Similar presentations:
Determination of the securities market and its types
1.
2. Contents:
1. Determination of the securities marketand its types
2. Functions of the securities market
3. The structure of the securities market
4. Types and models of legal regulation of
the stock market
3. 1. Determination of the securities market and its types
Stock Market - is a set of economic relations over theissue and circulation of securities among its
participants.
Kinds of securities markets:
- International and domestic securities markets;
- National and regional markets;
- Markets for specific types of securities (debt and
equity);
- Markets for government and corporate securities;
- Markets of the primary and derivative securities.
4. Capital investment is depending on many factors:
- The level of profitability of the market;- Terms of regulation and taxation;
- The level of risk as the probability of loss
of capital or non-receipt of expected
income;
- The perfection of market organization
and working conditions of participants,
especially investors.
5. Primary market & Stock market
Primary market & Stock market• Markets, where you can only invest, or the
primary market.
• The process of distribution and redistribution of
financial resources, capital is carried out on the
market of financial resources, the stock market
(Fig.1).
• Temporarily free funds received for the financial
markets, which provide the possibility of their
redistribution in different forms.
6.
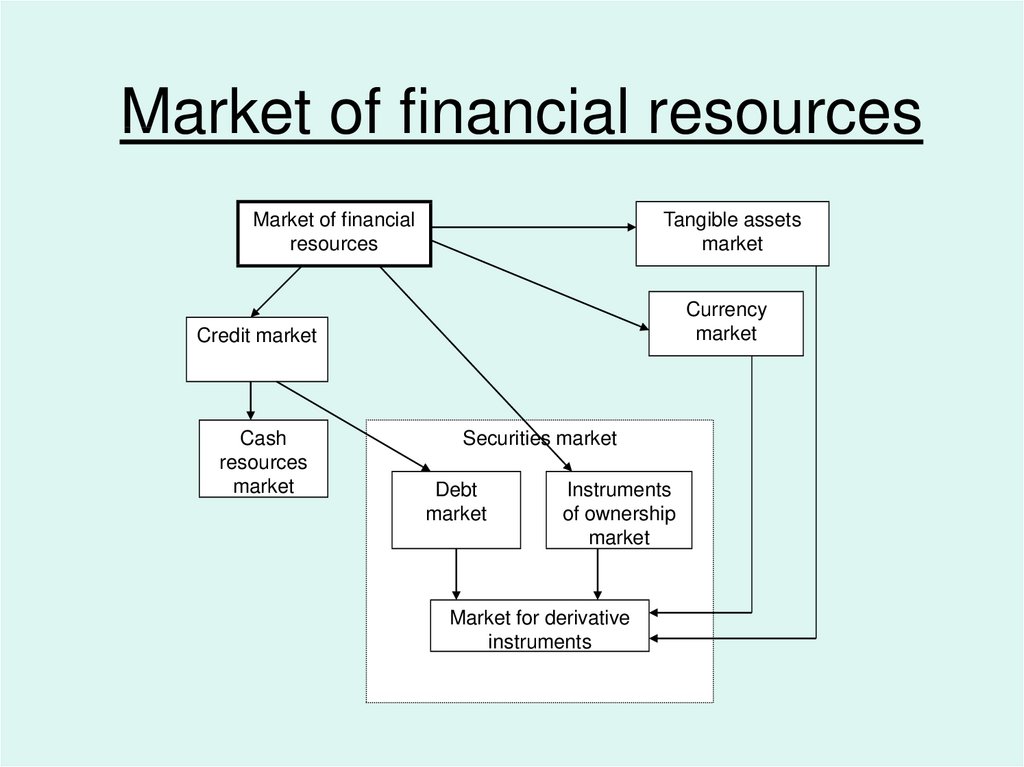
Market of financial resourcesMarket of financial
resources
Tangible assets
market
Currency
market
Credit market
Cash
resources
market
Securities market
Debt
market
Instruments
of ownership
market
Market for derivative
instruments
7. Credit market
• The credit market - a mechanism for therelationship between legal entities (enterprises,
state), which require funds for its development
and operation, on the one hand, and the
businesses and citizens on the other hand, who
can give (lend) the funds.
• Credit market possibilities:
- Integration of small and large funds from various
individuals and entities as a base for cash funds;
- Transformation of these funds in debt capital for
investment;
- The granting of loans government agencies,
businesses and the public.
8. Currency market & tangible assets market
Currency market & tangibleassets market
• Currency market - a mechanism for organizing
economic and legal relationships between consumers
and sellers of currencies, the state organs are the
regulators of the market, engaged in buying and selling
currencies.
• Conversion operations are called transactions in the
currency market to exchange a specified amount in one
currency for funds in another currency at an agreed rate
on a specified date.
• The market, which are bought and sold various material
or real resources - tangible assets market or
commodity markets (various food and commodity
exchanges)
9. Cash resources market & Debt market
Cash resources market & Debtmarket
• Cash resources market operates primarily in
the form of banking credits to cover the relations
arising on the provision by credit institutions
repayable loans and paid relating to the design
of special documents, which can not be sold,
bought or redeemed.
• The issue of bonds as the debt is usually carried
out with pre-fixed and pre-negotiated terms of
the full debt plus interest. This operation is
performed on the debt market.
10. Instruments of ownership market & Derivatives market
Instruments of ownership market& Derivatives market
• Attraction of additional owners of the funds through the
sale for each new shareholder of a certain number of
shares, which certifies the right to own a certain
percentage of stock company assets. This operation
relates to the instruments of ownership market.
• The market, which are converted to derivatives securities
(options and futures) is the market for derivative
instruments or derivative securities (derivatives).
Derivative securities - are instruments whose value is
determined by the value of certain assets, called the
base.
11. Securities market & Securities
Securities market & Securities• Securities market includes part of a credit relationship
(bond market) and the relations of co-ownership (stock
market).
• Securities - financial documents that indicate
ownership, or loans, determine the relationship between
the person who issued them and their owner, and
provide, as a rule, the payment of income in the form of
dividends or interest, as well as the possibility of
transferring money and other rights that derived from
these documents to others.
12. 2. Functions of the securities market
• General market functions:- Business function, function of getting profit from
operations in this market;
- Price function, market provides a process of folding of
market prices, their constant movement;
- Information function, market produces and brings to its
members information about the objects of trade and its
participants;
- Control function, market creates the rules of trade and
participation in, the procedure for settling disputes
between the parties, establishes priorities, control
bodies, or even control.
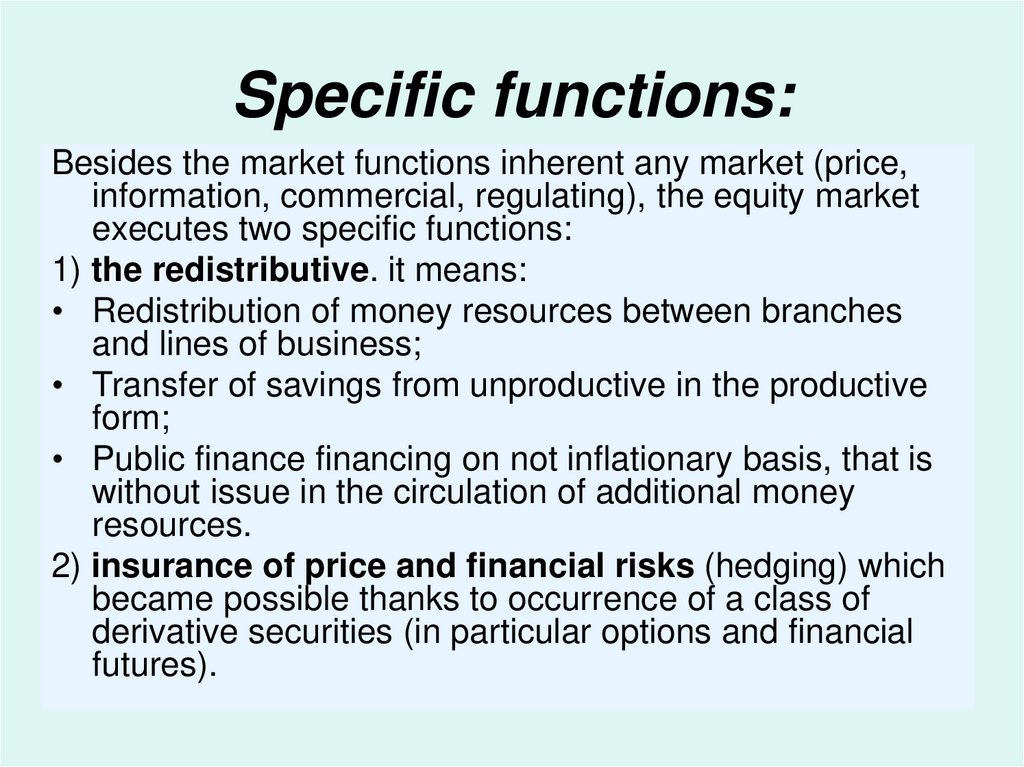
13. Specific functions:
Besides the market functions inherent any market (price,information, commercial, regulating), the equity market
executes two specific functions:
1) the redistributive. it means:
• Redistribution of money resources between branches
and lines of business;
• Transfer of savings from unproductive in the productive
form;
• Public finance financing on not inflationary basis, that is
without issue in the circulation of additional money
resources.
2) insurance of price and financial risks (hedging) which
became possible thanks to occurrence of a class of
derivative securities (in particular options and financial
futures).
14. 3. The structure of the securities market
Depend on the way of trade in this marketthere are such markets:
- Primary and secondary;
- Organized and unorganized;
- Stock and out stock;
- Traditional and computerized;
- Cash and term.
15. Primary market & Secondary market
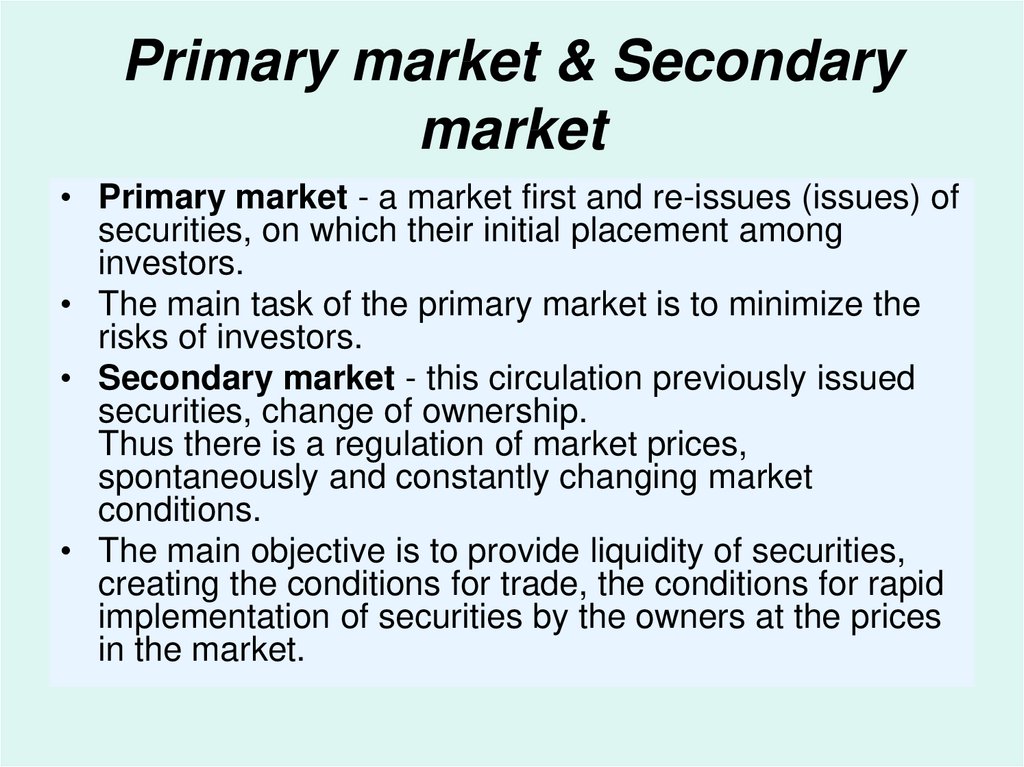
Primary market & Secondarymarket
• Primary market - a market first and re-issues (issues) of
securities, on which their initial placement among
investors.
• The main task of the primary market is to minimize the
risks of investors.
• Secondary market - this circulation previously issued
securities, change of ownership.
Thus there is a regulation of market prices,
spontaneously and constantly changing market
conditions.
• The main objective is to provide liquidity of securities,
creating the conditions for trade, the conditions for rapid
implementation of securities by the owners at the prices
in the market.
16.
• Organized securities market - their circulation on thebasis of firm rules between licensed professional
intermediaries – by the market participants on behalf of
other market participants.
• Unregulated market - is the circulation of securities
without compliance with the uniform for all participants of
the market rules.
• Stock Market - a trading of securities on stock markets.
This is the organized market with the maximum level of
control and regulation.
• Outstock market encompasses securities transactions
outside the stock exchange.
17. Traditional & Computerized Cash & Term Markets
Traditional & ComputerizedCash & Term Markets
Securities trading may be carried out on traditional and
computerized markets.
Computerized market characterized by:
- Lack of physical place where buyers and sellers, and
therefore, the lack of direct contact between them;
- Full automation of the trading process and its services,
the role of market participants is reduced mainly only for
delivery of their bids for the sale of securities in the
trading system.
Cash market securities (spot market) - is a market with
immediate execution of transactions, with full
implementation of transactions (delivery versus
payment) for 2 or 4 working days.
Term Market - a market in which transactions have the
term of execution more than 4-5 working days. Most of
the terms of execution for 3 months.
18. 4. Types and models of legal regulation of the stock market
• World standards of the stock market have beenworked out by "Group of Thirty" - nongovernmental experts on the organization of the
international financial system.
• The purpose of standards - reduction in time
between the transaction and its implementation,
as well as guaranteeing the performance of the
contract. Recommendations:
- All transactions by securities carried out on the
principle "delivery versus payment";
- Verification of all conditions of the parties made
not later than the day after the transaction (T +1);
19.
• - Agreements executed not later than2 business days after the conclusion of (T +3);
- Cash payments are the same for all
transactions procedures;
- Savings of securities are implemented by a
single central depository;
• To account documents on transactions with
securities and numbering used standards of
the International Organization for
Standardization
20.
Security markets regulation is concerned withoverseeing the circulation of information
about securities that are traded, monitoring
the market for the abuse of information or
financial resources to manipulate market and
prices and supervising the corporate
governance of organized markets.
21. Legal Regulation of Securities and Stock Market in Ukraine
• The EBRD’s 2008 Law in Transition reports that Ukraine’ssecurities legislation was in “high compliance” with the
Objectives and Principles of Securities Regulation established
by the International Organization of Securities Commissions
(IOSCO). Since then Ukraine has adopted the Joint-Stock
Companies Act and other regulations improving the legal
framework in the area of securities even further. Nevertheless,
as with many other laws in Ukraine, the practical application of
the laws and regulations is rather far from perfect.
22.
The Securities Commission is the main regulator of the Ukrainiansecurity market. The Security Commission is a state authority
subordinated to the President of Ukraine and accountable to the
Verkhovna Rada (the Ukrainian Parliament). It is responsible for
developing and implementing uniform state policy on the
functioning of the Ukrainian securities market as well as
monitoring the compliance of all Ukrainian securities market
participants with Ukrainian securities legislation. The Security
Commission has the power to apply sanctions against parties.
23.
Types of legal regulation1. General allowance: it is based on the whole allowance, from which we
take exclusions in the form of prohibitions. Its formula – everything is
allowed, except that ones, that are directly prohibited.
2. General permission: it is based on the whole prohibition of some
kind of action, but in the individual order some prohibited behavior
can be allowed. Its formula – everything, except directly permitted, is
prohibited.
24. How the U.S. Stock Markets are Regulated
Stock markets of different countries have different operatingmodel , its own rules and system of government. But despite their
differences, the organizational structure of the system of regulation
in the vast majority of states , based on the concept of two-tier
system of regulation.
25. Regulatory system
• The organizational structure of the regulatory systembased on the concept of a two-level system of
regulatory authorities. The first level - regulatory
agencies, the second - self-regulatory organizations
(SROs), created by professional securities market
participants. These include various kinds of unions,
associations, leagues of professional participants, stock
exchanges and the organizers of the outstocks trade.
• In almost all countries the investment business is
highlighted in a special area of economic legislation and
administrative oversight.
26. Two main models for regulating the securities market
The first model - the regulation of the stock market is mainlyconcentrated in government and only a small part of the authority
to oversee, control , establish binding rules of conduct passed state
SRO professional market participants. This approach is used in
the United States and France.
27.
The second model - the maximum possible amount ofpowers transferred CPO important in controlling not
take tough regulations and the negotiation process , the
individual agreements with professional market , while
the state reserves the basic control functions , the ability
to intervene at any point in the process of self-regulation .
An example of such a model is the United Kingdom.
28.
From more than 30 countries with developed securities marketsmore than 50% are independent agencies ( Commission on
Securities and Exchange Commission - the U.S. model , the
Bureau of Securities - Japan, the Federal Office for Banking
Supervision - Germany , the Council for Securities and Investment
- UK Commission on exchange transactions - France , the
Commission on securities and stock Exchange and the
Supervisory Board of the Securities - Korea) , about 15 % of the
countries in the stock market is the Ministry of Finance.
29. Ukrainian regulatory system
• In Ukraine, the regulatory system of the stockmarket took two stages. The first phase (1991 1995 years.) Characterized by the fact that the
main regulatory authority of the state was the
Ministry of Finance.
• The second phase began in 1995 when the
Presidential Decree “About the State
Commission on Securities and Stock Market”
was adopted.
30. The State Commission on Securities and Stock Market
• The purpose of the State Commission onSecurities and Stock Market is the policy-making
in the management and development of
securities market that would ensure fair trade
and competition between traders of securities
and ultimately - protect the rights of investors.
• Major tasks of the regulatory bodies:
- registration of Securities Dealers, as well as
those who advise investment
- ensuring transparency
- maintain law and order in the stock market
31. Self-regulation
• This is primarily Stock Exchange, representingthe auction, where the purchase - sale of
securities is, by exchanging oral instructions
between traders and the prices are formed
according to the law of supply and demand.
• Another body of industry self-monitoring and
self-regulation are a professional association
of investment business.
• In Ukraine, a similar function is fulfilled by the
Association of Securities Dealers.
32. IN USA
The U.S. Congress is at the top of the heap. It created most ofthe structure and it passes major laws that affect how the industry
operates. It also authorizes budgets for the Securities and
Exchange Commission and other agencies involved in regulatory
duties.
The SEC is the top regulatory agency responsible for
overseeing the securities industry. It registers new securities and
handles all the filings that public companies must make, such as
annual and quarterly reports.
33. USA
At the next level is the Financial Industry Regulatory Authority(FINRA). It was created in 2007 when the National Association of
Securities Dealers merged with the regulatory functions of the
New York Stock Exchange. This is an industry self-regulatory
body that is responsible for policing the securities industry.
FINRA set standards for stockbrokers and other industry
professionals and licenses them after comprehensive
examinations.





























 finance
finance








