Similar presentations:
Profit repatriation in Сhina
1. PROFIT REPATRIATION IN CHINA
1PROFIT
REPATRIATION IN
CHINA
Бизнес и предпринимательство в
странах Азии 2017
Сучкова Александра, Намсараева
Норжима, Птичкина Анастасия
2. For foreign companies with subsidiaries in China, repatriating profit from their subsidiaries has always been an important and
2For foreign companies
with subsidiaries in China,
repatriating profit from
their subsidiaries has
always been an important
and challenging issue
China maintains a strict system of foreign
exchange controls, meaning funds flowing into
and out of China are tightly regulated.
It is important for foreign investors to
incorporate a profit repatriation strategy into
the set-up planning of a subsidiary in China to
ensure its ability to access the profits earned
and to achieve significant cost savings.
3. WAYS TO REPATRIATE PROFIT FROM CHINA
31. Company’s China-based entity pays dividends
WAYS TO
REPATRIATE
PROFIT FROM
CHINA
directly to its foreign parent company.
BUT: only profits that have undergone annual audit
can be repatriated, and the gross profit will be
subject to 25 percent CIT (Corporate Income Tax).
Dividends are subject to a further 10 percent
withholding CIT when distributed to foreign
investors.
4. WAYS TO REPATRIATE PROFIT FROM CHINA
4WAYS TO REPATRIATE PROFIT FROM CHINA
FIE (Foreign Invested Enterprise) can only
distribute dividends out of its accumulated
profits (and its prior accumulated losses
must be more than offset by its profits in
other years, including the current year).
An FIE its prior accumulated losses must
be more than offset by its profits in other
years, including the current year
5.
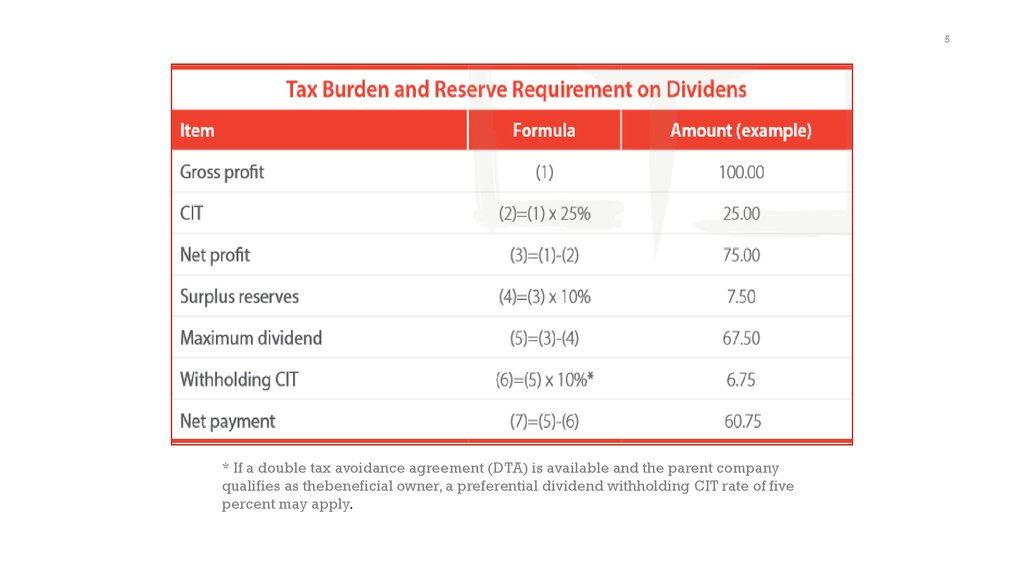
5* If a double tax avoidance agreement (DTA) is available and the parent company
qualifies as thebeneficial owner, a preferential dividend withholding CIT rate of five
percent may apply.
6.
6Procedure for the Declaration &
Repatriation of Dividends
7.
7Many multinational corporations
have adopted certain implicit
policies, such as minimizing their
profits in China in a legitimate
manner
via
intercompany
payments (i.e. charging their
Chinese entity royalty or service
fees);
These transactions will be subject
to turnover tax, and possible
withholding
CIT
(Corporate
Income Tax), the fees
are deductible from the CIT taxable
income and thus are exempt from
the 25 percent CIT, resulting
in significant cost savings.
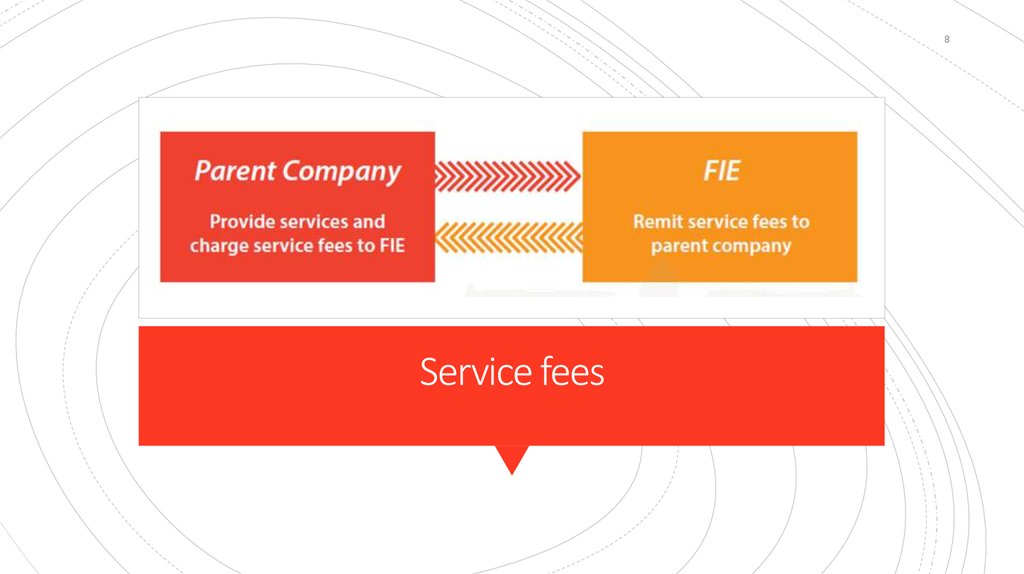
8. Service fees
8Service fees
9.
9Service fees paid to overseas related parties are deductible for CIT purposes
provided they are directly related to the FIE’s business operations and charged
at normal market rates - the service charges between a parent company and
its China subsidiary must be based on an arm’s length principle. Further, all
applicable taxes must have been withheld.
10. service fees are subject to:
10service fees are
subject to:
VAT (Value-Added Tax);
construction and maintenance tax (UCMT);
education surcharge (ES);
local education surcharge (LES);
The parent company is liable for these taxes.
The China subsidiary is responsible for withholding and
paying these taxes.
11.
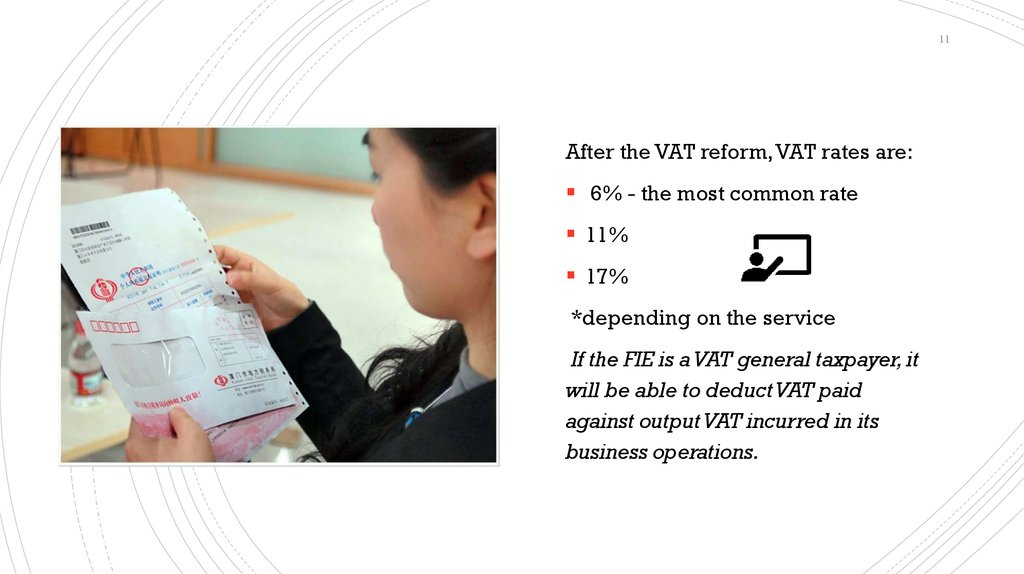
11After the VAT reform, VAT rates are:
6% - the most common rate
11%
17%
*depending on the service
If the FIE is a VAT general taxpayer, it
will be able to deduct VAT paid
against output VAT incurred in its
business operations.
12.
12Services rendered outside China are exempt from CIT (but are
still subject to VAT). The Chinese company should specify the
offshore services that it received in the relevant service
agreements and be prepared to clarify the nature of the services.
If the services are (or deemed to be) provided in China, the
service fees will be subject to CIT at 25% on the deemed profit
rate of 15-50%, unless a CIT exemption applies under a DTA.
13.
13Under most DTAs signed between
China and other countries/regions,
the provision of services in China by a
foreign enterprise overseas will,
constitute a permanen; establishment
(PE) if such activities continue for a
period of more than 183 days within
any 12-month period;
If the headquarter (HQ) is deemed to
have a PE in China, a 25 percent CIT is
payable on the service income;
Tax compliance burden for a PE is
heavier than for a non-PE;
the Chinese subsidiary and HQ should
carefully manage contracts and related
projects in China.
14. It is important to note that the tax officer always has the right to call into question the legitimacy of a service agreement.
14It is important to note that the tax officer always has the right to call into question the legitimacy of a service
agreement. The taxpayer should be prepared to provide further evidence, including a detailed service
agreement to clarify the nature of the services provided.
你有钱吗?
15. ROYALTY REMITTANCES
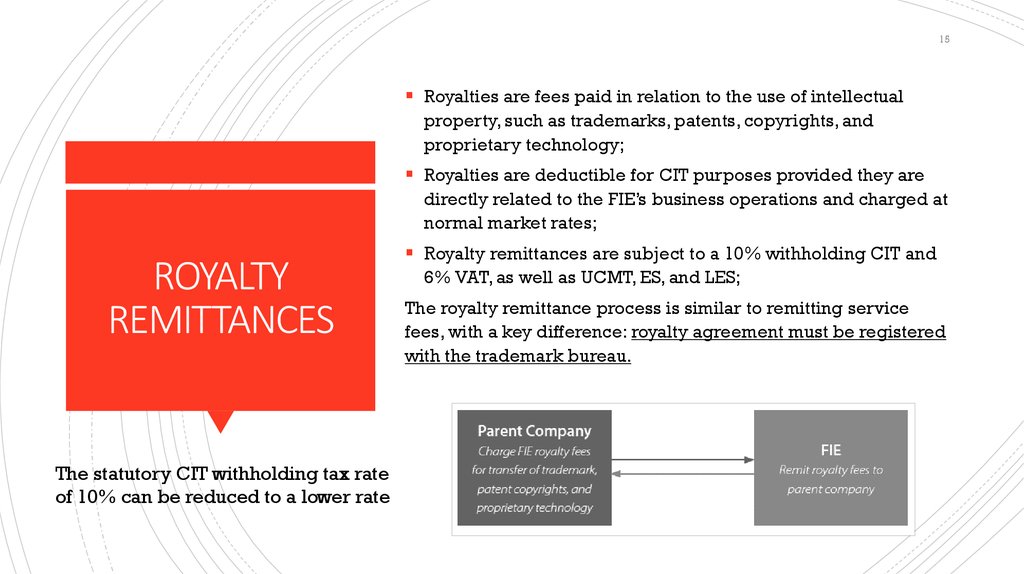
15Royalties are fees paid in relation to the use of intellectual
property, such as trademarks, patents, copyrights, and
proprietary technology;
Royalties are deductible for CIT purposes provided they are
directly related to the FIE’s business operations and charged at
normal market rates;
ROYALTY
REMITTANCES
The statutory CIT withholding tax rate
of 10% can be reduced to a lower rate
Royalty remittances are subject to a 10% withholding CIT and
6% VAT, as well as UCMT, ES, and LES;
The royalty remittance process is similar to remitting service
fees, with a key difference: royalty agreement must be registered
with the trademark bureau.
16. When services fees are deemed to be royalties
16When services
fees are deemed
to be royalties
The Notice of the State Administration of Taxation on Issues
Relevant to the Execution of the Royalty Clauses of Tax
Treaties (Guo Shui Han [2009] No. 507), where the service
provider uses certain expertise and technologies in the
provision of services under a service contract, but does not
transfer or license such technologies, then such services
shall not fall under the scope of royalties.
The results of the provision of services fall under the scope
of definition of royalties under a DTA (Direct Transfer
Agreement) then the service recipient shall merely have use
rights for such results and the service fees derived shall be
deemed as royalties.
17.
17If, in the course of the
transfer or licensing of
technical know-how, a
licensor assigns personnel
to support and guide the
licensee, then these service
fees will be deemed as
royalty fees.
Accordingly, even if these
services are provided
offshore, they will be
subject to VAT in addition
to 10% CIT withholding
tax.
18. LOANS
18LOANS
A WFOE (Wholly Foreign-Owned Enterprise)
may also remit undistributed profits to a foreign
related company with which it has an equity
relationship by extending a loan. The WFOE’s
interest income will be subject to 25% CIT and
6% VAT, although the CIT paid in China may
later be used to offset tax liability incurred in the
foreign country if there is a DTA in place;
Repatriating funds through an offshore loan has
traditionally not been very common because of
the intricate remittance procedure and
repayment issues.
19. WFOEs may now apply for longer-term offshore loans according to their business needs.
19The situation has changed since
WFOEs may now apply for
longer-term offshore
loans according to their
business needs.
the promulgation of the Hui Fa
[2014] No.2 (Circular 2) by SAFE
in January 2014. Under Circular
2, offshore lending is limited to
30% of the owner’s equity
in a Chinese WFOE unless
special approval has been
obtained from SAFE.
20. References
20References
Tax, Accounting and Audit in China, 2017 (9th
Edition). Ltd, Asia Briefing 2017. pp. 100-107.
21. Thank you for your attention!
21Thank you for your
attention!
















 economics
economics








