Similar presentations:
Lobular pneumonia
1.
Карагандинский Государственный Медицинский УниверситетКафедра иностранных языков
Выполнила: Кулмаганбетова Н2-064
Проверила: Дашкина Т.Г.
2.
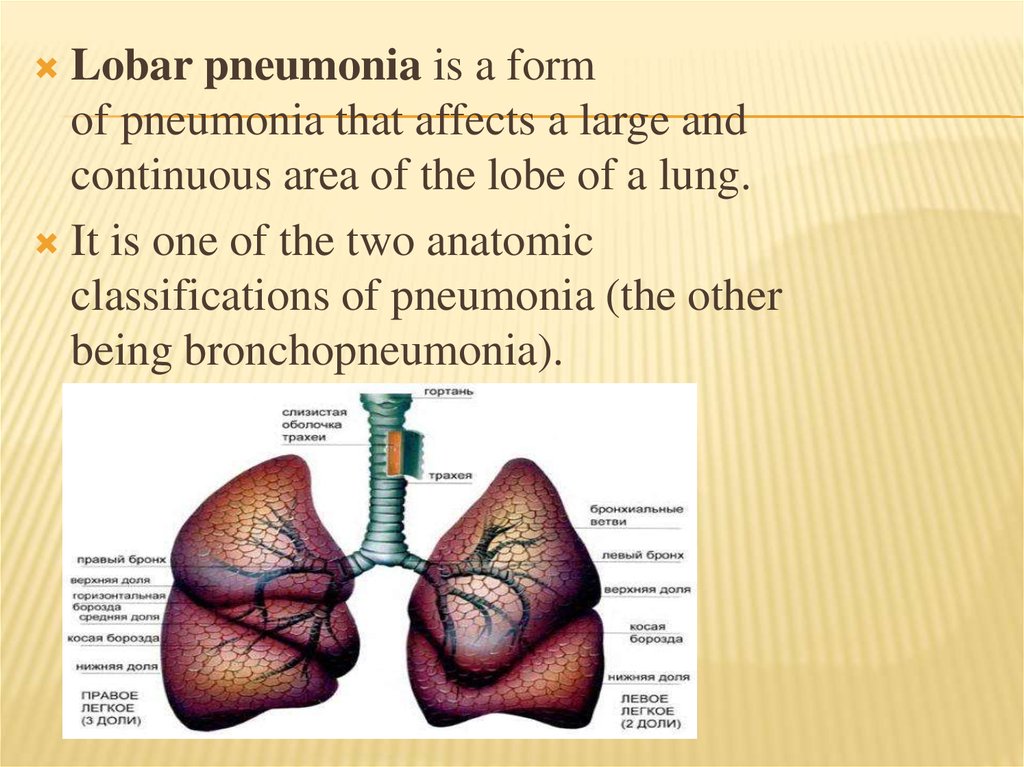
Lobar pneumonia is a formof pneumonia that affects a large and
continuous area of the lobe of a lung.
It is one of the two anatomic
classifications of pneumonia (the other
being bronchopneumonia).
3. Lobar pneumonia usually has an acute progression. Classically, the disease has four stages. Congestion in the first 24 hours:
LOBAR PNEUMONIA USUALLY HAS ANACUTE PROGRESSION. CLASSICALLY,
THE DISEASE HAS FOUR STAGES.
CONGESTION IN THE FIRST 24 HOURS:
THIS STAGE IS CHARACTERIZED
HISTOLOGICALLY BY VASCULAR
ENGORGEMENT, INTRA-ALVEOLAR
FLUIDLOBAR PNEUMONIA USUALLY
HAS AN ACUTE PROGRESSION.
CLASSICALLY, THE DISEASE HAS FOUR
STAGES. CONGESTION IN THE FIRST 24
HOURS: THIS STAGE IS
CHARACTERIZED HISTOLOGICALLY BY
VASCULAR ENGORGEMENT, INTRAALVEOLAR FLUID, SMALL NUMBERS OF
NEUTROPHILS, OFTEN
NUMEROUS BACTERIA., SMALL
NUMBERS OF NEUTROPHILS, OFTEN
NUMEROUS BACTERIA.
4.
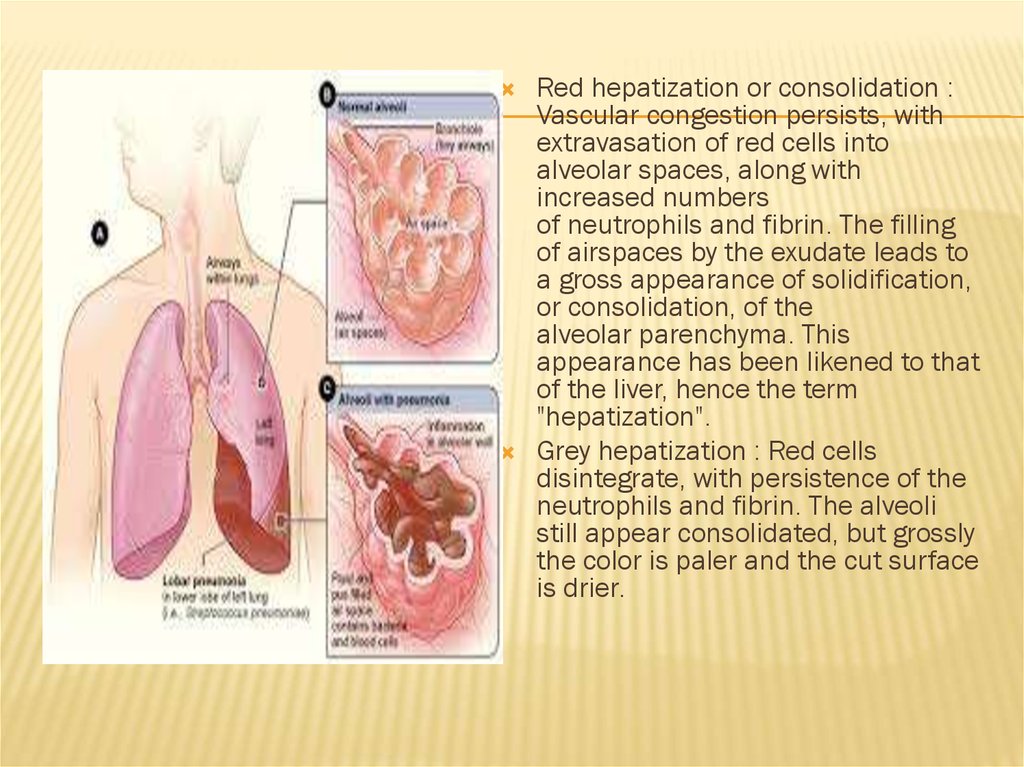
Red hepatization or consolidation :Vascular congestion persists, with
extravasation of red cells into
alveolar spaces, along with
increased numbers
of neutrophils and fibrin. The filling
of airspaces by the exudate leads to
a gross appearance of solidification,
or consolidation, of the
alveolar parenchyma. This
appearance has been likened to that
of the liver, hence the term
"hepatization".
Grey hepatization : Red cells
disintegrate, with persistence of the
neutrophils and fibrin. The alveoli
still appear consolidated, but grossly
the color is paler and the cut surface
is drier.
5.
1) Congestion in the first 24 hours: This stage ischaracterized histologically by vascular
engorgement, intra-alveolar fluid, small numbers of
neutrophils, often numerous bacteria. Grossly,
the lung is heavy and hyperemic.
2)
Red hepatization or consolidation : Vascular
congestion persists, with extravasation of red cells into
alveolar spaces, along with increased numbers
of neutrophils and fibrin. The filling of airspaces by the
exudate leads to a gross appearance of solidification, or
consolidation, of the alveolar parenchyma. This
appearance has been likened to that of the liver, hence
the term "hepatization"
6.
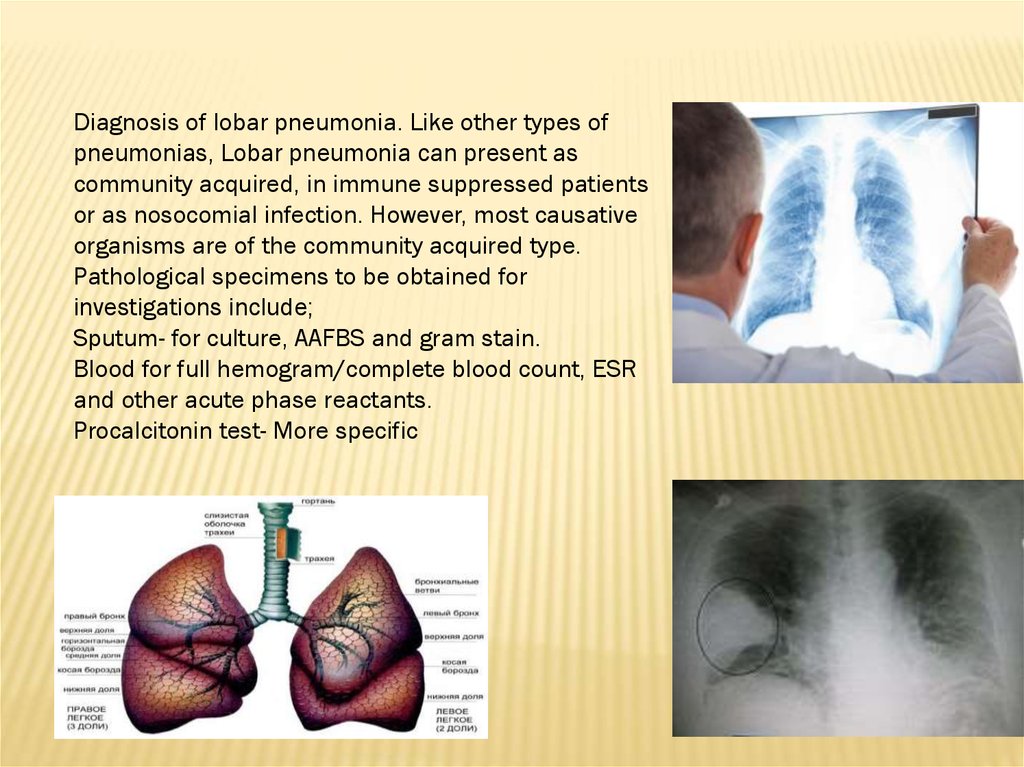
Diagnosis of lobar pneumonia. Like other types ofpneumonias, Lobar pneumonia can present as
community acquired, in immune suppressed patients
or as nosocomial infection. However, most causative
organisms are of the community acquired type.
Pathological specimens to be obtained for
investigations include;
Sputum- for culture, AAFBS and gram stain.
Blood for full hemogram/complete blood count, ESR
and other acute phase reactants.
Procalcitonin test- More specific
7. Passive Voice
PASSIVE VOICEУпотребляется обычно когда
неизвестно,кто выполняет действие
В английском языке употребляется
чаще,чем в русском.
Подлежащее в таких предложениях
пассивно, на него направлено
действие.
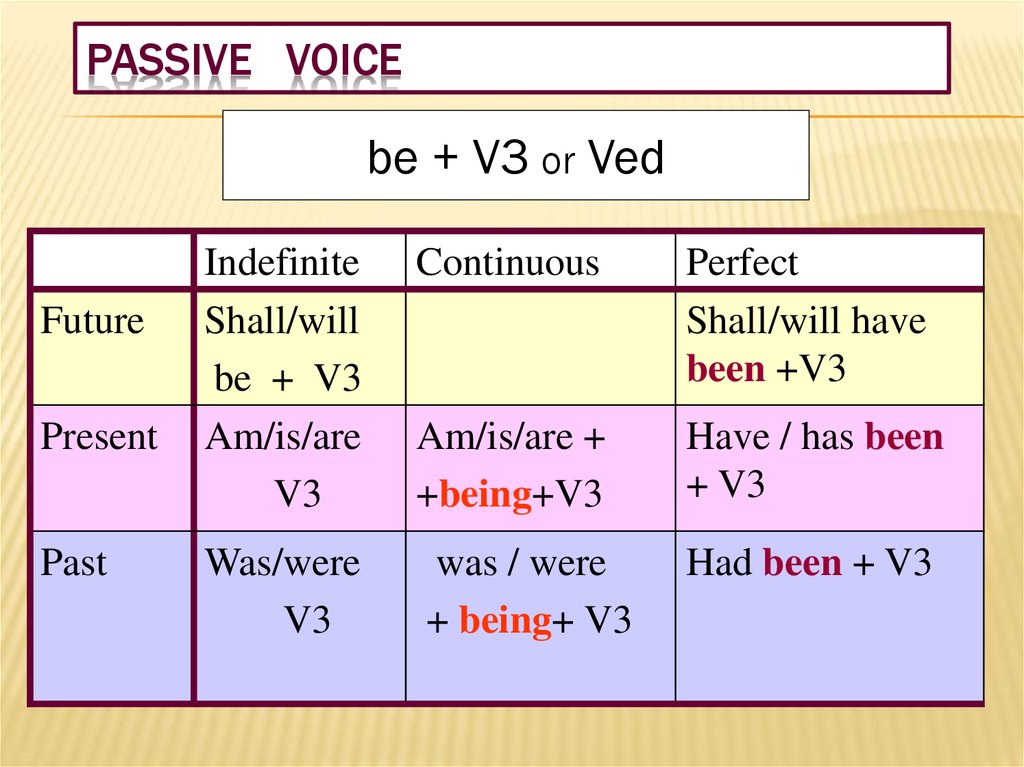
8. PASSIVE VOICE
be + V3 or VedFuture
Present
Past
Indefinite
Shall/will
be + V3
Am/is/are
V3
Continuous
Perfect
Shall/will have
been +V3
Am/is/are +
+being+V3
Have / has been
+ V3
Was/were
V3
was / were
+ being+ V3
Had been + V3
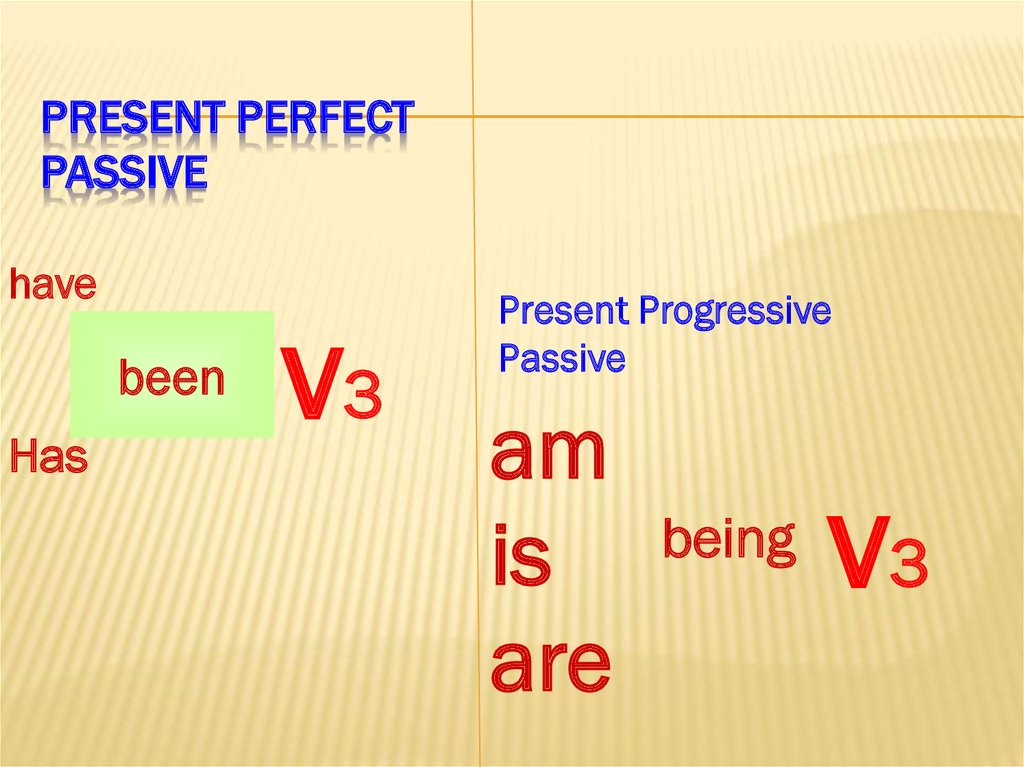
9. Present Perfect Passive
PRESENT PERFECTPASSIVE
have
been
Has
v3
Present Progressive
Passive
am
is
are
being
v3
10.
ThePassive Voice ПРИМЕРЫ
The Passive Voice показывает, что лицо или предмет,
обозначенные подлежащим, являются объектами действия,
выраженного сказуемым:
1)The arterial pressure was measured by doctor- Артериальное
давление было измеренно врачем
2)He had been developed lobular pneumonia gradually. -Постепенно у него
развилась очаговая пневмония.
3)The pain in the chest was felt by the patient- Боль в груди была
ощущенна пациентом.
4)Dry rales caused by diffuse bronchitis were heard all over the lungs.
Сухие хрипы вызванные диффузным бронхитом были слышны во всем
легкие.




 medicine
medicine








