Similar presentations:
Field programmable gate arrays
1. FIELD PROGRAMMABLE GATE ARRAYS
Introduction2.
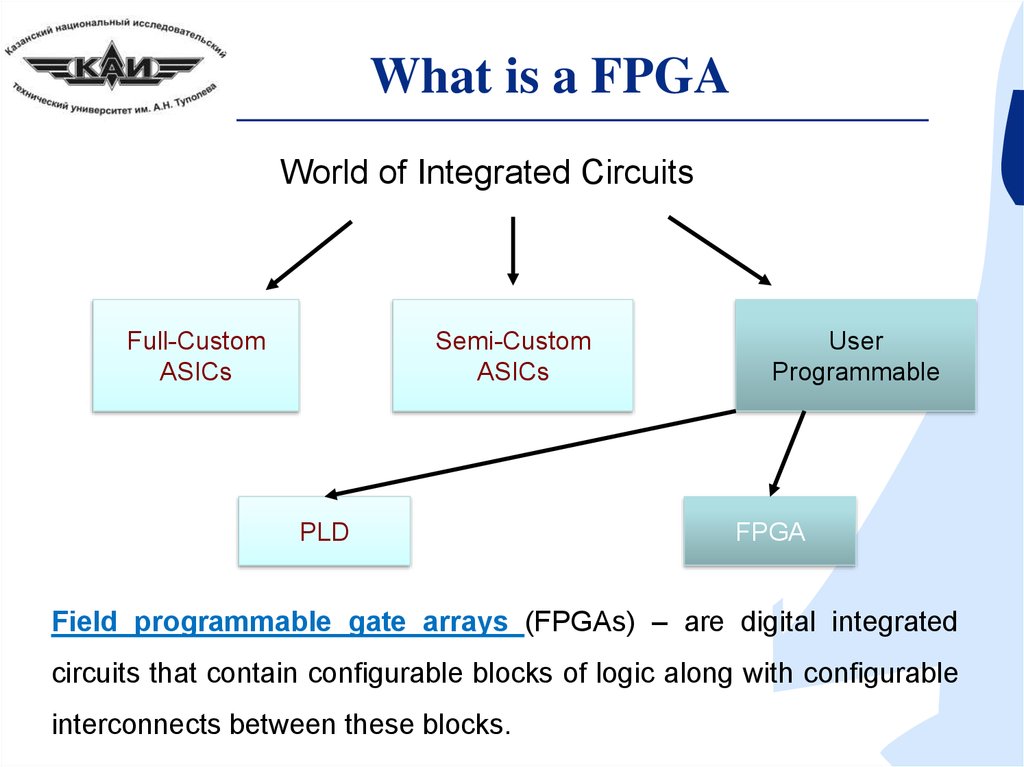
What is a FPGAWorld of Integrated Circuits
Full-Custom
ASICs
Semi-Custom
ASICs
PLD
User
Programmable
FPGA
Field programmable gate arrays (FPGAs) – are digital integrated
circuits that contain configurable blocks of logic along with configurable
interconnects between these blocks.
3.
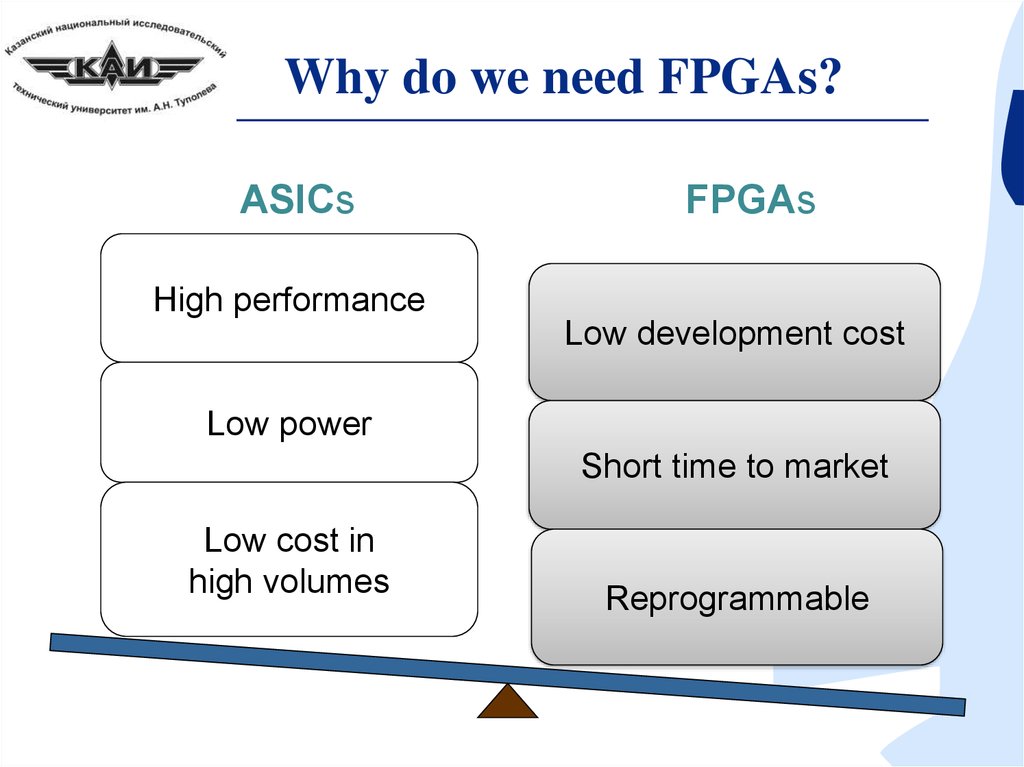
Why do we need FPGAs?ASICs
FPGAs
High performance
Low development cost
Low power
Short time to market
Low cost in
high volumes
Reprogrammable
4.
Other FPGA advantages
• Manufacturing cycle for ASIC is very costly, lengthy
and engages lots of manpower
• Mistakes not detected at design time have large
impact on development time and cost
• FPGAs are perfect for rapid prototyping of digital
circuits
• Easy upgrades like in case of software
• Unique applications
5.
Architecture of FPGAThe architecture of
FPGA is very simple than other
programmable devices
Elements of FPGA
The basic elements of an Field Programmable Gate Array
are:
Configurable logic blocks(CLBs)
Configurable input output blocks(IOBs)
Two layer metal network of vertical and horizontal lines for
interconnecting the CLBS and FPGAs (programmable
interconnect)
6.
Architecture of FPGAA simple modern architecture of FPGA is shown below:
All FPGAs include a regular,
programmable,
and
flexible
architecture
logic
blocks
of
surrounded by input/output blocks
on
the
functional
perimeter.
blocks
are
These
linked
together by a hierarchy of highly
versatile
interconnects.
programmable
7.
A simple programmable function8.
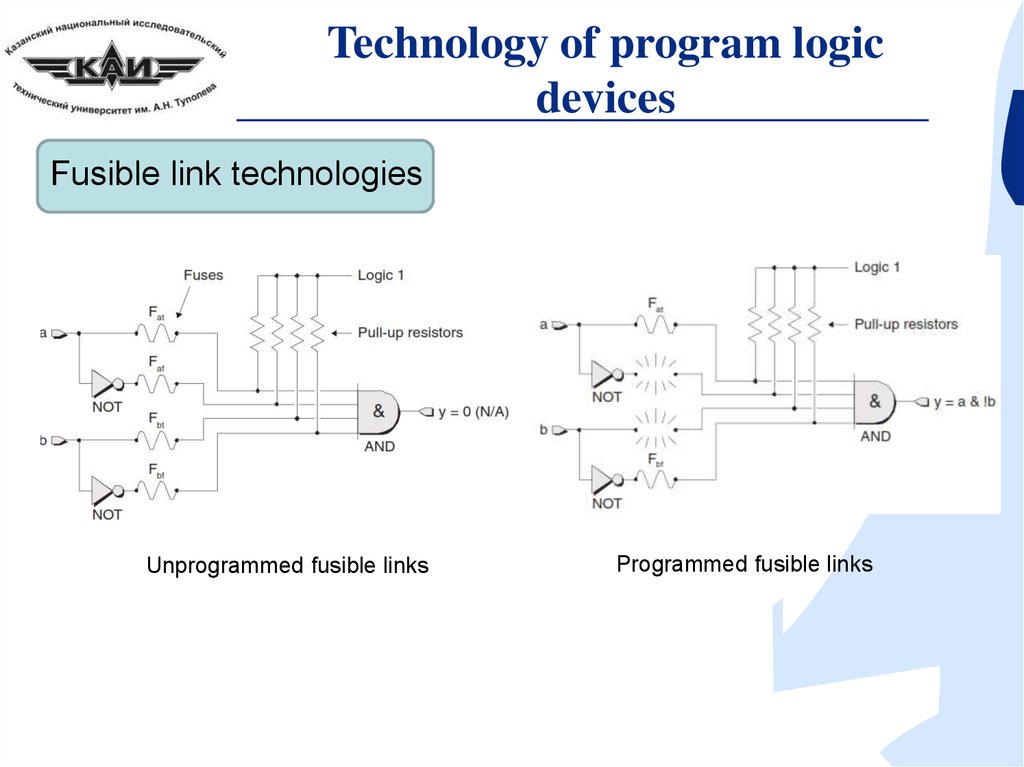
Technology of program logicdevices
Fusible link technologies
Unprogrammed fusible links
Programmed fusible links
9.
Technology of program logicdevices
Antifuse technologies
Unprogrammed antifuse links
Programmed antifuse links
The act of programming particular
element effectively grows a link by
converting the insulating amorphous
silicon into conducting polysilicon
10.
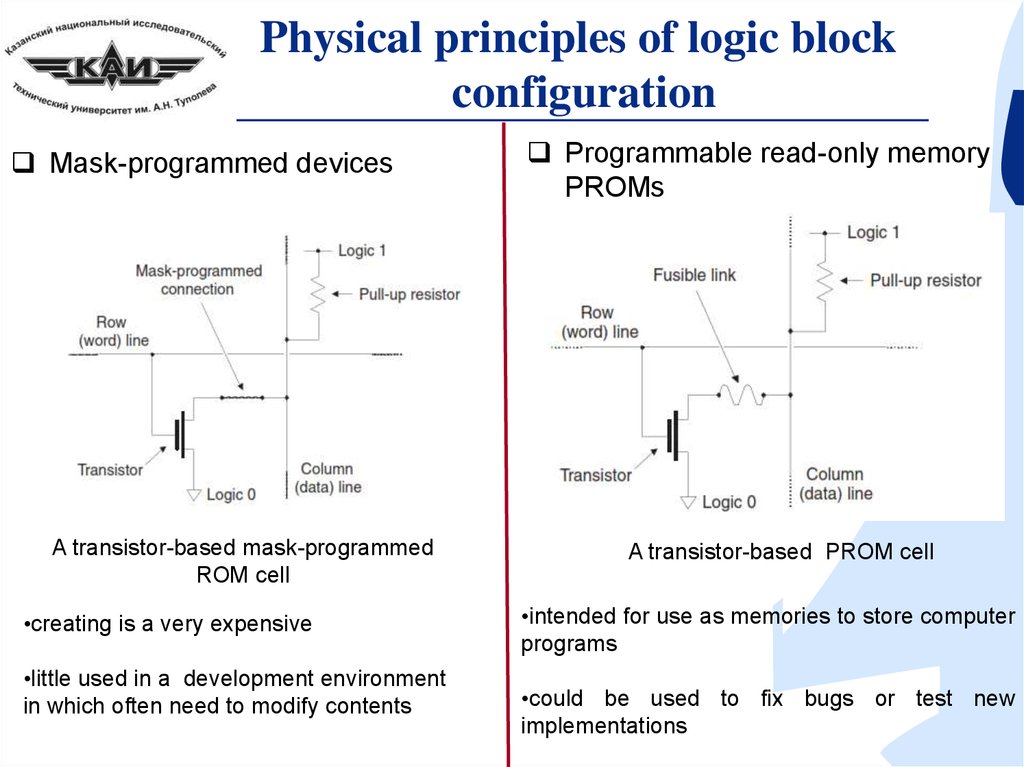
Physical principles of logic blockconfiguration
Mask-programmed devices
A transistor-based mask-programmed
ROM cell
•creating is a very expensive
•little used in a development environment
in which often need to modify contents
Programmable read-only memory
PROMs
A transistor-based PROM cell
•intended for use as memories to store computer
programs
•could be used to fix bugs or test new
implementations
11.
Physical principles of logic blockconfiguration
EPROM-based technologies
EEPROM-based technologies
An EEPROM-cell
An EPROM transistor-based memory
cell
•expensive packages with quartz windows
and the time takes to erase
•use as a programmable memories
•EEPROM transistor contains a floating gate, but
the insulating oxide layers surrounding this gate
are very much thinner
•the second transistor can be used to erase the
cell electrically
12.
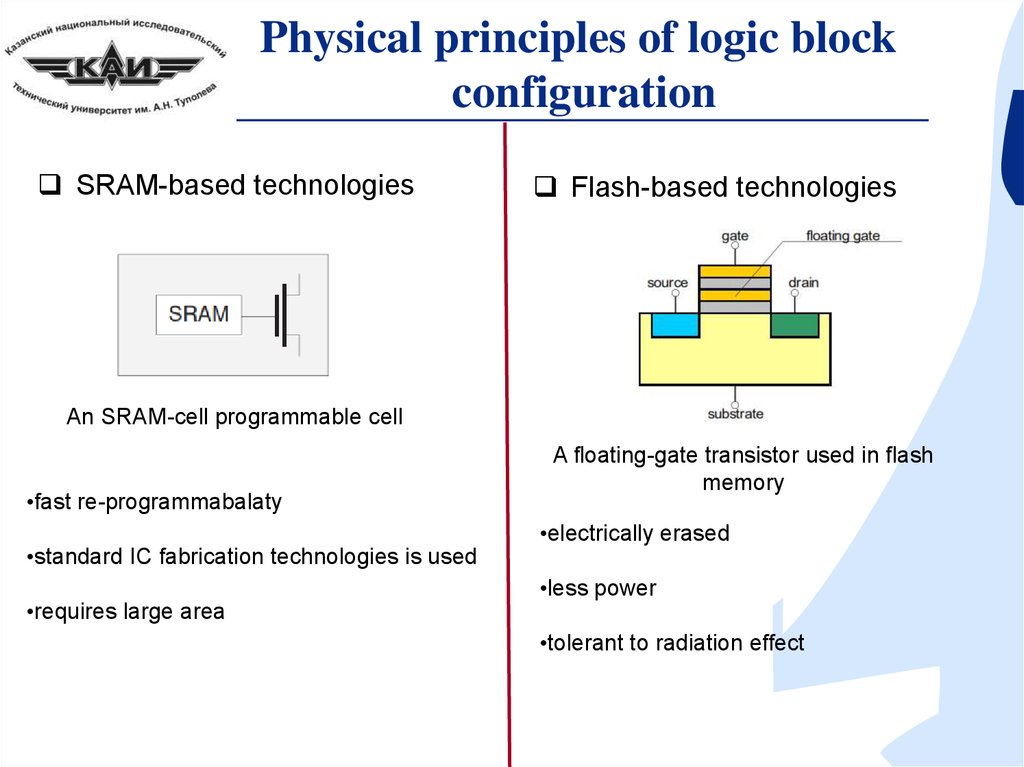
Physical principles of logic blockconfiguration
SRAM-based technologies
Flash-based technologies
An SRAM-cell programmable cell
•fast re-programmabalaty
•standard IC fabrication technologies is used
•requires large area
A floating-gate transistor used in flash
memory
•electrically erased
•less power
•tolerant to radiation effect
13.
Summary of programmingtechnologies








 programming
programming








