Similar presentations:
Evaluating Strategic Options and Risk Assessment Business Planning
1. CH11. Evaluating Strategic Options and Risk Assessment
Business Planning2. Qualitative Evaluation of Strategic Choice
Consistency
Validity
Feasibility
Business Risk
Flexibility
3. Valuation Techniques Involving Comparable Business
Price/Earnings Ratio
EV/EBITDA Ratio
EV/Sales Ratio
EV/Customer Ratio
4. Discounted Cash Flow Analysis
• Principle 1. $1 today is worth morethan $1 tomorrow.
• Principle 2. A safe $1 is worth more
than a risky $1.
• Risk and Reward
• The Capital Asset Price Model
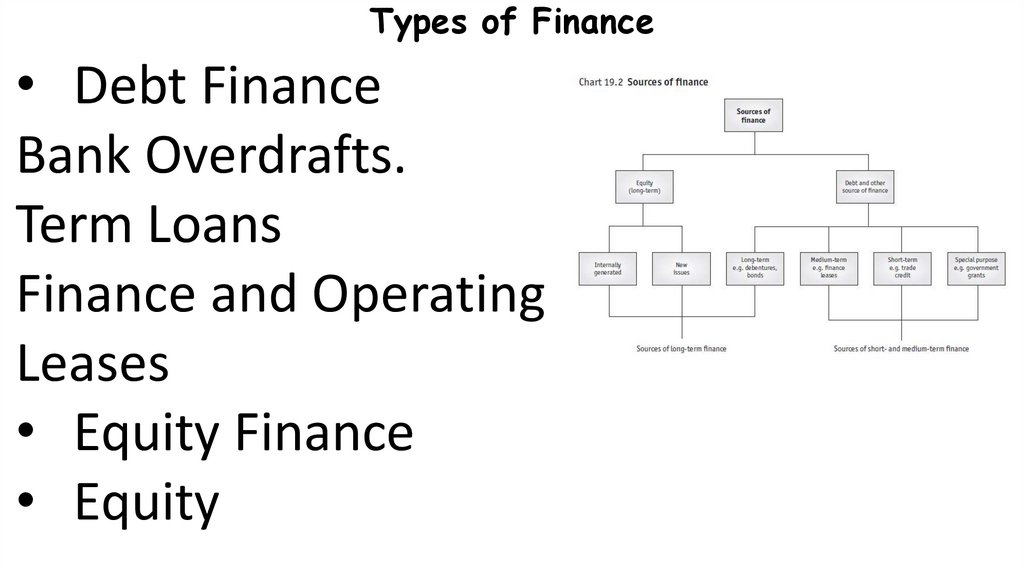
5. Types of Finance
• Debt FinanceBank Overdrafts.
Term Loans
Finance and Operating
Leases
• Equity Finance
• Equity
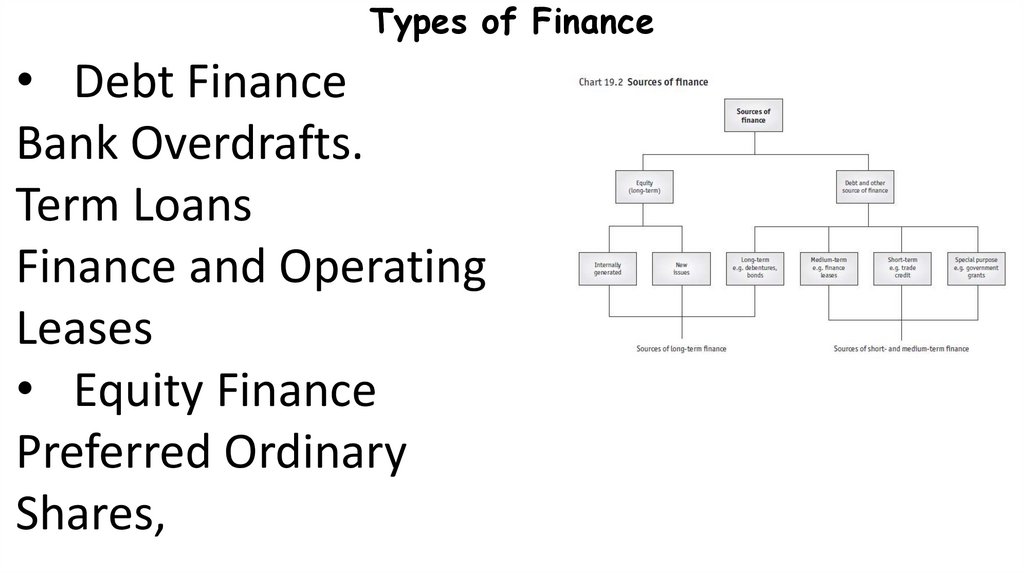
6. Types of Finance
• Debt FinanceBank Overdrafts.
Term Loans
Finance and Operating
Leases
• Equity Finance
Preferred Ordinary
Shares,
7. Risk Analysis
The dimensions of risk
The value of resources devoted to the project.
The proportion of total business resources represented by those resources.
The length of time for which the resources will be devoted to the project.
The inherent risk of the project.
The cost of exiting the project.
The recoverable costs were the project to fail
.
8. Risk Analysis
Types of Risk
Business risks can be categorized as:
1.Operational
2.Industry
3.Financial
4.Political
9. Operational Risks
Operational Risks
Key staff resign or are poached by a competitor.
Unforeseen problems occur in the production process.
Machinery breaks down or is incompatible with the raw materials.
Stocks become damaged.
Fire, theft and floods.
Information technology problems occur.
The product is so successful that the business cannot meet
demand.
The actions of a rogue employee result in large liabilities for the
business.
10. Industry Risks
Industry risks are caused by external developments in the industryand may develop as a result of actions by the business itself. They
include the following:
• A new firm enters the market.
• A key supplier closes and prevents the supply of crucial raw
materials.
• Demand for the product falls or fails to materialize.
• A competitor aggressively cuts prices.
• A new technology is developed making existing products
obsolete.
• Two competitors merge providing them with a major cost
advantage.
11. Financial Risks
Potential financial risks include the following:• A stockmarket collapse prevents a crucial fundraising equity issue
or a merger with a competitor.
• Interest rates increase dramatically, raising the cost of servicing
the business’s debts.
• There is a significant devaluation, which increases the costs of raw
materials purchased from abroad.
• High demand for the product leads to overtrading and a lack of
available working capital to fund the business’s activities.
12. Political Risks
Political risks include not only governmental risks but also thoseresulting from the actions of trade unions, lobbyists and activists.
They include the following:
• Sanctions imposed on a country prevent access to customers or
raw materials.
• Taxation rates are changed or taxation policy is altered.
• Grants, loans and subsidies are altered.
• Trade unions organise industrial action, preventing production
from continuing.
• Pressure from lobbyists requires a change in the business
practices of the business.
• The business suffers organised vandalism by radical protesters.
13. Risk Assessment
Quantifying the risksThe business planning model can be used to examine the financial
impact of risk. A useful technique is to run a sensitivity analysis
across the key inputs in the model that best relate to the identified
risks. Examples of typical inputs are as follows:
• The quantity demanded of the product.
• The selling price of the product.
• Distribution costs.
• Sales and marketing costs.
• The cost of raw materials.
• Interest rates.
• Taxation rates.
• Exchange rates.
14. Risk Assessment
Quantifying the risksThe business planning model can be used to examine the financial
impact of risk. A useful technique is to run a sensitivity analysis
across the key inputs in the model that best relate to the identified
risks. Examples of typical inputs are as follows:
• The quantity demanded of the product.
• The selling price of the product.
• Distribution costs.
• Sales and marketing costs.
• The cost of raw materials.
• Interest rates.
• Taxation rates.
• Exchange rates.










 business
business








