Similar presentations:
Renewable energy
1. Renewable Energy
Ana Romaliischi1
2. Contents
What is Renewable Energy?
Key Renewable Energy Sources
Why Renewables?
Renewable Energy Overview
– Solar Power
– Wind Power
– Biofuels
– Hydropower
• Global Investment
• Sources
2
3. What is Renewable Energy?
• Derived from naturalprocesses that are
replenished constantly.
• Ressources exist over
wide geographical
areas.
• Provides energy in four
important areas.
3
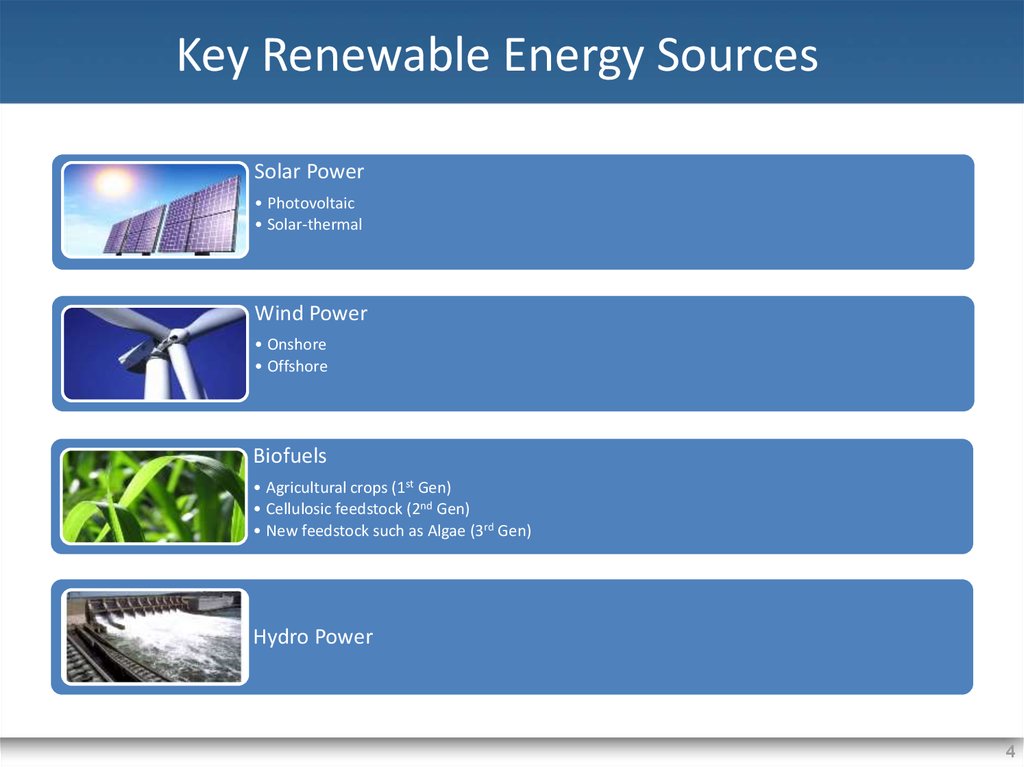
4. Key Renewable Energy Sources
Solar Power• Photovoltaic
• Solar-thermal
Wind Power
• Onshore
• Offshore
Biofuels
• Agricultural crops (1st Gen)
• Cellulosic feedstock (2nd Gen)
• New feedstock such as Algae (3rd Gen)
Hydro Power
4
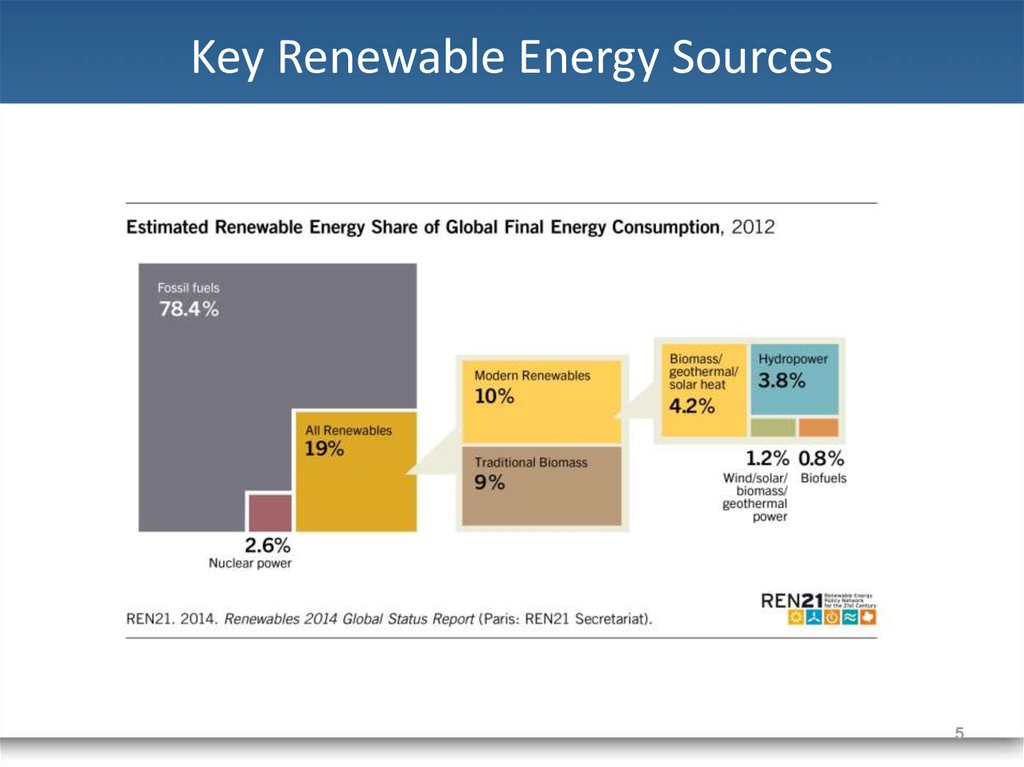
5. Key Renewable Energy Sources
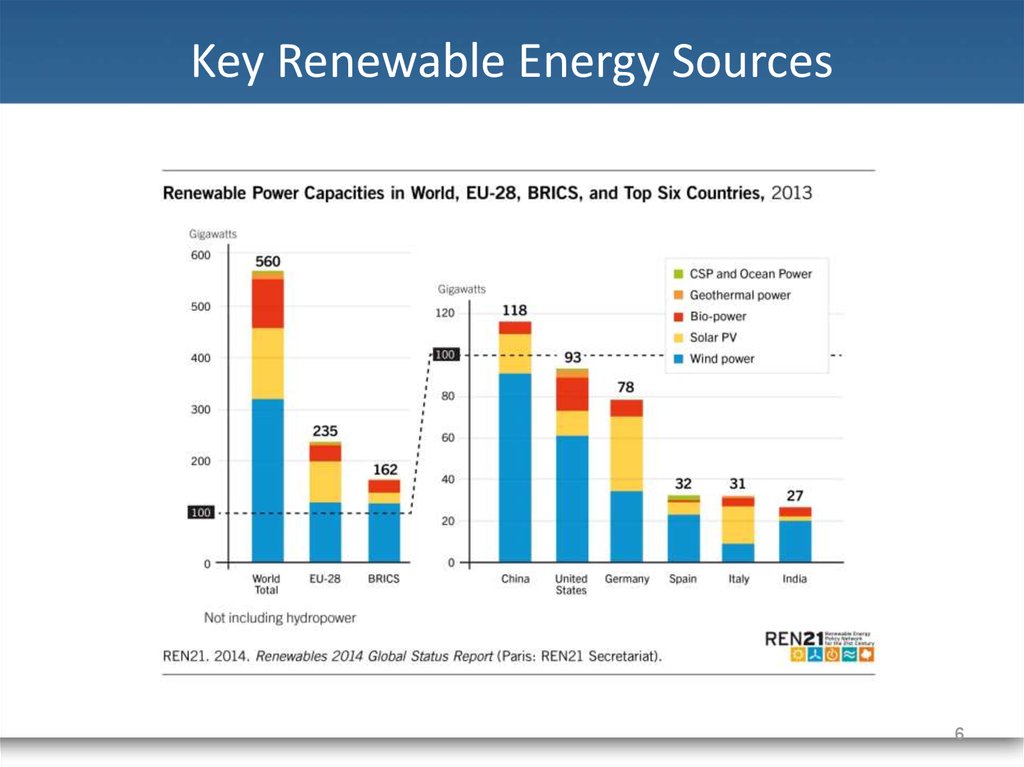
56. Key Renewable Energy Sources
67. Why Renewables?
Do not deplete natural resources.
Effective method to reduce CO2 emissions.
Economic benefits
Reliable energy source
Guarantee energy security for countries deploying it.
Legislation being passed making renewables more
attractive.
7
8.
89.
Solar Power9
10. Solar Power
• Generally captured intwo forms.
• Remains an expensive
method of generating
electricity.
• Advances in technology
and support from
certain governments.
10
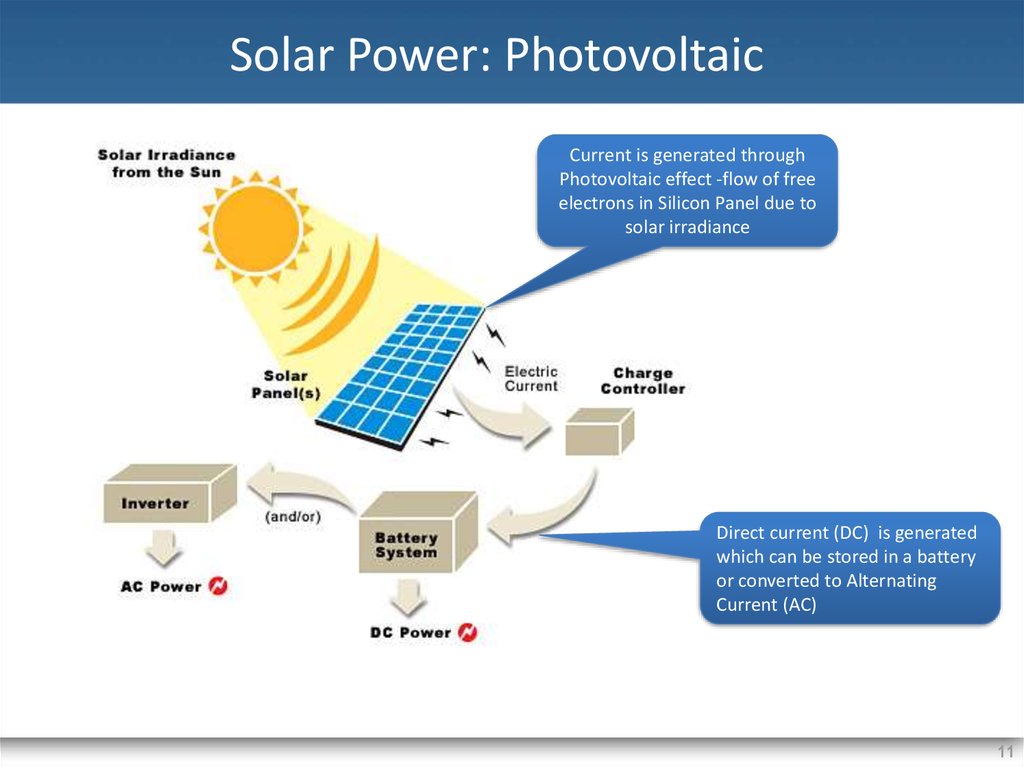
11. Solar Power: Photovoltaic
Current is generated throughPhotovoltaic effect -flow of free
electrons in Silicon Panel due to
solar irradiance
Direct current (DC) is generated
which can be stored in a battery
or converted to Alternating
Current (AC)
11
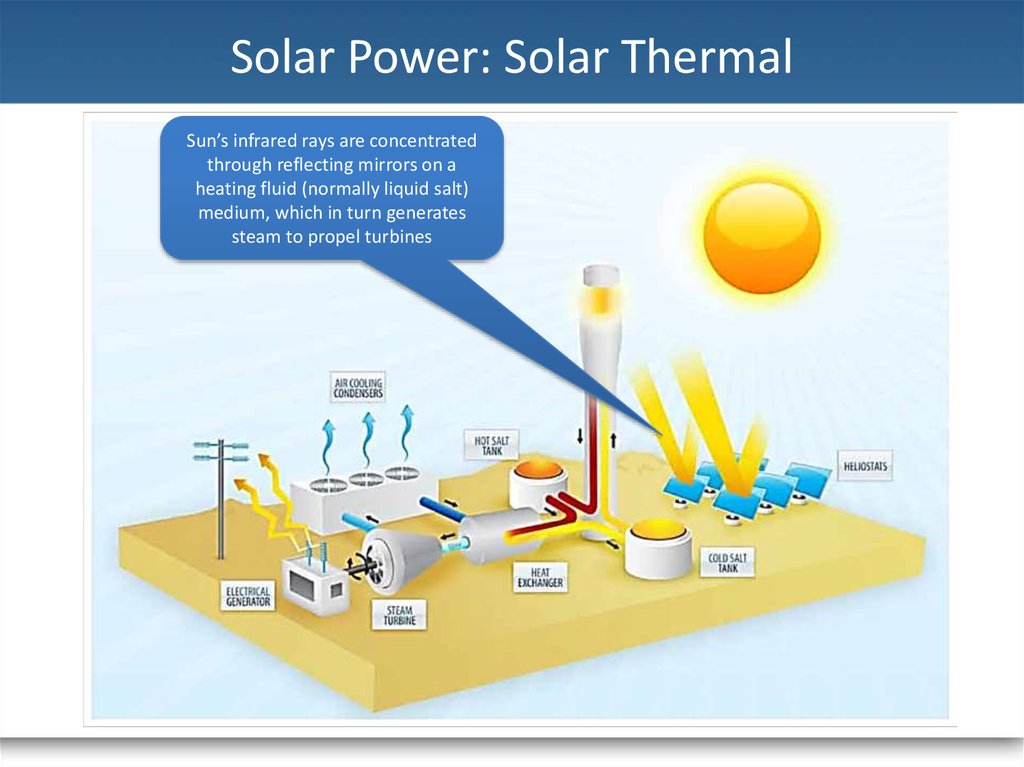
12. Solar Power: Solar Thermal
Sun’s infrared rays are concentratedthrough reflecting mirrors on a
heating fluid (normally liquid salt)
medium, which in turn generates
steam to propel turbines
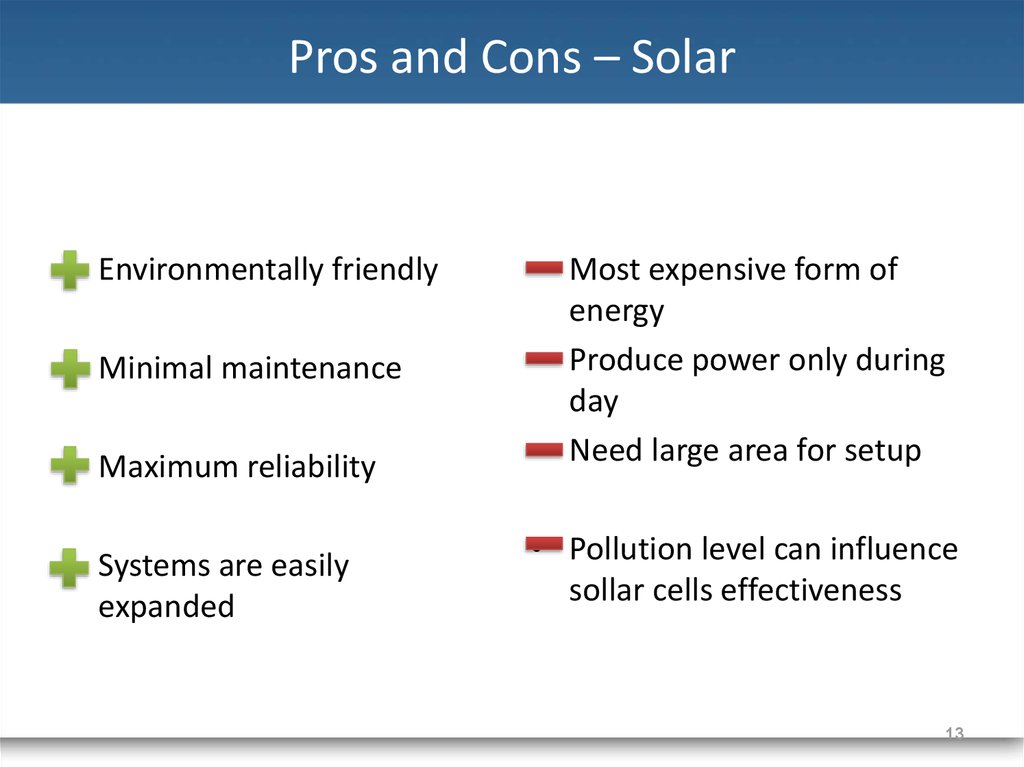
13. Pros and Cons – Solar
• Environmentally friendly• Maximum reliability
• Most expensive form of
energy
• Produce power only during
day
• Need large area for setup
• Systems are easily
expanded
• Pollution level can influence
sollar cells effectiveness
• Minimal maintenance
13
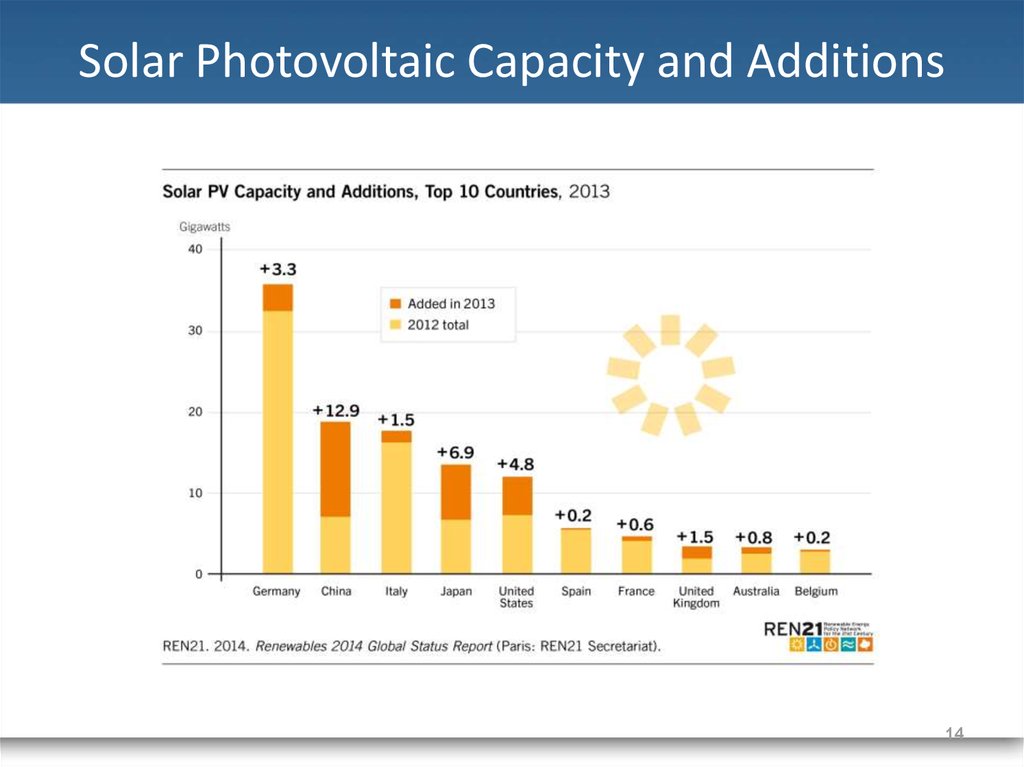
14. Solar Photovoltaic Capacity and Additions
1415.
Wind Power15
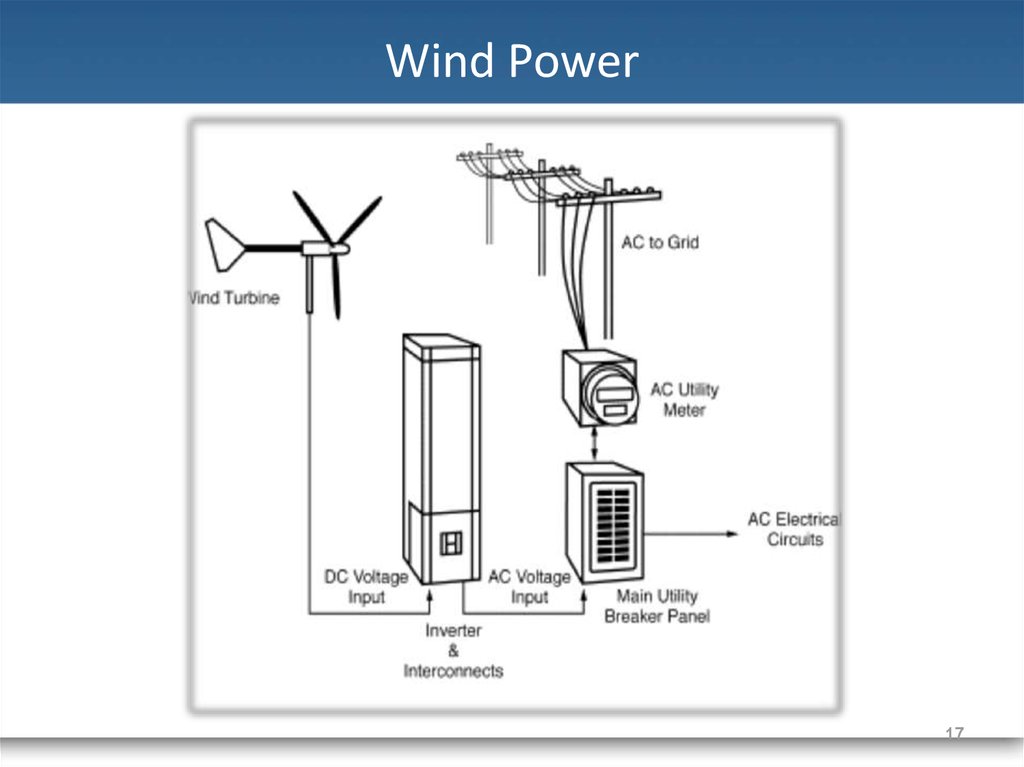
16. Wind Power
• Converts kinetic energy ofwind to electrical energy.
• Renewable of choice in
Europe and the United
States.
• Competitive alternative to
more traditional methods of
power generation.
16
17. Wind Power
1718. Pros and Cons – Wind
• Smaller Land requirementwhen compared to Solar,
Hydro
• Can be built off-shore
• The strength of the wind is
not constant and it varies
from zero to storm force
• Wind turbines are noisy
• Cheaper than Solar
• Wind sites are often located
in remote locations, so
transmission lines must be
built
18
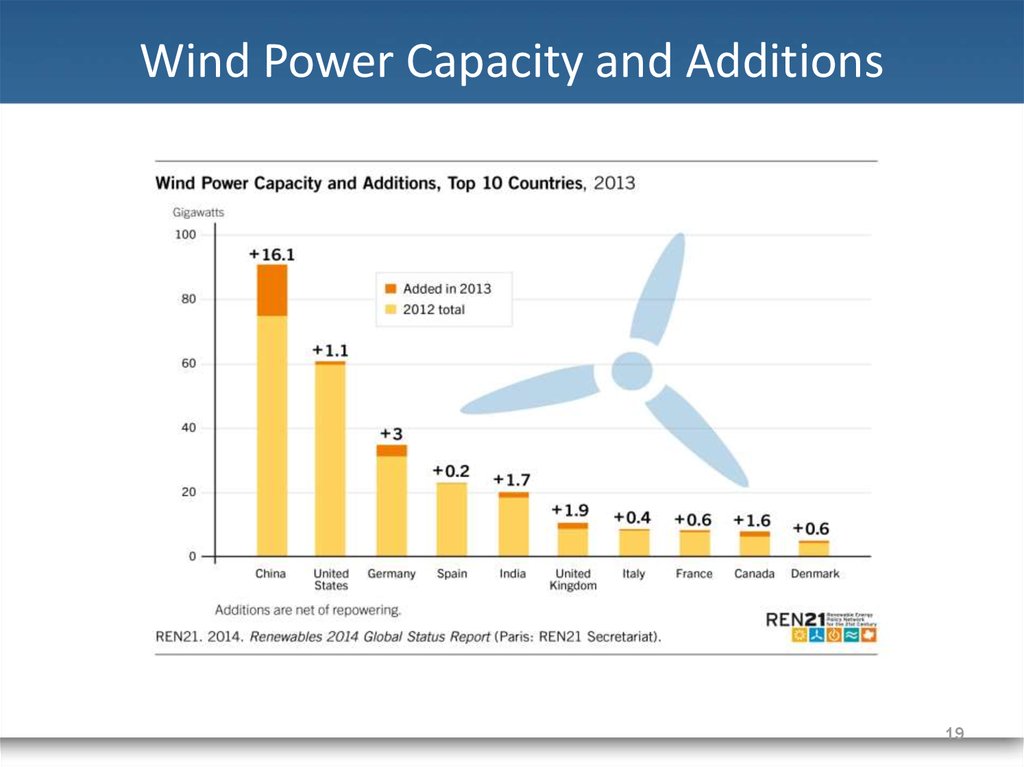
19. Wind Power Capacity and Additions
1920.
Biofuels20
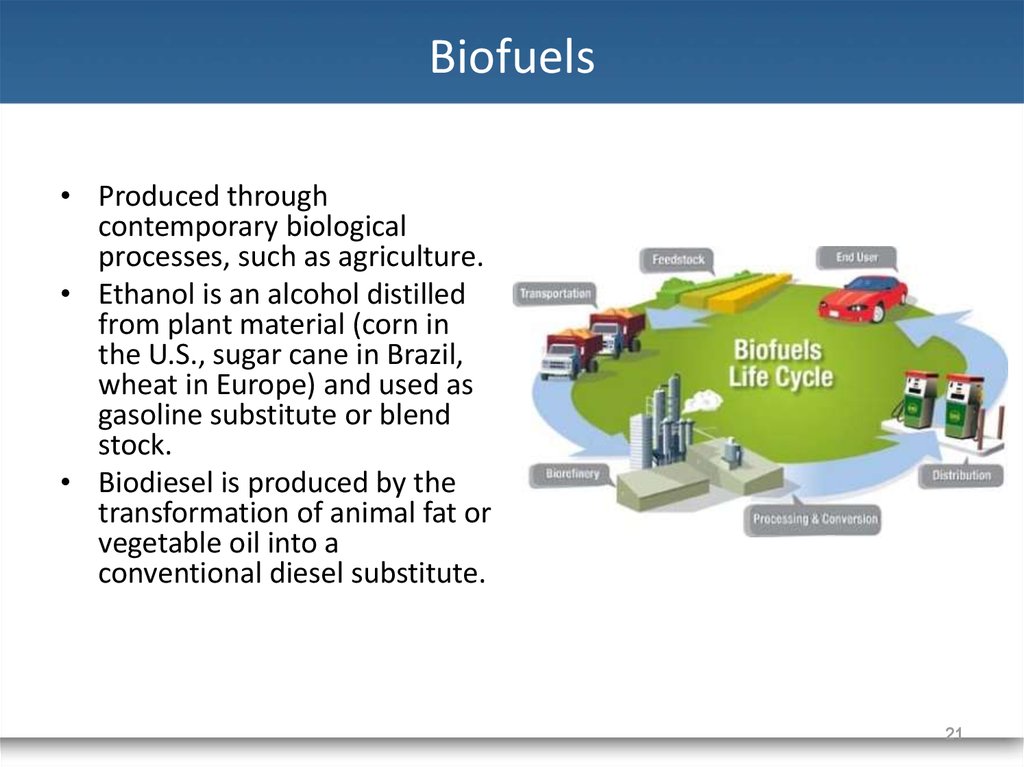
21. Biofuels
• Produced throughcontemporary biological
processes, such as agriculture.
• Ethanol is an alcohol distilled
from plant material (corn in
the U.S., sugar cane in Brazil,
wheat in Europe) and used as
gasoline substitute or blend
stock.
• Biodiesel is produced by the
transformation of animal fat or
vegetable oil into a
conventional diesel substitute.
21
22. Pros and Cons – Biofuels
• Inherently renewable• Emit less pollution than
traditional petroleum based
gasoline and diesel fuels
• Easier to transition to
without special
infrastructure needs
• Not enough land space to
grow crops for biofuel
demand
• Producing them actually
requires more energy than
they generate
• Still polluting when
compared to wind or solar
22
23. The Bio-bean Start-up
• Recycles waste coffeegrounds into biomass fuel
pellets and coals.
• In the five-stage system,
the grounds are refined,
agitated and dried out.
• A 1 tonne pellet-bag is
enough to heat a family
home for a year.
• Cheaper than wood
pellets.
24.
Hydropower24
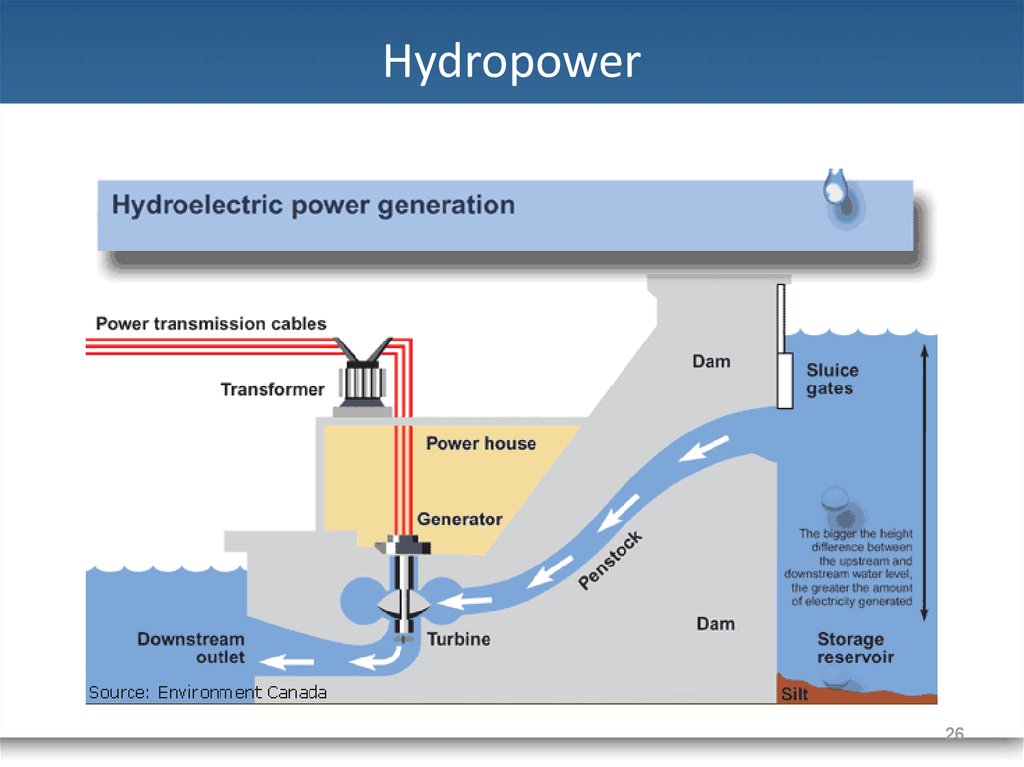
25. Hydropower
• Power derived fromthe energy of falling
water or fast running
water
• Largest global
contributor amongst all
renewable energies.
• Most mature of
renewable energies
25
26. Hydropower
2627. Pros and Cons – Hydropower
• The cheapest way togenerate electricity today.
• Dams are extremely
expensive to build.
• The flow of water can be
controlled to produce
electricity on demand.
• Limited in number of
potential sites/locations.
• Flooding of land.
• Capable of large scale
production.
27
28. Hydropower
2829.
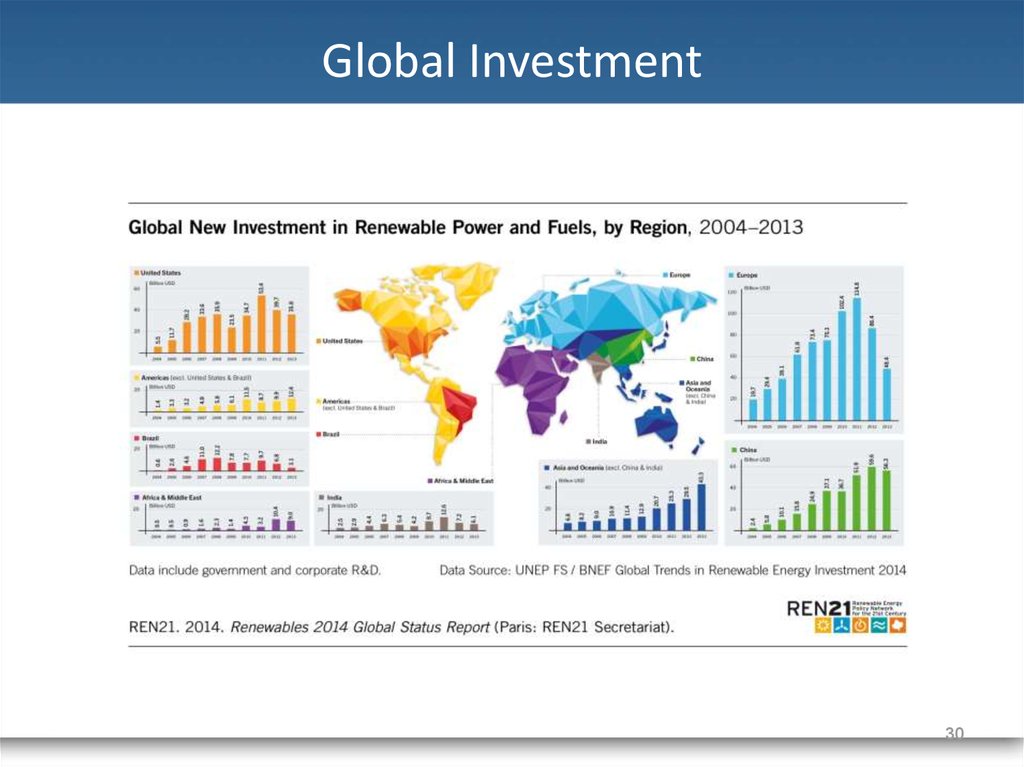
Global Investment29
30. Global Investment
3031. Sources
• https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Renewable_energy• http://www.ren21.net/status-of-renewables/global-status-report/
• http://www.theguardian.com/business/2016/feb/14/the-innovators-howyour-coffee-can-light-up-your-barbecue-and-boiler
• http://environment.nationalgeographic.com/environment/globalwarming/hydropower-profile/
• http://environment.nationalgeographic.com/environment/globalwarming/biofuel-profile/
• http://web.mit.edu/taalebi/www/scitech/pvtutorial.pdf
• http://www.tc.umn.edu/~dama0023/solar.html
31
32. Thank you for Attention!
Quelle: Jm-Projektinvest GmbH &Co. KGTHANK YOU FOR ATTENTION!
32

















 economics
economics ecology
ecology