Similar presentations:
He system of english consonant phonemes
1. THE SYSTEM OF ENGLISH consonant PHONEMES
THE SYSTEM OF ENGLISHCONSONANT PHONEMES
B Y F I L I M O N O VA A . E L E N A
2.
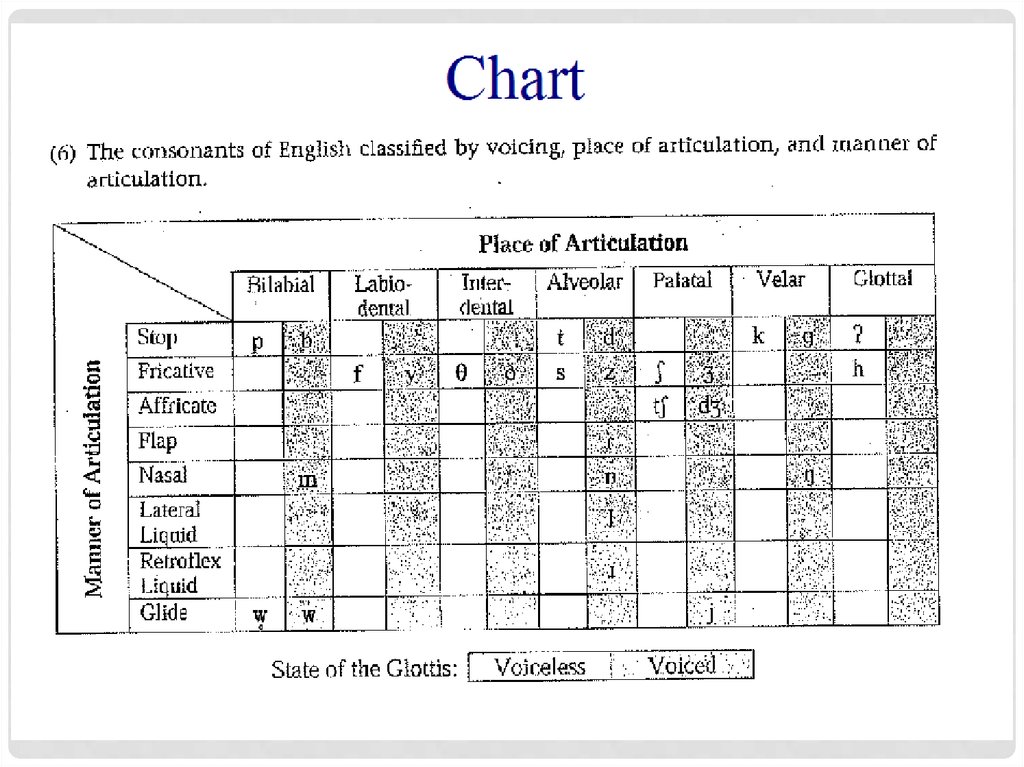
Describing Speech SoundsIs the air-flow blocked?
vowel vs. consonant
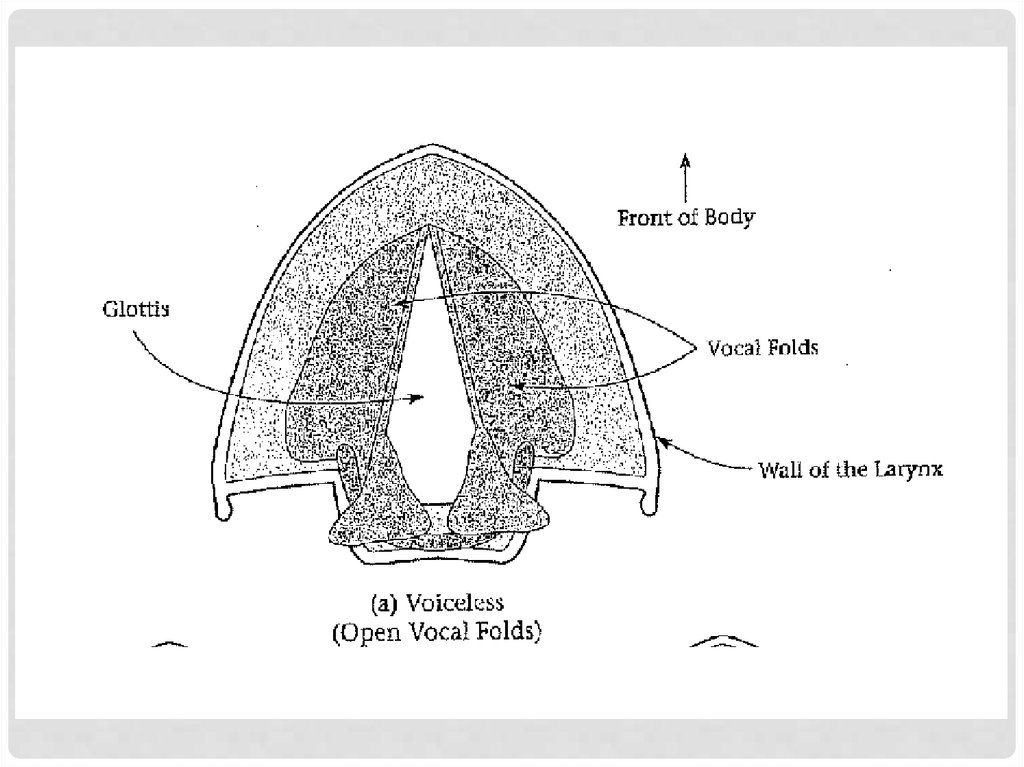
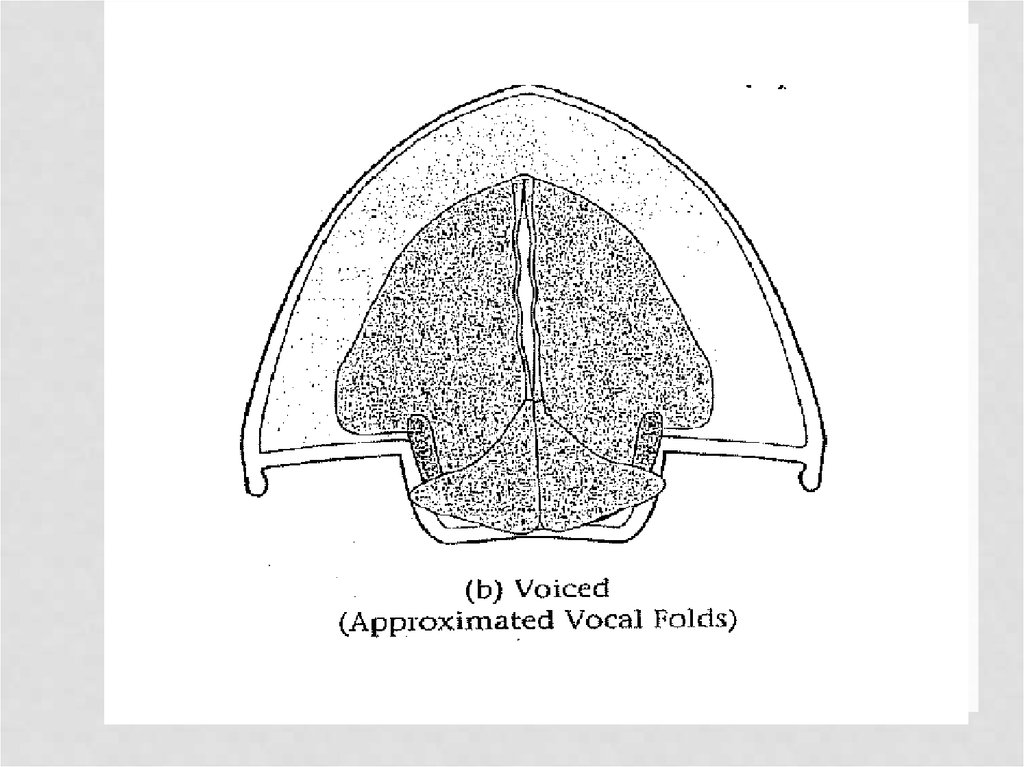
What are the vocal folds doing? (=voicing)
voiced vs. voiceless
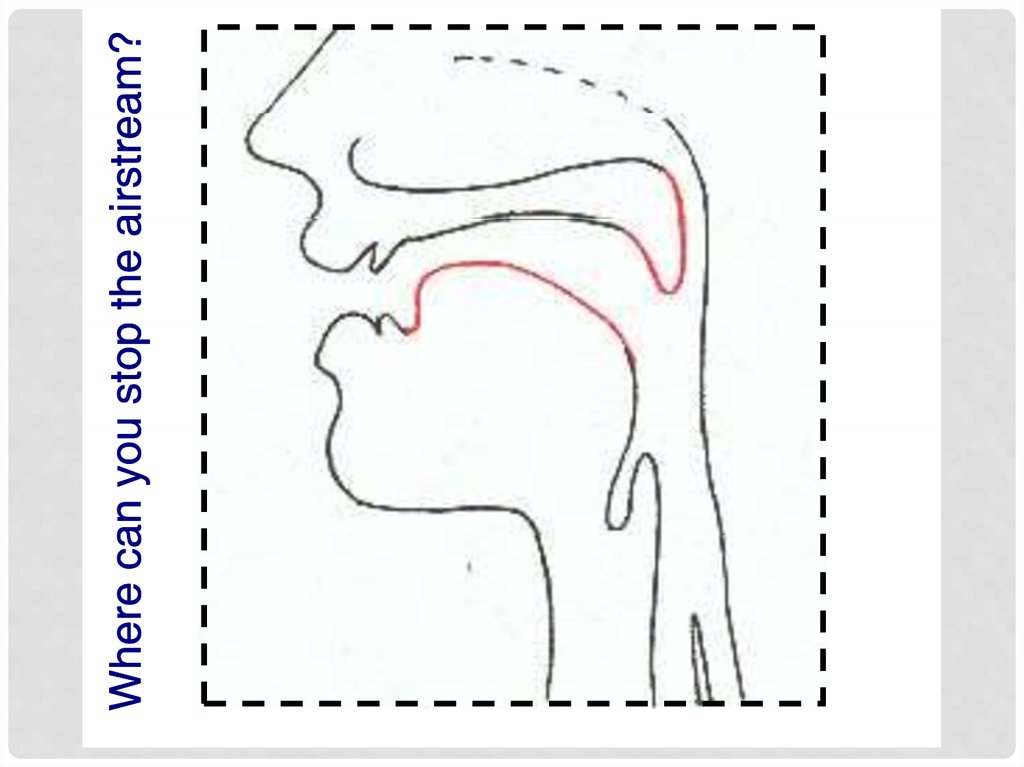
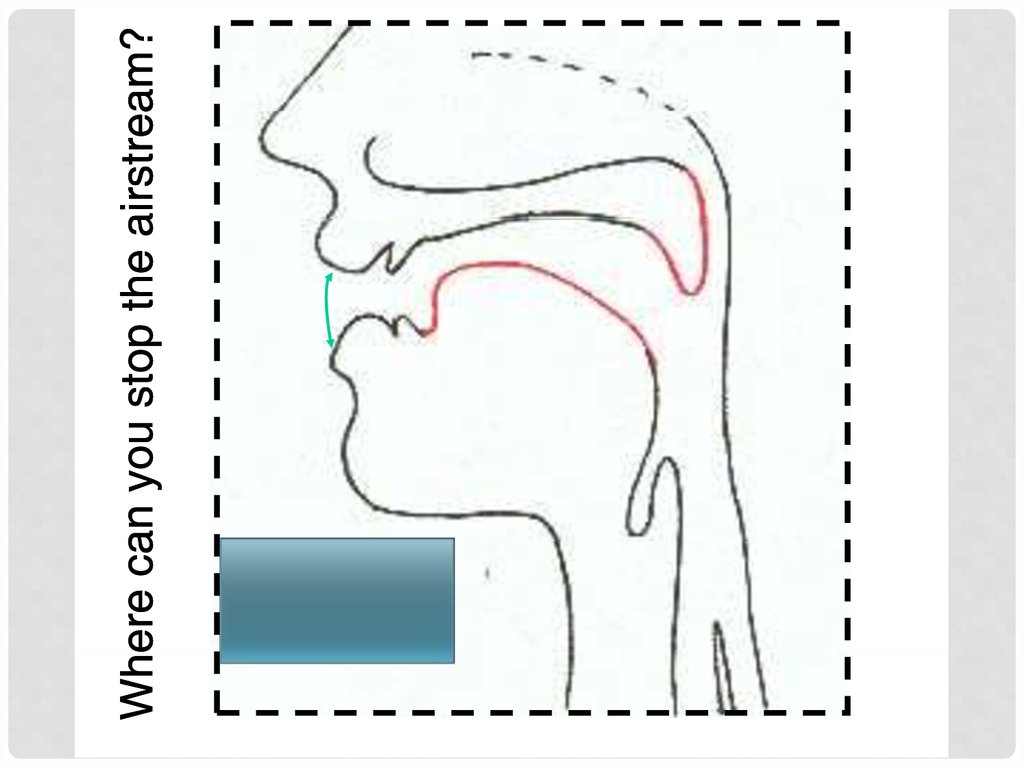
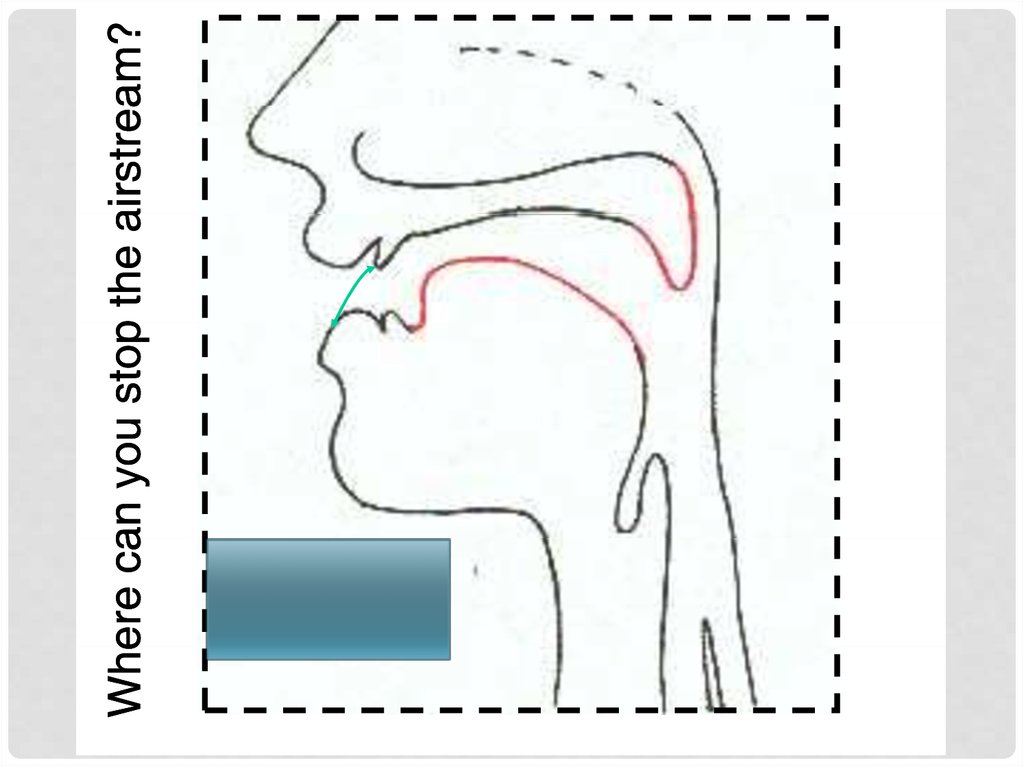
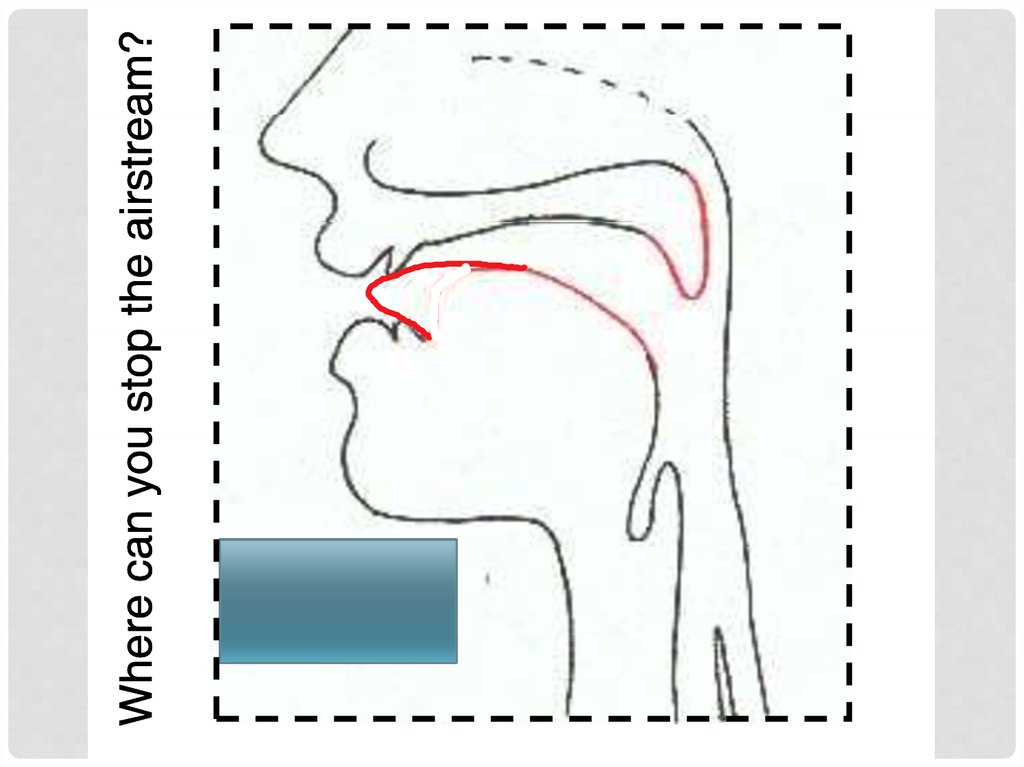
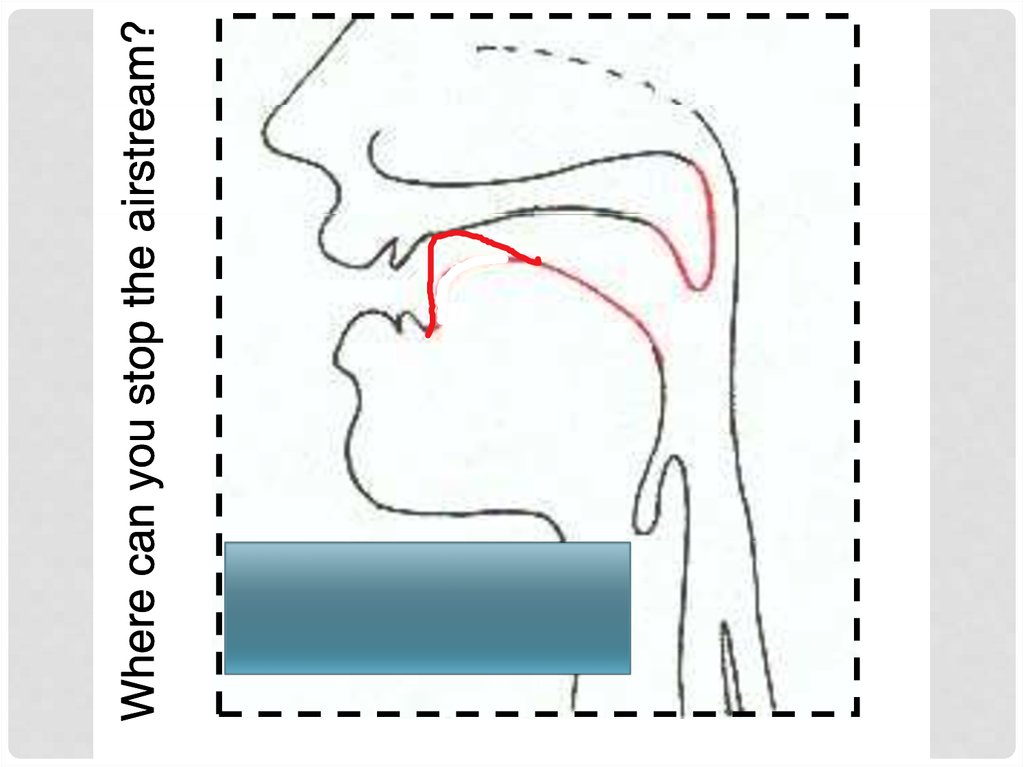
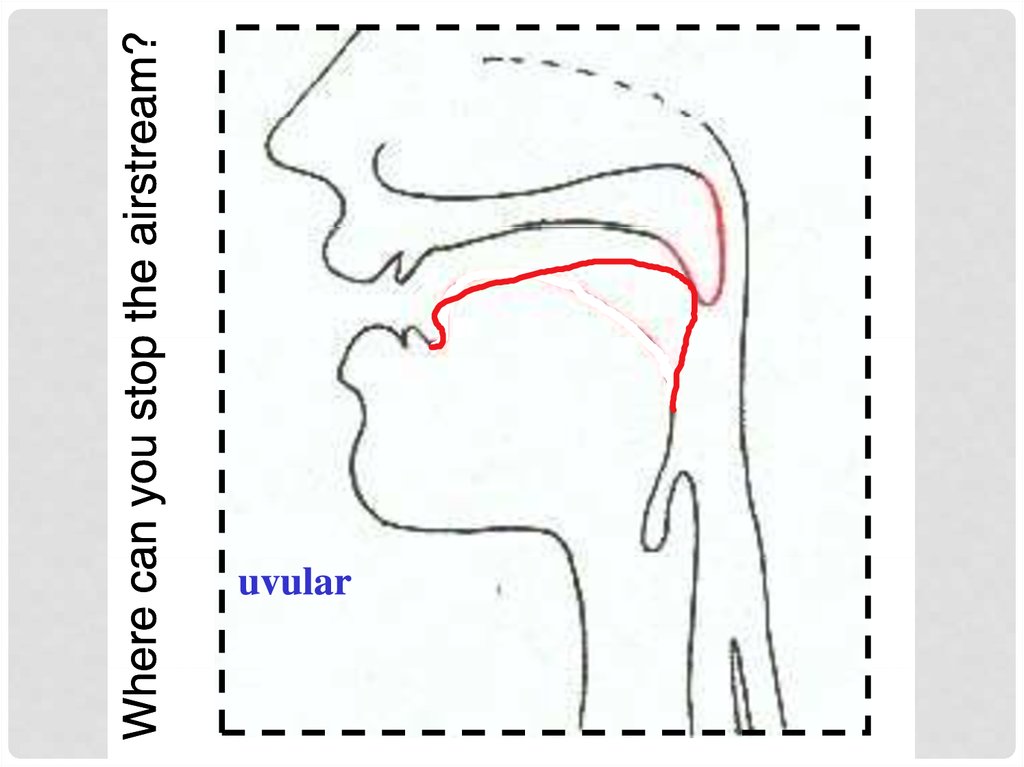
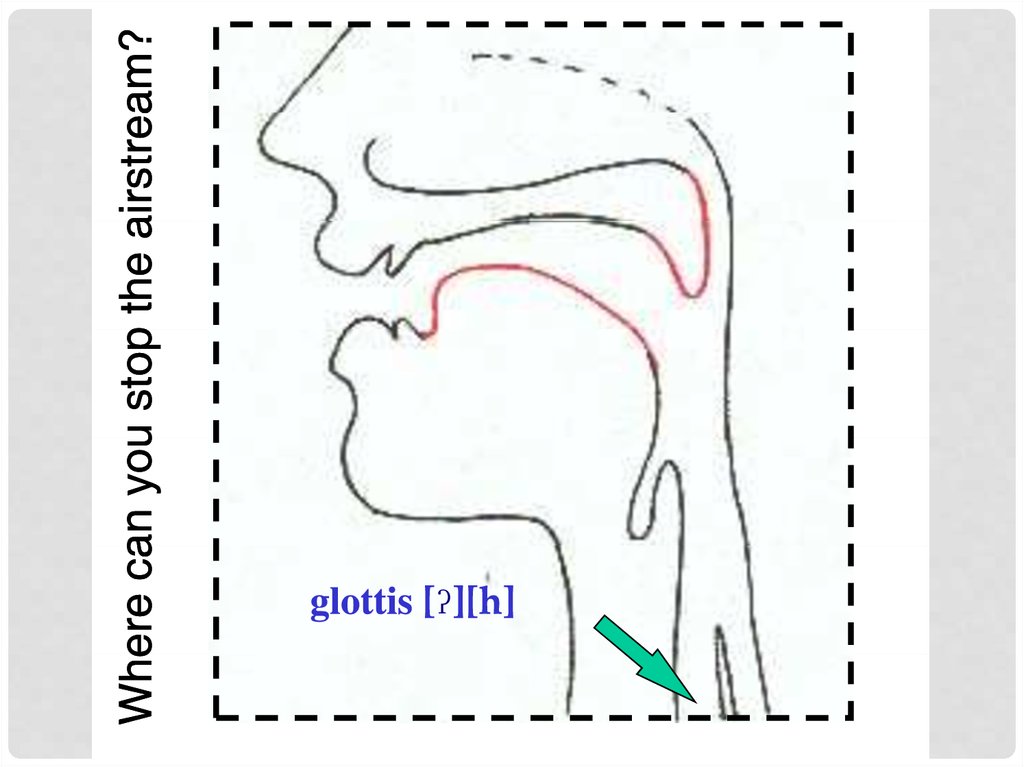
Where is the air-flow blocked? (=place)
labial,, alveolar,, p
palatal,, velar etc.
Where/how is the air flowing? (=manner)
nasal/oral,, stop,
p, ffricative,, liquid
q etc.
3.
Describing Speech SoundsIs the air-flow blocked?
vowel vs. consonant
What are the vocal folds doing? (=voicing)
voiced vs. voiceless
Where is the air-flow blocked? (=place)
labial,, alveolar,, palatal,
p
, velar etc.
Where/how is the air flowing? (=manner)
nasal/oral,, stop,
p, ffricative,, liquid
q etc.
4.
5.
6.
7.
Describing Speech SoundsIs the air-flow blocked?
vowel vs. consonant
What are the vocal folds doing? (=voicing)
voiced vs. voiceless
Where is the air-flow blocked? (=place)
labial,, alveolar,, p
palatal,, velar etc.
Where/how is the air flowing? (=manner)
nasal/oral,, stop,
p, ffricative,, liquid
q etc.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
14.
15.
16.
17.
Describing Speech SoundsIs the air-flow blocked?
vowel vs. consonant
What are the vocal folds doing? (=voicing)
voiced vs. voiceless
Where is the air-flow blocked? (=place)
labial,, alveolar,, p
palatal,, velar etc.
Where/how is the air flowing? (=manner)
nasal/oral,, stop,
p, ffricative,, liquid
q etc.
18.
19.
20.
Liquids, glidesLiquids
[ ][ ]
[l][r]
Lateral [l] : air escapes along sides of tongue
Retroflex
Retroflex [r]: tongue is bunched upward and
back in mouth
Glides:
Glides: semi
semi-vowels
vowels, semi
semi-consonants
consonants
[w] [j]
21.
22.
Putting them all togethertogether
Voicing, Place, Manner
how do we describe [p]?
Voiceless bilabial stop
Voiceless,
Wh about
What
b
[b]?
23.
FeaturesWays of describing sounds
e.g.,
g , [p] = voiceless bilabial stopp
Stronger claim: features are the smallest
building blocks of language,
language used to store
sounds in the mind
Atoms of Speech
Roman Jakobson, 1896-1982
24.
25.
More consonant exercises1.
2.
3.
4.
5
5.
6.
Write the symbol that corresponds to each
of the phonetic descriptions, then give an
English word that contains this sound.
voiceless bilabial stop
voiced labiodental fricative
voiced alveolar lateral liquid
q
voiceless palatal affricate
voiced alveolar nasal
voiced bilabial glide
26.
27. PRINCIPLES OF CLASSIFICATION
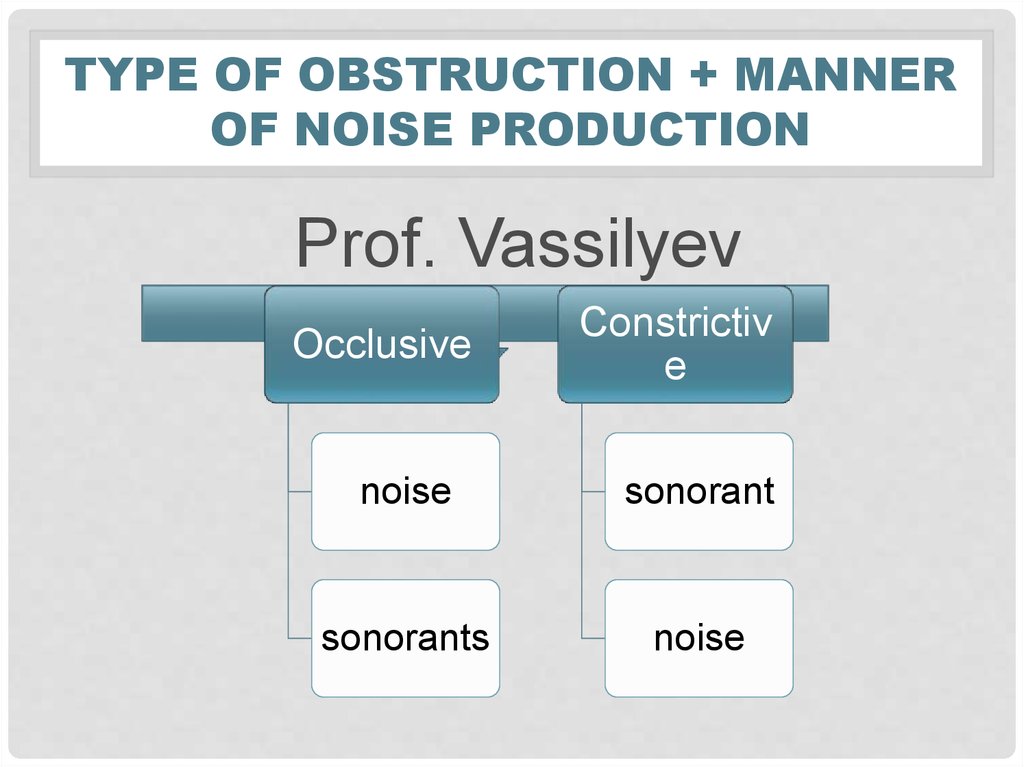
28. Type of obstruction + manner of noise production
TYPE OF OBSTRUCTION + MANNEROF NOISE PRODUCTION
Prof. Vassilyev
Occlusive
Constrictiv
e
noise
sonorant
sonorants
noise
29. Degree of noise (sokolova, Gintovt)
DEGREE OF NOISE (SOKOLOVA,GINTOVT)
noise
sonorant
occlusive
occlusive
constrictive
constrictive
Occlusiveconstrictive
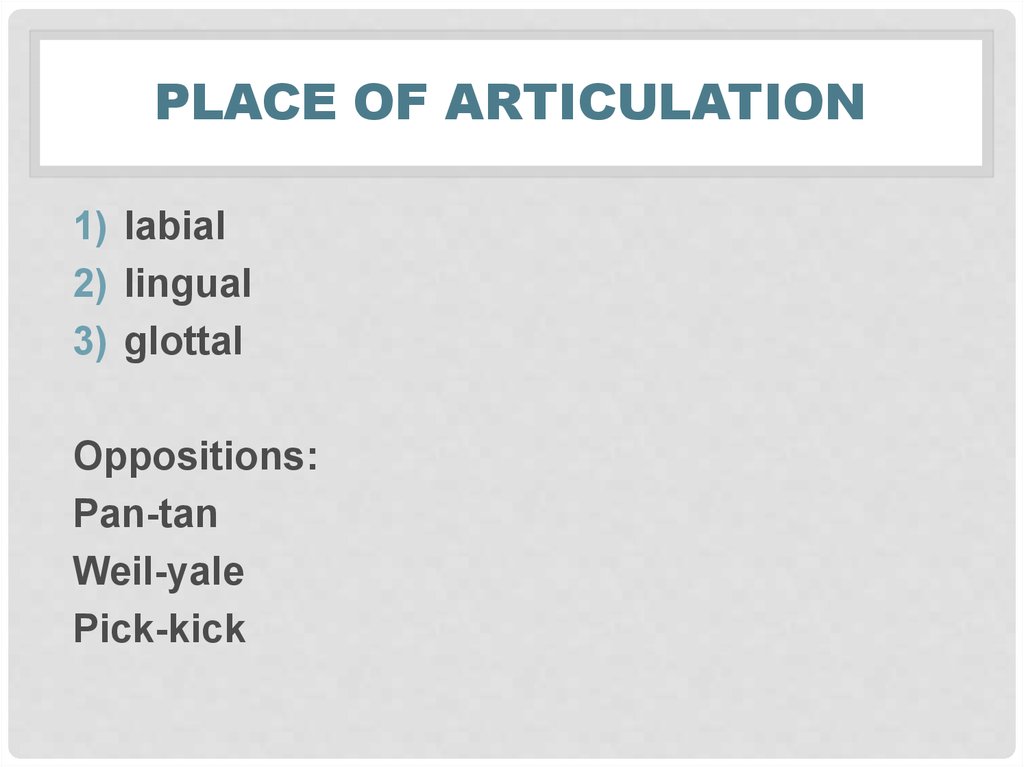
30. Place of articulation
PLACE OF ARTICULATION1) labial
2) lingual
3) glottal
Oppositions:
Pan-tan
Weil-yale
Pick-kick
31. Work of the vocal cords
WORK OF THE VOCAL CORDSTone + Energy
32. Position of the soft palate
POSITION OF THE SOFT PALATEOral
Nasal
33. Prof. Dikushina
PROF. DIKUSHINAClassification by oppositions:
1)
2)
3)
4)
5)
6)
7)
8)
9)
Manner of articulation (stops - constrictives)
Articulating organ (labial – bilabial)
Passive speech organ (dental, alveolar, palatal, velar)
Shape of the narrowing (slit or aperture)
Voice presence (voiced-voiceless)
Prevalence of voice/tone (noises and sonorants)
Kind of resonance (oral-nasal)
1 or 2 producing obstacles (single-point – double-point)
Manner of releasing closure (plosives – affricates)
34. affriates
AFFRIATESMonophonemic?
Trubetskoy:
1)Belong to the same syllable
2)1 articulatory effort
3)Duration does not exceed
duration of either element (+-)
35.
D.Johnes:Number of affricates = number of fricatives
6 affricates + [tr, dr, ts, ds]
Gimson:
8 affricates = phonological extreme,
indivisible entities
36. Relevant principles
RELEVANT PRINCIPLES•1) type of obstruction
•2) place of obstruction + active
speech organ
•3) force of articulation
37. Thank you for attention!
THANK YOU FORATTENTION!

























 english
english








