="Subscribe me!" th:attr="value=#{subscribe.submit}"/>
Forms:
<form action="subscribe.html" th:action="@{/subscribe}">
Iteration:
<tr th:each="item : ${list}">
<td th:text="${item.name}">Onions</td>
<td th:text="${item.count}">2.41</td>
</tr>
21.
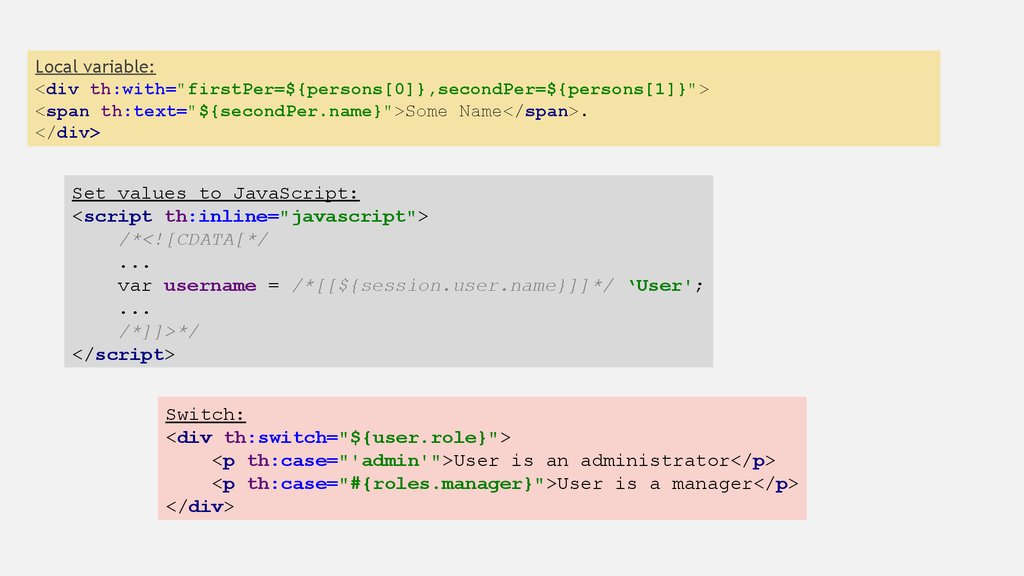
Local variable:<div th:with="firstPer=${persons[0]},secondPer=${persons[1]}">
<span th:text="${secondPer.name}">Some Name</span>.
</div>
Set values to JavaScript:
<script th:inline="javascript">
/*<![CDATA[*/
...
var username = /*[[${session.user.name}]]*/ ‘User';
...
/*]]>*/
</script>
Switch:
<div th:switch="${user.role}">
<p th:case="'admin'">User is an administrator</p>
<p th:case="#{roles.manager}">User is a manager</p>
</div>
22. Summary
Advatages:Java template
engine for XML, XHTML and HTML5.
Works
both in web and non-web (offline) environments. No hard dependency on
the Servlet API.
Several
template modes: XML, XHTML 1.0 and 1.1, HTML5:
Internationalization support.
Parsed
Is
template cache
extensible
Not
very complex in usage
Many
documentation
Disadvatages:
It's
slowly than other templates.


















 programming
programming informatics
informatics








