Similar presentations:
The Role and Function of a Stock Exchange
1.
2. The Role and Function of a Stock Exchange
ByEnid E Bissember
GASCI
3. Outline
Overview of financial
markets
Institutional infrastructure
Role and functions of stock
exchange
4. Overview of Financial Markets
Two types of financial markets
• Money markets
• Capital markets
• Primary market
• Secondary market
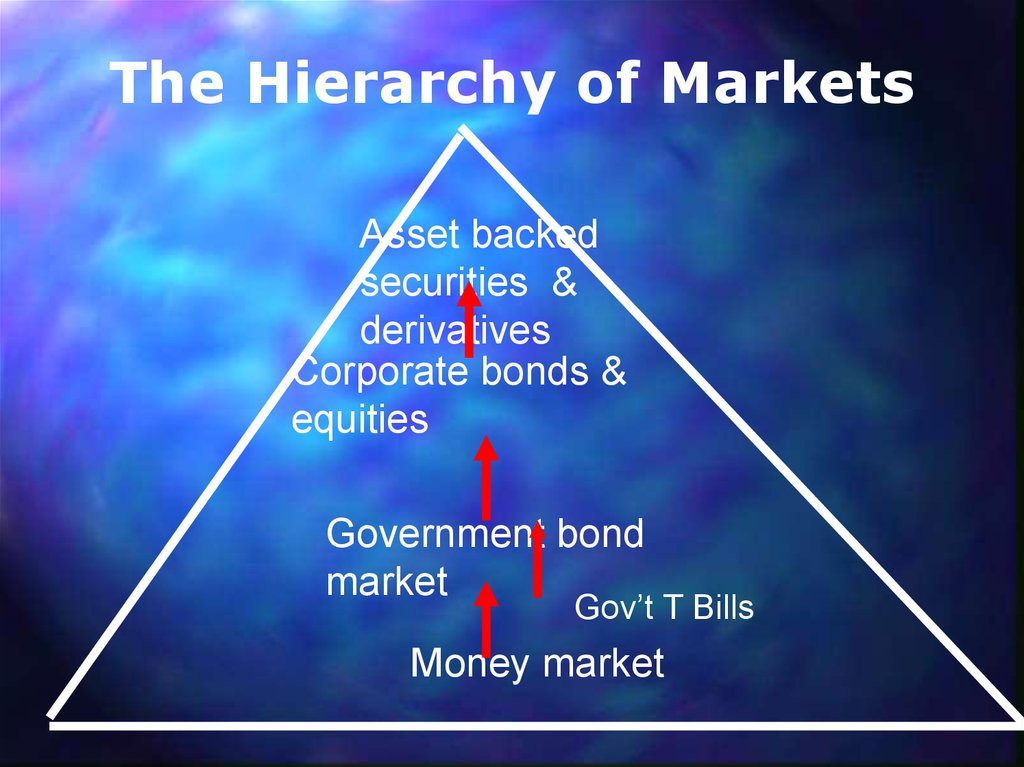
5.
The Hierarchy of MarketsAsset backed
securities &
derivatives
Corporate bonds &
equities
Government bond
market
Gov’t T Bills
Money market
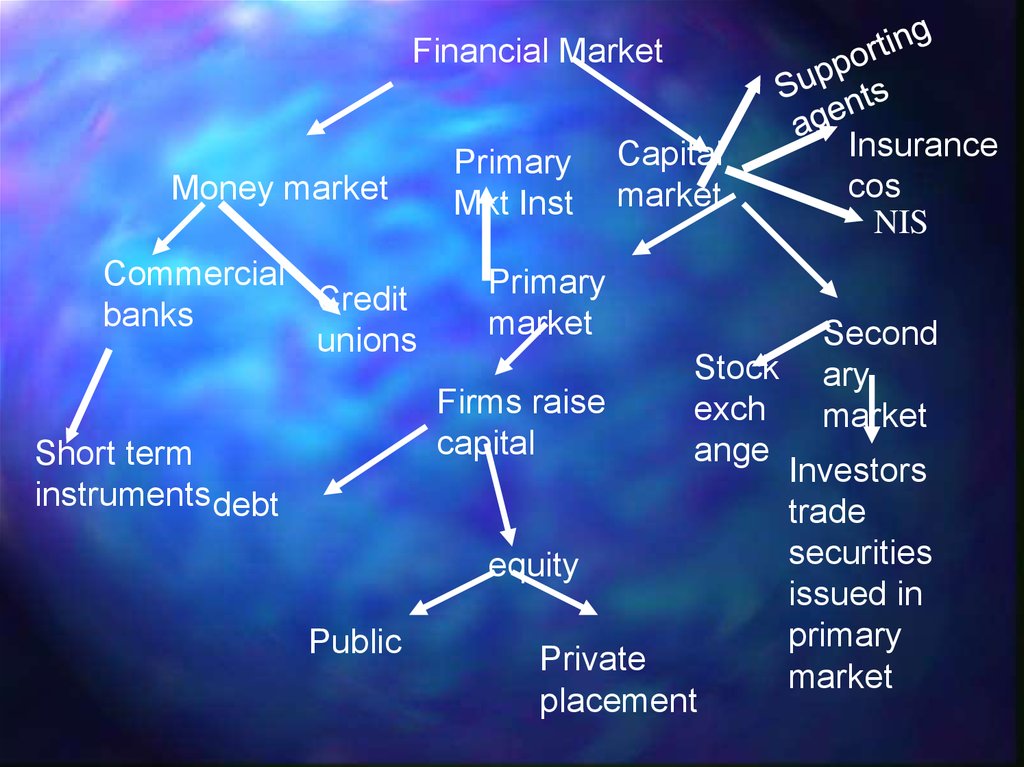
6.
Financial MarketMoney market
Commercial
Credit
banks
unions
Primary
Mkt Inst
Primary
market
Firms raise
capital
Short term
instruments debt
Capital
market
Stock
exch
ange
equity
Public
Private
placement
Insurance
cos
NIS
Second
ary
market
Investors
trade
securities
issued in
primary
market
7. Market infrastructure
• Stock exchange• Clearing and settlement
• Education and training
• Investors’ protection
• Rating agency
8. Instruments
• EquitiesMost popular investing
instruments
Stocks and shares
Bonus issues
Rights issues
• Bonds
Corporate
Government
9. Intermediaries
• Brokerage houses• Stock brokers
• Advisors
Hand in Hand
Beharry
stockbrokers
Trust company
GuyAmerica
10. Regulation & Supervision
Regulation & SupervisionA few questions
• Ever wondered how the capital
markets work
• Who sets the rules
• What does the stock exchange do
• What is the role of the stock broker
• How to become a registered broker
11. The Regulator
• Foremost authority presiding over thecapital markets
• With mission to promote and maintain
Fair, efficient , secure and transparent
market and to facilitate the orderly
development of the stock exchange
12. Role and Functions of a stock exchange
Established for thepurpose of assisting,
regulating and controlling
business of buying,
selling and dealing in
securities
13. Role and Functions of a stock exchange cont’d
• Provides a market for the trading ofsecurities to individuals and
organizations seeking to invest
their saving or excess funds
through the purchase of securities
14. Role and Functions of a stock exchange cont’d
Provides a physical locationfor buying and selling
securities that have been
listed for trading on that
exchange
15. Role and Functions of a stock exchange cont’d
Establishes rules for fairtrading practices and
regulates the trading
activities of its members
according to those rules
16. Role and Functions of a stock exchange cont’d
The exchange itselfdoes not buy or sell the
securities, nor does it
set prices for them
17. Fair
The exchange assuresthat no investor will have
an undue advantage over
other market participants
18. Efficient market
This means that ordersare executed and
transactions are settled
in the fastest possible
way
19. Transparency
Investor make informedand intelligent decision
about the particular stock
based on information
20. Transparency cont’d
Listed companies mustdisclose information in
timely, complete and
accurate manner to the
Exchange and the public
on a regular basis
21. Transparency cont’d
Required information includestock price, corporate
conditions and developments
dividend, mergers and joint
ventures, and management
changes etc
22. Doing business
People who buy or sellstock on an exchange do
so through a broker
23. Doing business cont’d
The broker takes your orderto the floor of the exchange
looks for a broker
representing someone
wanting to buy/sell
• If a mutually agreeable price
is found the trade is made
24. Some type of orders
Limit order
Market order
Day order
Open
All or none
Any part
Good through
25. Price
At any point in time, theprice of previously
issued stock is
determined by the ebb
and flow of supply and
demand
26. Listing requirements
There are specificrequirements for allowing a
public company to list its
securities on the Stock
Exchange these are set out
in the legislation
27. Benefits of listing
• Visibility• Market support
• Investors confidence
• Increased demand for products and
services
• Overall increase in profitability
28. Once traded
• Aura of reliability• Accuracy in reporting
financial data
• Reputation
• Strength
29. Delisting
Stock exchange can delist companiesfor a number of reasons including :• Merger with another company
• Solvency problems
• Name change company asked to be
removed
• Failure to comply with exchange rules
30. Desirable Characteristics of a stock market
LiquidityAbility to sell an asset
quickly at a fairly
known price Low
transactions costs
31. Desirable Characteristics of a stock market cont’d
• Availability of informationMarket efficiency
• Prices react quickly to new
information
• Small price fluctuations
• Narrow price spread
32. Financing the exchange
• Transaction fees paid by members foreach order executed
• Fees paid by firms when their securities
are originally listed
• Annual fees by firms
• Entrance fees from new members
• sale of historic trading and market
information
33. Major challenges for the Exchanges
• Cross border trading• Issuers and investors are
expanding their horizons beyond
their home markets
• Investors becoming much more
demanding
34. Regulatory improvement Transparency and Corporate Governance
•Regulatory improvementTransparency and Corporate
Governance
Protection to
minority
Shareholders
Corporate
Governance
Disclosure
Enhance
market
confidence
Strong
industry
regulator
35.
OwnersOwnership of the
company is by the
public in the form of
shares one share,
one vote
Board is elected by
shareholders to
represent the best
interests of the owners
Managers
Board hires and fires the
management of the
company


































 finance
finance








