Similar presentations:
kinesiotaping as trauma treatment method: analysis of efficiency
1. kinesiotaping as trauma treatment method: analysis of efficiency
Moscow State University of Medicine and Dentistry named after A.I.EvdakimovKINESIOTAPING AS TRAUMA TREATMENT
METHOD: ANALYSIS OF EFFICIENCY
Author: Yurchenko M.V. 6th grade student of the Faculty of Medicine
Scientific Advisor: Ph.D. Smislov A.V.
Moscow 2018.
2. Materials and methods
MATERIALS AND METHODSThe following materials were used in this study:
«Forearm Skin Blood Flow After Kinesiology Taping in Healthy Soccer Players. Woodward KA, Unnithan V,
Hopkins N.» Staffordshire University, Stoke-on-Trent, UK;Liverpool John Moores University, UK.;
«Kinesiology tape does not facilitate muscle performance: A deceptive controlled trial. K.Y. Poona, S.M. Lia, M.G.
Ropera, M.K.M. Wonga, O. Wongb, R.T.H. Cheunga.»Department of Rehabilitation Sciences, Hong Kong
Polytechnic University, Hung Hom, Kowloon, Hong Kong, China;
«Current evidence does not support the use of Kinesio Taping in clinical practice: a systematic review. Parreira Pdo C,
Costa Lda C, Hespanhol LC Jr, Lopes AD, Costa LO.»Masters and Doctoral Programs in Physical Therapy,
Universidade Cidade de São Paulo, Brazil; Musculoskeletal Division, The George Institute for Global Health,
Australia;
«Kinesio Taping does not decrease swelling in acute, lateral ankle sprain of athletes: a randomised trial. Guilherme S
Nunes, Valentine Zimermann Vargas, Bruna Wageck, Daniela Pacheco dos Santos Hauphental, Clarissa Medeiros da
Luz, Marcos de Noronha» Department of Physiotherapy, Center of Health and Sport Sciences, Santa Catarina State
University, Brazil; La Trobe University, Rural Health School, Bendigo, VIC, Australia
3. Structure of the study
STRUCTURE OF THE STUDYActuality: Nowadays, the popularity of new
conservative methods of treating musculoskeletal
injuries is growing. One of those methods is
"Kinesiotaping". It is in the interest of the doctor and
the patient to determine method’s efficiency and
safety .
Objective: The purpose of this study was to consider
functioning principles of Kinesiotaping method, to
identify its efficiency and reliability and to find its
scientific basis.
4. definition
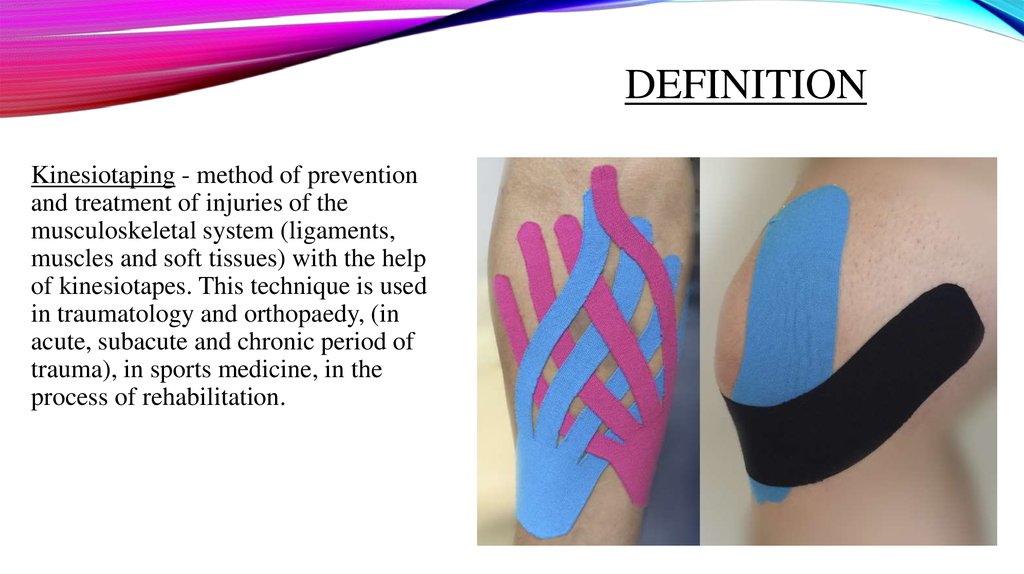
DEFINITIONKinesiotaping - method of prevention
and treatment of injuries of the
musculoskeletal system (ligaments,
muscles and soft tissues) with the help
of kinesiotapes. This technique is used
in traumatology and orthopaedy, (in
acute, subacute and chronic period of
trauma), in sports medicine, in the
process of rehabilitation.
5. Indications
INDICATIONSKinesiotaping is prescribed as an independent method, as well as in combination with drug
treatment, manual therapy, physiotherapy in the following situations:
• prevention of sports injuries;
• posttraumatic pain syndromes;
• bruises of soft tissues;
• musculo-fascial pain syndromes;
• injuries of tendons and ligaments;
• scoliosis;
Et cetera.
6. Kinesiotaping’s effect according to practitioners
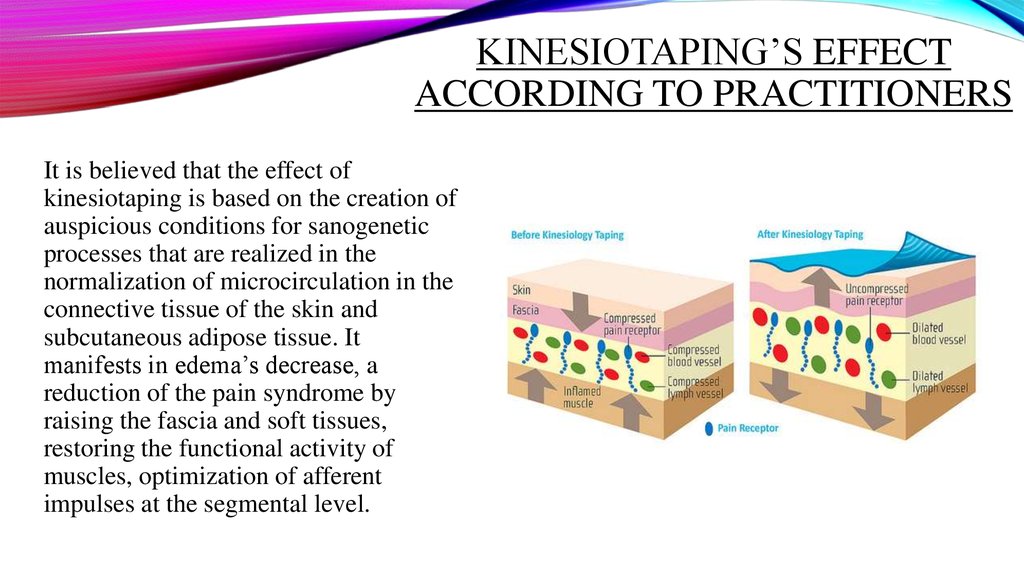
KINESIOTAPING’S EFFECTACCORDING TO PRACTITIONERS
It is believed that the effect of
kinesiotaping is based on the creation of
auspicious conditions for sanogenetic
processes that are realized in the
normalization of microcirculation in the
connective tissue of the skin and
subcutaneous adipose tissue. It
manifests in edema’s decrease, a
reduction of the pain syndrome by
raising the fascia and soft tissues,
restoring the functional activity of
muscles, optimization of afferent
impulses at the segmental level.
7. normal anatomy
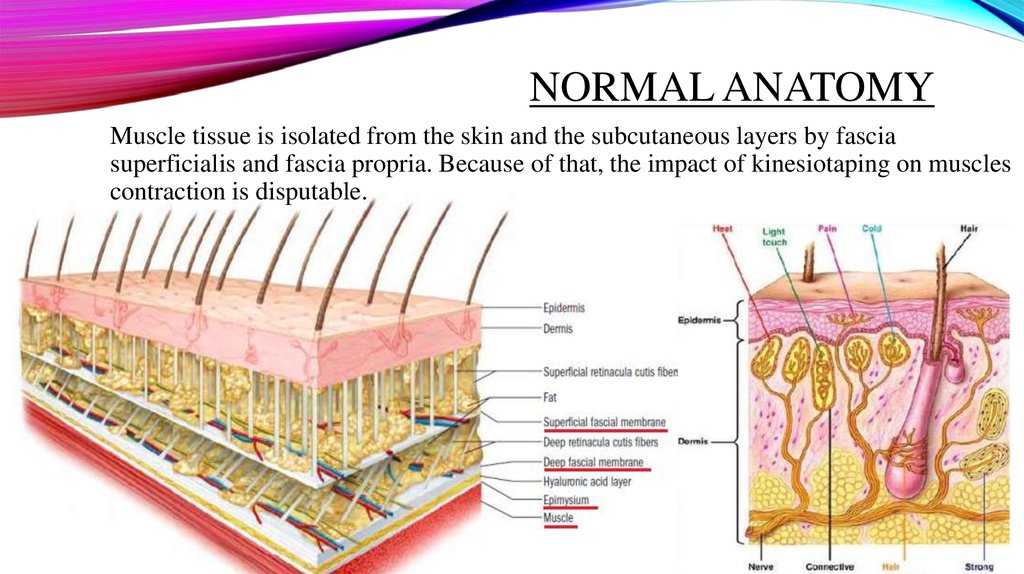
NORMAL ANATOMYMuscle tissue is isolated from the skin and the subcutaneous layers by fascia
superficialis and fascia propria. Because of that, the impact of kinesiotaping on muscles
contraction is disputable.
8. Influence on muscular strength
INFLUENCE ON MUSCULAR STRENGTHThe study«Kinesiology tape does not facilitate muscle
performance: A deceptive controlled trial. K.Y. Poona,
S.M. Lia, M.G. Ropera, M.K.M. Wonga, O. Wongb, R.T.H.
Cheunga.» proved the absence of kinesiotaping’s effect on
muscle strength.
For the control of the results were used: triple
measurements of the normalized maximum torque,
normalized total work, time to the maximum torque of the
knee joint using an isokinetic dynamometer.
9. Influence on microcirculation
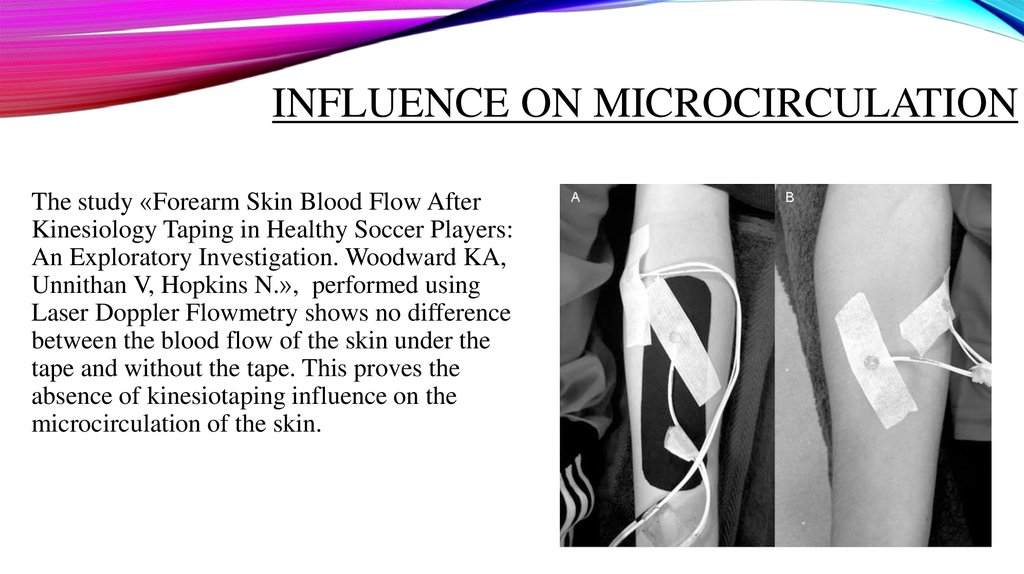
INFLUENCE ON MICROCIRCULATIONThe study «Forearm Skin Blood Flow After
Kinesiology Taping in Healthy Soccer Players:
An Exploratory Investigation. Woodward KA,
Unnithan V, Hopkins N.», performed using
Laser Doppler Flowmetry shows no difference
between the blood flow of the skin under the
tape and without the tape. This proves the
absence of kinesiotaping influence on the
microcirculation of the skin.
10. efficiency of kinesiotaping as a treatment method
EFFICIENCY OF KINESIOTAPINGAS A TREATMENT METHOD
Systematic review «Current evidence does not support
the use of Kinesio Taping in clinical practice: a
systematic review. Parreira Pdo C, Costa Lda C,
Hespanhol LC Jr, Lopes AD, Costa LO.» is the latest
and most complete in the field of studying the
effectiveness of kinesiotaping as a method of treating
injuries of the musculoskeletal system.
11. Clinical studies of Kinesiotaping as a treatment method
CLINICAL STUDIES OF KINESIOTAPINGAS A TREATMENT METHOD
The 275 potentially relevant studies in this area were
published between 2008 and 2013, of which only 12 were
considered eligible for data analysis.
Of those, 10 studies showed no effect of kinesiotaping.
Only 2 studies showed any insignificant clinically useful
effect from the use of this method.
12. the effectiveness of kinesiotaping in the traumatic edema treatment
THE EFFECTIVENESS OF KINESIOTAPING INTHE TRAUMATIC EDEMA TREATMENT
Clinical study «Kinesio Taping does not decrease
swelling in acute, lateral ankle sprain of athletes: a
randomised trial. Guilherme S Nunes, Valentine
Zimermann Vargas, Bruna Wageck, Daniela
Pacheco dos Santos Hauphental, Clarissa
Medeiros da Luz, Marcos de Noronha» revealed
the absence of kinesiotaping influence on the
dynamics of edema. To control the results,
threefold measurements of the volume and
perimetry of the ankle were used on the 1st, 3rd,
15th day after the lateral ankle sprain.
13. Clinical study
CLINICAL STUDYThe aim of the study is to determine the
degree of kinesiotaping’s efficiency
relatively to placebo and classic
desmurgy methods.
A comparative analysis of the efficiency
of the above-mentioned methods was
conducted in treatment of the 1st degree
collateral ligaments sprain of the knee
joint.
14. Structure of clinical research
STRUCTURE OF CLINICALRESEARCH
A clinical study was conducted on 30 patients of the Clinical Hospital №68. Patients
enrolled in the study group requested medical help due to 1st degree collateral
ligaments sprain of the knee joint within 48 hours after the trauma.
Patients were divided into 3 groups:
1) The first experimental group: 10 patients (6 men, 4 women). For the treatment of
patients in this group, kinesiotapes were used, the technique of applique 3 I-cuts,
tension=20%.
2) The second experimental group: 10 patients (7 men, 3 women) For the treatment of
patients of this group, inert tapes were used, the technique of applique 1 I-cut.
3) Control group: 10 patients (3 men, 7 women). For the treatment of patients in this
group, the immobilization of the knee joint by elastic "turtle bandage“ was used.
15. Structure of study groups
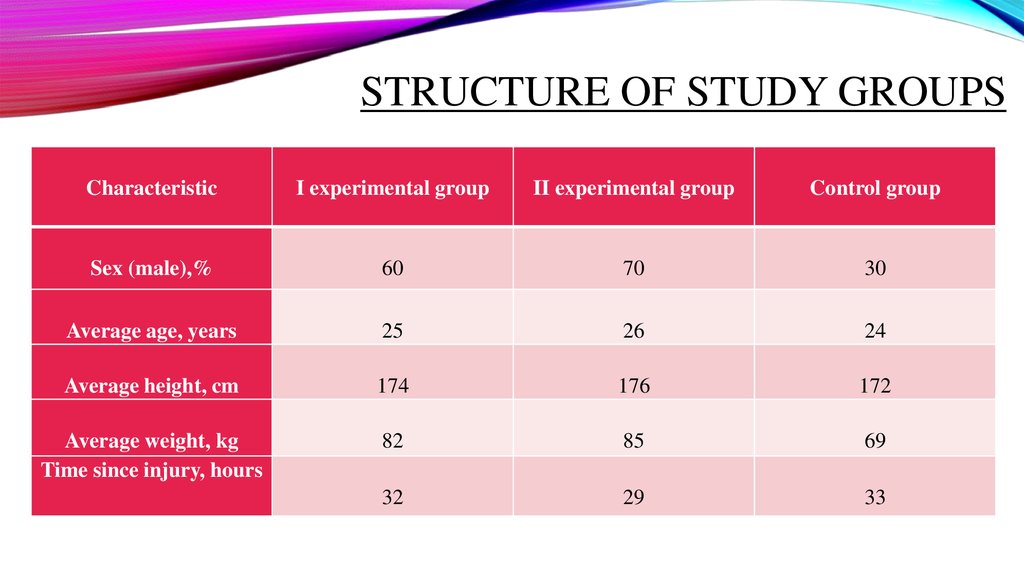
STRUCTURE OF STUDY GROUPSCharacteristic
I experimental group
II experimental group
Control group
Sex (male),%
60
70
30
Average age, years
25
26
24
Average height, cm
174
176
172
Average weight, kg
Time since injury, hours
82
85
69
32
29
33
16. Control parameters
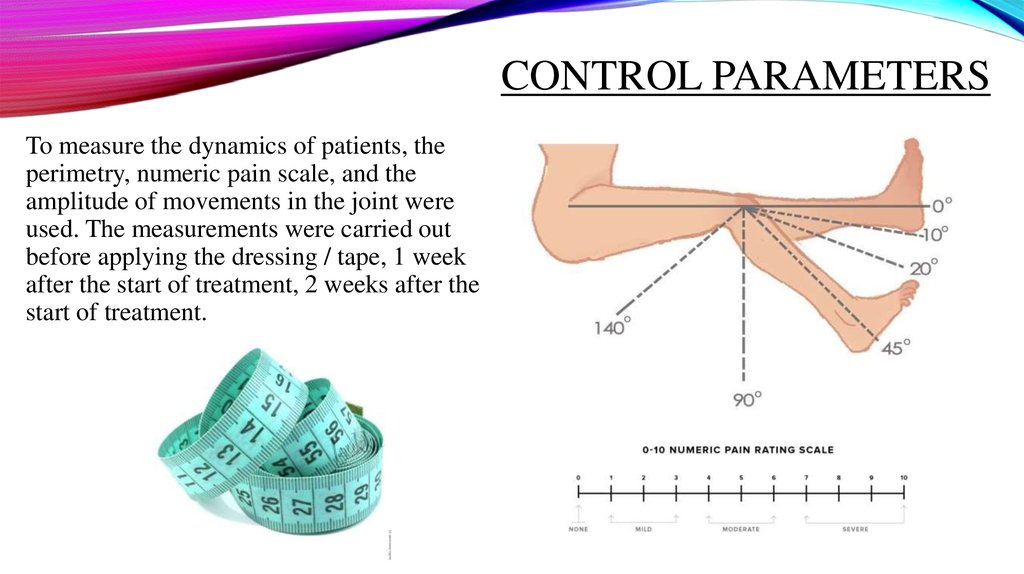
CONTROL PARAMETERSTo measure the dynamics of patients, the
perimetry, numeric pain scale, and the
amplitude of movements in the joint were
used. The measurements were carried out
before applying the dressing / tape, 1 week
after the start of treatment, 2 weeks after the
start of treatment.
17. The received data
THE RECEIVED DATAI experimental group
II experimental group
Control group
Options
day 0
day 7
day 14
day 0
day 7
day 14
day 0
day 7
day14
Perimetry, cm
42
40
40
43
41
39
39
37
36
Score by NPS
6
4
3
5
4
3
6
3
2
95/160
68/169
62/174
93/161
67/166
60/176
90/159
The amplitude
of movements,
°
Flexing /
Extension
62/171 51/179
18. results of the study
RESULTS OF THE STUDYIt was concluded, that Kinesiotaping method does not have any specific advantages in
treatment of knee sprains including in relation to classic immobilization methods and do
not have any specific properties of enhancing microcirculation of blood or lymph due to
its inability to interact with deep layers of tissues beneath the skin, which was shown by
absence of swelling reduction compared to classical desmurgy methods,.
19. Conclusion
CONCLUSIONKinesiotaping has become popular in treatment
of musculo-sceletal injuries. However, its
functioning principles and clinical efficiency
was disproved by the results of various
scientific studies.












 medicine
medicine