Similar presentations:
Bronchitis
1.
Theme:BronchitisFaculty:GM
Group: 16-003
Done by: Аdylzhanova D.
Cheked by:Sagantaeva S.H.
2. Plan:
Bronchitis1 Classification
2 Acute bronchitis
2.1 Etiology (causes of)
2.2 Pathogenesis
2.3 The course of the disease and prognosis
2.4 Treatment
3 Chronic bronchitis
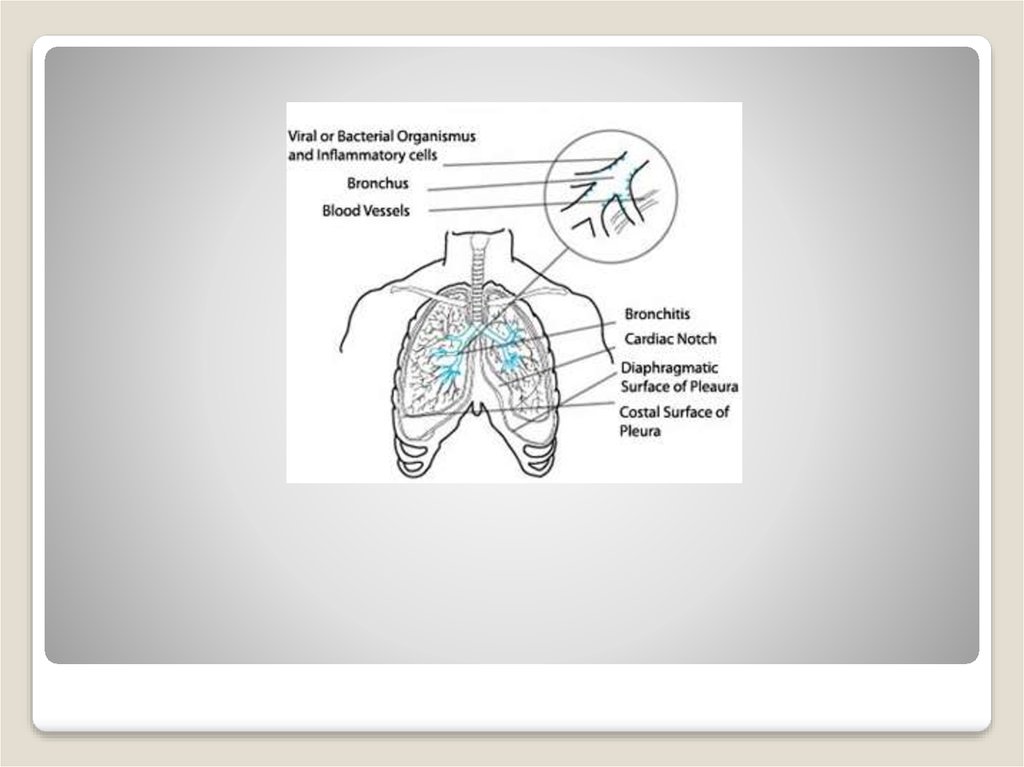
3. Bronchitis
(lat. Bronchitis, bronchus by + -itis - inflammation) a disease of the respiratory system in which the inflammatoryprocess involved in the bronchi. It is one of the most frequent
reasons for seeking medical care.In the majority of cases of
acute bronchitis its cause is an infection, such as viral or
bacterial, and require treatment with antibiotics or antiviral
drugs. Chronic bronchitis may develop as a complication of
acute or as a result of long-acting non-infectious irritants, such
as dust. In some cases, bronchitis developing bronchial
obstruction due to swelling of the mucous membrane, such is
called obstructive bronchitis. Treatment of bronchitis depends
on a provoking factor, such as the flow and form of the disease.
Bronchitis
4.
5. Classification
"International Classification of Diseases" includes two forms ofbronchitis:
Acute bronchitis - acute diffuse inflammation of the mucosa of
the tracheobronchial tree, characterized by an increase in the
volume of bronchial secretion with cough and sputum.
Chronic bronchitis - diffuse progressive damage of the bronchial
tree to the restructuring of the secretory apparatus of the mucous
membrane with the development of the inflammatory process,
accompanied by hypersecretion of mucus, a violation of the
cleaning and protective function of the bronchi.
Acute and chronic bronchitis differ significantly from each other
in the etiology, pathogenesis and therapeutics.
Classification
6. Acute bronchitis
Etiology (causes of) In most cases, the cause of acutebronchitis are viruses (influenza, parainfluenza, adenovirus,
rhinoviruses, and others.) And bacteria (pneumococci,
Haemophilus influenzae, Streptococcus, and others.). Less
common causes as bronchitis protrude fungi, contact with
allergens or inhalation of toxic substances. The most
common route of infection - airborne, ie inhalation of
infected droplets of saliva in contact with the ailing man
(while talking, coughing, sneezing, kissing).
7. Risk Factors
SmokingAsthma
Genetic
Social class (Independent ? Of
other factors)
Pollution
Occupational dust exposure
Recurrent infection
8.
9.
PathogenesisViruses or chemical, physical impact damage epithelial cells of the
bronchial mucosa and cause their death, which creates favorable
conditions for the penetration of the tissue of the bronchi of the
bacterial flora (most pneumococcus and gemmofilnoy sticks). The
bacterial flora is usually attached to the viral infection of the
respiratory tract with 2-3 days of illness. This determines the further
course of the inflammation has arisen, which is aggravated violation of
microcirculation, trophic and nervous mikrotrombozov. Usually, the
inflammation disappears and mucosal lesions of the respiratory tract is
restored within a few weeks. In some patients the disease process does
not regress and becomes chronic. In mild cases, the morphological
changes limited to the mucosa, heavy - captured all the layers of the
bronchial wall. The mucosa appears edematous, hyperemic, with the
presence of mucous, mucopurulent or purulent exudate on the surface.
In severe hemorrhage is often seen in the mucous membrane, exudate
may acquire a hemorrhagic character. In some cases there is complete
obstruction of the lumen secret small bronchi and bronchioles.
10.
The disease and the prognosisAcute bronchitis usually lasts about 10 days. Like other respiratory
diseases, bronchitis can accompany a cold or flu, or arise as a result,
but may start by itself, without apparent prior occasion. The disease
usually begins with a dry cough, which may be strong, especially at
night, and may thus deprive suffering from the disease of normal sleep
and rest. After a few days of dry cough turns into productive cough
that may be accompanied by a slight fever, fatigue, headaches. Fever,
malaise, fatigue and apathy of the state can take just a few days, but
the cough can last for several weeks. In some people, the cough can
last several months, as the healing of the inflammation of the bronchial
passages - a slow process.
If the cough lasts for more than a month, it is necessary to consult a
specialist, pulmonologist and find out whether there have respiratory
irritation and coughing any other reason, apart from inflammation. In
some patients, prolonged bronchitis for several months irritation of the
bronchial passages can lead to asthma.
Be sure to consult a doctor if the patient is coughing up phlegm with
blood, to prevent serious diseases such as tuberculosis or lung cancer.
11.
TreatmentIn most cases, acute bronchitis is caused by a virus and not a bacterial infection, and
acute stage usually takes place without the use of antibiotics by itself within a week.
Antibiotics can be used to treat bronchitis, having a bacterial origin, and sometimes as an
aid in cases of suspected possible complications or comorbidities.
Recently uncomplicated acute bronchitis is considered as a more inflammatory and not
infectious process, and therefore the anti-inflammatory therapy is more justified than
antimicrobial. However, in a randomized, placebo-controlled study conducted in Spain, it
was shown slight differences in the efficiency of anti-inflammatory treatment (ibuprofen
600 mg every 8 hours for 10 days) compared to placebo and antibiotic (amoxicillin +
clavulanic acid 500 / 125 mg every 8 hours for 10 days).
There are effective non-pharmacological methods of treatment of cough, including acute
bronchitis, which is useful to apply as in the presence of a prescribed drug treatment, and
in his absence.
The patient needs a lot of rest and drink a lot. Requires sufficient number of noncaffeinated beverages, such as water or juice or herbal tea (2 - 4 liters of fluid per day).
[8] In a cold climate to treat cough traditionally recommended warm drink tea with
raspberry, honey, lime color; warmed alkaline mineral water.
Since inflammation of the bronchial passages, usually accompanied by inflammation of
the throat and, during bronchitis recommended soft, unsharp, without causing irritation of
the throat food.
12.
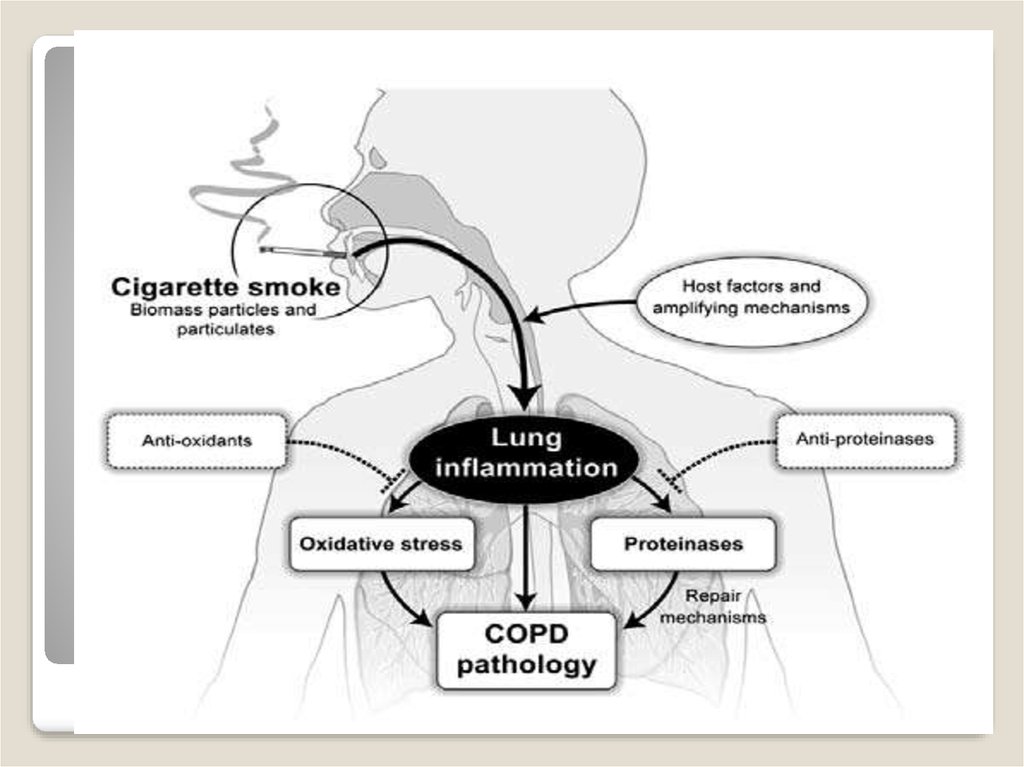
Chronic bronchitisBronchitis is considered chronic if the cough with
sputum lasts at least three months a year for two years
or more. Chronic bronchitis (CB) is the most common
chronic non-specific diseases of the respiratory system.










 medicine
medicine








