Similar presentations:
The Integumentary System
1. The Integumentary System
2. Integumentary System
• Only 1.5 to 4 mm thickbut is body’s largest
organ
– 7% of body weight
• Contains all four tissue
types
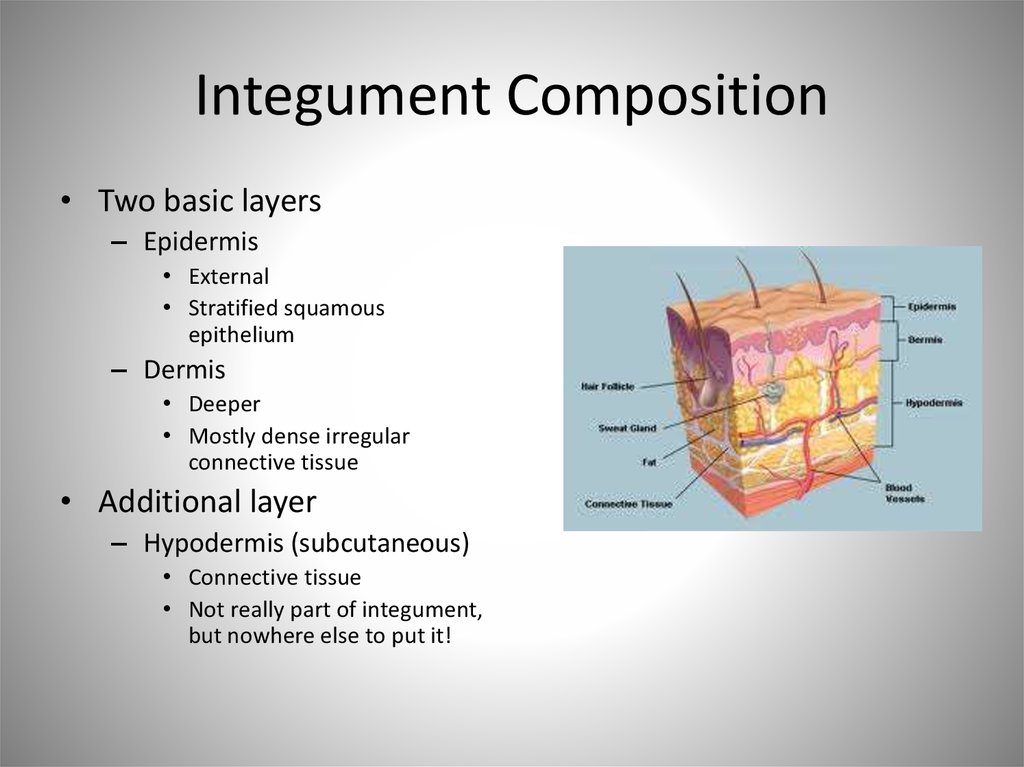
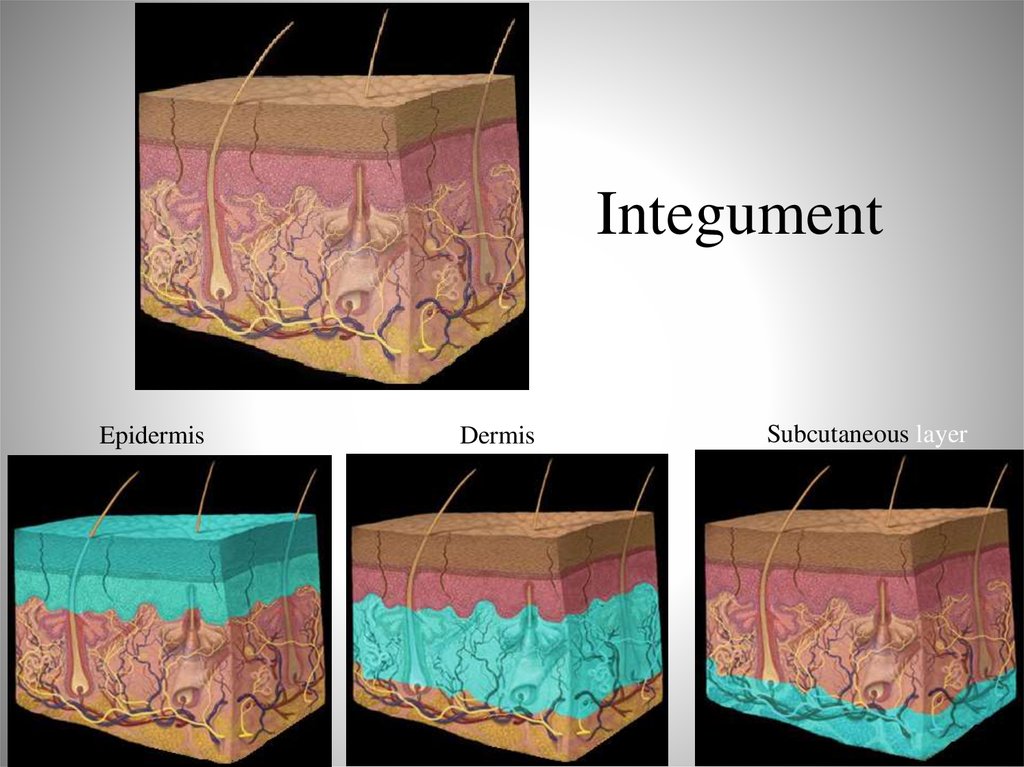
3. Integument Composition
• Two basic layers– Epidermis
• External
• Stratified squamous
epithelium
– Dermis
• Deeper
• Mostly dense irregular
connective tissue
• Additional layer
– Hypodermis (subcutaneous)
• Connective tissue
• Not really part of integument,
but nowhere else to put it!
4. General Functions
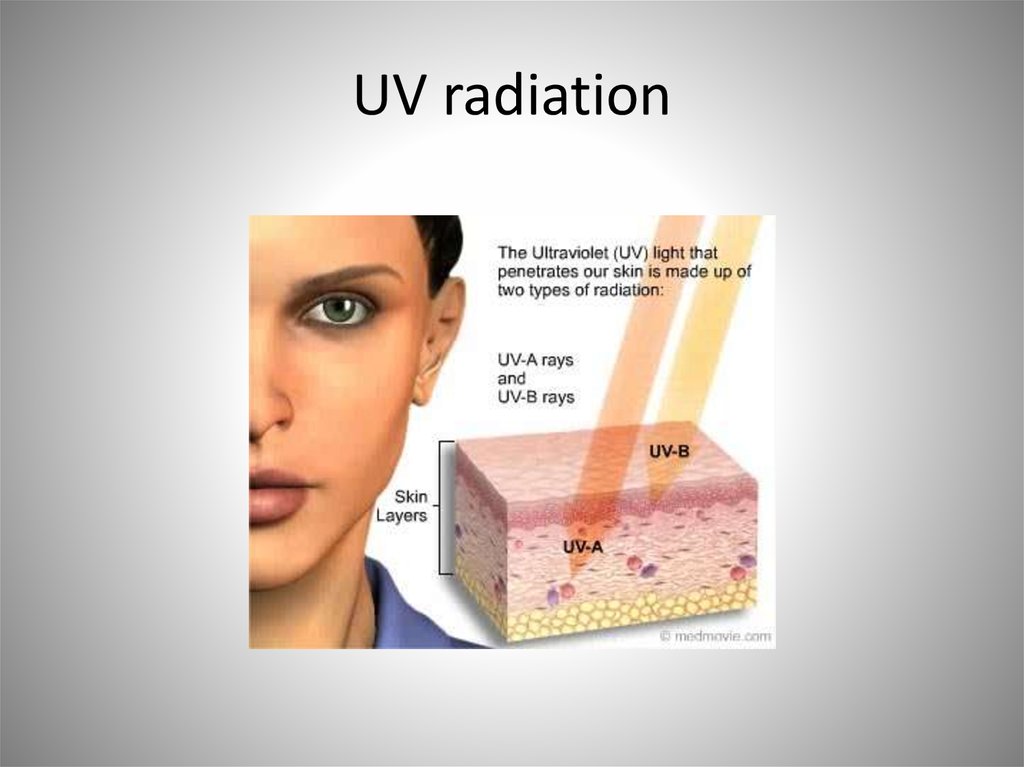
• Protection– Mechanical damage
– UV radiation
– Resists microbes (1st and
second lines of defense)
– Dehydration
• Secretion and absorption
– Sweat glands
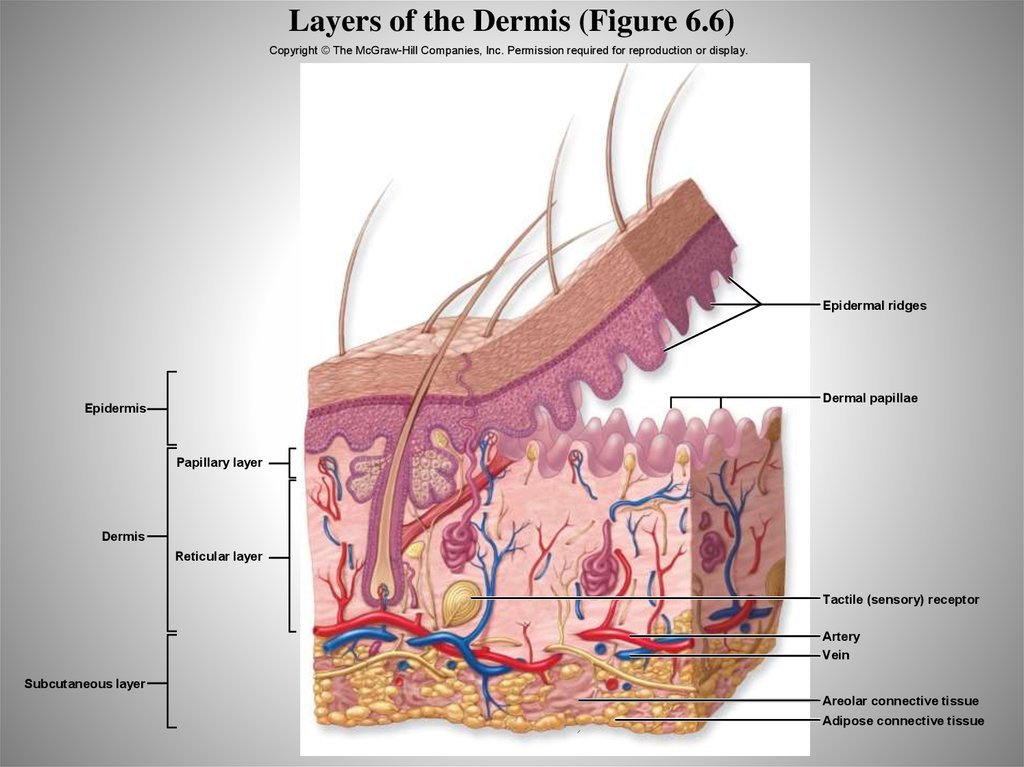
• Metabolic regulation
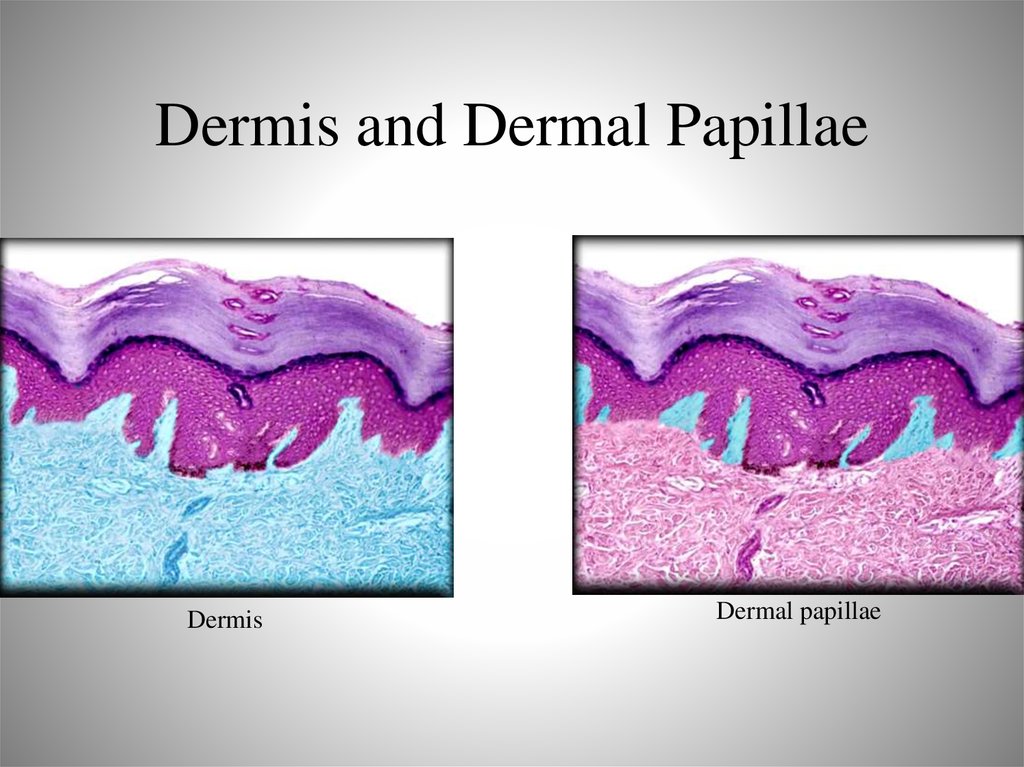
– Vitamin D
• Thermoregulation
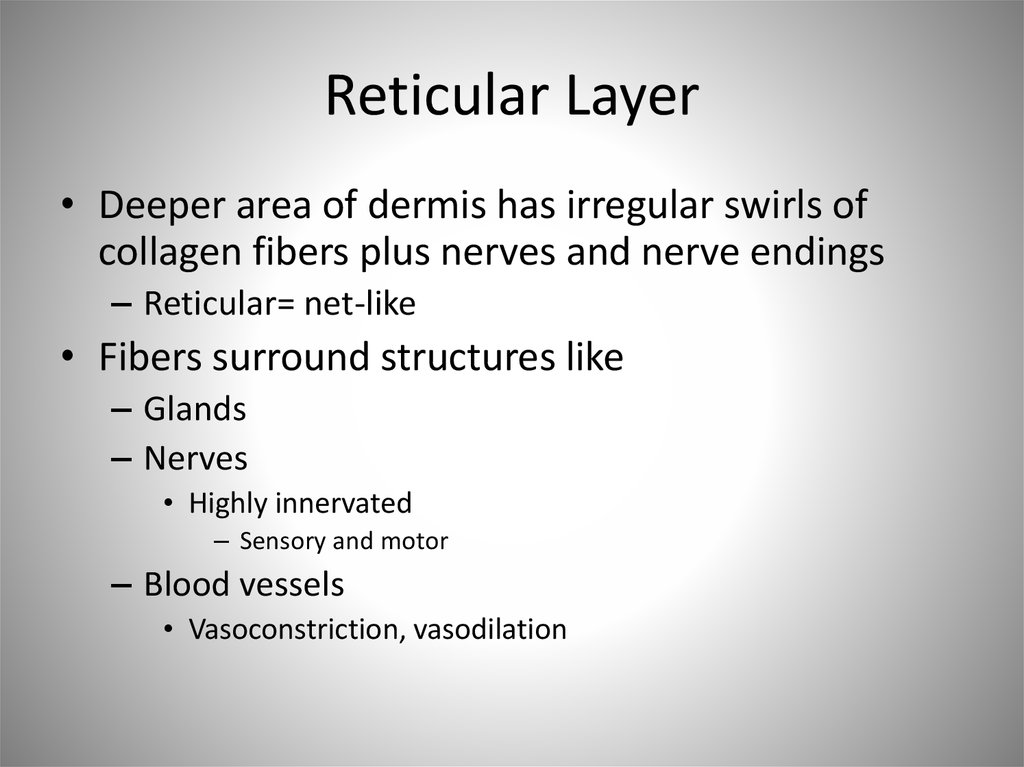
• Sensation
5. Integument
EpidermisDermis
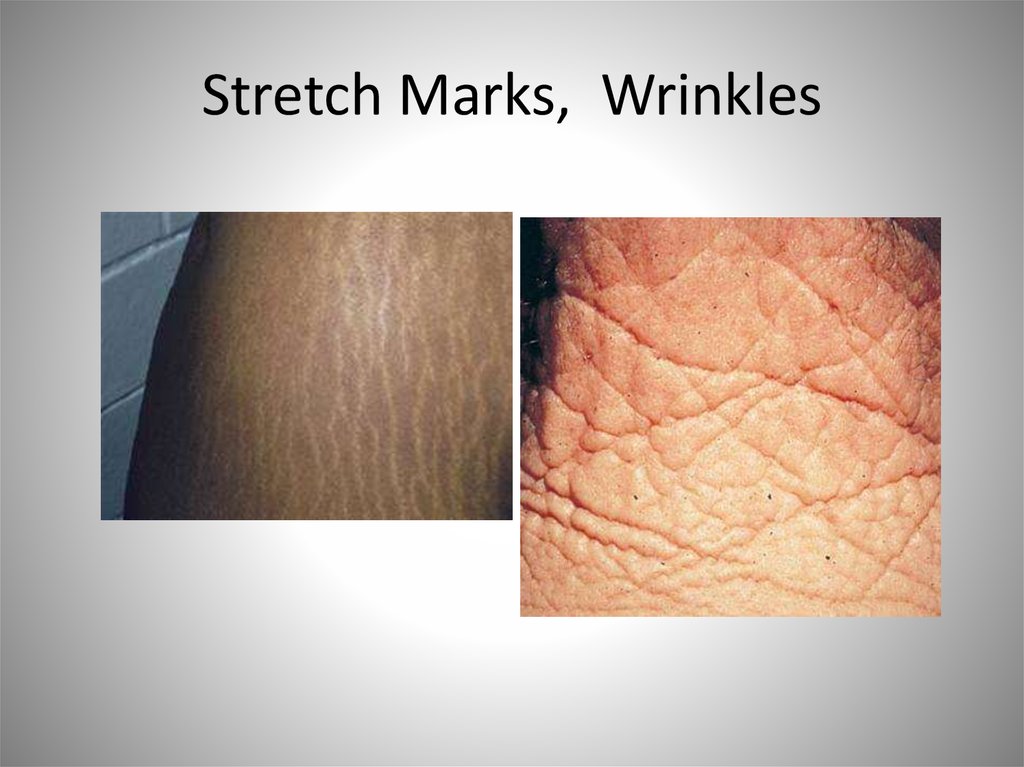
Subcutaneous layer
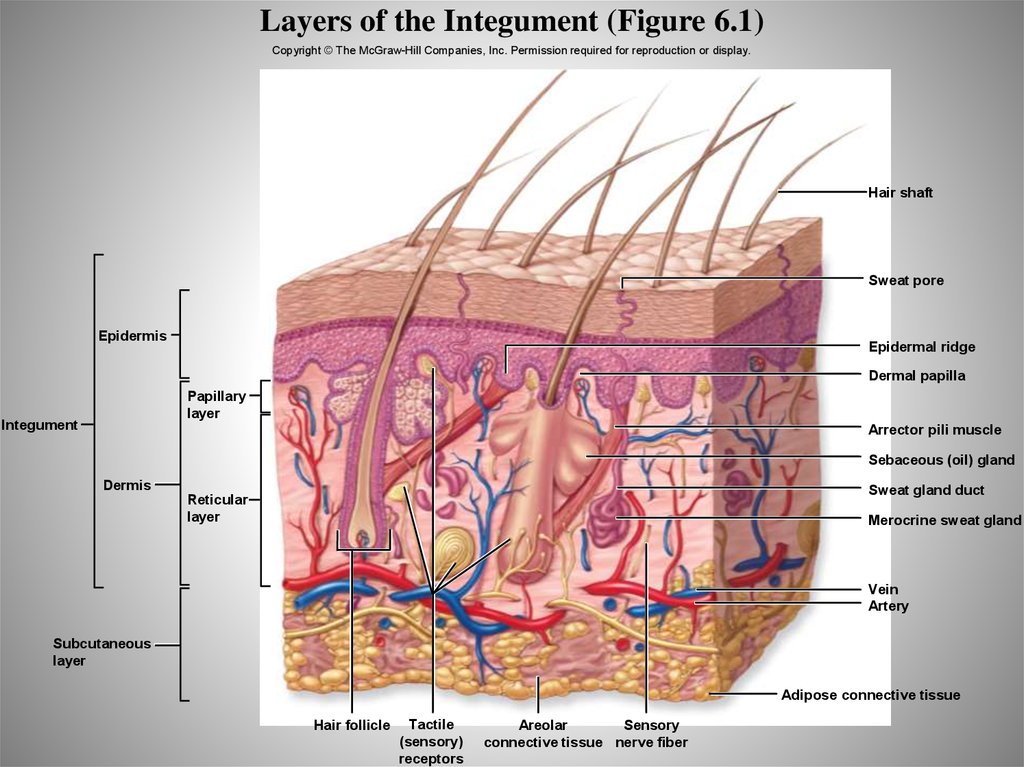
6. Layers of the Integument (Figure 6.1)
Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.Hair shaft
Sweat pore
Epidermis
Epidermal ridge
Dermal papilla
Papillary
layer
Integument
Arrector pili muscle
Sebaceous (oil) gland
Dermis
Sweat gland duct
Reticular
layer
Merocrine sweat gland
Vein
Artery
Subcutaneous
layer
Adipose connective tissue
Hair follicle
Tactile
(sensory)
receptors
Areolar
Sensory
connective tissue nerve fiber
7. Epidermis
• Epithelial tissue arranged in 5 layers or strata– Cells divide in only in base layer and are pushed
outward
– Form a keratinized layer on surface
– Cell division is regulated by growth factor (EGF)
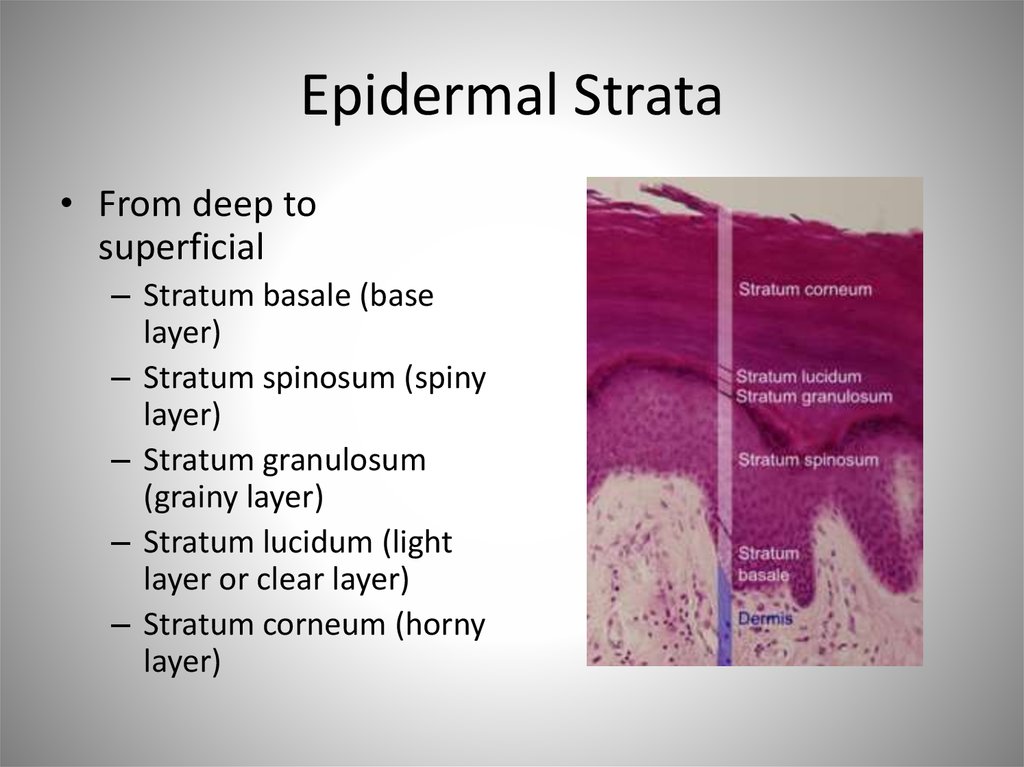
8. Epidermal Strata
• From deep tosuperficial
– Stratum basale (base
layer)
– Stratum spinosum (spiny
layer)
– Stratum granulosum
(grainy layer)
– Stratum lucidum (light
layer or clear layer)
– Stratum corneum (horny
layer)
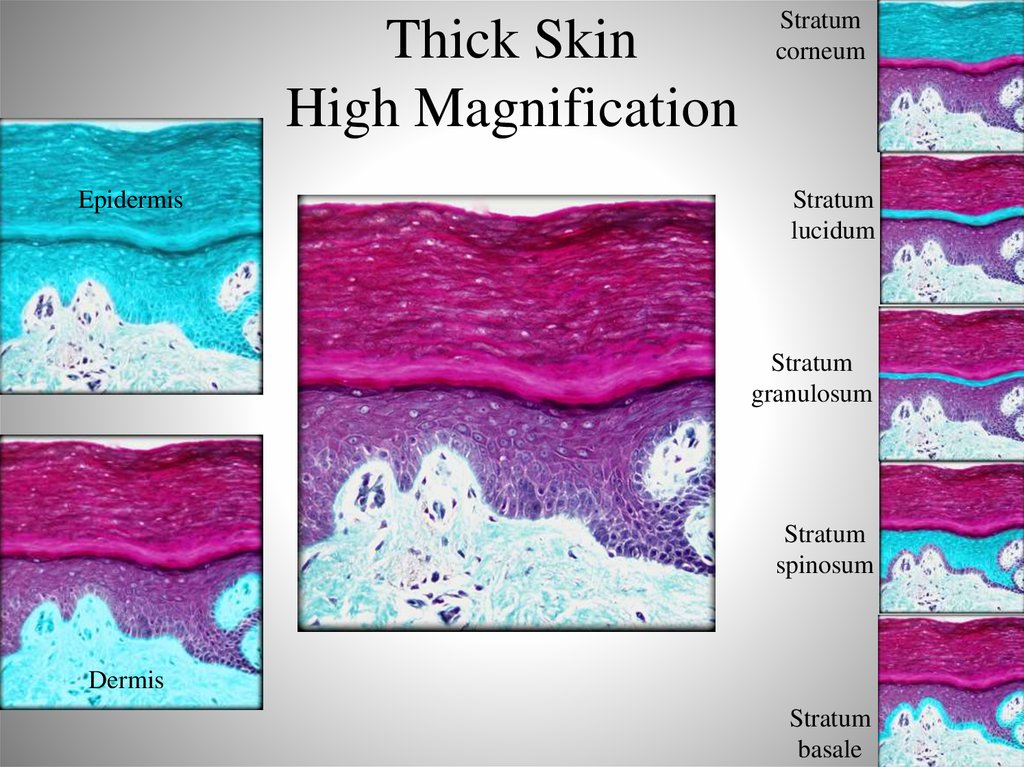
9. Thick Skin High Magnification
EpidermisStratum
corneum
Stratum
lucidum
Stratum
granulosum
Stratum
spinosum
Dermis
Stratum
basale
10. Stratum Basale
• Single layer of cuboidal to low columnar cells attached to abasement membrane
• Include
– Keratinocytes
• Keratin is a tough, water-resistant protein
– Melanocytes
• Melanin is a brown protein pigment
• Transfer melanin to keratinocytes for protection against UV damage
• Skin color
– Tactile cells (Merkel cells)
• Touch receptors
11. Stratum Spinosum
• Cells are pushed up from below and become“squished” and look spiny on cross sectional
view
– Spiny appearance comes from connections
(desmosomes) between cells
– Cells are further from blood supply so alive, but
not dividing
• Epidermal dendritic cells
– Phagocytic immune cells
12. Stratum Granulosum
• Cells in this layer start to keratinize (fill withkeratin) and look grainy
– Keratohyalin- precursor to keratin
• As they go through the process, the organelles
in these cells disintegrate
• Cells die
13. Stratum Lucidum
• Keratinocytes with transforming keratohyaline– Keratohyaline transforms to clear substance
eleidin
– Found only in thick skin
– Dead cells
14. Stratum Corneum
• 20-30 layers of dead keratinocytes• Keratin now fully formed
• Cells are dead
– Keratinized stratified squamous epithelium
– Migration process from stratum basale about 2
weeks
– Remain in stratum corneum for about 2 weeks
and then are shed
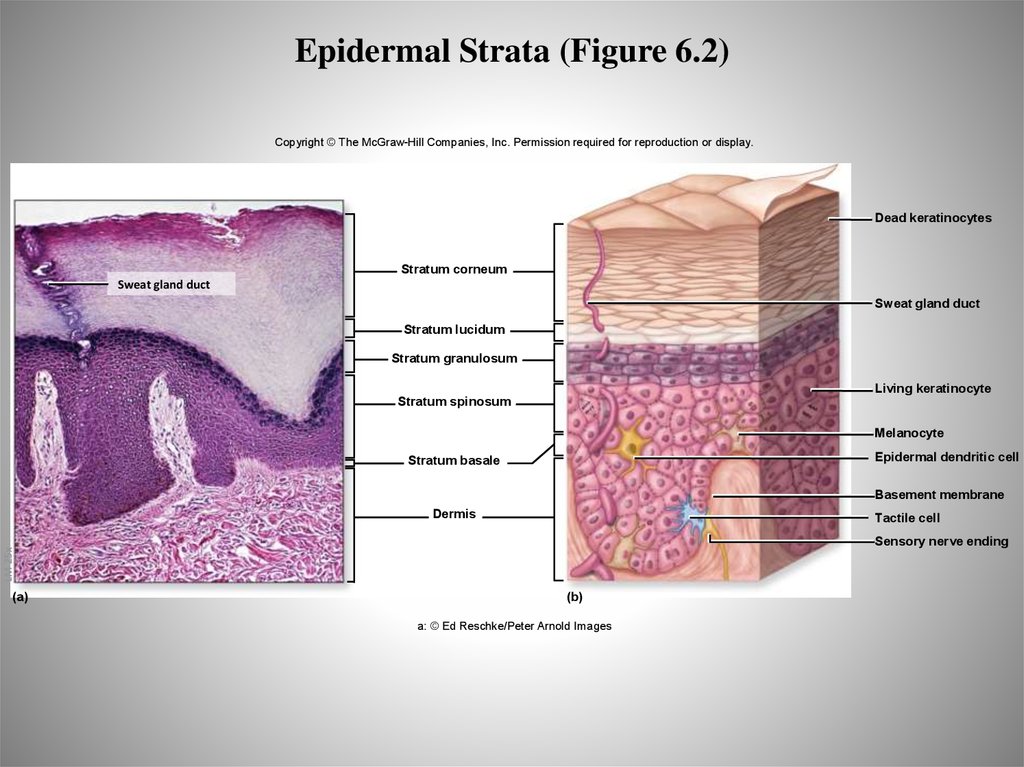
15. Epidermal Strata (Figure 6.2)
Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.Dead keratinocytes
Stratum corneum
Sweat gland duct
Sweat gland duct
Stratum lucidum
Stratum granulosum
Living keratinocyte
Stratum spinosum
Melanocyte
Epidermal dendritic cell
Stratum basale
Basement membrane
Dermis
Tactile cell
LM 25x
Sensory nerve ending
(a)
(b)
a: © Ed Reschke/Peter Arnold Images
16. Variations in the Epidermis
• Epidermis is not the same thickness over allportions of the body or for all people
– Thick skin
• Soles of feet, fingers, toes
• Has all 5 layers, but no hair follicles or sebaceous glands
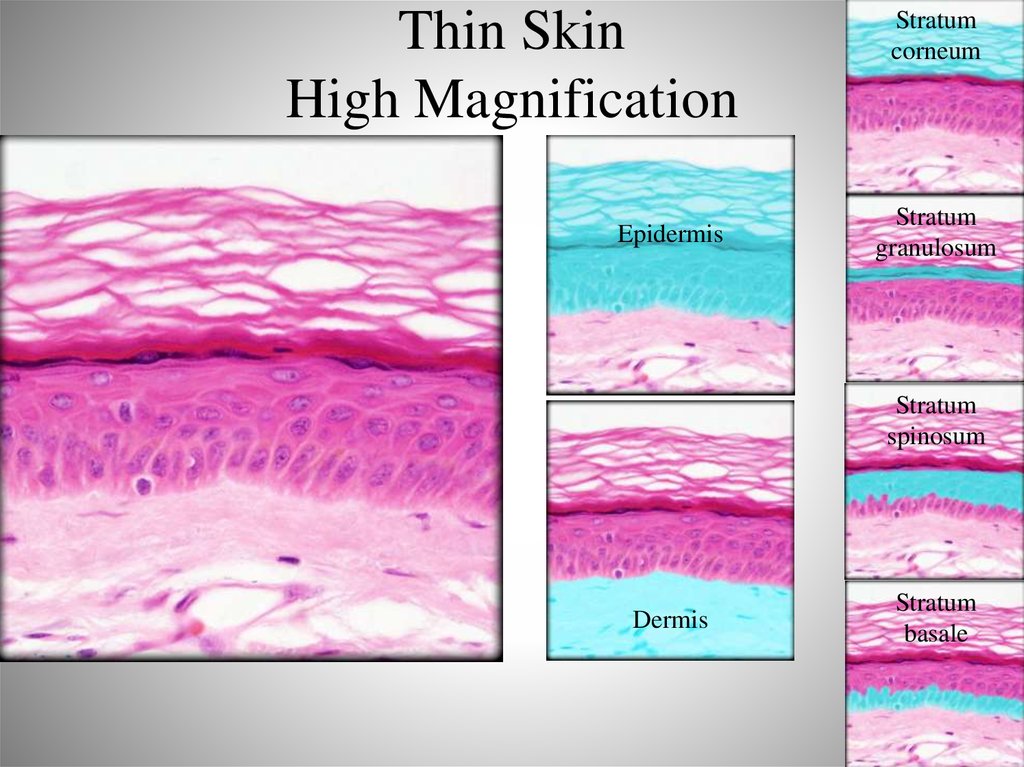
– Thin skin
• Rest of body
• Doesn’t have 5 layers, has hair follicles and sebaceous
glands
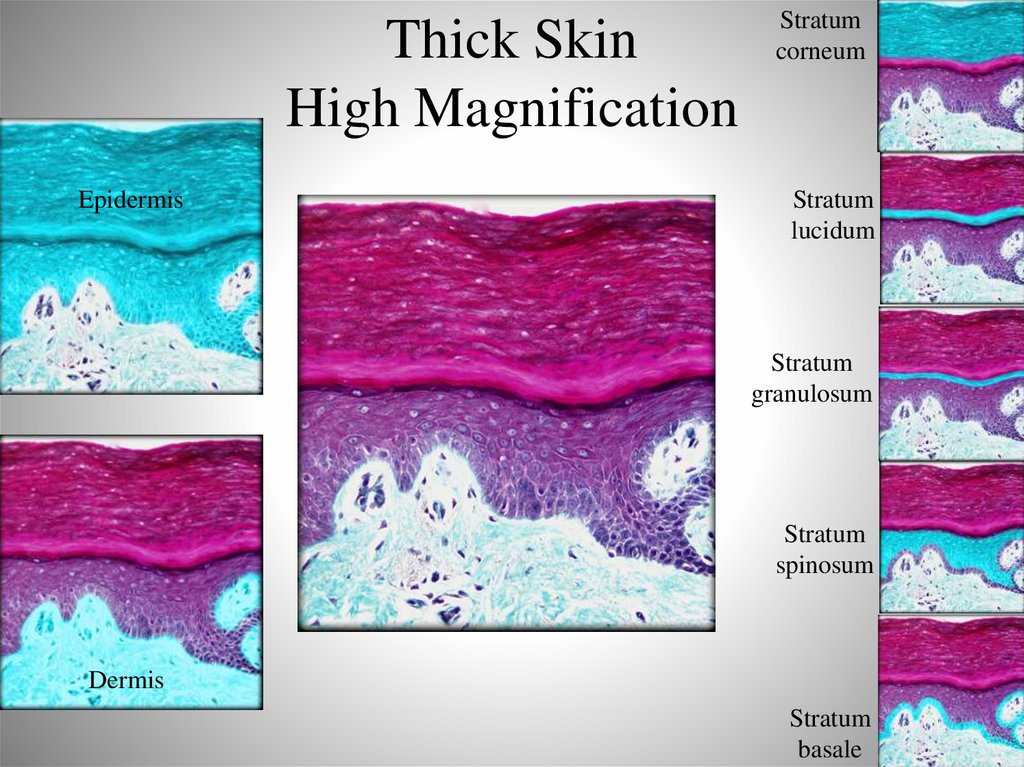
17. Thick Skin
Thin Skin18. Thick Skin High Magnification
EpidermisStratum
corneum
Stratum
lucidum
Stratum
granulosum
Stratum
spinosum
Dermis
Stratum
basale
19. Thin Skin High Magnification
EpidermisStratum
corneum
Stratum
granulosum
Stratum
spinosum
Dermis
Stratum
basale
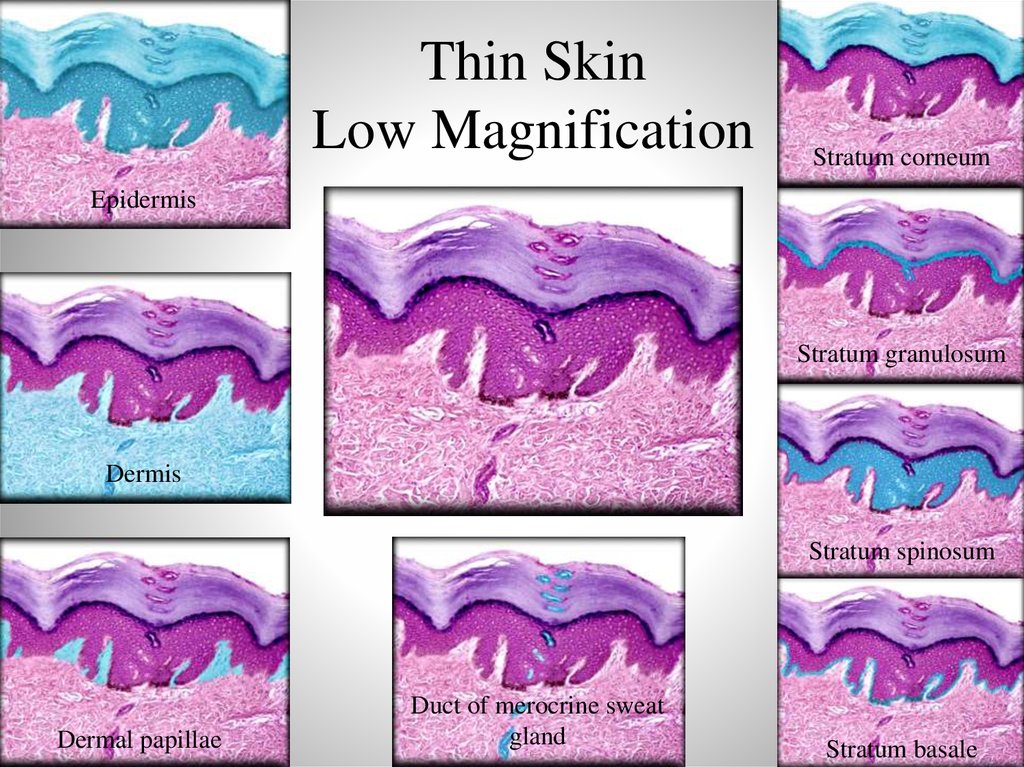
20. Thin Skin Low Magnification
Stratum corneumEpidermis
Stratum granulosum
Dermis
Stratum spinosum
Dermal papillae
Duct of merocrine sweat
gland
Stratum basale
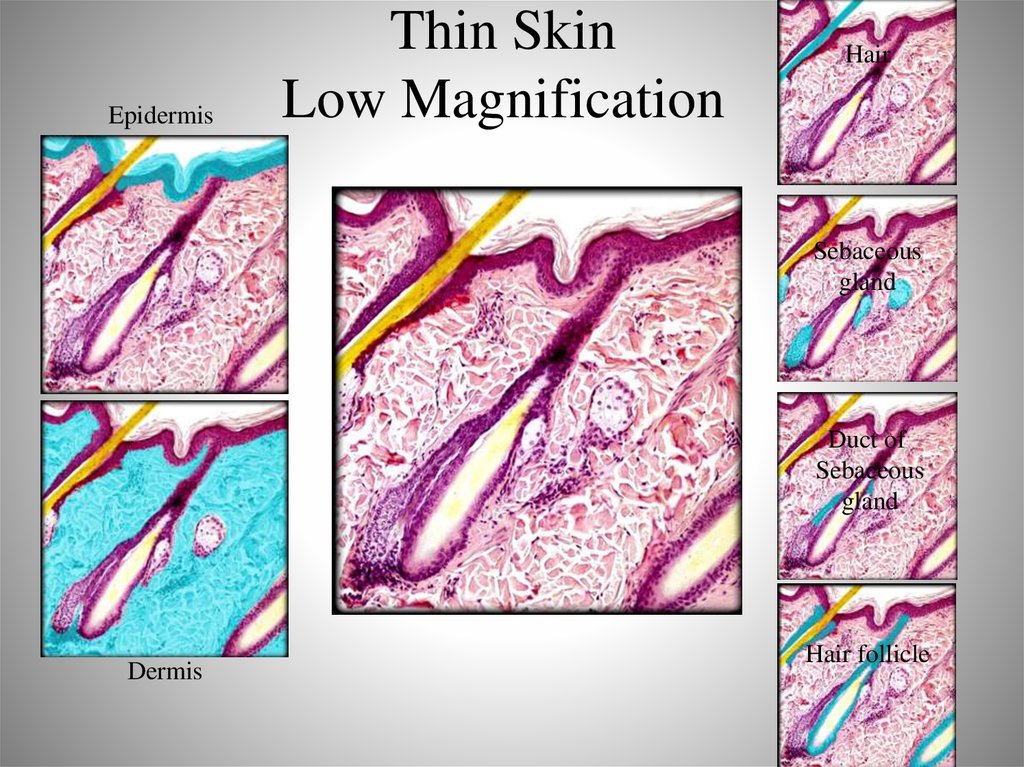
21. Thin Skin Low Magnification
EpidermisThin Skin
Low Magnification
Hair
Sebaceous
gland
Duct of
Sebaceous
gland
Dermis
Hair follicle
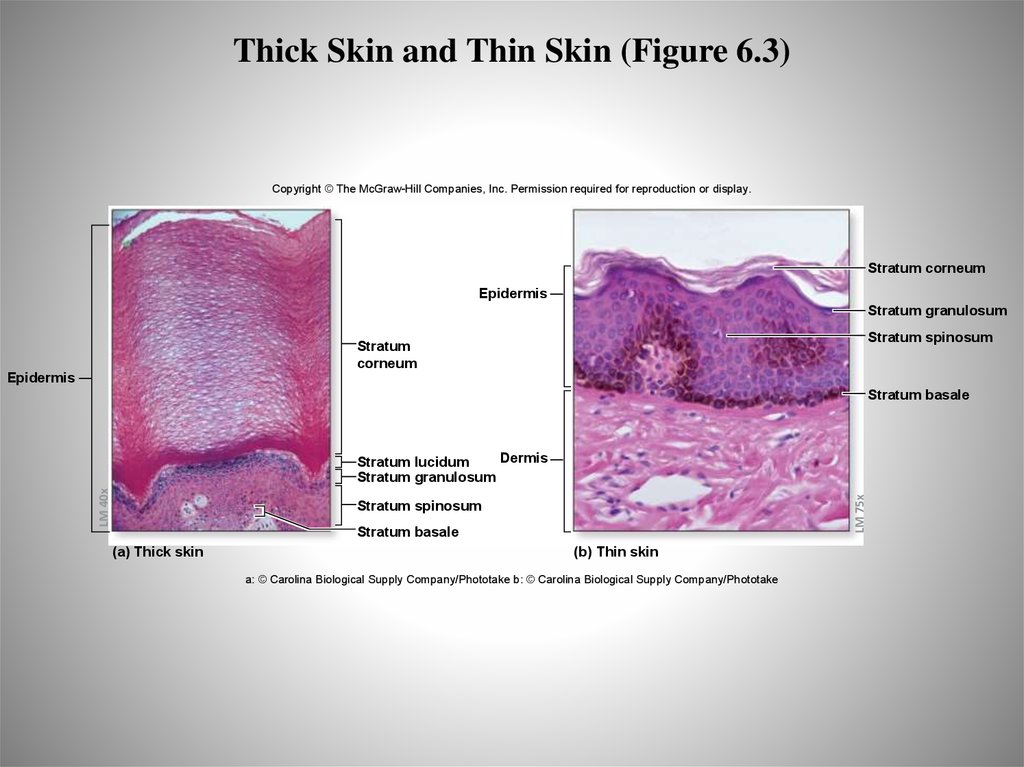
22. Thick Skin and Thin Skin (Figure 6.3)
Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.Stratum corneum
Epidermis
Stratum granulosum
Stratum spinosum
Stratum
corneum
Epidermis
Stratum basale
LM 75x
LM 40x
Dermis
Stratum lucidum
Stratum granulosum
Stratum spinosum
Stratum basale
(a) Thick skin
(b) Thin skin
a: © Carolina Biological Supply Company/Phototake b: © Carolina Biological Supply Company/Phototake
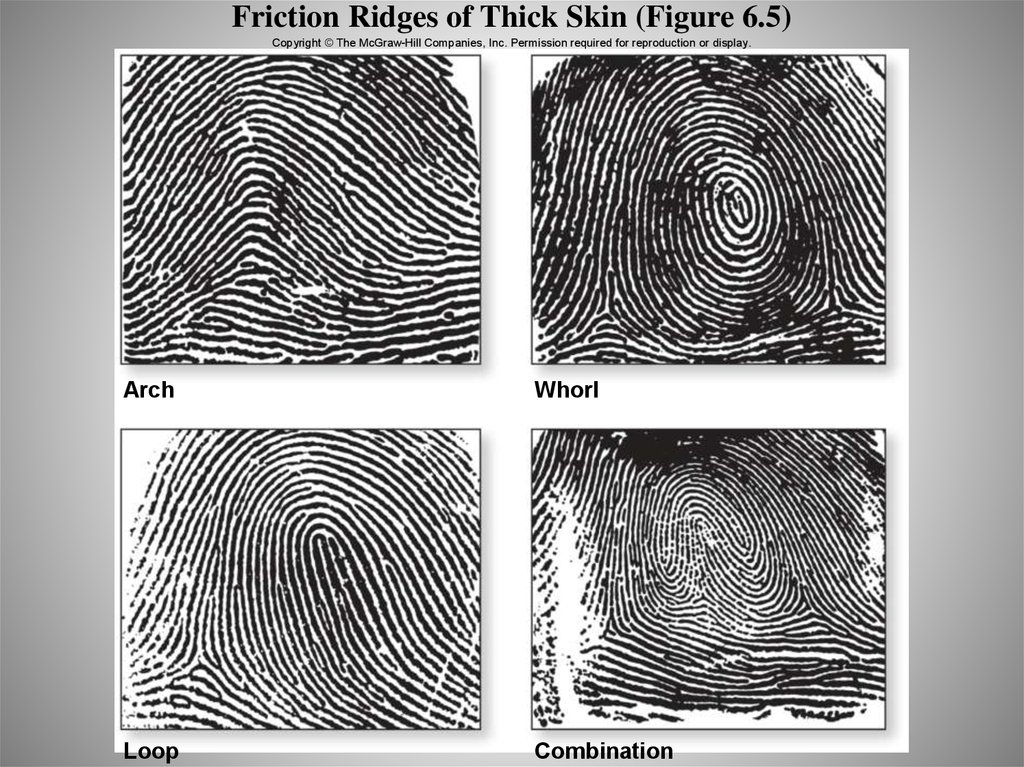
23. Variations in the Epidermis: Friction Ridges
• Ridge patterns in skin– Thick skin of fingers,
hands, feet, toes
– Friction ridges
• Enhance grip or contact
– Arise from folds in
epidermis and dermis
24. Friction Ridges of Thick Skin (Figure 6.5)
Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.Arch
Whorl
Loop
Combination
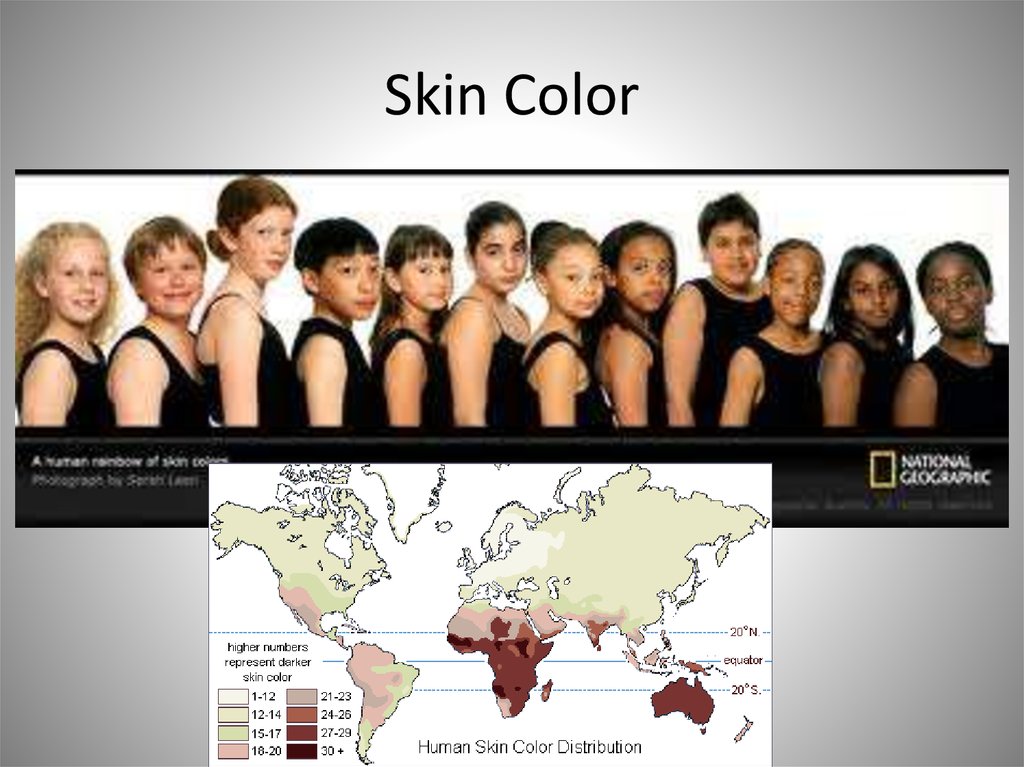
25. Variations in the Epidermis: Skin Color
• Melanin– Brown, black, yellow-brown shades
– All people have the same number of melanocytes, but
some have more active melanin production than others
• Variations due to heredity, UV exposure
• Hemoglobin
– Red in oxygen, bluer in lower oxygen
• Carotenes
– From food, yellows or oranges
• Other chemicals
– Bilirubin, biliverdin
26. Skin Color
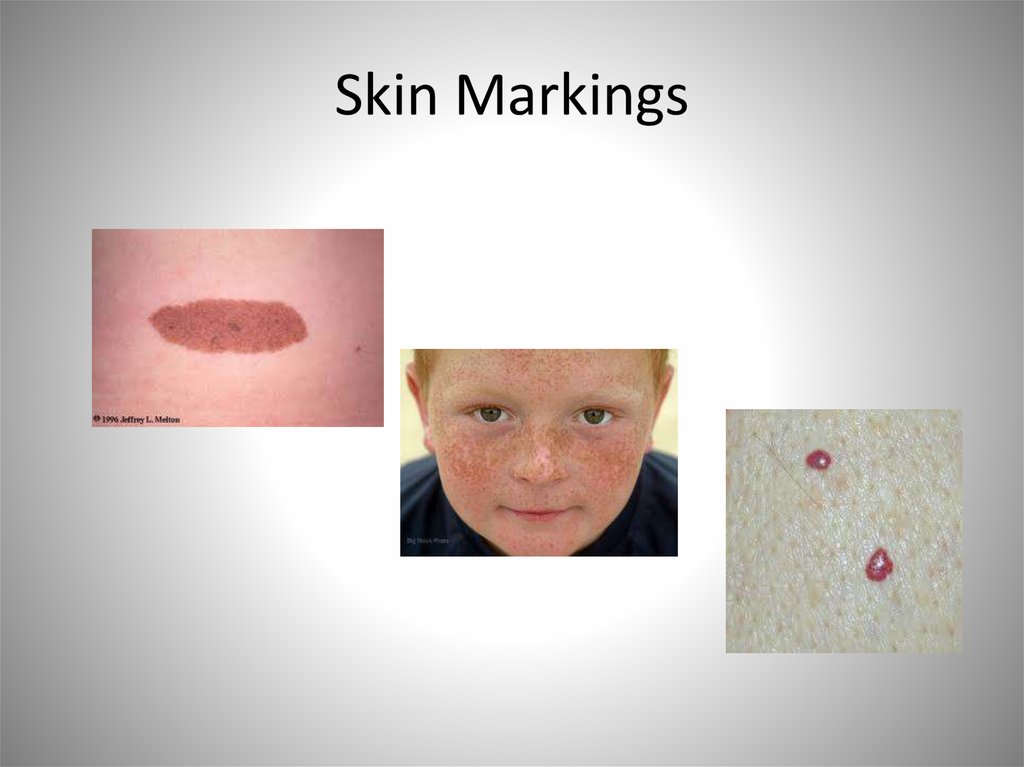
27. Skin Markings
28. UV radiation
29. Dermis
• Deep to the epidermis– Is thicker layer than epidermis
• Dense Irregular Connective Tissue
– Mostly collagen, but some elastic and reticular
fibers
• Two Layers
– Papillary layer
– Reticular layer
30. Dermis
31. Layers of the Dermis (Figure 6.6)
Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.Epidermal ridges
Dermal papillae
Epidermis
Papillary layer
Dermis
Reticular layer
Tactile (sensory) receptor
Artery
Vein
Subcutaneous layer
Areolar connective tissue
Adipose connective tissue
32. Dermis and Dermal Papillae
DermisDermal papillae
33. Papillary Layer
• Increased surface area– More contact with epidermal ridges to hold more
tightly
• Arranged on rows in thick skin to form
pressure ridges
• Also amplify touch sensations
34. Reticular Layer
• Deeper area of dermis has irregular swirls ofcollagen fibers plus nerves and nerve endings
– Reticular= net-like
• Fibers surround structures like
– Glands
– Nerves
• Highly innervated
– Sensory and motor
– Blood vessels
• Vasoconstriction, vasodilation
35. Lines of Cleavage, Stretch Marks, Wrinkles
• Collagen and elastic fibers give skin many of itsproperties
– Arranged in parallel bundles
– Allow for stretch and recoil
• Lines of cleavage
– Cuts parallel to lines heal faster than perpendicular
cuts
• Stretch marks
– Tearing of fibers due to rapid weight gain, pregnant
• Wrinkles
– Flexibility of dermis decreases with age, UV
36. Lines of Cleavage (Figure 6.7)
Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.An incision
perpendicular
to cleavage lines may
gape and delay healing.
An incision parallel to
cleavage lines is more
likely to heal quickly and
not gape open.
37. Stretch Marks, Wrinkles
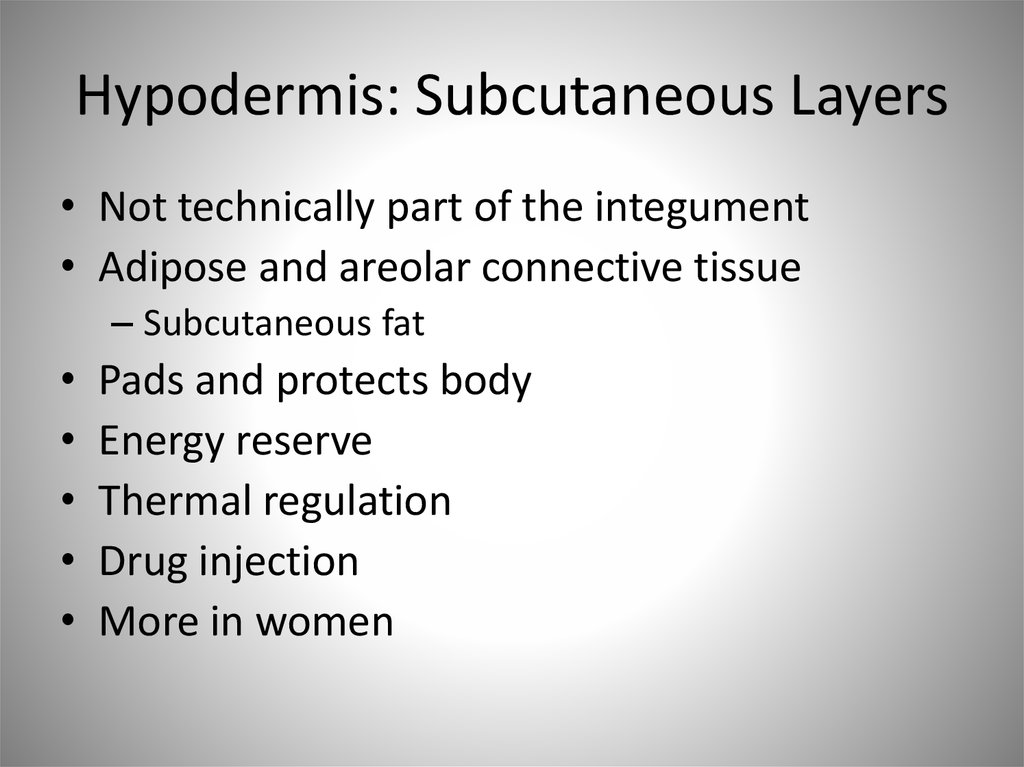
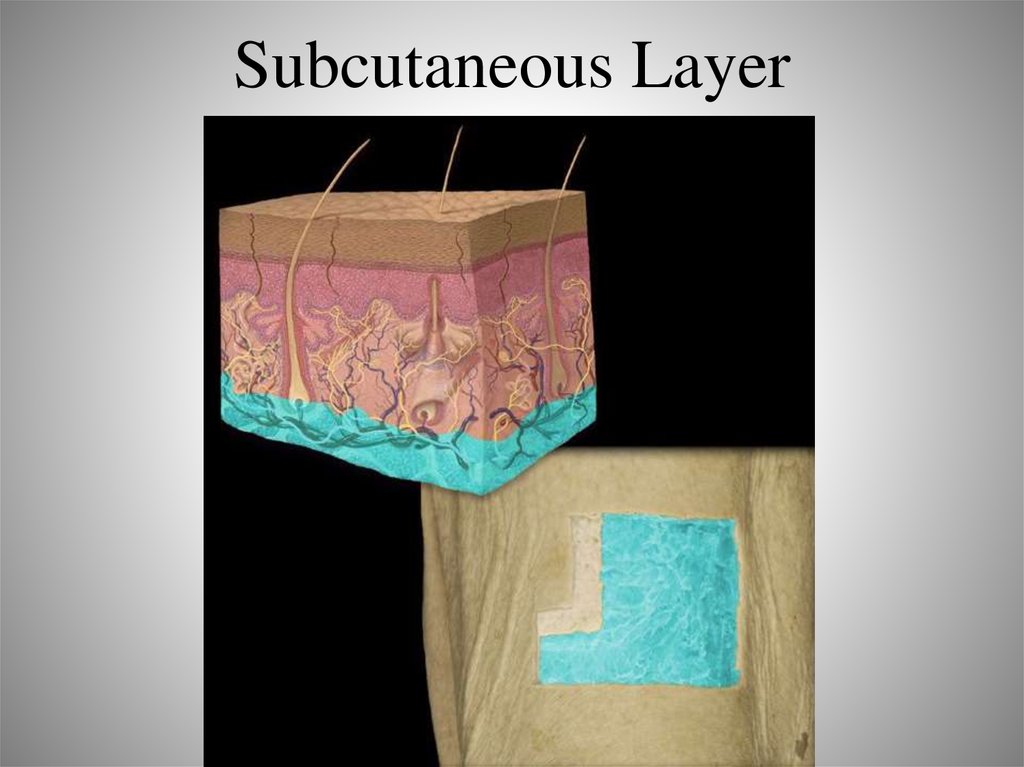
38. Hypodermis: Subcutaneous Layers
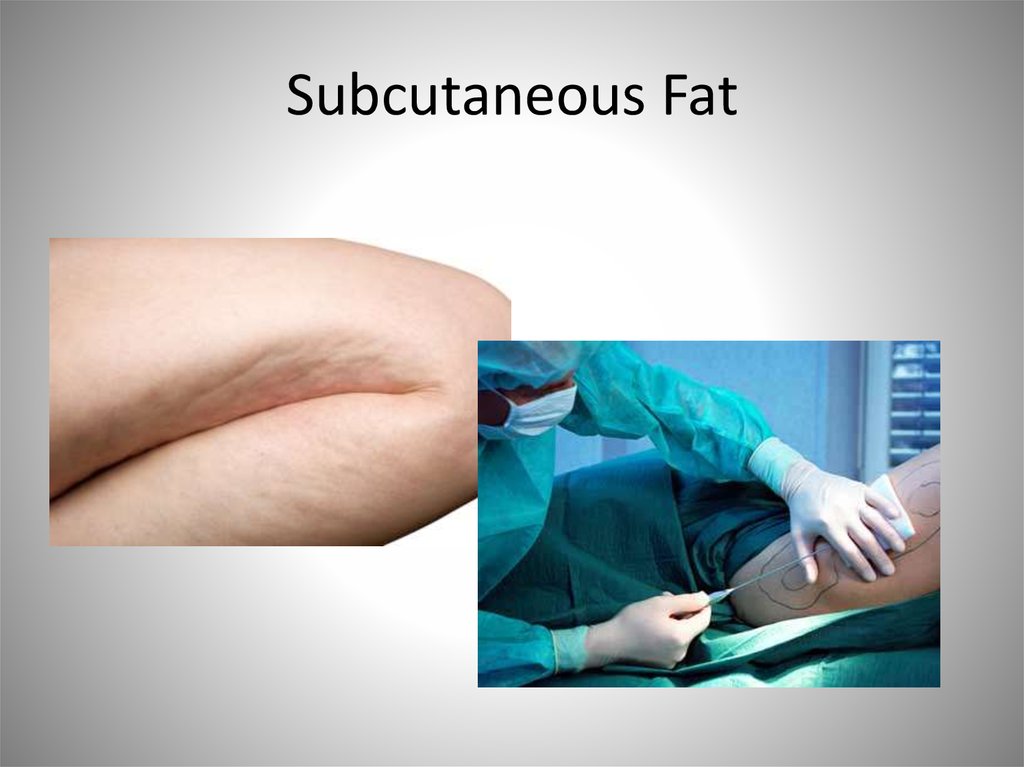
• Not technically part of the integument• Adipose and areolar connective tissue
– Subcutaneous fat
Pads and protects body
Energy reserve
Thermal regulation
Drug injection
More in women
39. Subcutaneous Layer
40. Subcutaneous Fat
41. Structures Derived from Epidermis
• Hair and nails are both derived from dead,keratinized epidermal cells
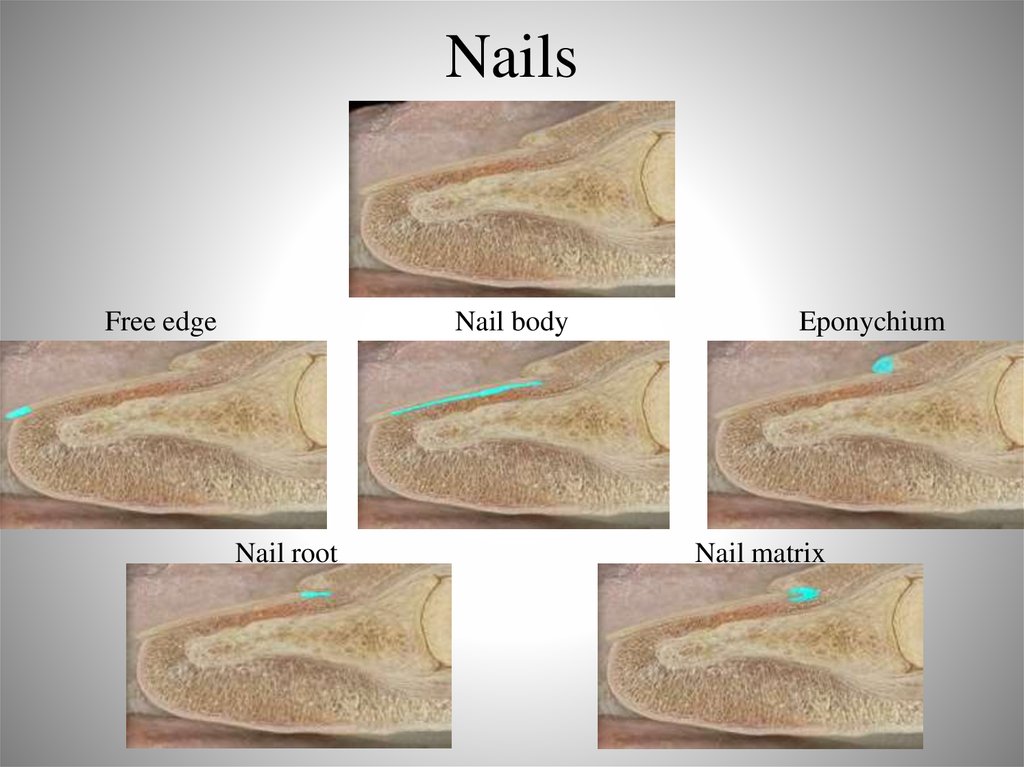
42. Nails
• Nail plate– Nail body
• Visible part, pinkish due to underlying capillaries
– Nail root
• In the skin
– Free edge
• Whitish edge
• Nail bed
– Under nail
• Nail matrix
– Actively growing
43. Nails
Free edgeNail body
Nail root
Eponychium
Nail matrix
44. Hair
• Almost everywhere on body– Patterns based on heredity
• Single hair is called pilus
• Composed of keratinized cells growing from a
follicle (little pocket)
45. Three Kinds of Hair
• Lanugo– Fine, on fetus
– Falls out by birth
– Preemies have lots of it!
• Vellus
– Primary hair
– Fine, unpigmented, lightly
pigmented
– Limbs
• Terminal
– Head
– Eyebrows, eyelashed
– Pubic haiit
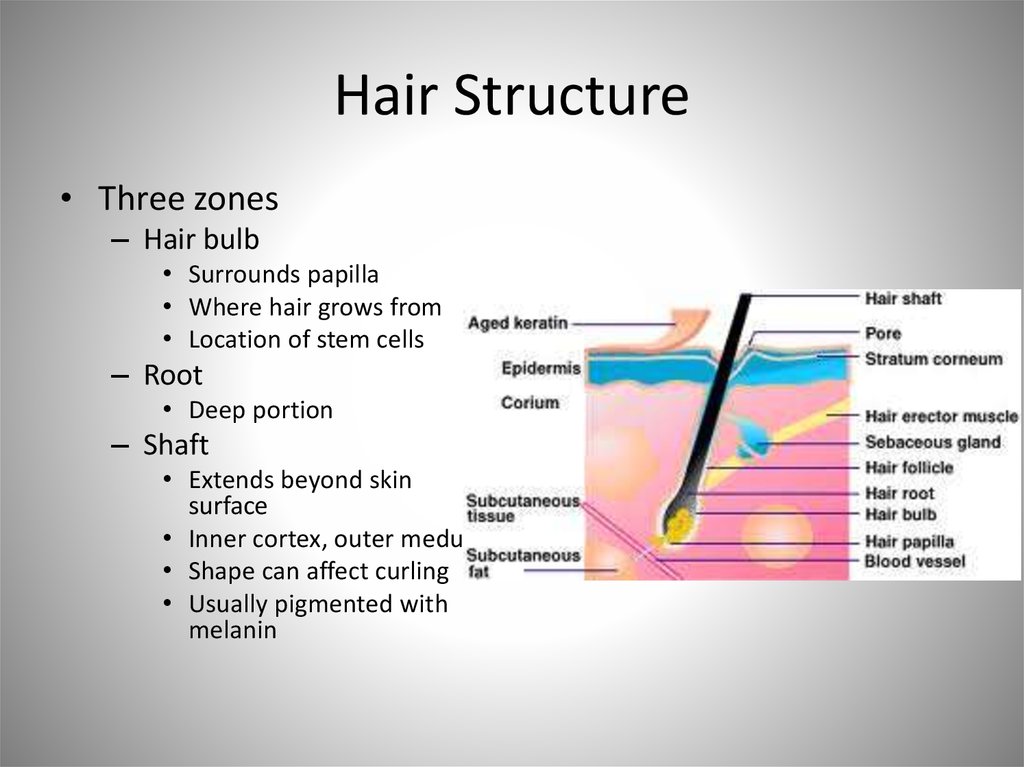
46. Hair Structure
• Three zones– Hair bulb
• Surrounds papilla
• Where hair grows from
• Location of stem cells
– Root
• Deep portion
– Shaft
• Extends beyond skin
surface
• Inner cortex, outer medulla
• Shape can affect curling
• Usually pigmented with
melanin
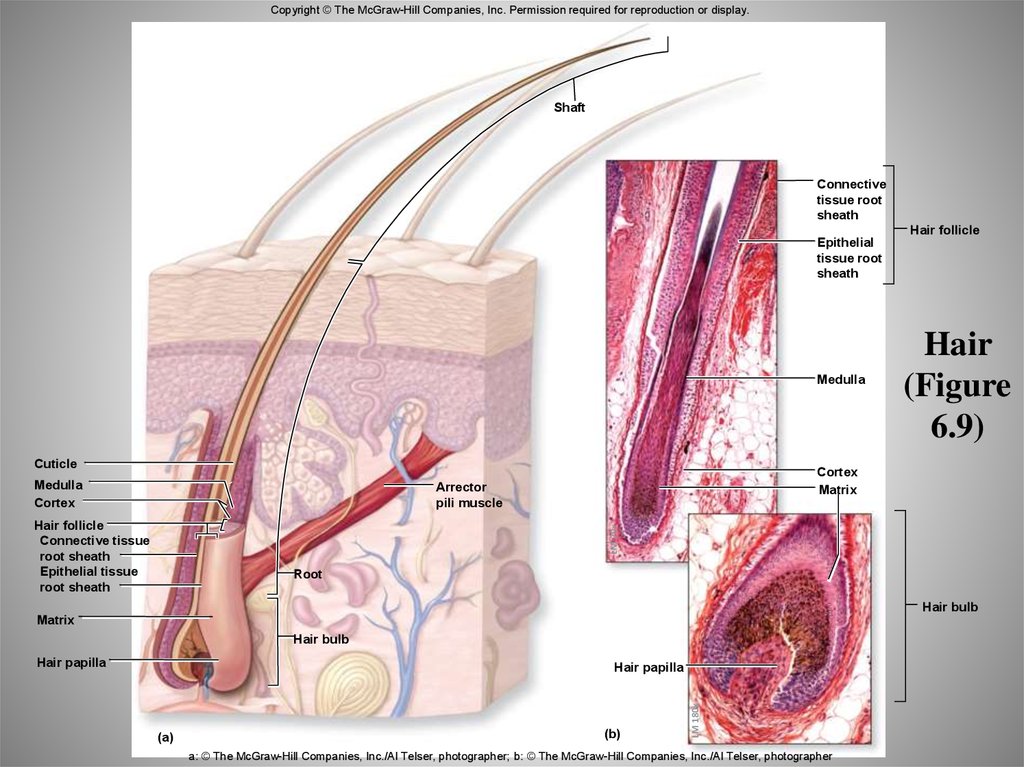
47. Hair (Figure 6.9)
Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.Shaft
Connective
tissue root
sheath
Hair follicle
Epithelial
tissue root
sheath
Medulla
Cuticle
Medulla
Cortex
Cortex
Matrix
Arrector
pili muscle
LM 70x
Hair follicle
Connective tissue
root sheath
Epithelial tissue
root sheath
Hair
(Figure
6.9)
Root
Hair bulb
Matrix
Hair bulb
Hair papilla
(a)
(b)
LM 180x
Hair papilla
a: © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc./Al Telser, photographer; b: © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc./Al Telser, photographer
48. Arrector Pili
49. Hair Functions
• Protects– Sun
– Inhaled particles
• Heat retention
• Sensory reception
– Hair root plexuses
• Visual identification
• Chemical signals
– pheromones
50. Hair Color
51. Hair Growth and Replacement
Grows .3mm/day for 2-5 y
Dormant phase 3-4 months
Falls out- normal hair loss=10-100 hairs/day
Hair thinning=alopecia
52. Pattern Baldness
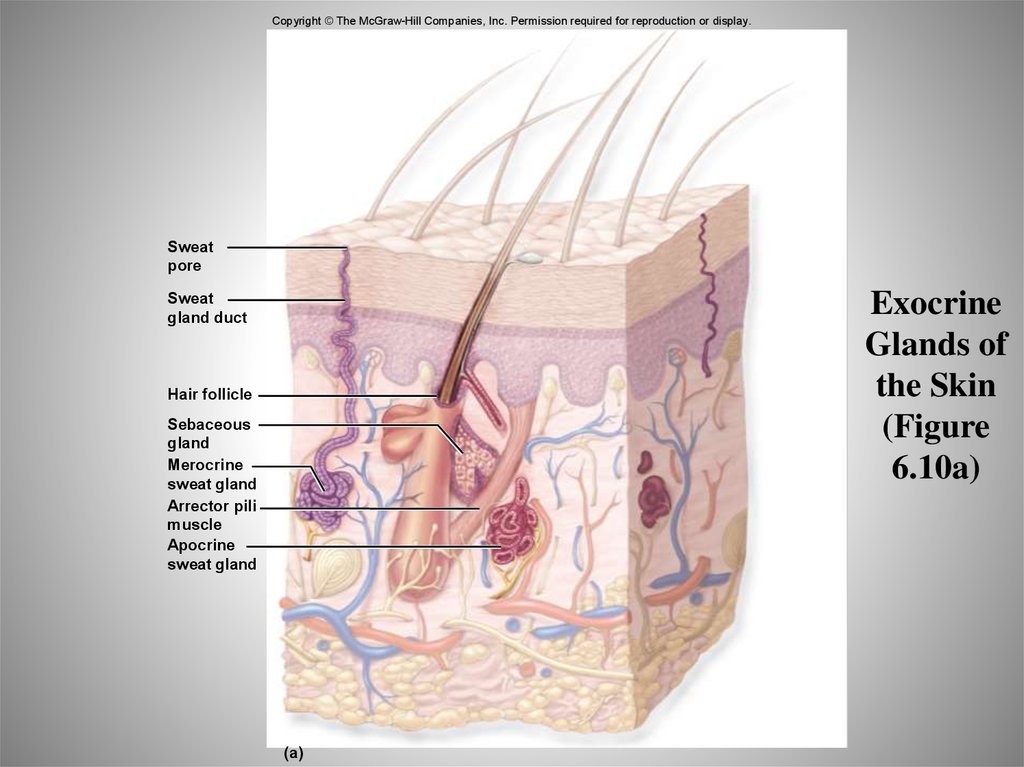
53. Sweat Glands
• Sweat glands (also called sudoriferous glands)are exocrine (ducted) glands
• Sweat contains mostly water plus some
excretions and secretions (such as
pheromones [sex attractants])
• Two types
– Merocrine – thermal regulation
– Apocrine-smelly secretions, stress response
54. Sebaceous Glands
• Sebaceous glands are exocrine glands• Secrete sebum or "skin oil“ into hair follicles
• Sebum conditions hair and skin to prevent
damage
55. Other Glands
• Ceruminous glands– Ear wax
• Mammary glands
– Milk production
56. Exocrine Glands of the Skin (Figure 6.10a)
Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.Sweat
pore
Exocrine
Glands of
the Skin
(Figure
6.10a)
Sweat
gland duct
Hair follicle
Sebaceous
gland
Merocrine
sweat gland
Arrector pili
muscle
Apocrine
sweat gland
(a)
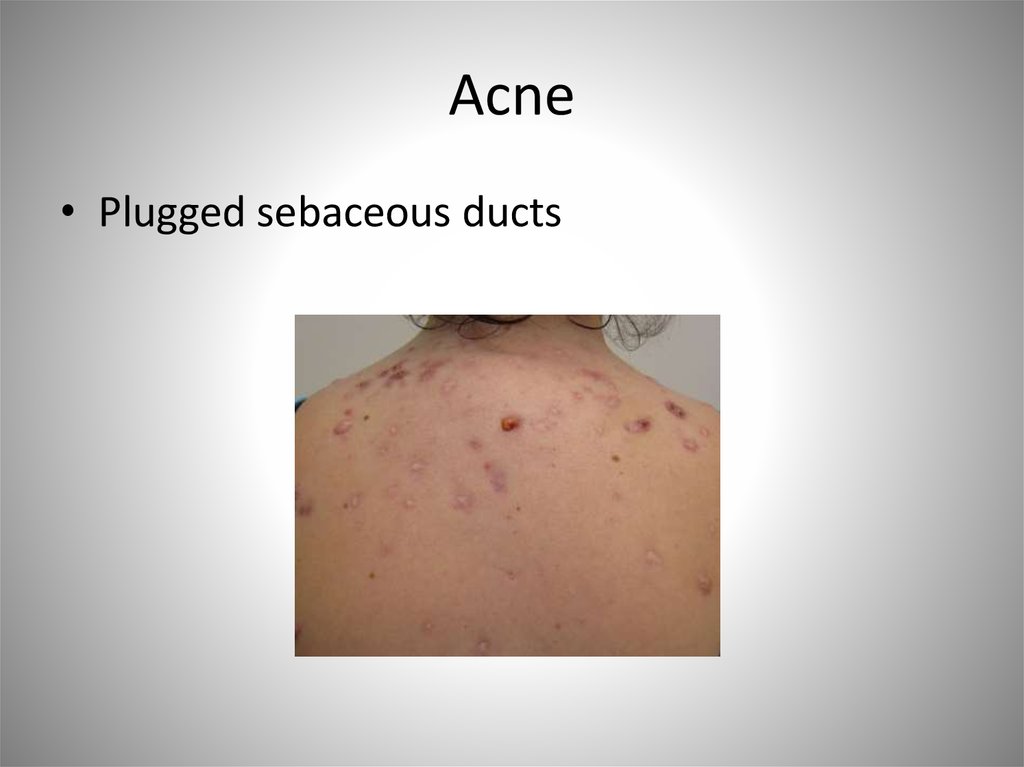
57. Acne
• Plugged sebaceous ducts58. Skin Functions
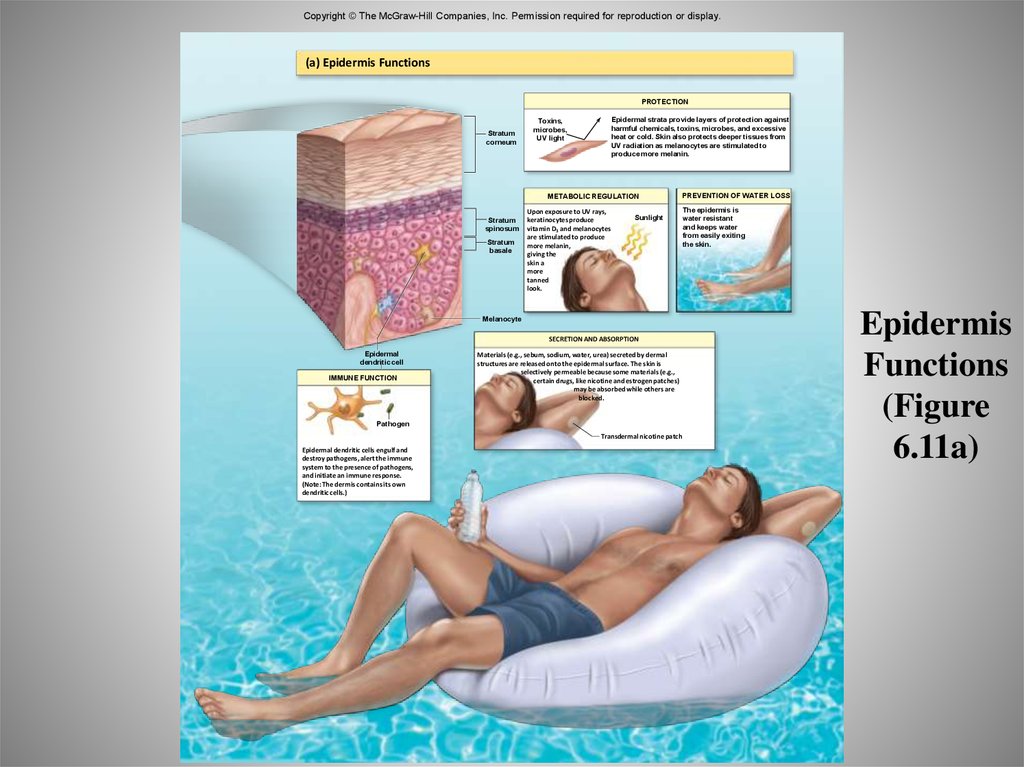
59. Epidermis Functions (Figure 6.11a)
Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.(a) Epidermis Functions
PROTECTION
Stratum
corneum
Epidermal strata provide layers of protection against
harmful chemicals, toxins, microbes, and excessive
heat or cold. Skin also protects deeper tissues from
UV radiation as melanocytes are stimulated to
produce more melanin.
Toxins,
microbes,
UV light
METABOLIC REGULATION
Stratum
spinosum
Stratum
basale
Upon exposure to UV rays,
keratinocytes produce
vitamin D3 and melanocytes
are stimulated to produce
more melanin,
giving the
skin a
more
tanned
look.
PREVENTION OF WATER LOSS
Sunlight
Melanocyte
SECRETION AND ABSORPTION
Epidermal
dendritic cell
IMMUNE FUNCTION
Materials (e.g., sebum, sodium, water, urea) secreted by dermal
structures are released onto the epidermal surface. The skin is
selectively permeable because some materials (e.g.,
certain drugs, like nicotine and estrogen patches)
may be absorbed while others are
blocked.
Pathogen
Transdermal nicotine patch
Epidermal dendritic cells engulf and
destroy pathogens, alert the immune
system to the presence of pathogens,
and initiate an immune response.
(Note: The dermis contains its own
dendritic cells.)
The epidermis is
water resistant
and keeps water
from easily exiting
the skin.
Epidermis
Functions
(Figure
6.11a)
60. Dermis Functions (Figure 6.11b)
Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.Keratinized
stratified
squamous
epithelium
Epidermis
Areolar
connective
tissue
Dense
irregular
connective
tissue
Dermis
Dermis
Functions
(Figure
6.11b)
Subcutaneous layer
(b) Dermis Functions
TEMPERATURE REGULATION
Dilating blood vessels in the dermis release
heat; constricting vessels conserve heat.
Sensory receptors
Sweat glands release fluid onto the skin surface,
and the body cools off by
evaporation of the sweat.
Sensory nerve fiber
SENSORY RECEPTION
Sensory receptors
SECRETION AND ABSORPTION
Sweat glands secrete sodium,
water, and urea onto the epidermal
surface, and in so doing help
maintain electrolyte homeostasis.
Sweat
gland
Sebaceous glands
secrete sebum,
which lubricates
the skin and also
helps make the
integument
water resistant.
Sebaceous
gland
A variety of sensory receptors
structures detect and relay pain,
heat, cold, touch, pressure, and
vibration. (Note: There also are
some sensory receptors in the
epidermis.)
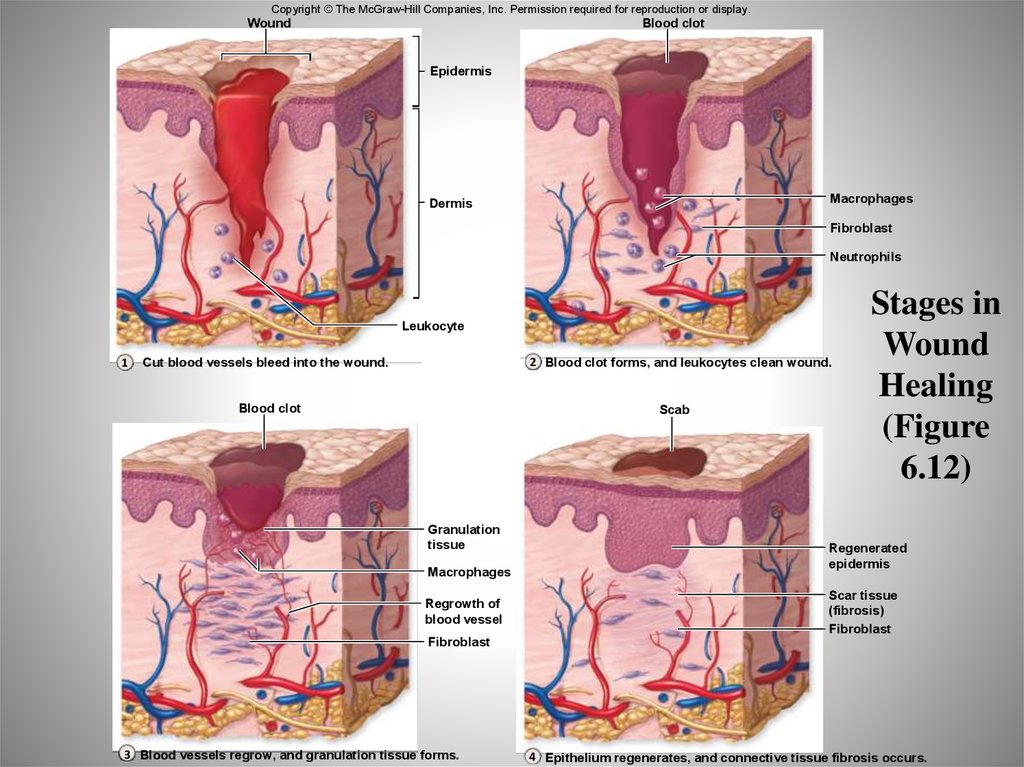
61. Stages in Wound Healing (Figure 6.12)
Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.Wound
Blood clot
Epidermis
Macrophages
Dermis
Fibroblast
Neutrophils
Leukocyte
1
2 Blood clot forms, and leukocytes clean wound.
Cut blood vessels bleed into the wound.
Blood clot
Scab
Granulation
tissue
Macrophages
Regrowth of
blood vessel
Stages in
Wound
Healing
(Figure
6.12)
Regenerated
epidermis
Scar tissue
(fibrosis)
Fibroblast
Fibroblast
3 Blood vessels regrow, and granulation tissue forms.
4 Epithelium regenerates, and connective tissue fibrosis occurs.



























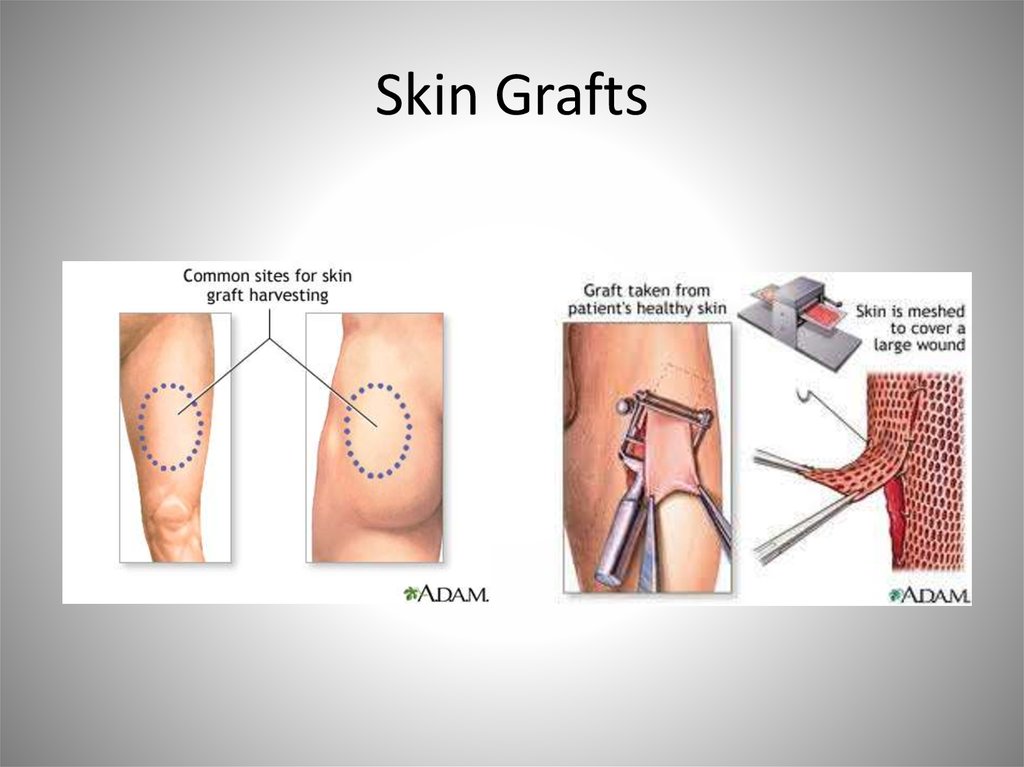
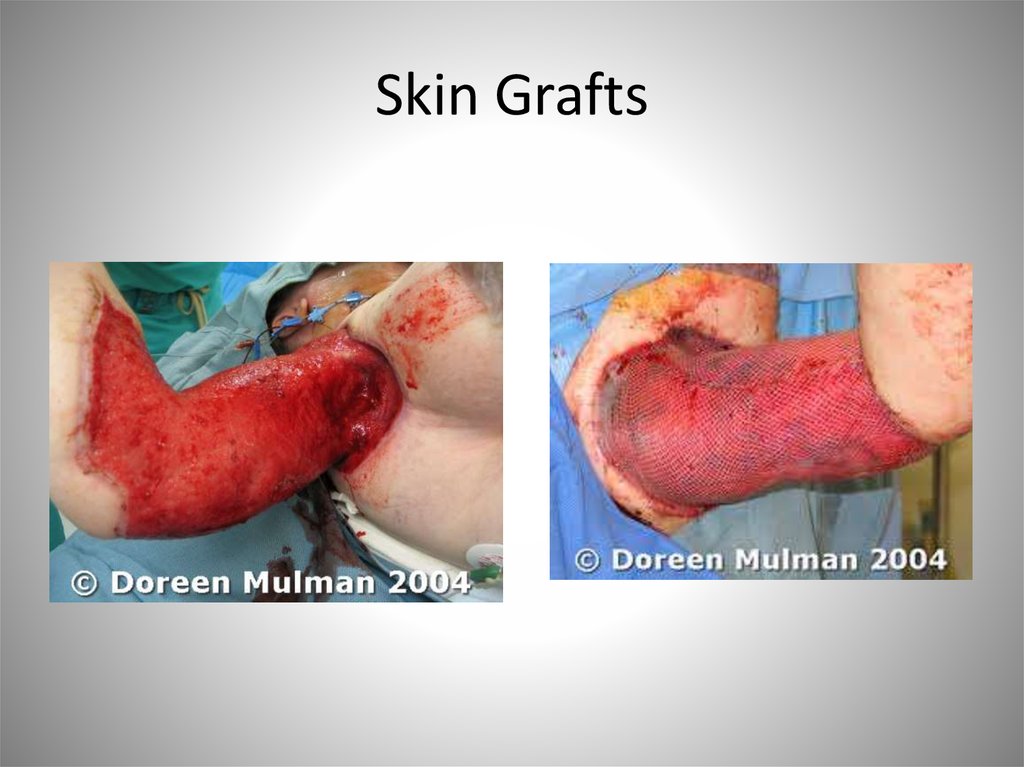
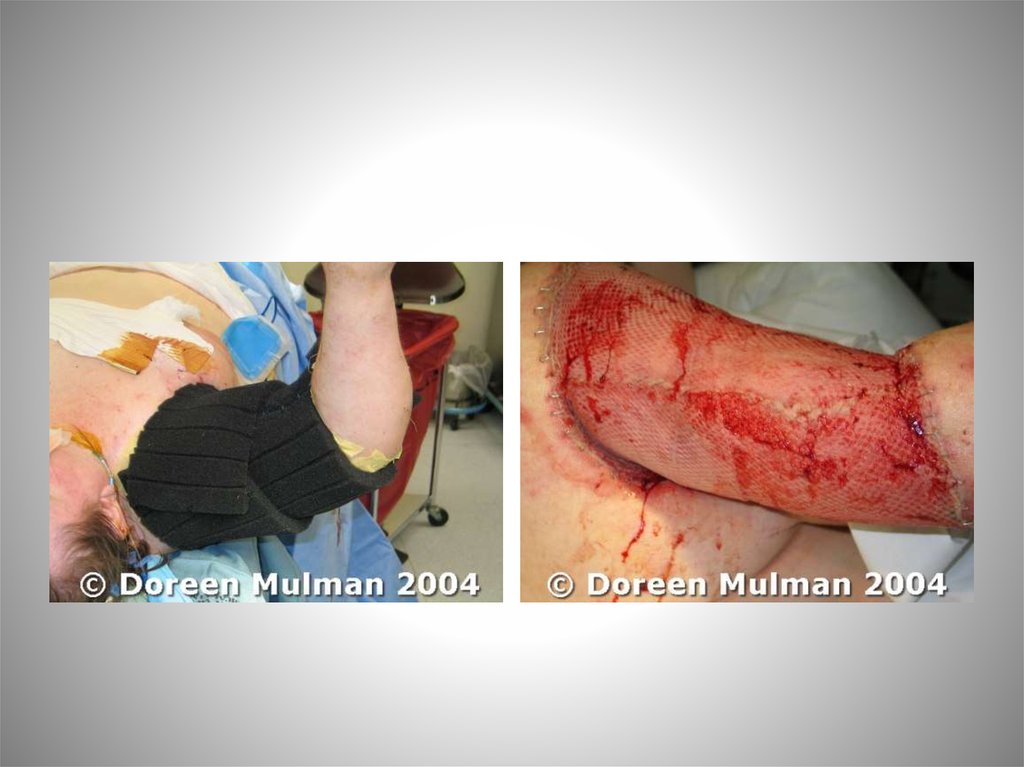

 biology
biology