Similar presentations:
Fertilizers
1. fertilizers
FERTILIZERS2. Fertilizers
FERTILIZERS▪ Function of elements
▪ Symptoms of lack of elements
▪ Elements in soil
▪ Strategy:
▪ Soil
▪ Fertigation
▪ Foliar
▪ Water management
3. fertilizers
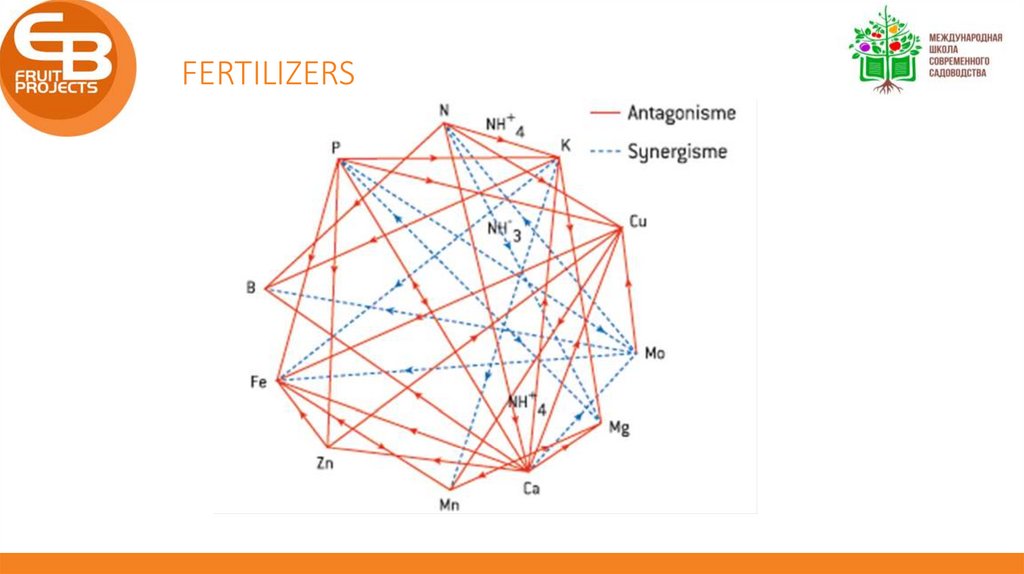
FERTILIZERSIt is about balance between elements
More of 1 element does NOT mean: more production
Some elements are concurrent to others
4. fertilizers
FERTILIZERS5. fertilizers
FERTILIZERSKeep in mind:
▪ Roots are for uptake of elements and water
▪ Leaves are for assimilation
It has to be good in the root zone
% organic material
6. fertilizers
FERTILIZERS7. fertilizers
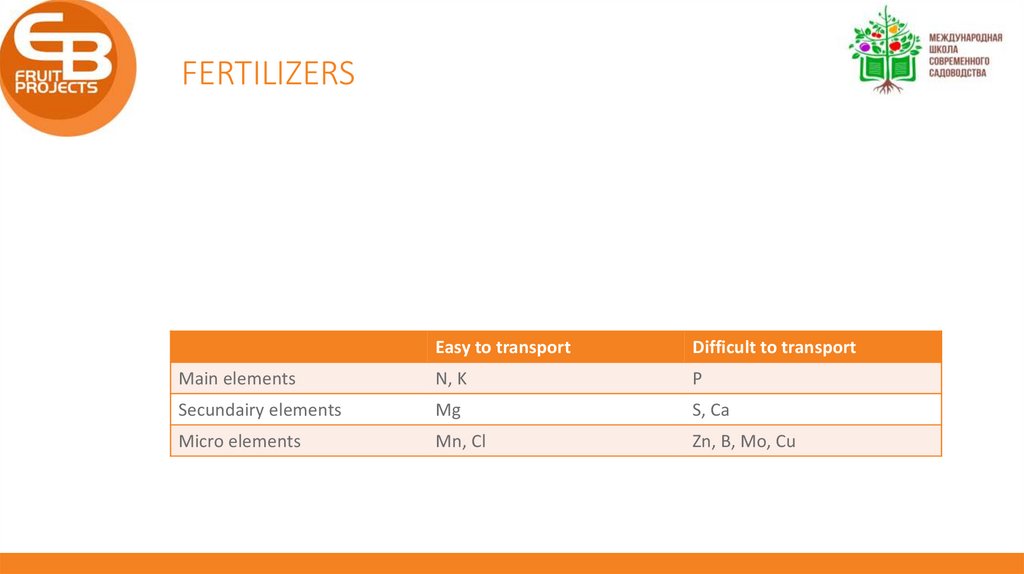
FERTILIZERSEasy to transport
Difficult to transport
Main elements
N, K
P
Secundairy elements
Mg
S, Ca
Micro elements
Mn, Cl
Zn, B, Mo, Cu
8. N = nitrogen
N = NITROGENIn quantity needed, the most important of all
For metabolism of plant:
▪ Amino-acids
▪ chlorofyl
9. N = nitrogen
N = NITROGENUptake: by roots, little by leaves
Uptake of:
▪ NO3 = nitrate
▪ NH4 = ammonium
NH4 works for longer time, because it is binded to soil parts
NH3 more effective on the short term
10. N = nitrogen
N = NITROGENIf there is a lack:
▪ Small leaves not green, more yellow
▪ Weak quality of flowers
▪ Bad fruit set
▪ Fruit size too small
▪ Early ripe emergency ripe
▪ Good storable
11. N = nitrogen
N = NITROGENToo much N:
▪ Big leaves dark green
▪ Strong vegetative growth
▪ Big fruit size
▪ Bad colour
▪ Weak in storage
▪ More diseases, like bitter pit and Gloeosporium
12. P = phosphate
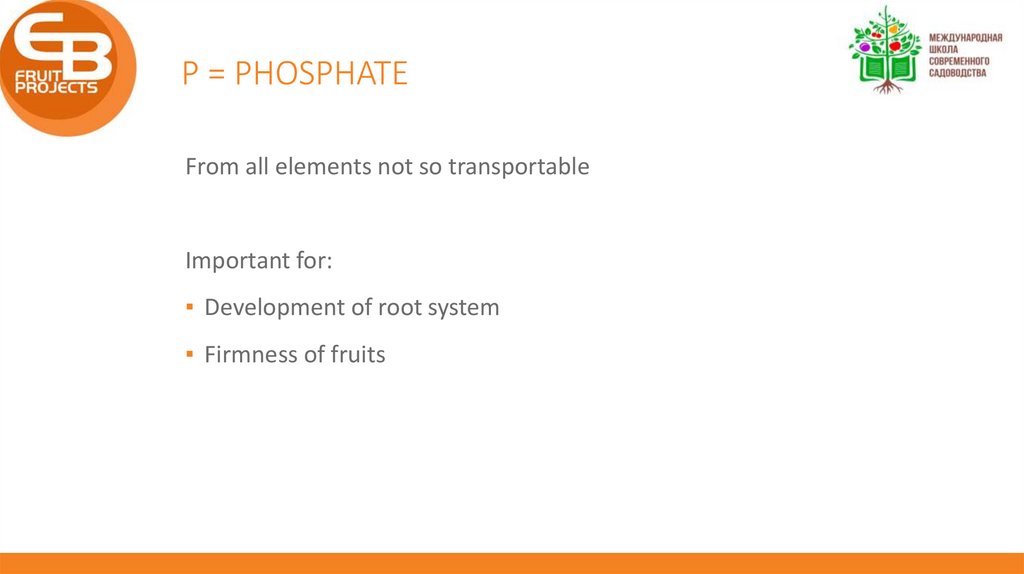
P = PHOSPHATEFrom all elements not so transportable
Important for:
▪ Development of root system
▪ Firmness of fruits
13. P = phosphate
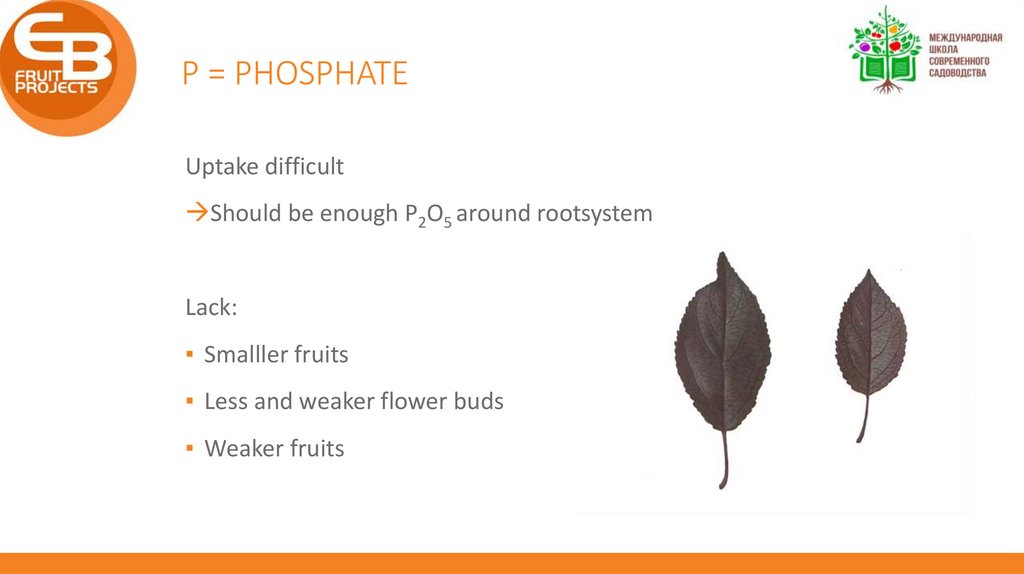
P = PHOSPHATEUptake difficult
Should be enough P2O5 around rootsystem
Lack:
▪ Smalller fruits
▪ Less and weaker flower buds
▪ Weaker fruits
14. K = potassium
K = POTASSIUMImportant for water uptake
And transport of other elements
Very mobile
Good for:
▪ Fruit size
▪ New growth
15. K = potassium
K = POTASSIUMLack:
▪ Abnormal evaporation
▪ Small fruits
▪ More N in leaves
16. K = potassium
K = POTASSIUMK is concurrent for:
▪ Magnesium (Mg)
▪ Calcium (Ca)
▪ Borium (B)
▪ And also Natrium (Na).
Natrium is not fertilizer, but can cause lack of usefull elements
17. Mg = magnesium
MG = MAGNESIUMMagnesium is part of chlorofyll.
15% of all Mg is in het leaves.
Mg makes leaves a bit harder
More resistent against intruding diseases (like Scab)
18. Mg = magnesium
MG = MAGNESIUMLack:
▪ Especially on soil with lower pH
▪ After dry period
▪ Low temperatures during season
19. Ca = Calcium
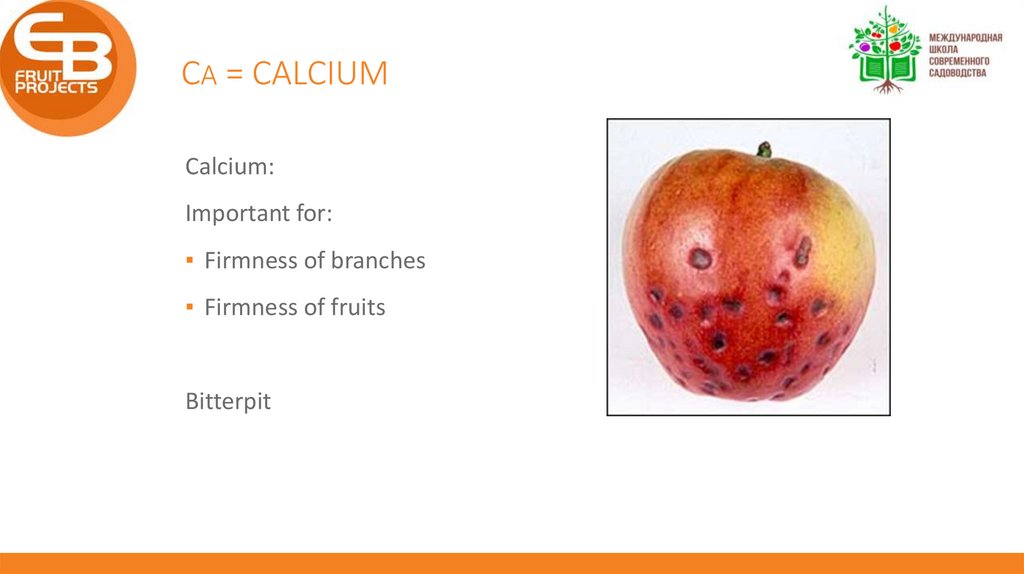
CA = CALCIUMCalcium:
Important for:
▪ Firmness of branches
▪ Firmness of fruits
Bitterpit
20. Ca = Calcium
CA = CALCIUMCalcium:
Bitterpit:
▪ Too much vegetative growth
▪ Ca transported to new leaves, not to fruits
▪ Too much N and too much water
▪ Too much K, Mg, Na
Balance between vegetative growth and production important
21. B = Borium
B = BORIUMBorium important for:
▪ Formation of flower buds
▪ Quality of flower buds winter hardness
▪ Quality of the pollen
▪ Fruit set
In water: risk of too much B
22. Mn = mangane
MN = MANGANEImportant for:
▪ Fotosynthesis growth
▪ Firmness of fruits
In plant not easy to transport
Soil high pH: more risk
23. Zn = zinc
ZN = ZINCImportant for:
▪ Growth
▪ Winterhardness
▪ Lack:
Small leaves
24. FE = iron
FE = IRONImportant for:
▪ Basic colour of fruits better storage
▪ Assimiliation green leaves
Soil with:
▪ High pH
▪ High humus
More risk
25. strategy
STRATEGYWhat do we need?
We give per hectare
Better is per kilogram or ton
per hectare
26. strategy
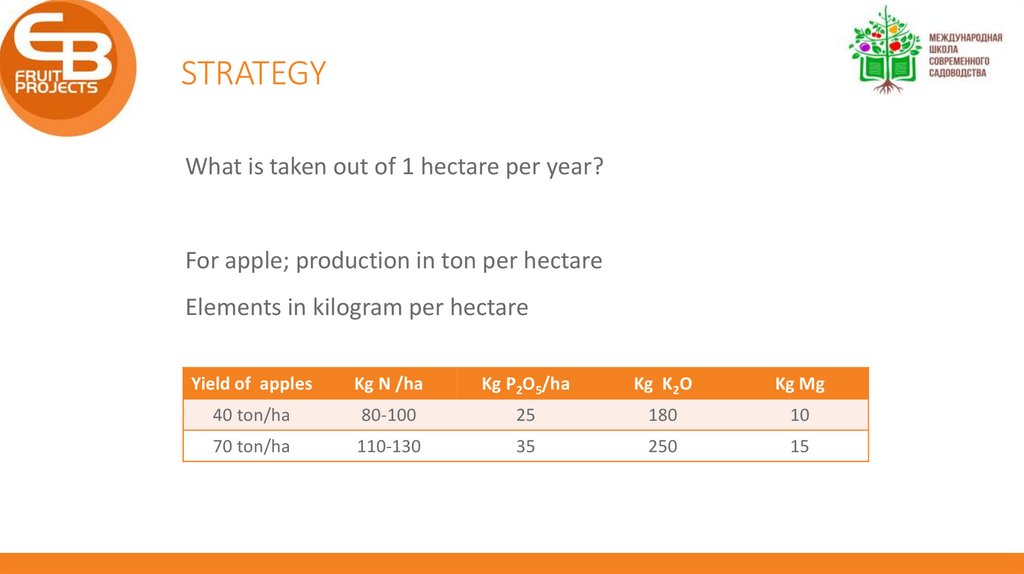
STRATEGYWhat is taken out of 1 hectare per year?
For apple; production in ton per hectare
Elements in kilogram per hectare
Yield of apples
Kg N /ha
Kg P2O5/ha
Kg K2O
Kg Mg
40 ton/ha
80-100
25
180
10
70 ton/ha
110-130
35
250
15
27. On the soil
ON THE SOILOn light, sandy soils:
Shortly for flowering
On other soils:
▪ 35-50 kg N under the trees
▪ Additional foliar
▪ June: extra 35 kg, depending on production
28. On the soil
ON THE SOILPotassium:
▪ Not necessary before flowering
▪ During the season
Phosphate:
▪ On good soil: not every year necessary
▪ Especially in the first years important
29. foliar
FOLIAR▪ Just additional
▪ Never the basic
▪ Especcially the elements which are difficult to transport by the trees.
▪ In many cases: just cosmetic effect
▪ Or useful when soil is still cold
30. foliar
FOLIART: 0031-616508773
E: info@ebfruit.nl
I: www.ebfruit.nl
Onafhankelijk fruitteeltadvies
Private Obstbauberatung
Independent advice for fruit growers
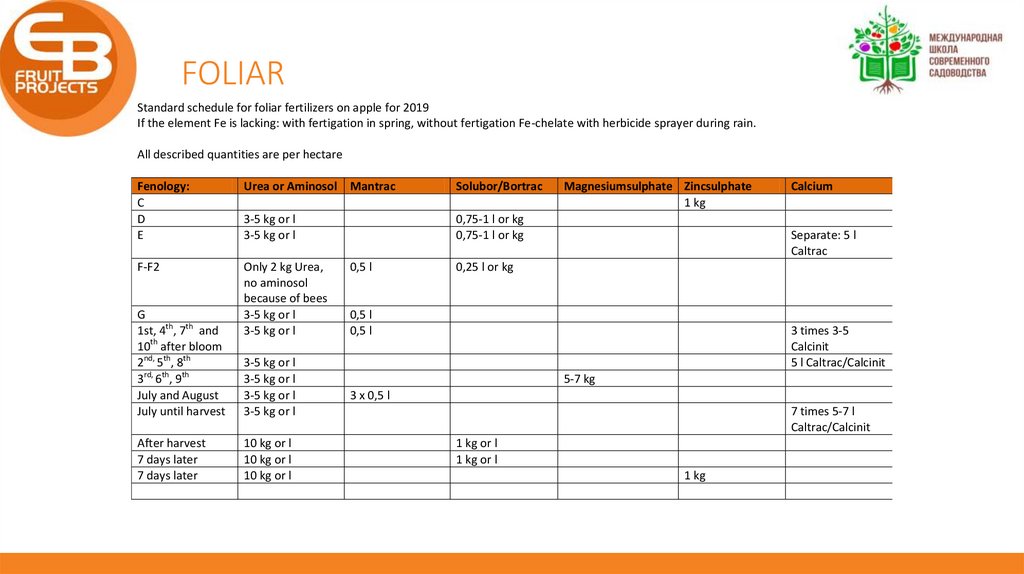
Standard schedule for foliar fertilizers on apple for 2019
If the element Fe is lacking: with fertigation in spring, without fertigation Fe-chelate with herbicide sprayer during rain.
All described quantities are per hectare
Fenology:
C
D
E
Urea or Aminosol Mantrac
Solubor/Bortrac
3-5 kg or l
3-5 kg or l
0,75-1 l or kg
0,75-1 l or kg
F-F2
Only 2 kg Urea,
no aminosol
because of bees
3-5 kg or l
3-5 kg or l
G
1st, 4th, 7th and
10th after bloom
2nd, 5th, 8th
3rd, 6th, 9th
July and August
July until harvest
After harvest
7 days later
7 days later
3-5 kg or l
3-5 kg or l
3-5 kg or l
3-5 kg or l
10 kg or l
10 kg or l
10 kg or l
0,5 l
Magnesiumsulphate Zincsulphate
1 kg
Calcium
Separate: 5 l
Caltrac
0,25 l or kg
0,5 l
0,5 l
3 times 3-5
Calcinit
5 l Caltrac/Calcinit
5-7 kg
3 x 0,5 l
7 times 5-7 l
Caltrac/Calcinit
1 kg or l
1 kg or l
1 kg
31. Water and fertigation
WATER AND FERTIGATIONWithout water: not possible with M9
Not necessary the whole year
Water and fertigation:
▪ More production
▪ More control of the growth
32. Water and fertigation
WATER AND FERTIGATIONOften used:
Tensiometers: amount of water in kPa
Also tensiometers that give %
33. Water and fertigation
WATER AND FERTIGATIONWhat does it means for tree?
kPa
soil
For tree
0
Full with water; no air
Roots die: stop of growth
5-20
Wet
Unlimited water; enough oxygen
40-60
Almost dry
Hard to take water; growth is less
100-200
Completely dry
Complete stop of growth
34. Water and fertigation
WATER AND FERTIGATIONRecommended during growing season:
Depending on:
▪ Climate: dry or rain
▪ Production
Flowering-6 weeks after 6 weeks after –stop vegetative growth Growth of fruits
10-25 kPa
25-60 kPa
10-25 kPa
35. Water and fertigation
WATER AND FERTIGATIONFertigation = additional, especially older trees
N during spring important: 50-60% needed.
Advantage:
Give what trees need
Flexible during the season
36. Water and fertigation
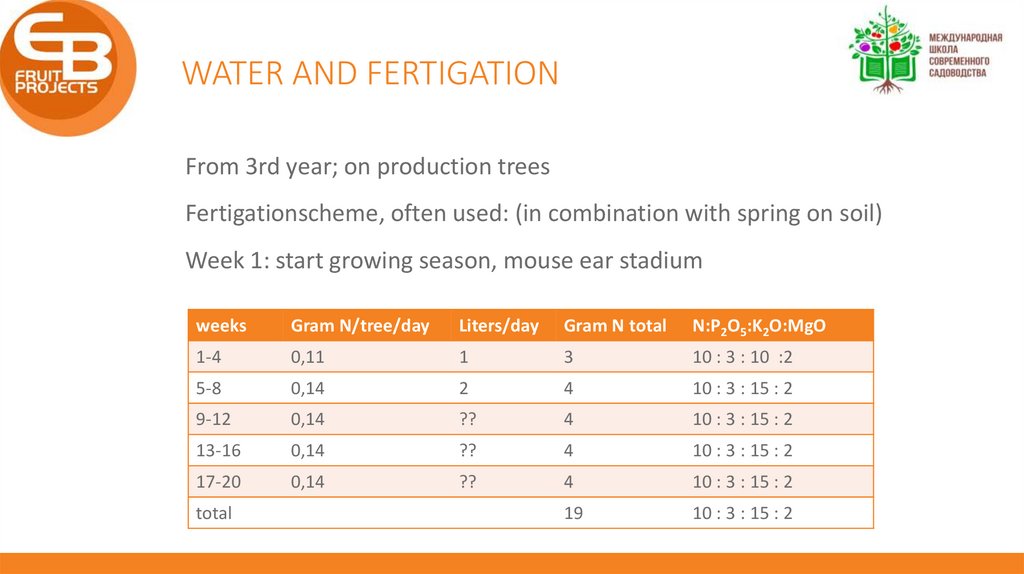
WATER AND FERTIGATIONFrom 3rd year; on production trees
Fertigationscheme, often used: (in combination with spring on soil)
Week 1: start growing season, mouse ear stadium
weeks
Gram N/tree/day
Liters/day
Gram N total
N:P2O5:K2O:MgO
1-4
0,11
1
3
10 : 3 : 10 :2
5-8
0,14
2
4
10 : 3 : 15 : 2
9-12
0,14
??
4
10 : 3 : 15 : 2
13-16
0,14
??
4
10 : 3 : 15 : 2
17-20
0,14
??
4
10 : 3 : 15 : 2
19
10 : 3 : 15 : 2
total
37. Water and fertigation
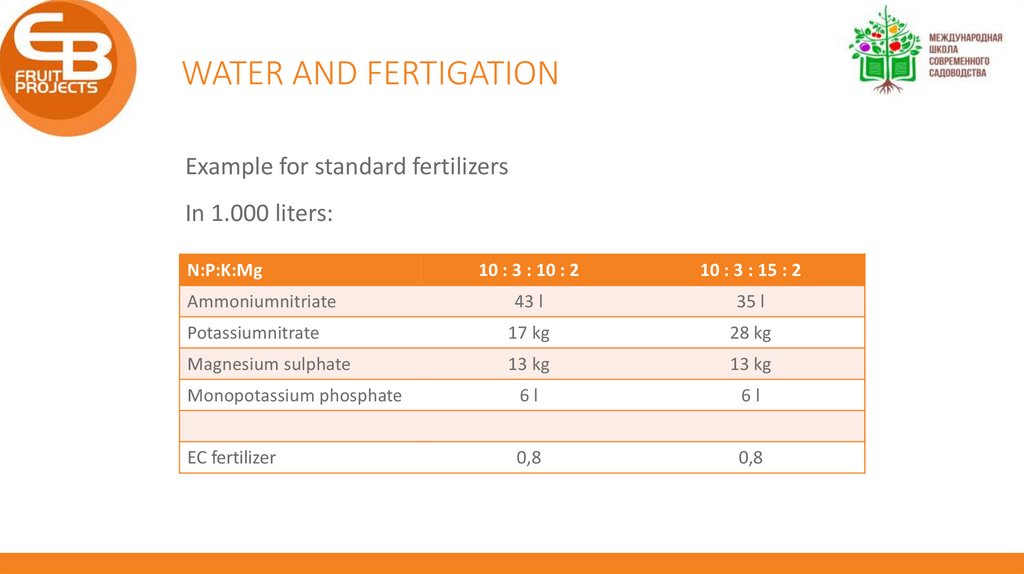
WATER AND FERTIGATIONExample for standard fertilizers
In 1.000 liters:
N:P:K:Mg
10 : 3 : 10 : 2
10 : 3 : 15 : 2
43 l
35 l
Potassiumnitrate
17 kg
28 kg
Magnesium sulphate
13 kg
13 kg
Monopotassium phosphate
6l
6l
EC fertilizer
0,8
0,8
Ammoniumnitriate
38. Water and fertigation
WATER AND FERTIGATION▪ Calcium: always separate from other elements
▪ Only with N possible
▪ EC must not be too high
Maximum: 2,3 at dripping point at tree
EC at dripping point:
= EC Fertilizer + EC water
39. WAter
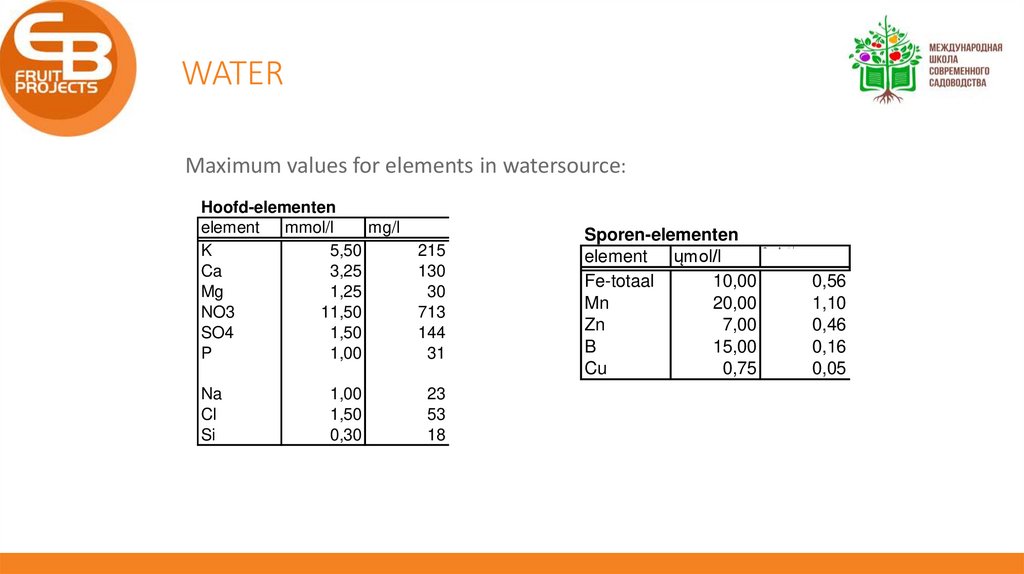
WATERMaximum values for elements in watersource:
Hoofd-elementen
element
mmol/l
mg/l
K
5,50
Ca
3,25
Mg
1,25
NO3
11,50
SO4
1,50
P
1,00
Na
Cl
Si
1,00
1,50
0,30
215
130
30
713
144
31
23
53
18
Sporen-elementen
element
ųmol/l
Fe-totaal
10,00
Mn
20,00
Zn
7,00
B
15,00
Cu
0,75
m
g
/
l
0,56
1,10
0,46
0,16
0,05
40. WAter
WATERpH in water:
Range at drip point:
between 5 and 7
Low pH:
macro elements
better uptake micro elements, but more problems
(Mg)
High pH:
deficit micro elements
41. WAter
WATERpH in water:
If too high:
use acid to decrease
Like: fosfor acid, nitrate-acid
If too low:
use more calcium fertilizers
Very hard to get stabile solution
42. WAter
WATEREC = Electric Conductivity
Measure of content of salt in water
In many cases, EC is too high
Maximum EC at dripping point = 2,3
This is EC of water + EC of fertilizer ( in formula)
43. WAter
WATEREC formula:
Gram N/tree/day X EC Fertilizer X 100
%N fertilizer X liters/tree/day
= EC fertilizer
+ EC water
Check at tree
44. analysis
ANALYSIS▪ Soil:
▪ Before planting
▪ Each 3 years
▪ Leaves:
▪ Begin of June: possible to adapt, but not stabile
▪ End of July/August: to adapt for next year
▪ Fruits: during harvest: for storage and next year
45. Thanks for your attention
Questions?Erik Buitenhuis
info@ebfruit.nl
e.buitenhuis@delphy.nl
THANKS
FOR YOUR
ATTENTION



































 biology
biology industry
industry