Similar presentations:
Heart valves: functionality and treats
1. Heart Valves: functionality and treats
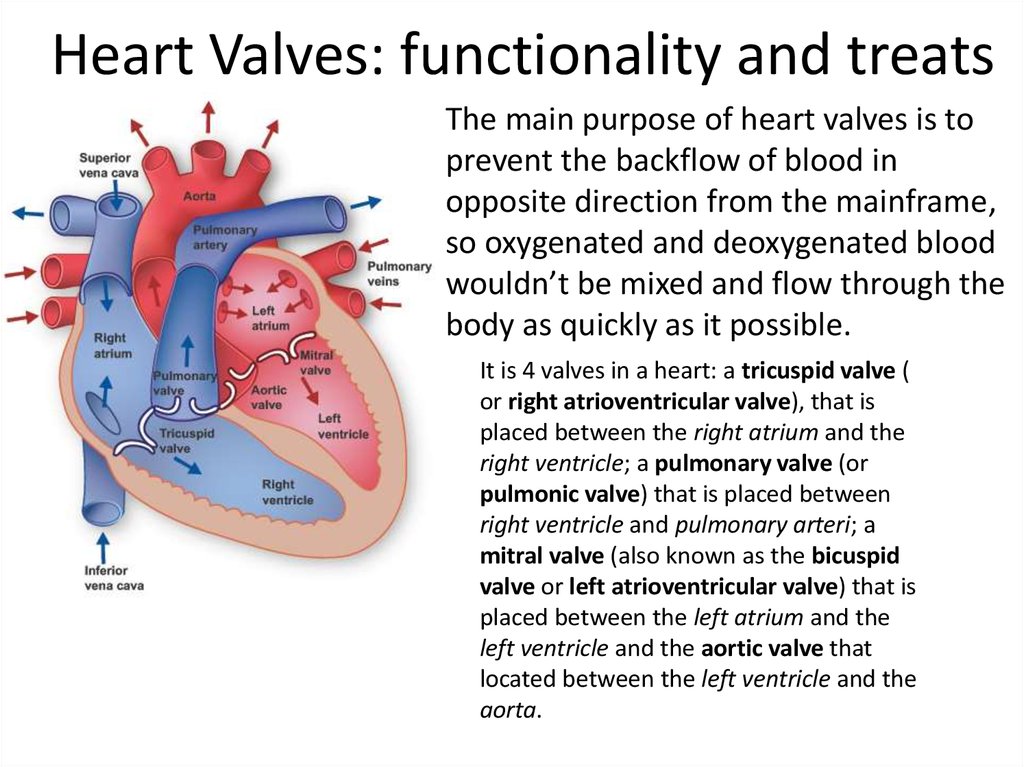
The main purpose of heart valves is toprevent the backflow of blood in
opposite direction from the mainframe,
so oxygenated and deoxygenated blood
wouldn’t be mixed and flow through the
body as quickly as it possible.
It is 4 valves in a heart: a tricuspid valve (
or right atrioventricular valve), that is
placed between the right atrium and the
right ventricle; a pulmonary valve (or
pulmonic valve) that is placed between
right ventricle and pulmonary arteri; a
mitral valve (also known as the bicuspid
valve or left atrioventricular valve) that is
placed between the left atrium and the
left ventricle and the aortic valve that
located between the left ventricle and the
aorta.
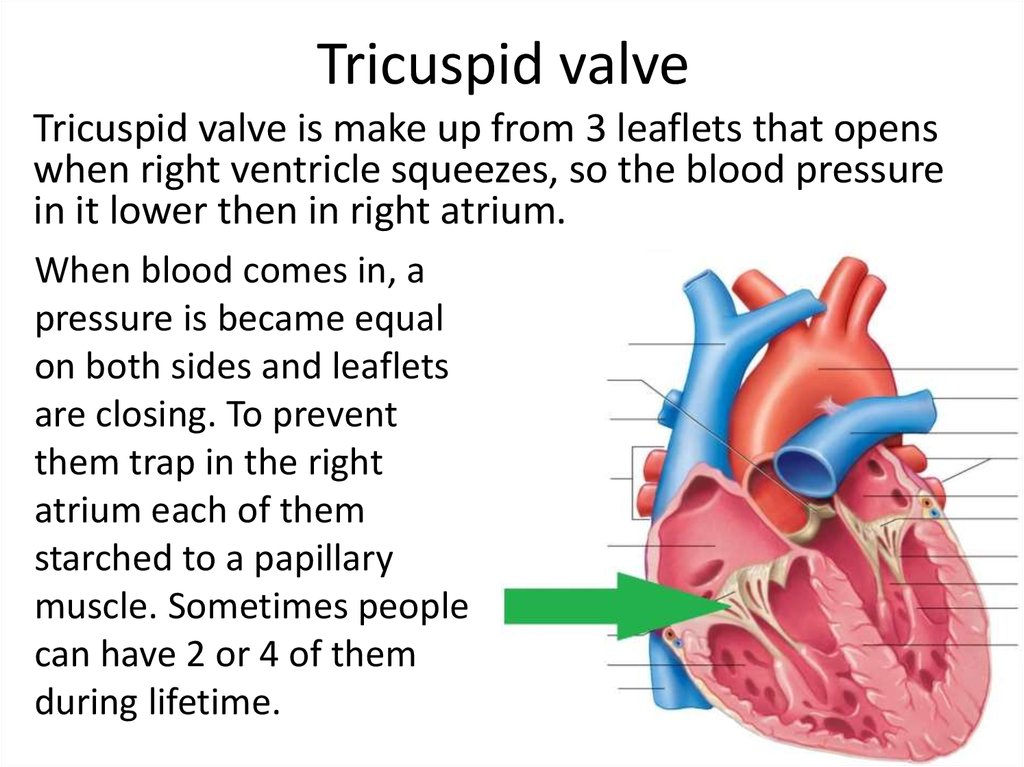
2. Tricuspid valve
Tricuspid valve is make up from 3 leaflets that openswhen right ventricle squeezes, so the blood pressure
in it lower then in right atrium.
When blood comes in, a
pressure is became equal
on both sides and leaflets
are closing. To prevent
them trap in the right
atrium each of them
starched to a papillary
muscle. Sometimes people
can have 2 or 4 of them
during lifetime.
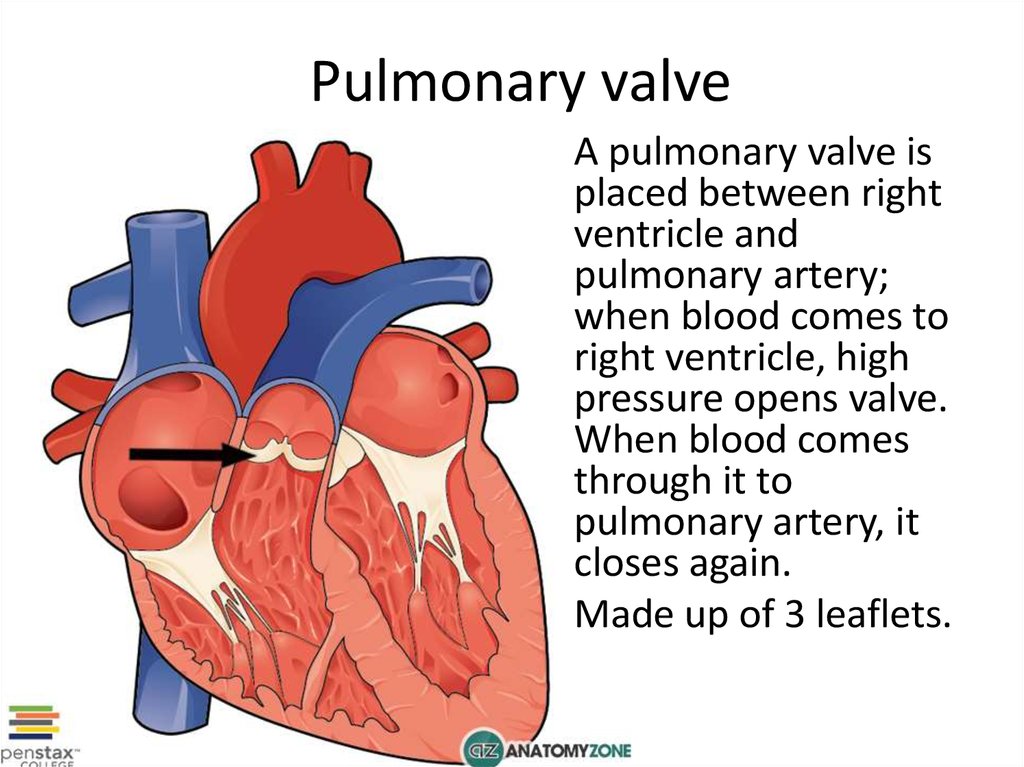
3. Pulmonary valve
A pulmonary valve isplaced between right
ventricle and
pulmonary artery;
when blood comes to
right ventricle, high
pressure opens valve.
When blood comes
through it to
pulmonary artery, it
closes again.
Made up of 3 leaflets.
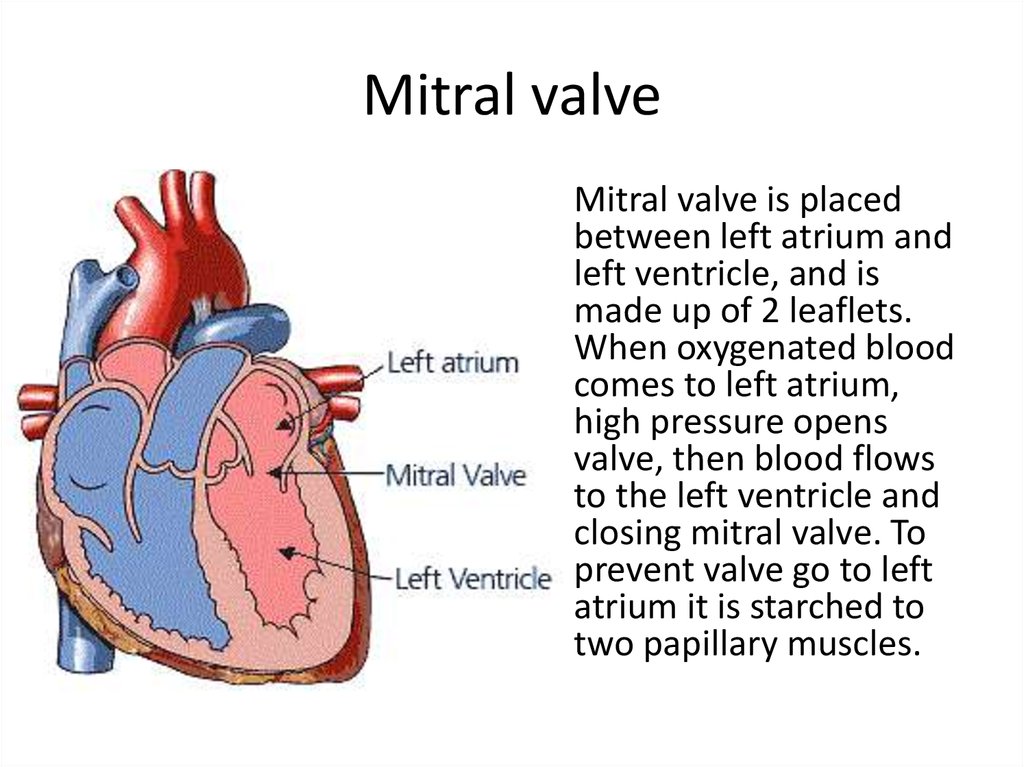
4. Mitral valve
Mitral valve is placedbetween left atrium and
left ventricle, and is
made up of 2 leaflets.
When oxygenated blood
comes to left atrium,
high pressure opens
valve, then blood flows
to the left ventricle and
closing mitral valve. To
prevent valve go to left
atrium it is starched to
two papillary muscles.
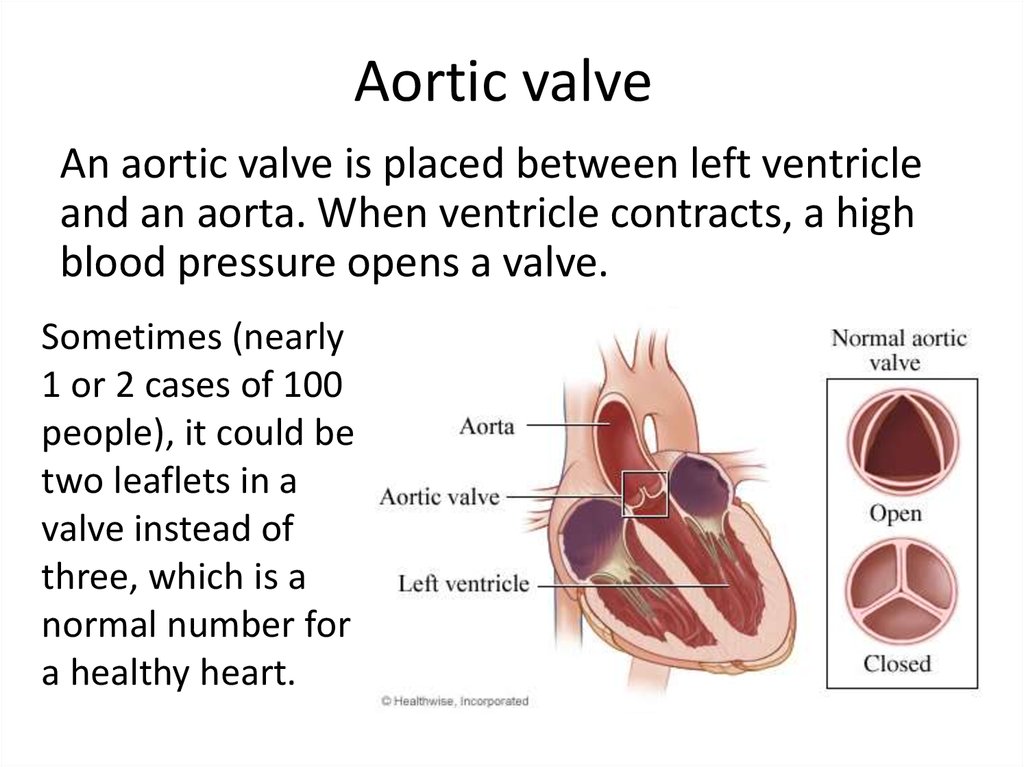
5. Aortic valve
An aortic valve is placed between left ventricleand an aorta. When ventricle contracts, a high
blood pressure opens a valve.
Sometimes (nearly
1 or 2 cases of 100
people), it could be
two leaflets in a
valve instead of
three, which is a
normal number for
a healthy heart.
6. Why do heart valves go wrong?
Heart valves can have three basic kinds of problems:regurgitation, stenosis, and atresia
Regurgitation, or backflow, occurs if a valve doesn't close
tightly. Blood leaks back into the chambers rather than
flowing forward through the heart or into an artery.
Stenosis occurs if the flaps of a valve thicken, stiffen, or
fuse together. This prevents the heart valve from fully
opening. As a result, not enough blood flows through the
valve. Some valves can have both stenosis and backflow
problems.
Atresia occurs if a heart valve lacks an opening for blood
to pass through.
7. What causes heart valves disease?
• The main causes of heart valve disease are:• being born with an abnormal valve or valves
(congenital heart disease)
• having had rheumatic fever
• cardiomyopathy - a disease of the heart muscle
• damage to the heart muscle from a heart attack
• getting older
• a previous infection with endocarditis.
8. Symptoms of heart valve disease;
• being out of breath• swelling of the ankles and feet
• being unusually tired.
9.
pg 1- bothpgs 2-5 – grisha
pgs 6-8 – Nazanin.




 biology
biology