Similar presentations:
Chicken Pox
1.
Chicken Pox2. Chicken Pox a.k.a Varicella
Occurs primarily in children, although adults who are notimmune can contract it. It is quite contagious and is spread by
breathing in infected respiratory droplets or unprotected direct
contact with the rash when it has ruptured. In person’s who
have had chickenpox, the virus can cause shingles later in life.
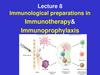
3. What is Chicken Pox?
Chicken pox is caused by avirus called varicella
zoster. People who get the
virus often develop a rash
of spots that looks like
blisters all over their
bodies.The blisters are
small and sit on a area of
red skin that can be
anywhere from the size of
a pencil, eraser to the size
of a dime.
4. What are the Symptoms?
• The early symptoms ofchicken pox may include
cold symptoms, fever,
abdominal pain,
headaches and a general
feeling of illness. These
can come with the rash
or a day or two before it.
The fever may be high
the first few days.
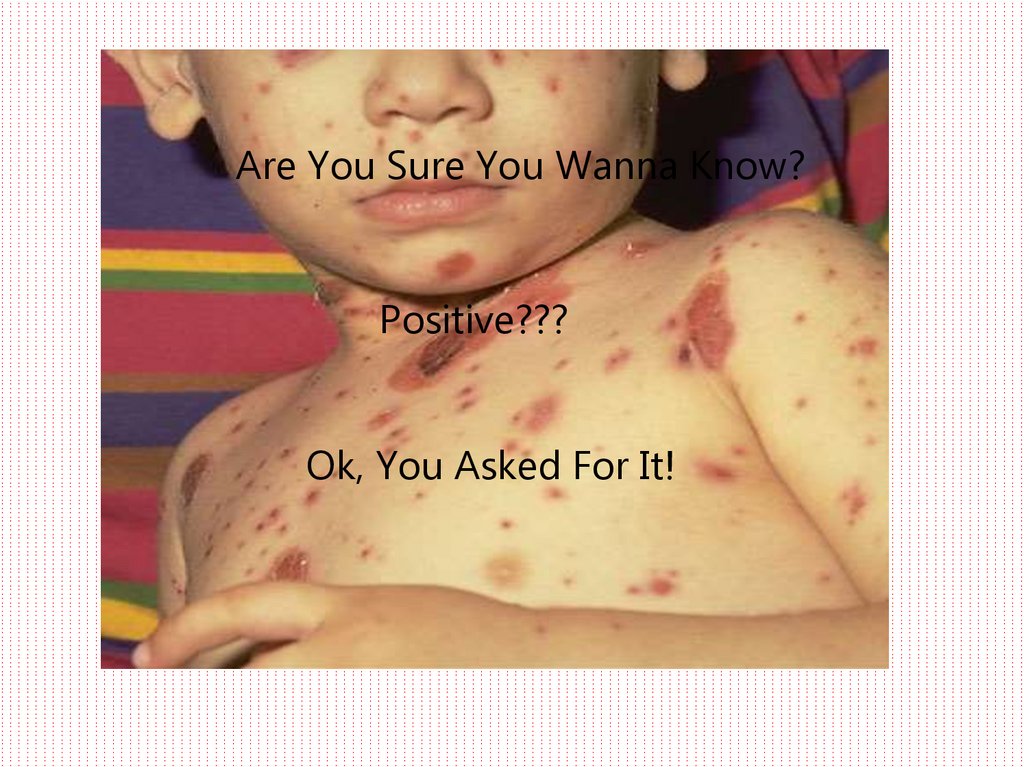
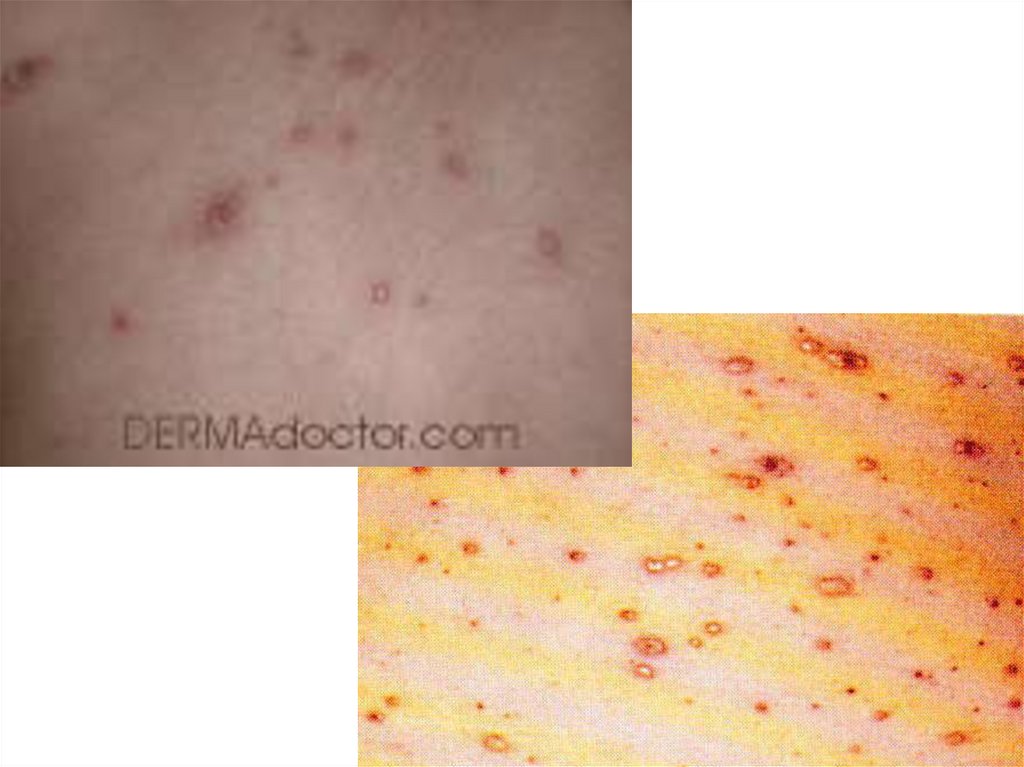
5. Itchy and Scratchy
The best known symptom of chickenpox is the itchy, redrash that breaks out on the face, scalp, chest, back, and
sometimes arms and legs. The rash usually appears about
2 weeks after exposure to the virus and begins as
superficial spots.
The spots quickly fill with a clear fluid, rupture, and
turn crusty. The scabs then fall off in a week or two. The
rash continues to break out for the first 1 to 5 days, so
spots at various stages of development may be present at
the same time. Chickenpox seldom lasts for more than 2
weeks, from the appearance of the first rash to the
disappearance of the last one. A secondary infection of the
ruptured rash by bacteria may cause high fever and skin
scarring.
6. So…What Do These Pox Look Like??
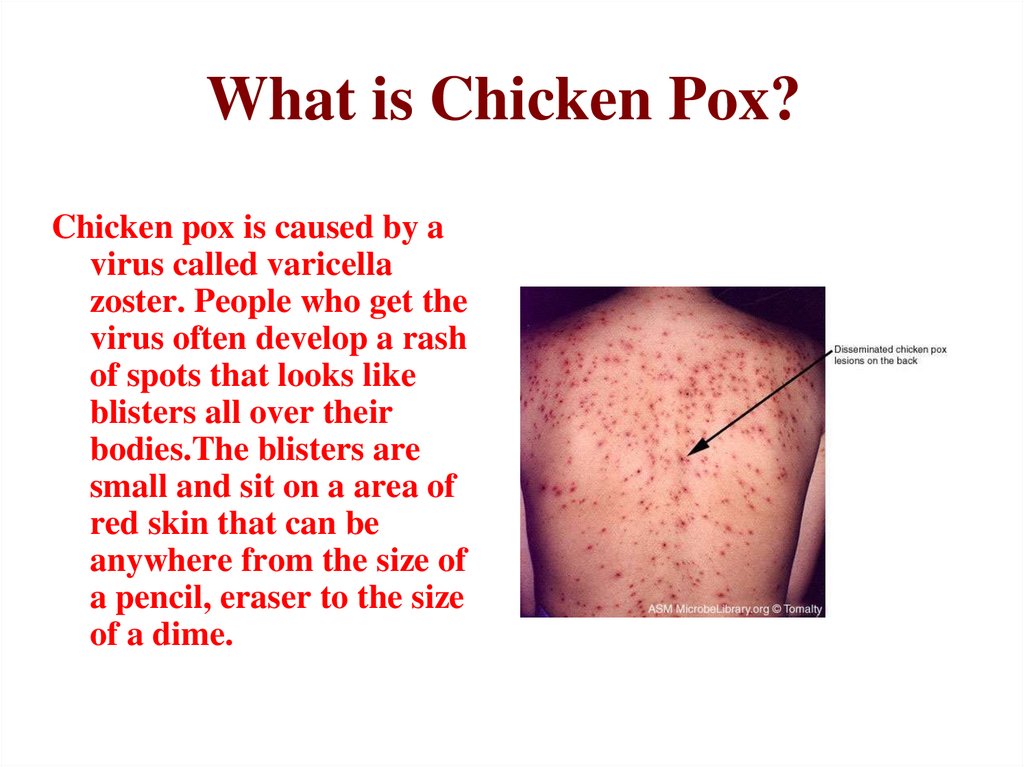
7.
Are You Sure You Wanna Know?Positive???
Ok, You Asked For It!
8.
9.
10. Treatment
• Isolate the diseased until the rashcrusts.
• Keep skin clean by frequent baths
or, once the fever has subsided,
showers. Cool, wet compresses or
tepid water baths help to relieve
itching. Complications are
treated according to symptoms;
Secondary bacterial pneumonia is
treated with antibiotics.
11. Prevention
Children between 12 and 18months should receive a dose of
chickenpox vaccine, Varicellazoster immune globulin. Now,
more than 20 states have passed
legislation
requiring
the
chickenpox vaccine for child care
and school entry.
Healthy
children older than 13, and adults
who
have
no
history
of
chickenpox and have never been
12. Autosomal Issue
If a pregnant woman contractschickenpox during the first or
second trimester, there is a small
risk that her child will be born
with a congenital malformation.
When a pregnant woman
contracts the disease within 5








 medicine
medicine