Similar presentations:
Practical pharmacology. Part 1
1.
Practical pharmacologyPart 1
2.
What is pharmacology?pharma ology
It is science of the drugs
Drug
Science
3.
What is Drug?It is the chemical that affect
physiological body function
through interaction with
receptors
4.
What is Drug?It is the chemical that affect
physiological body function
through interaction with
receptors
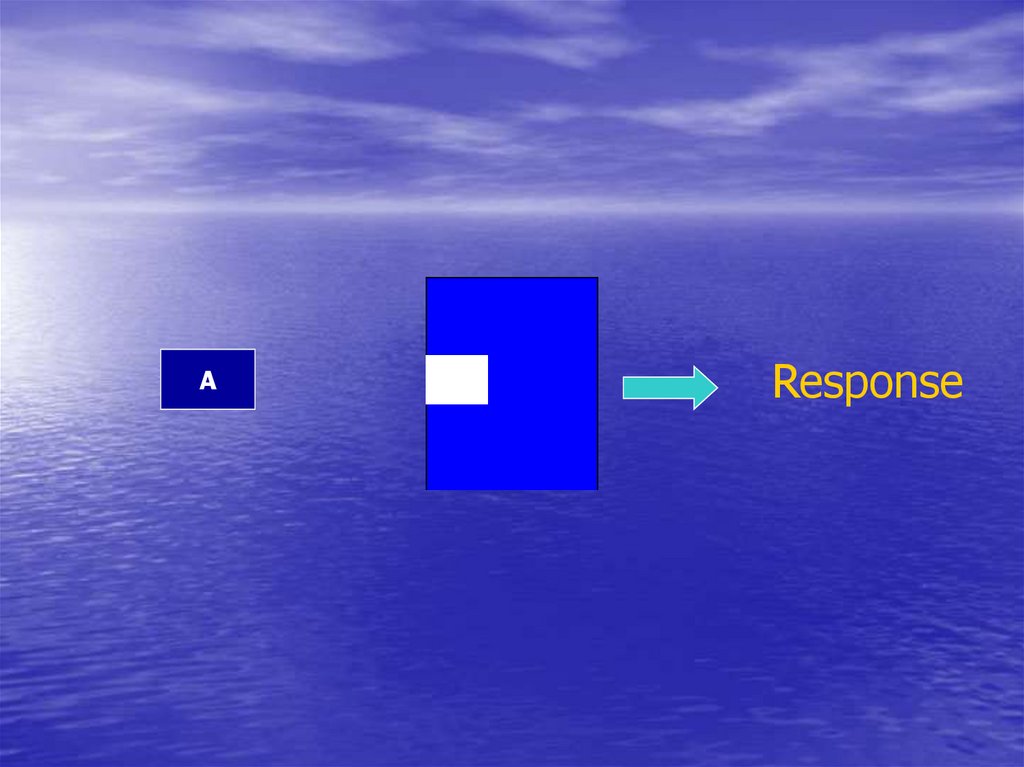
5.
AResponse
6. Forces involved in D-R interaction
Covalent bondsIonic bonds
Hydrogen bonds
Vander waals bonds
7. Forces involved in D-R interaction
Covalent bondsIonic bonds
Hydrogen bonds
Vander waals bonds
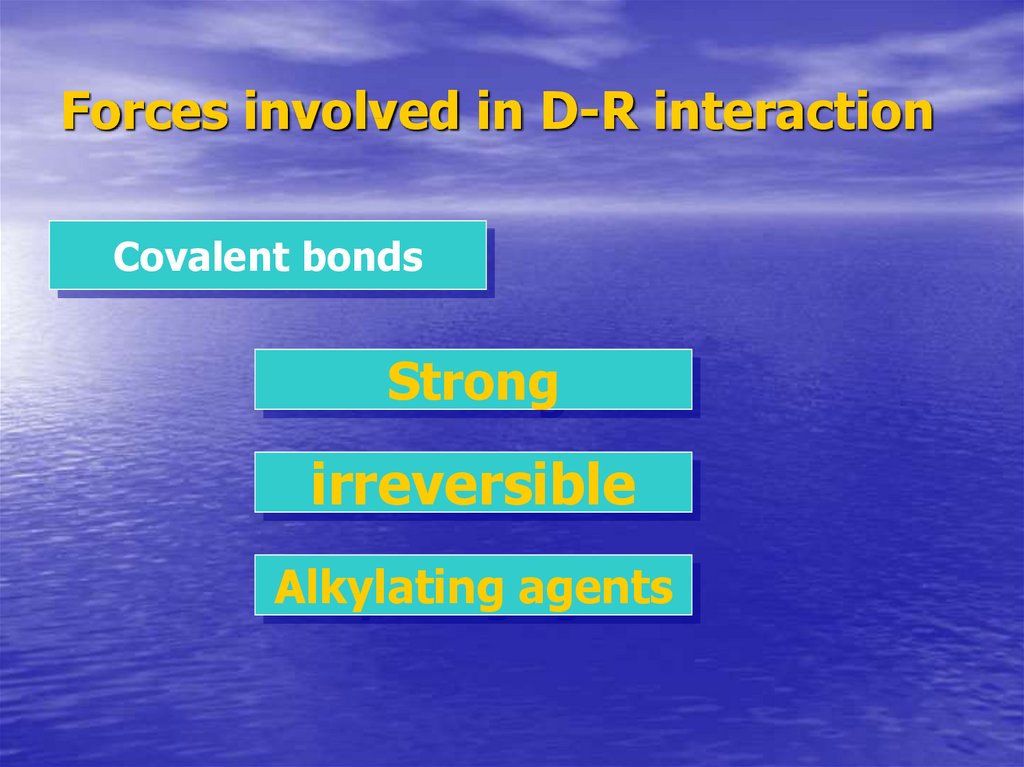
8. Forces involved in D-R interaction
Covalent bondsStrong
irreversible
Alkylating agents
9. Forces involved in D-R interaction
Covalent bondsIonic bonds
Hydrogen bonds
Vander waals bonds
10. Forces involved in D-R interaction
Ionic bondscommon
Affected by pH
11. Forces involved in D-R interaction
Covalent bondsIonic bonds
Hydrogen bonds
Vander waals bonds
12. Forces involved in D-R interaction
Hydrogen bonds?
13. Forces involved in D-R interaction
Covalent bondsIonic bonds
Hydrogen bonds
Vander waals bonds
14. Forces involved in D-R interaction
Vander waals bonds?
15. Receptors types
On cell membraneIntracellular
GPCR
Receptor with intrinsic ion channel
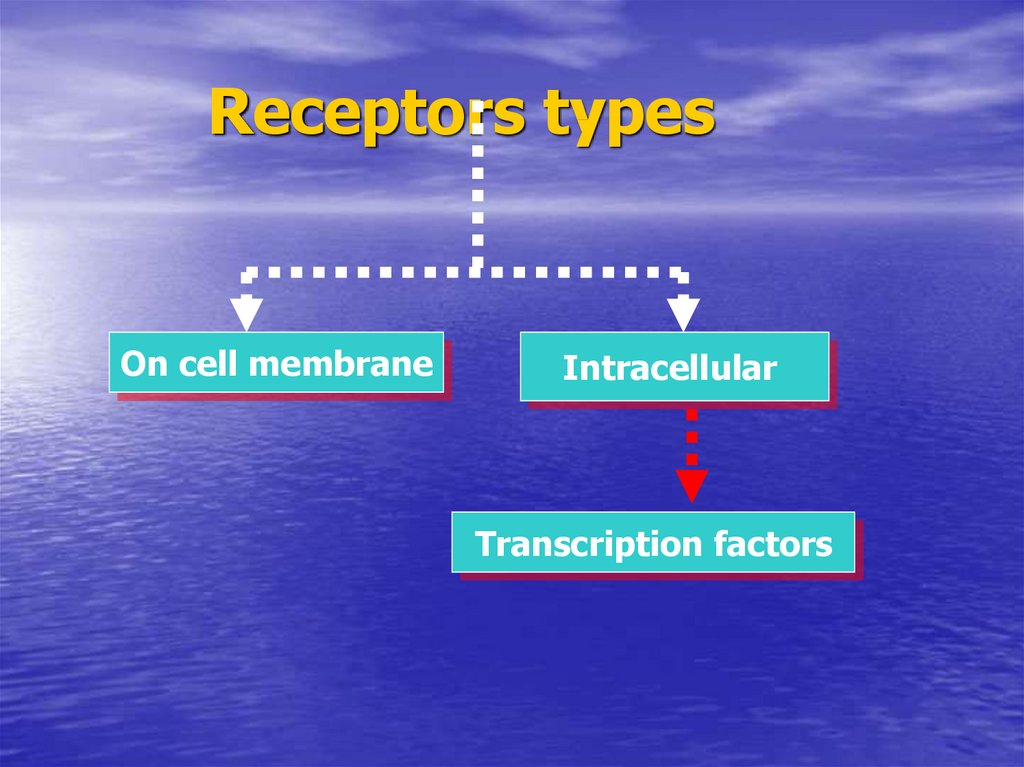
Enzyme linked receptors
16. Receptors types
On cell membraneIntracellular
Transcription factors
17.
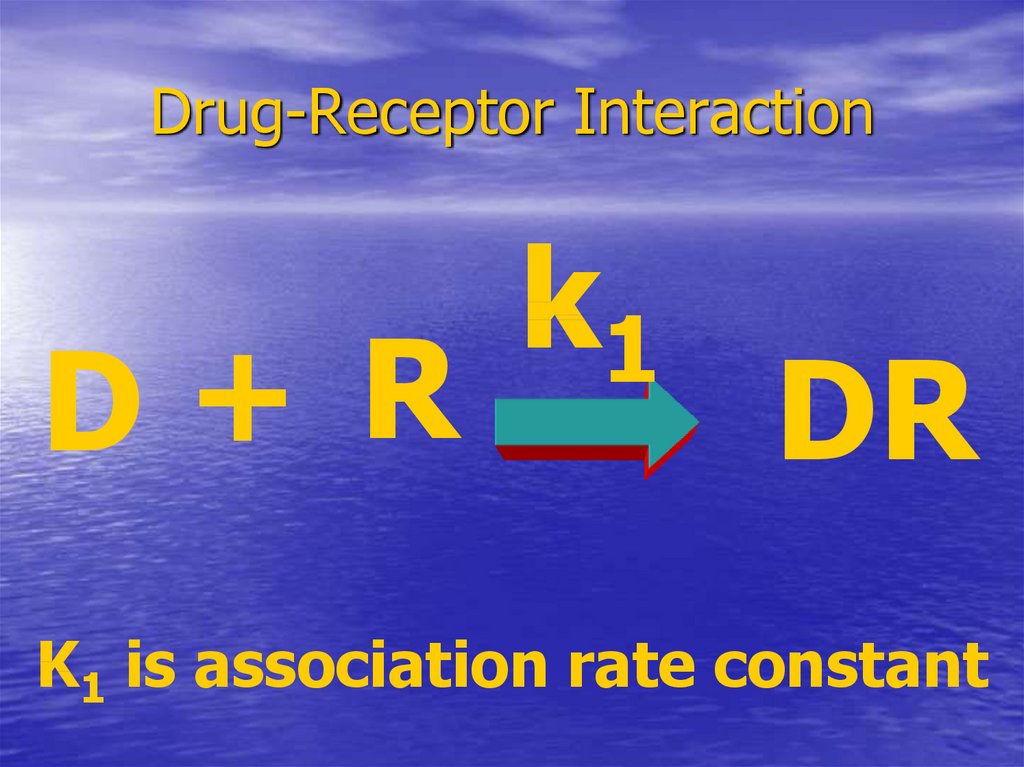
18. Drug-Receptor Interaction
D+ Rk1
DR
K1 is association rate constant
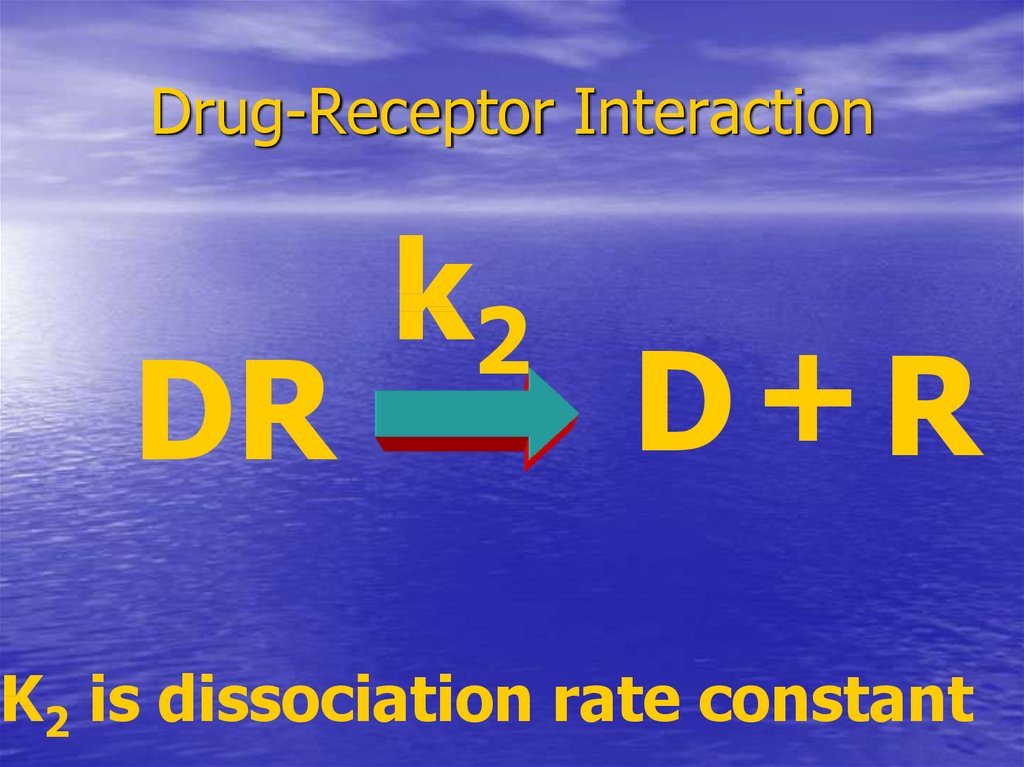
19. Drug-Receptor Interaction
DRk2
D+R
K2 is dissociation rate constant
20. Drug-Receptor Interaction
At equilibriumD+ R
k1
k2
DR
21. Drug-Receptor Interaction
At equilibrium[D] [R] k1
= [DR]
k2
22. Drug-Receptor Interaction
At equilibrium[D] [R] k1
= [DR]
k2
23. Drug-Receptor Interaction
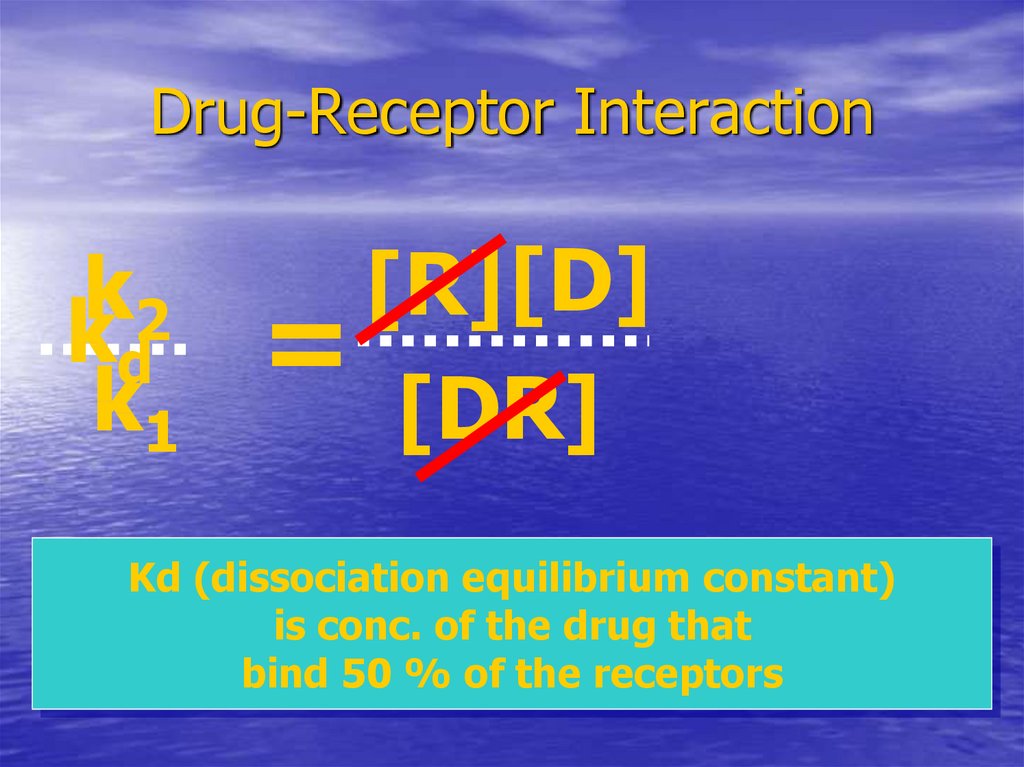
k2
kd
k1
[R] [D]
=
[DR]
Kd (dissociation equilibrium constant)
is conc. of the drug that
bind 50 % of the receptors
24. kd
• It is a measure of drug affinity• Its units is conc. units
Drug A
Has higher Kd than
Drug B
Which one has a higher affinity ?
25. Important concepts
• Affinity• Efficacy
• potency
26. Affinity
• The ability of the drug to bind to thereceptor
• Measured by Kd
• Both agonist and antagonist have
affinity to their receptors
27. Efficacy
• It is the ability of the drugs to elicitpharmacological effect
• Measured by Emax
• Agonist has efficacy and antagonist has no
efficacy
28. potency
• The ability of the drug to produceresponse at lower conc.
• Measured by ED50
29. The drug may be
• Agonist• Antagonist
• Partial agonist
30. Agonist
• Has affinity and efficacy• IA=1
31. Antagonist
• Has affinity but no efficacy• IA=0
32. Partial agonist
• Has affinity and efficacy• IA=0-1
33. antagonism
• Physical• Chemical
• Physiological
• Pharmacokinetic
• pharmacodynamic
34. Chemical antagonism
• One drug reacts chemically with an activedrug to form an inactive compound,
It involves precipitation, complexation,
neutralization redox reaction.
Intended treatment of heavy metal
toxicity by complexation with chelators.
Incidental complexatin of tetracycline
calcium in dairy products.
35. Physiological antagonism
• 2 drugs act on different sites in the sameor different system.
• a- Intended Norepinephrine in case of
anaphylaxis.
b-Incidental patient taking barbiturates
for anxiety, co-administration of antitussive (ephedrine).
36. Pharmacokinetic antagonism (ADME)
• a- Intended forced alkaline diuresis inmanagement of barb Poisoning.
• b- Incidental Barb. + other drugs
Induction of the metabolism of concomitant
drugs, their decrease plasma level.
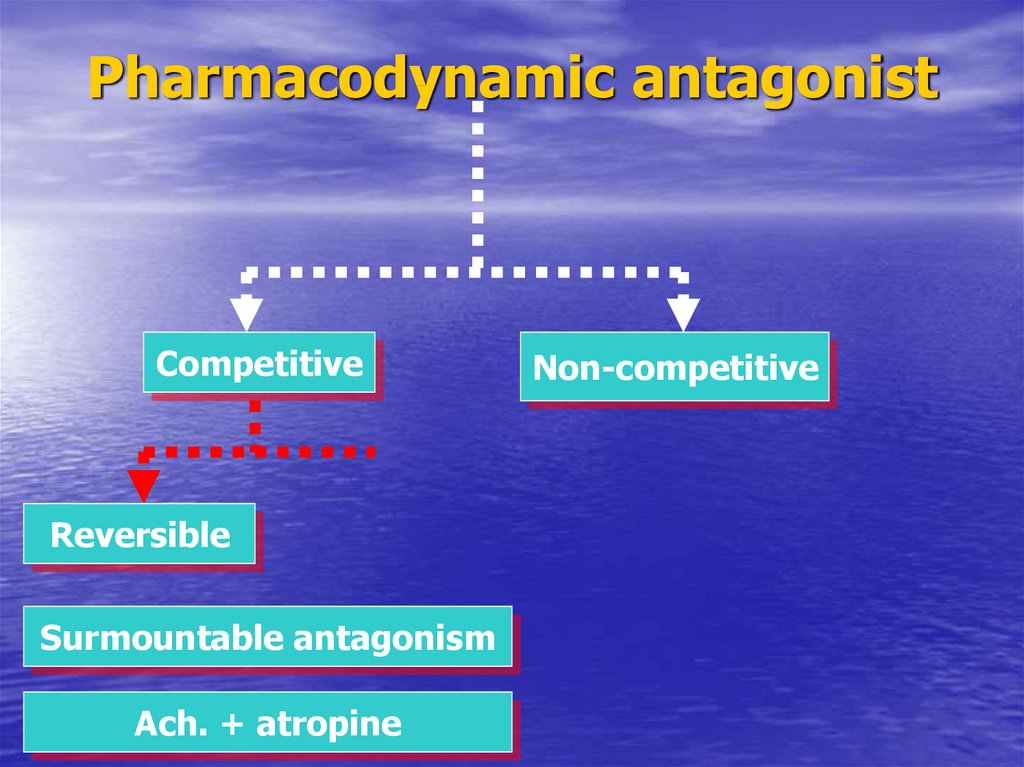
37. Pharmacodynamic antagonist
CompetitiveReversible
Surmountable antagonism
Ach. + atropine
Non-competitive
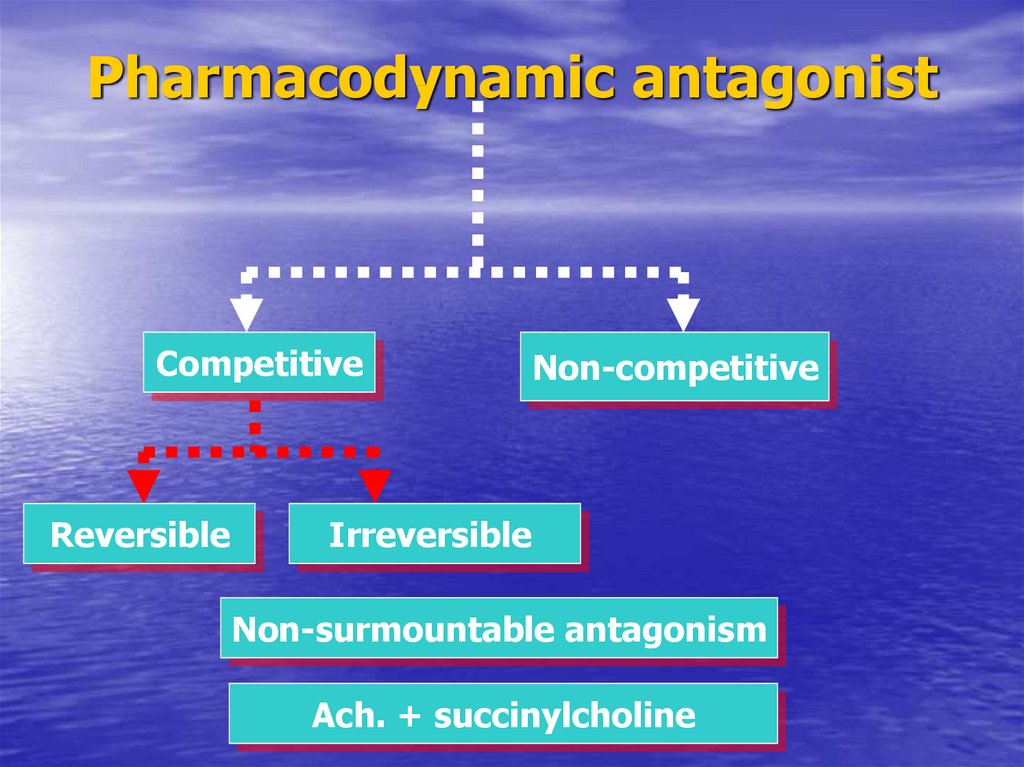
38. Pharmacodynamic antagonist
CompetitiveReversible
Non-competitive
Irreversible
Non-surmountable antagonism
Ach. + succinylcholine
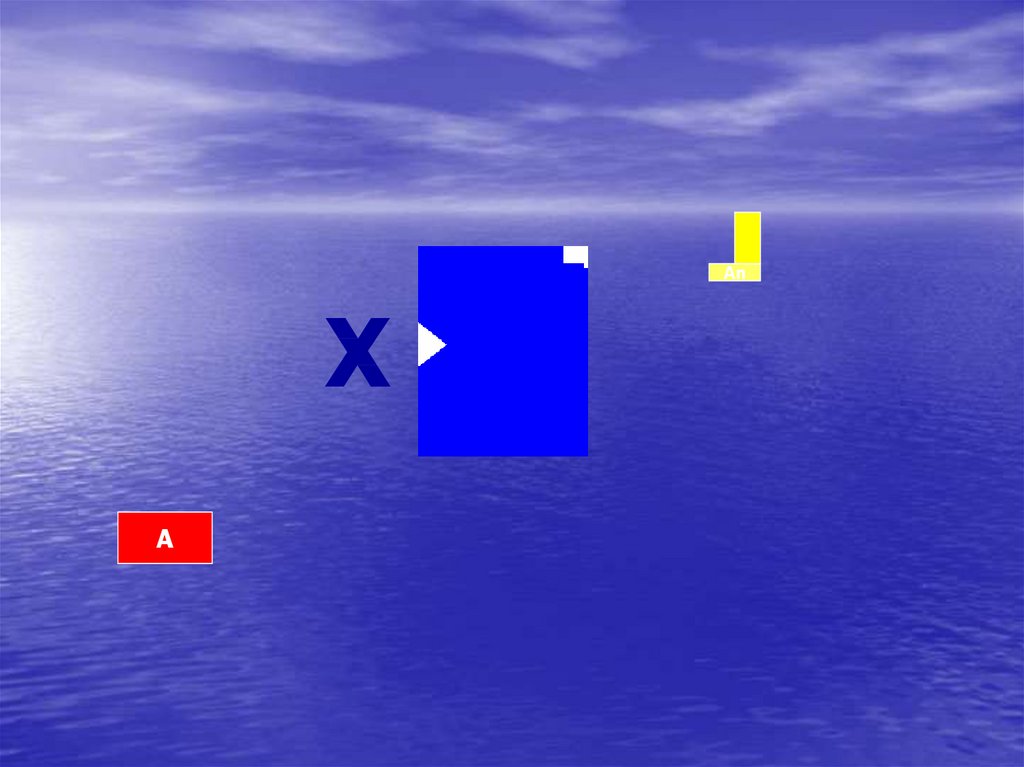
39.
XAn
A
40.
AnX
A
41. Dose-Response Curve
• What ?• Types ?
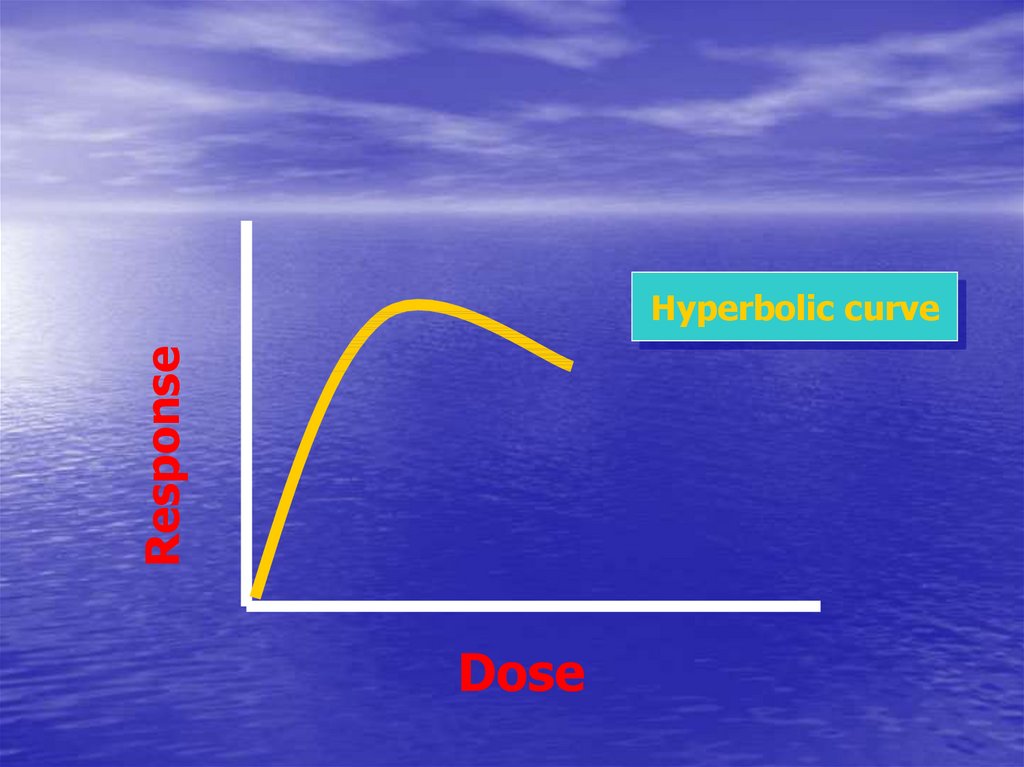
42.
ResponseHyperbolic curve
Dose
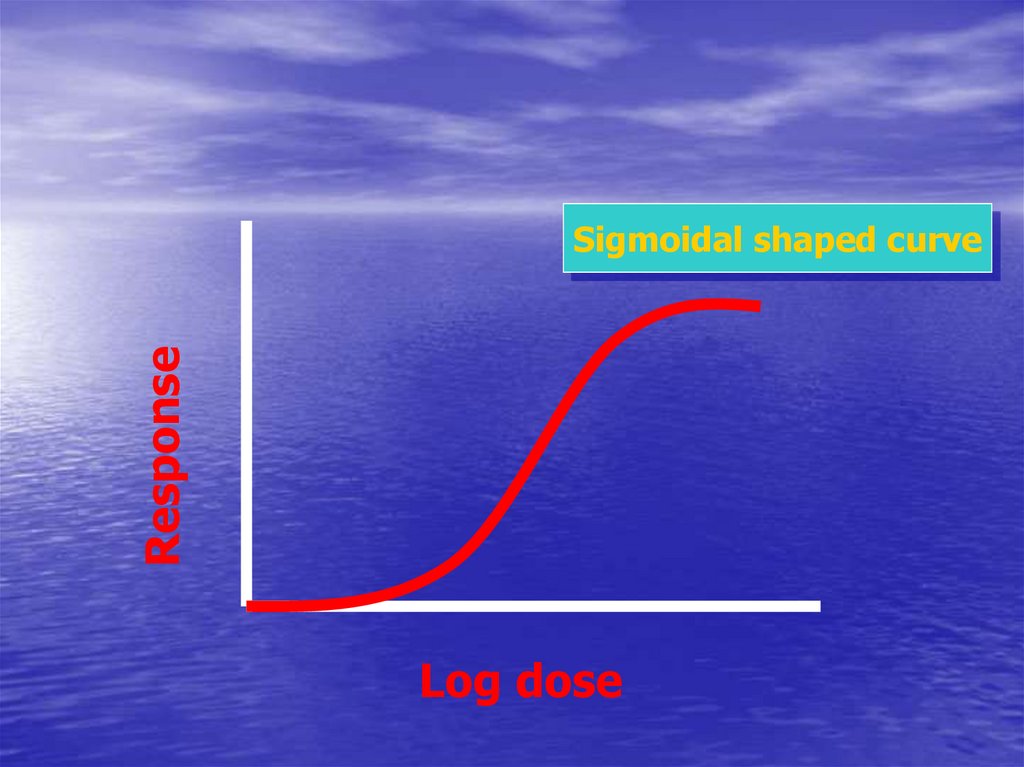
43.
ResponseSigmoidal shaped curve
Log dose
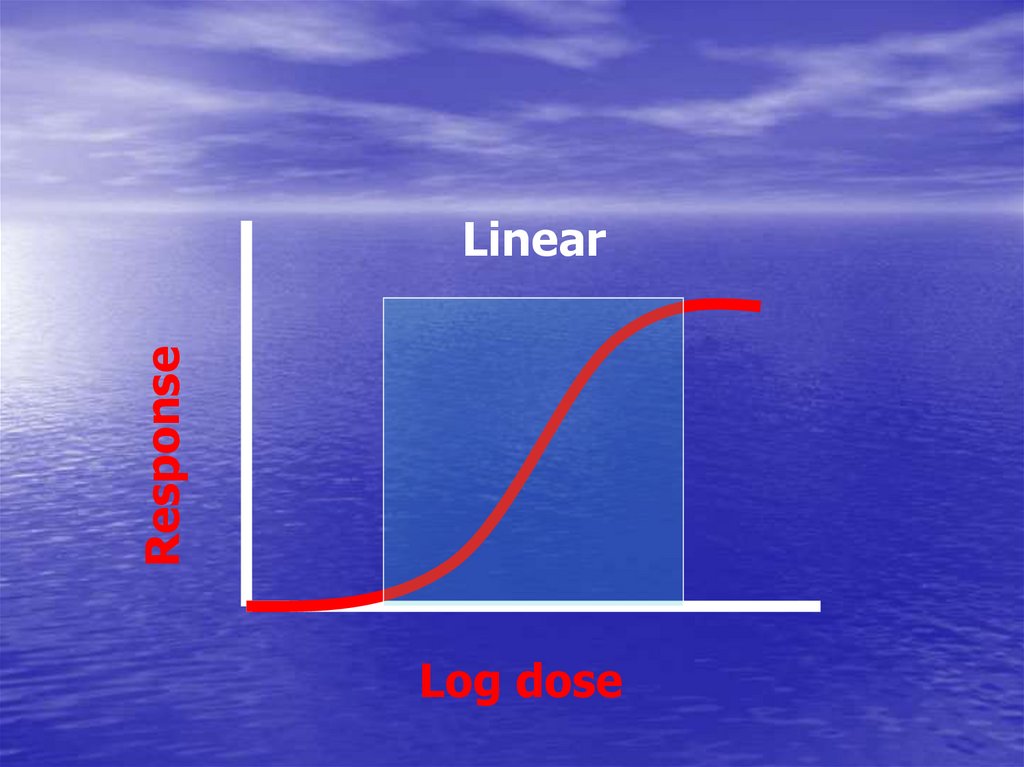
44.
ResponseLinear
Log dose
45.
ResponseWide range of doses
Log dose
46.
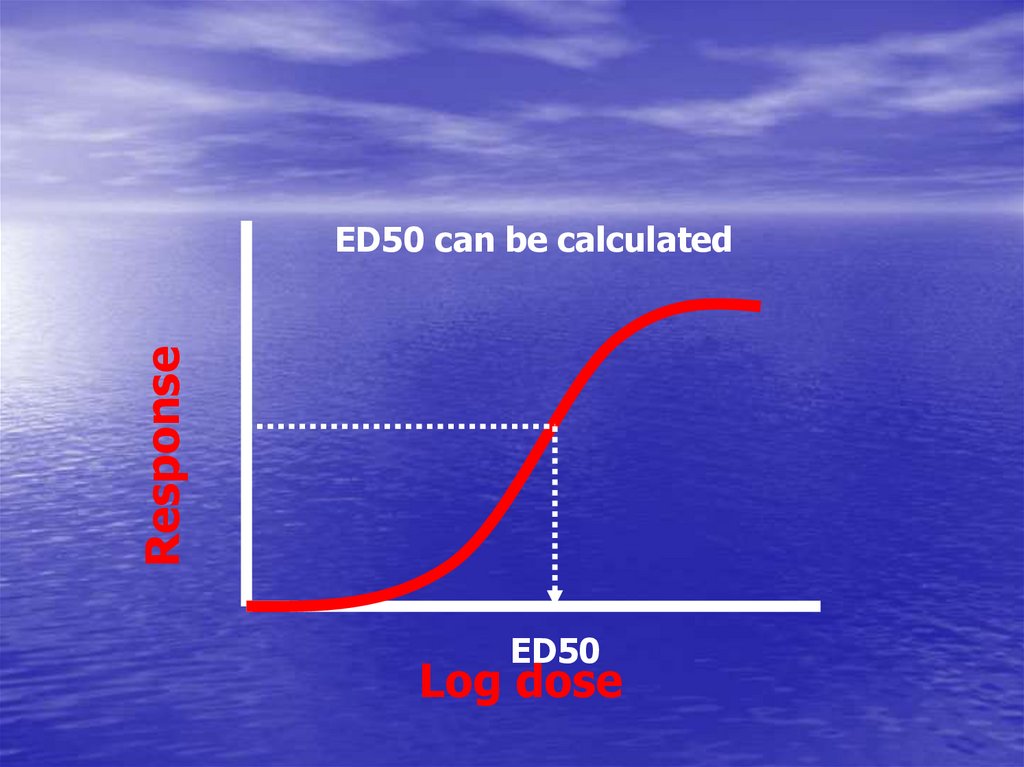
ResponseED50 can be calculated
ED50
Log dose
47. Graded DRC
• Depends on graded response• ED50 ?
The dose that give 50% of maximal response
48.
Response50%
ED50
Log dose
49. Quantal DRC
• Depends on quantal response• ED50 ?
The dose that give response in 50% of population
50.
%Response50%
ED50
Log dose
51. ED50
• Compare between potencies of twodrugs
Drug A
Has higher ED50 than
Drug B
Which one is more potent ?
52. ED50
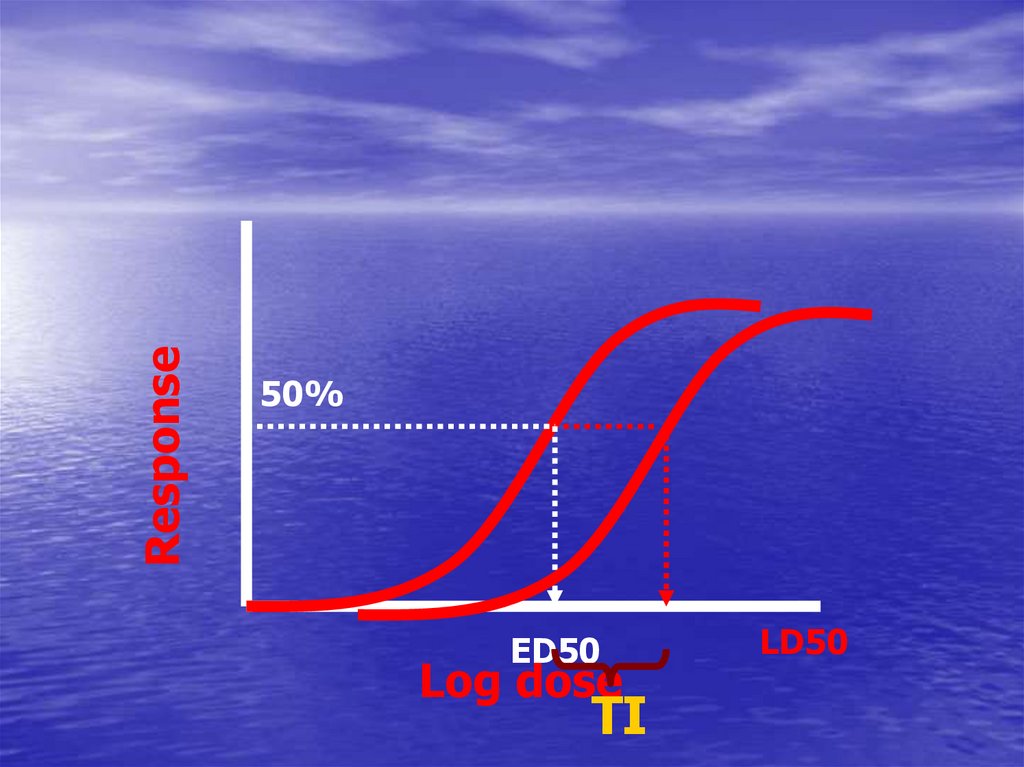
• Calculation of the therapeutic indexLD50
TI
=
ED50
Is a measure of drug safety
53.
Response50%
LD50
ED50
Log dose
TI
54.
Response50%
ED50
Log dose
TI
LD50
55.
Drug AHas higher TI than
Drug B
Which one is more safer ?
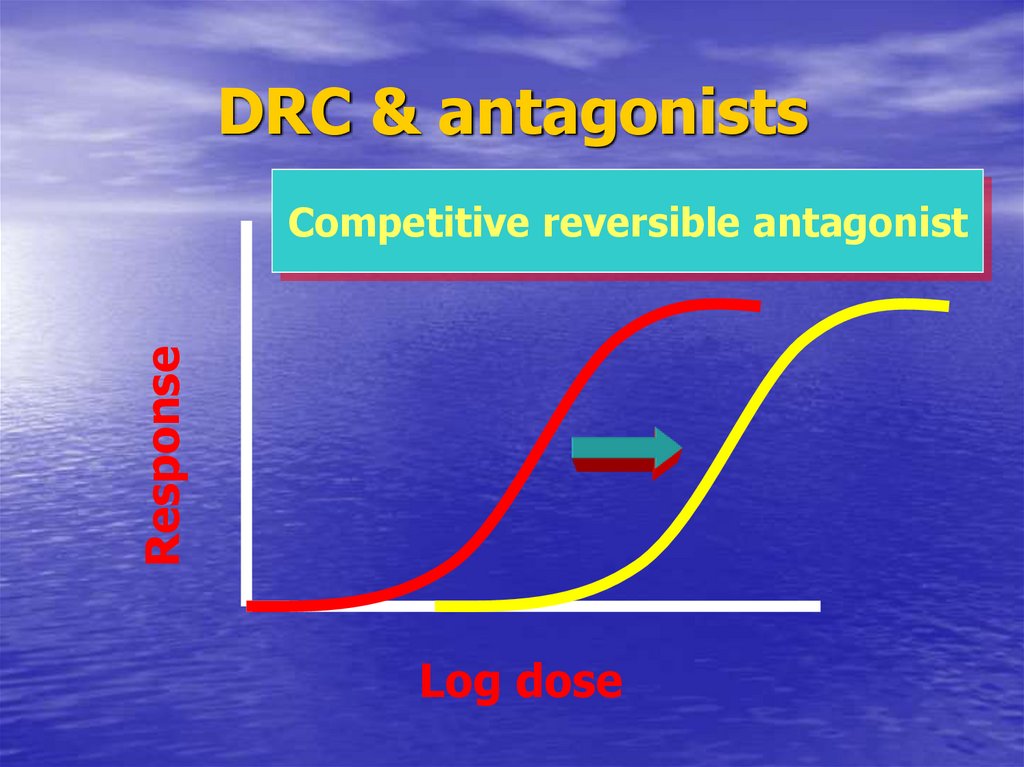
56. DRC & antagonists
DRC & antagonistsResponse
Competitive reversible antagonist
Log dose
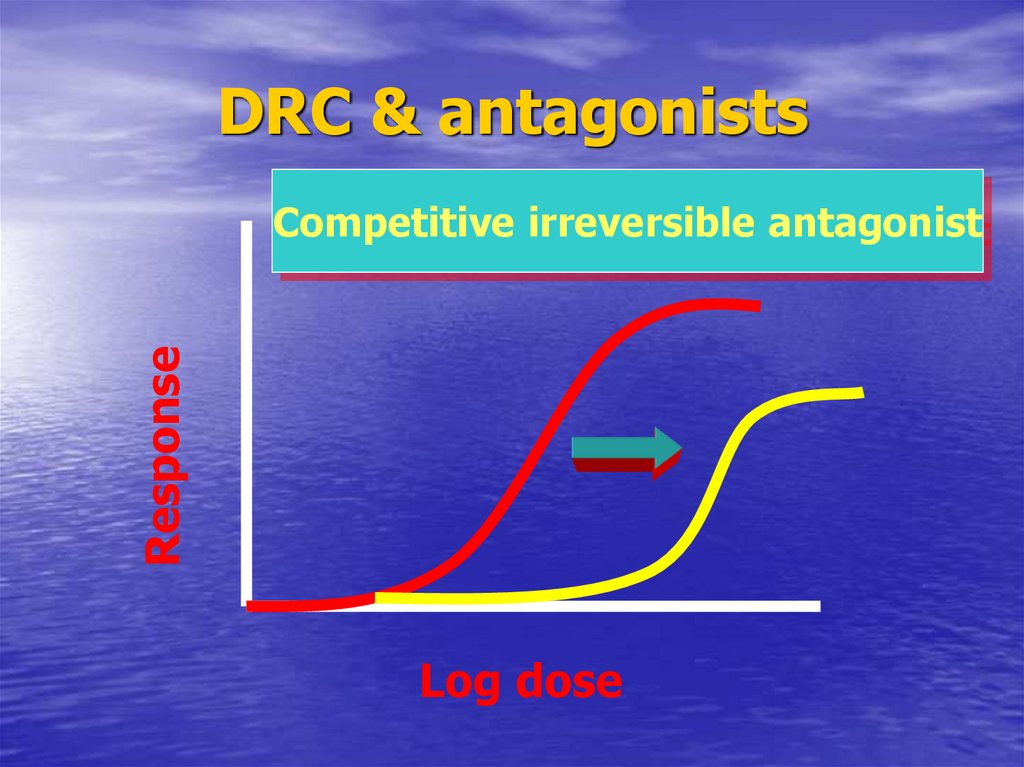
57. DRC & antagonists
DRC & antagonistsResponse
Competitive irreversible antagonist
Log dose
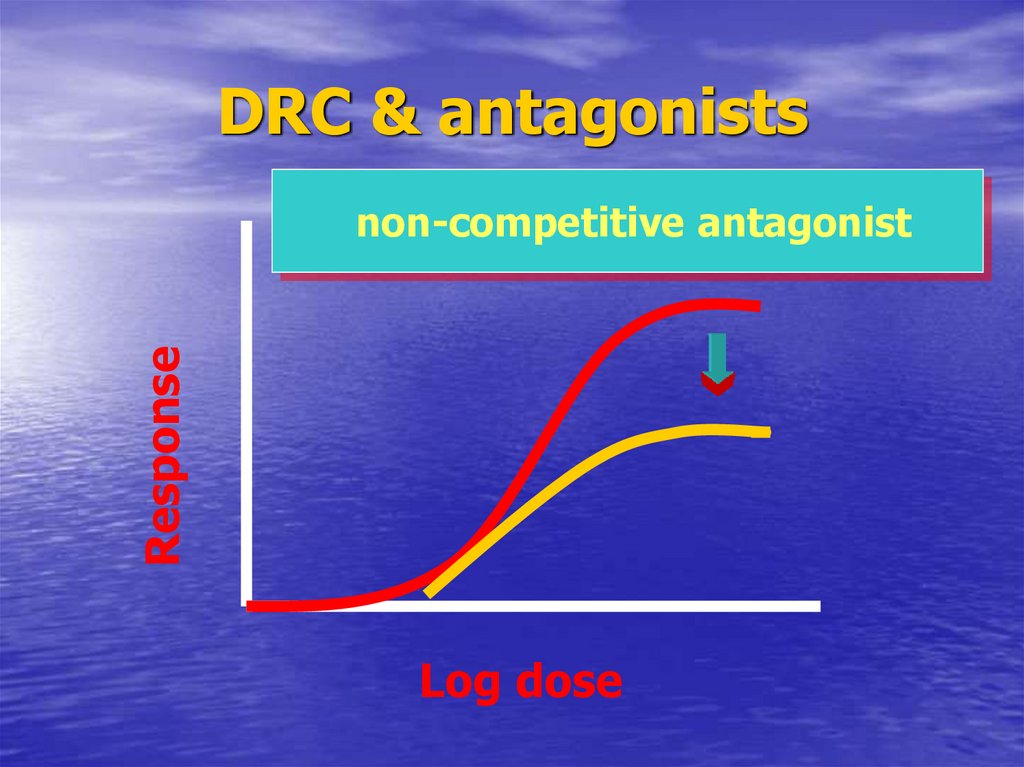
58. DRC & antagonists
DRC & antagonistsResponse
non-competitive antagonist
Log dose
59. Important notes
ParrallismIndicate competition
60. Important notes
EmaxIndicate reversibility












































 english
english








