Similar presentations:
Modelling and simulation
1. MODELLING and SIMULATION
Oxana Zamyatina, Associate Professor,Control System Optimization Department,
Tomsk Polytechnic University
zamyatina@tpu.ru
Замятина О.М.
1
2. Course structure
Lectures 36 hoursLabs 36 hours
Exam
Замятина О.М.
2
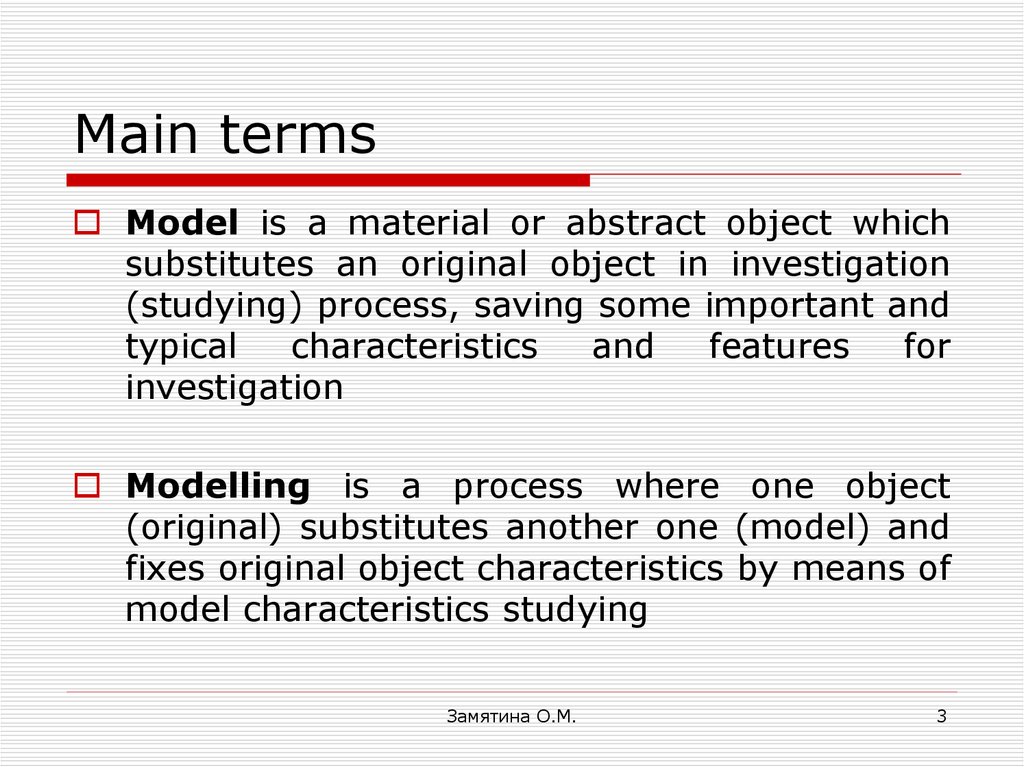
3. Main terms
Model is a material or abstract object whichsubstitutes an original object in investigation
(studying) process, saving some important and
typical
characteristics
and
features
for
investigation
Modelling is a process where one object
(original) substitutes another one (model) and
fixes original object characteristics by means of
model characteristics studying
Замятина О.М.
3
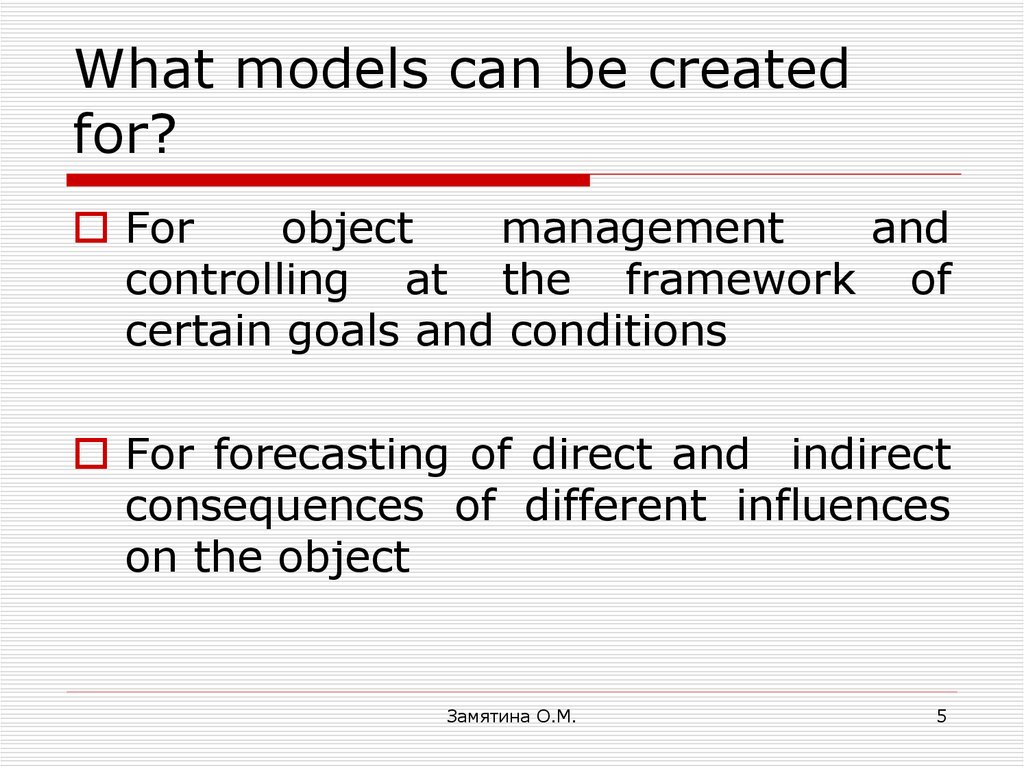
4. What models can be created for?
For understanding:1. What is the object structure?
2. What are main object properties and
characteristics?
3. What are object evolution laws and
object interaction with environment?
Замятина О.М.
4
5. What models can be created for?
Forobject
management
and
controlling at the framework of
certain goals and conditions
For forecasting of direct and indirect
consequences of different influences
on the object
Замятина О.М.
5
6. The model allows to
manage the original object by meansof changing and approving different
control methods over the model;
avoid and decrease financial costs;
carry out experiments with the model
in case when a real object is
unavailable.
Замятина О.М.
6
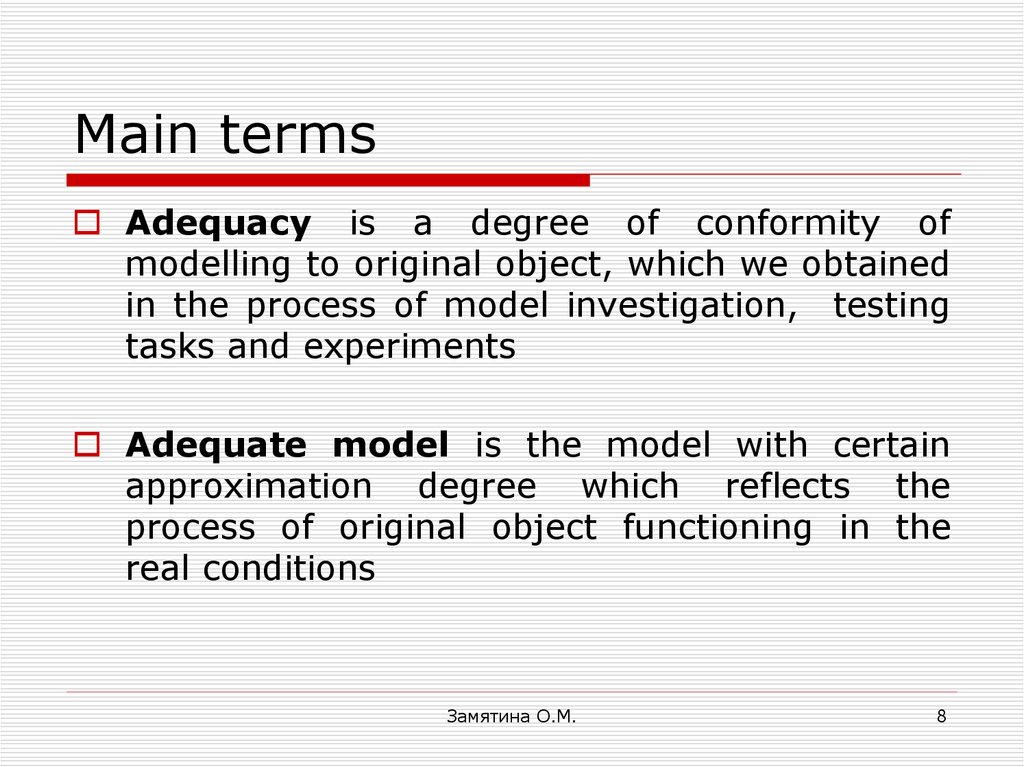
7. Main terms
System boundaryHierarchy level
Alternative solutions
Замятина О.М.
7
8. Main terms
Adequacy is a degree of conformity ofmodelling to original object, which we obtained
in the process of model investigation, testing
tasks and experiments
Adequate model is the model with certain
approximation degree which reflects the
process of original object functioning in the
real conditions
Замятина О.М.
8
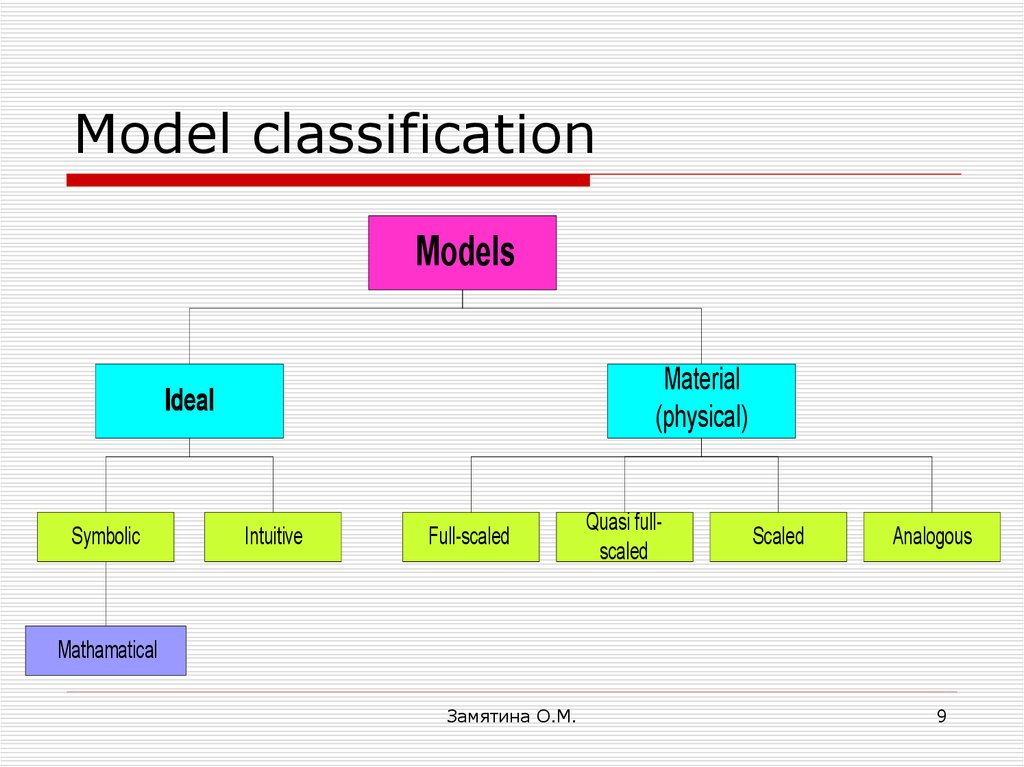
9. Model classification
ModelsMaterial
(physical)
Ideal
Symbolic
Intuitive
Full-scaled
Quasi fullscaled
Scaled
Analogous
Mathamatical
Замятина О.М.
9
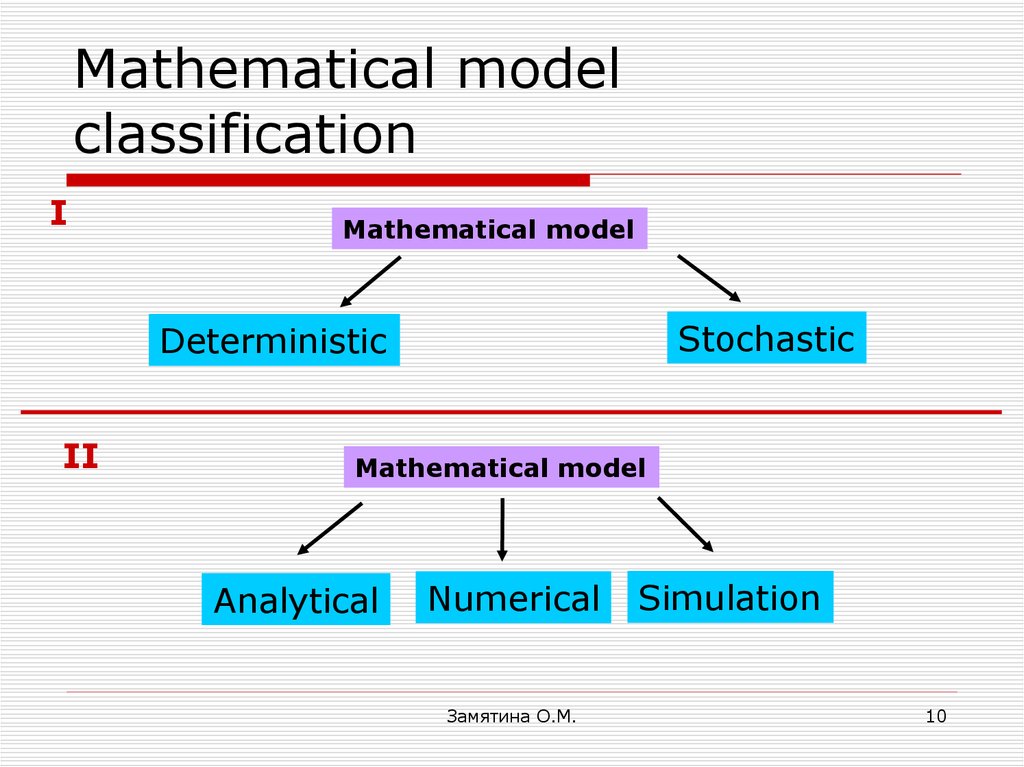
10. Mathematical model classification
IMathematical model
Stochastic
Deterministic
II
Mathematical model
Analytical
Numerical
Замятина О.М.
Simulation
10
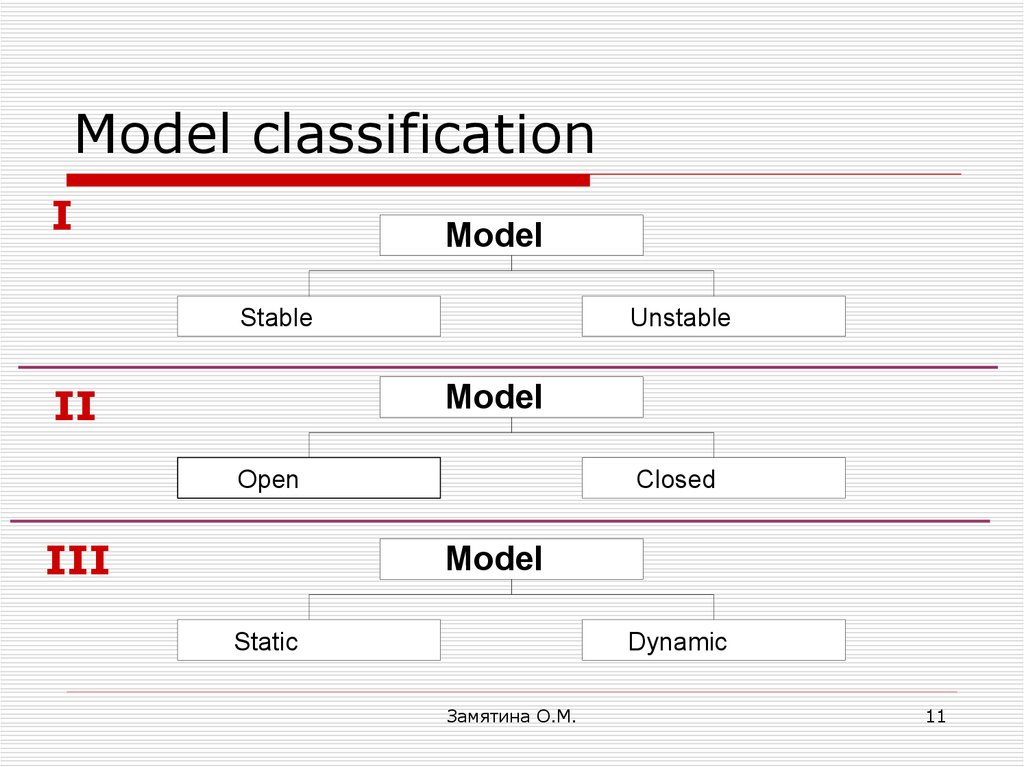
11. Model classification
IModel
Stable
II
Unstable
Model
Open
III
Closed
Model
Static
Dynamic
Замятина О.М.
11
12. Stages of complex model development
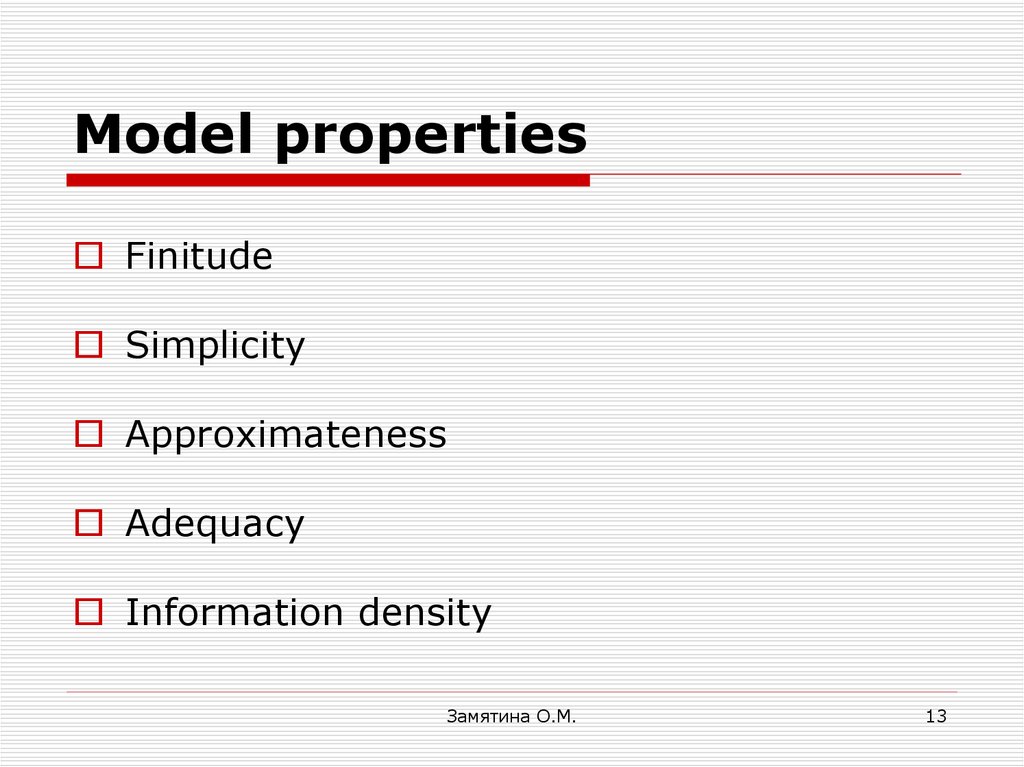
13. Model properties
FinitudeSimplicity
Approximateness
Adequacy
Information density
Замятина О.М.
13
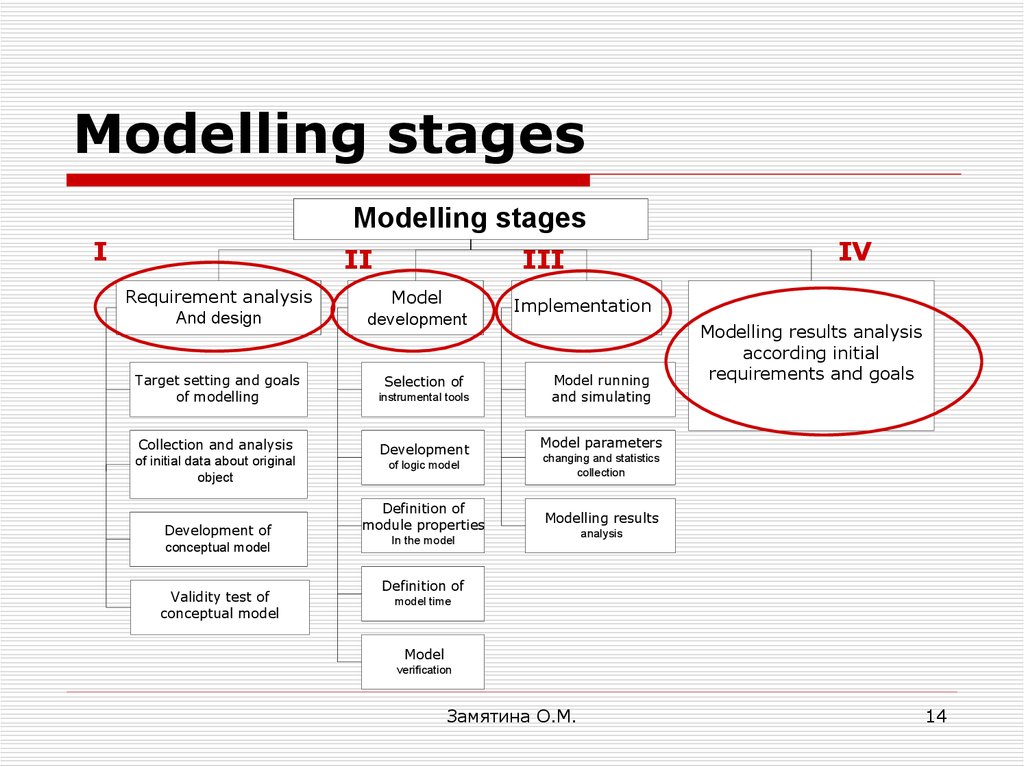
14. Modelling stages
Modelling stagesI
II
Requirement analysis
And design
Target setting and goals
of modelling
Collection and analysis
of initial data about original
object
Development of
conceptual model
Validity test of
conceptual model
IV
III
Model
development
Selection of
instrumental tools
Development
Implementation
Model running
and simulating
Modelling results analysis
according initial
requirements and goals
Model parameters
of logic model
changing and statistics
collection
Definition of
module properties
Modelling results
In the model
analysis
Definition of
model time
Model
verification
Замятина О.М.
14
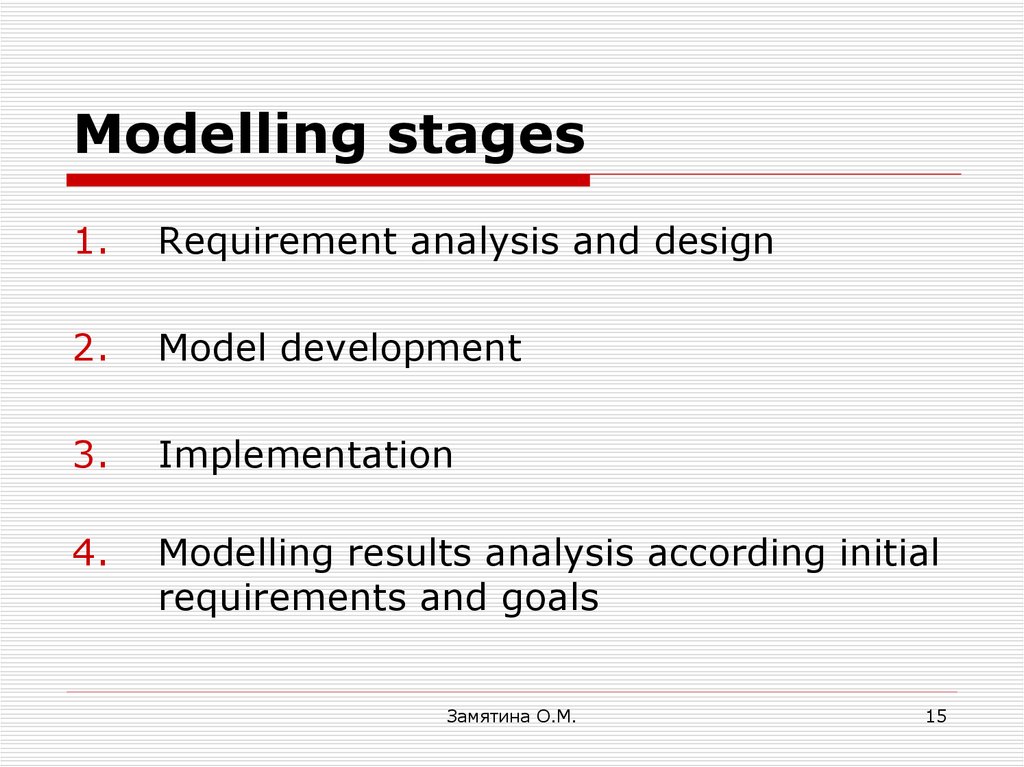
15. Modelling stages
1.Requirement analysis and design
2.
Model development
3.
Implementation
4.
Modelling results analysis according initial
requirements and goals
Замятина О.М.
15
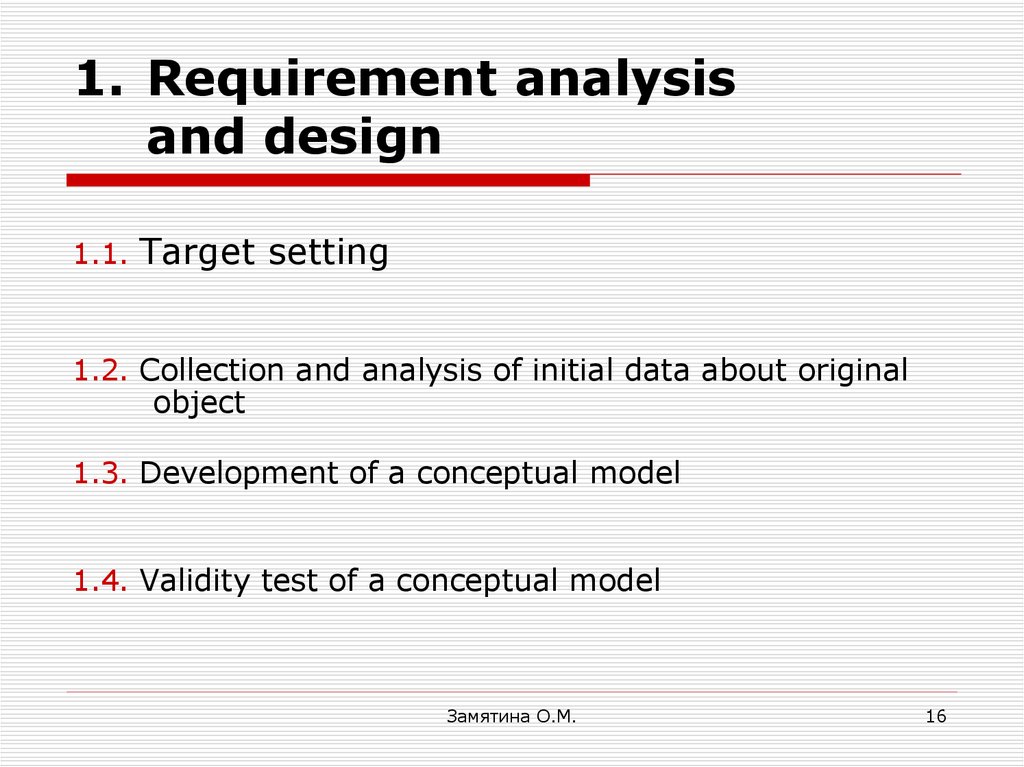
16. Requirement analysis and design
1. Requirement analysisand design
1.1.
Target setting
1.2. Collection and analysis of initial data about original
object
1.3. Development of a conceptual model
1.4. Validity test of a conceptual model
Замятина О.М.
16
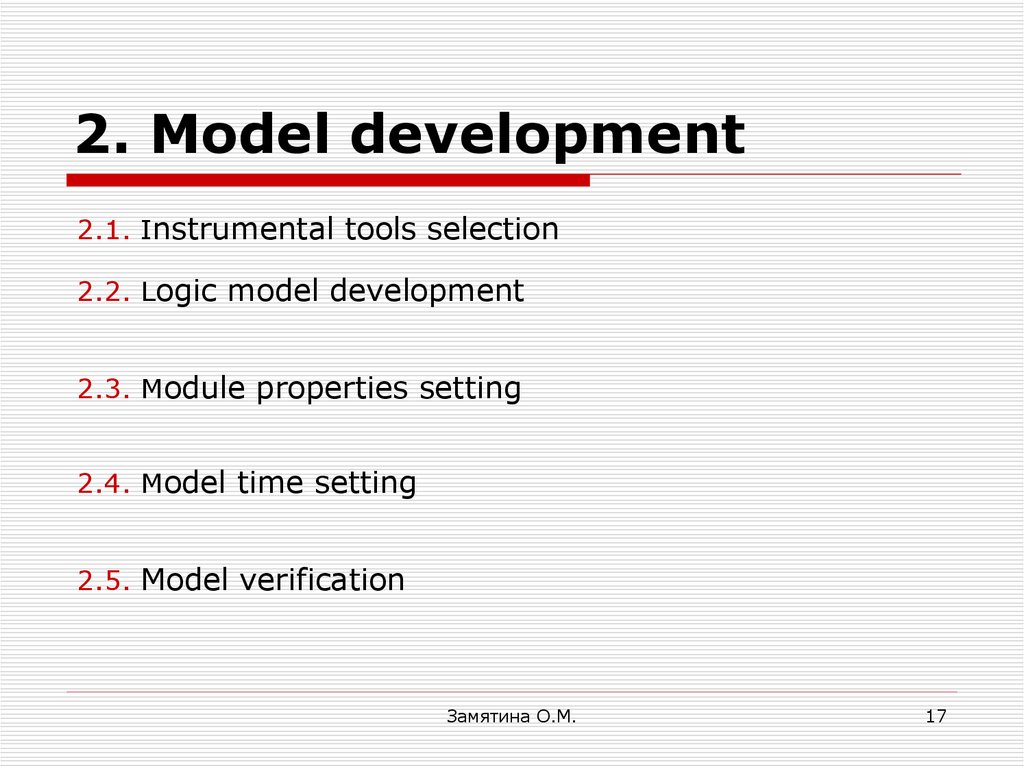
17. 2. Model development
2.1. Instrumental tools selection2.2. Logic model development
2.3. Module properties setting
2.4. Model time setting
2.5. Model verification
Замятина О.М.
17
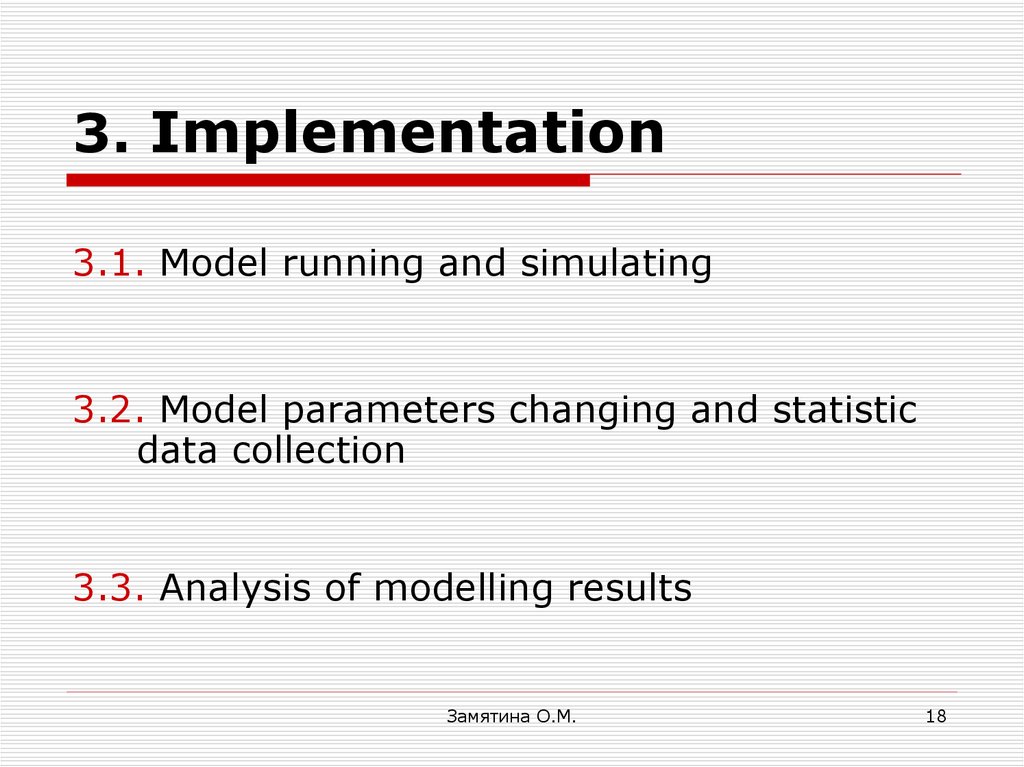
18. 3. Implementation
3.1. Model running and simulating3.2. Model parameters changing and statistic
data collection
3.3. Analysis of modelling results
Замятина О.М.
18
19.
Thank you for attention!Замятина О.М.
19





 english
english








