Similar presentations:
The Peculiarities of Upbringing work in the Organization of Working in Groups and Teams
1.
The Peculiarities of Upbringingwork in the Organization of
Working in Groups and Teams
2.
3. Why TEAM work?
Together Everyone Achieves MoreNever doubt that a small group of thoughtful,
committed people can change the world: indeed it is
the only thing that ever has.
Margaret Mead
Innovation is simply group intelligence having fun
Tom Peters
4. What is Teamwork?
How would you define it?What do we think of as the qualities of a good team?
With a partner, make a list of what makes a winning
team:
Team list:
What Makes a Winning Team?
5. What makes an Effective Team?
Basic Elements of Effectiveness:• Good Communication & Social Skills
• Positive Interdependence: We instead of me
• Individual Accountability/ Personal Responsibility
• Group Processing
• Shared goals
• Processes for Conflict Resolution
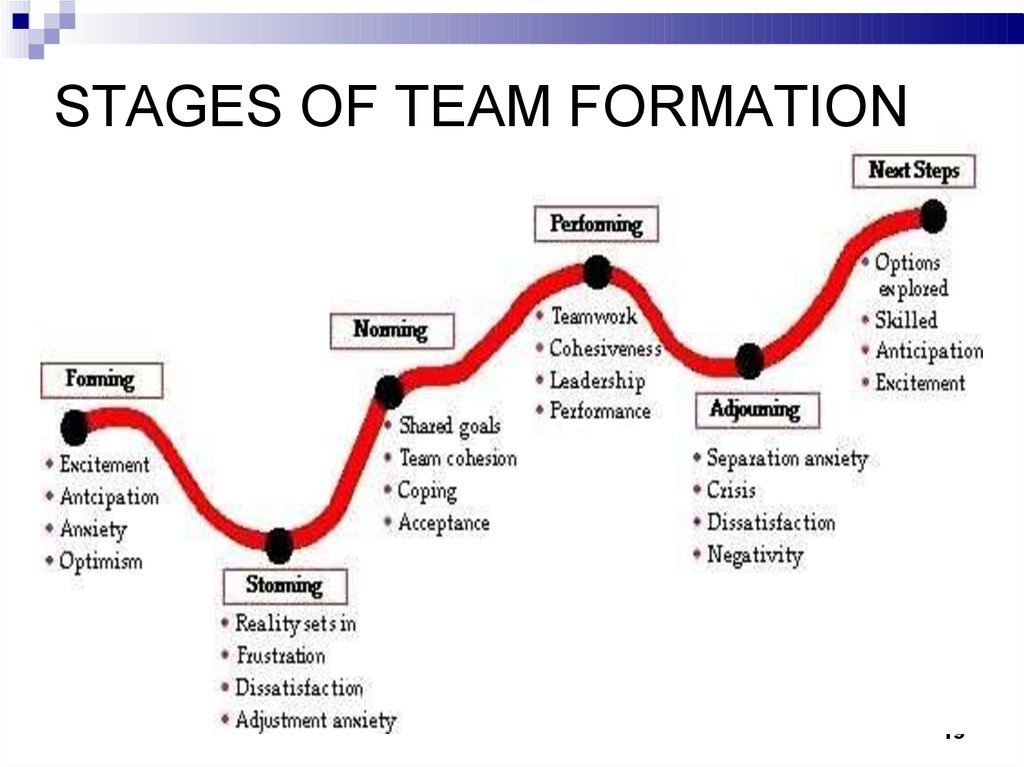
6. STAGES OF TEAM FORMATION
197.
Forming ….. Am I a member of this group?Storming ….. Who controls this group?
Norming ….. What are the rules of this group?
Performing ….. How high can this group go?
Mourning ….. Where do we go from here?
8. Basic Team Skills
The following features are fundamental to goodteamwork:
trust: making sure you meet all commitments and maintain
confidentiality when required
coaching: using your skills, knowledge and experience to
assist others or ask for help
sharing information: to assist others do their job
flexibility: show a willingness to cooperate and help others
when possible
good manners: doing small, simple things, eg. thanking
colleagues for their help
9. Team Communication
Teams need to master 3 types of communications:The team members need to communicate well
with each other. They rely on each other’s work;
they are each other’s internal customers
The team needs to communicate well with other
teams at work. These are also internal customers
The team has to communicate directly with their
external customers.
10. Communication Behaviours
Assertiveness(drive, confidence)Listening Responsively
Speaking Confidently
Contributing to Decisions
11. Assertiveness
Communicates clearly and honestlyExpects that s/he has as much right as
anyone else in the team to be heard
Can say ‘no’
Respects and listens to others
Admits to errors without feeling s/he has
lost face
Knows s/he deserves respect
Gives the same rights to others as s/he
claims for her/ himself
12. Listening Responsively
Listening is part of assertive behaviour: ·Aggressive: always talks·
Assertive: listens and talks appropriately·
Passive: always listens
How can you use questions to check that you
have understood?
13. Team Maintenance
• Coming together is a beginning• Working together is progress
• Staying together is a triumph
14.
The process of training can be realized according to six closelyassociated basic components
Goal
The training purpose includes: increasing of problem coping
level; positive motivation forming; training and development of
adaptive behavior skills
Participants
Training methods confirming to maintenance of training
depend on a special group goal.
Maintenance
The maintenance of training also depends on a special group goal
Methods
In this context method of studies is the way of training goal
realization limited by the scopes terms through the work of
educational activity subjects (participants and teacher-trainer).
Scopes terms
During organization and holding of training different details are
important, because they can influence the efficiency of studies,
for example: condition of the class training takes place in,
availability of all necessary equipment for the training holding,
time when the training begins, its duration and etc.
Teacher-trainer
On the skills of teacher-trainer, his qualification the success of
training and subsequent activity of its participants depends
15. Collective Impact
16. Collective Impact is…
…positive and consistent progress at scale.17. Used for Many Complex Issues
Teen PregnancyHomelessness
Health
Community Safety
Education
Poverty
18. The Phases of Collective Impact
Phases of Collective ImpactThe Phases of Collective Impact
Components
for Success
Phase I
Generate Ideas
and Dialogue
Phase II
Initiate Action
Governance Convene community Identify champions
and form crossand
stakeholders
sector group
Infrastructure
Phase III
Organize for
Impact
Phase IV
Sustain Action
and Impact
Create
infrastructure
(backbone and
processes)
Facilitate and
refine
Strategic
Planning
Hold dialogue about
Map the landscape
Create common
issue, community
and use data to
agenda (common
context, and
make case
goals and strategy)
available resources
Support
implementation
(alignment to goal
and strategies)
Community
Involvement
Facilitate
community outreach
specific to goal
Determine if there is
Evaluation
consensus/urgency
And
Improvement to move forward
Facilitate
community
outreach
Engage community
and build public will
Continue
engagement and
conduct advocacy
Analyze baseline
data to ID key
issues and gaps
Establish shared
metrics (indicators,
measurement, and
approach)
Collect, track, and
report progress
(process to learn
and improve)
19. The Five Conditions of Collective Impact
CommonAgenda
Shared
Measurement
Mutually
Reinforcing
Activities
Continuous
Communication
Backbone
Support
All participants have a shared vision for change including a
common understanding of the problem and a joint approach to
solving it through agreed upon actions
Collecting data and measuring results consistently across all
participants ensures efforts remain aligned and participants hold
each other accountable
Participant activities must be differentiated while still being
coordinated through a mutually reinforcing plan of action
Consistent and open communication is needed across the many
players to build trust, assure mutual objectives, and appreciate
common motivation
Creating and managing collective impact requires a dedicated staff and
a specific set of skills to serve as the backbone for the entire
initiative and coordinate participating organizations and agencies
11
20.
2021.
Seminar Tasks1. The social construction of reality
2. Toward the problem of stages in the mental development of
children
3. Social Approaches to communication
4. Communicative Activity among Children with Disabilities
5. Ethics in Sociocultural Theory
6. The cultural development of the child
7. The child`s intiative in buildning up cooperation: the key to
problems of children`s independence
8. The Inheritance and Development of Social Constructionism
9. Methods of individual approach
10. Work training, relations, style, tone



















 english
english








