Similar presentations:
Evolution: Artificial Selection
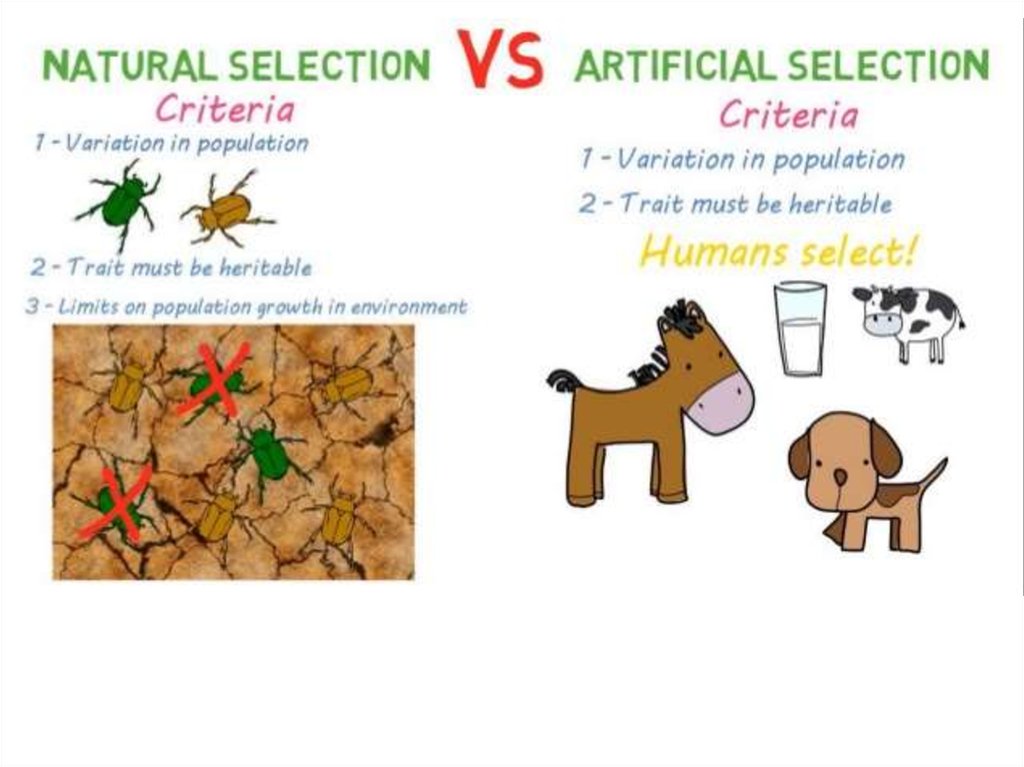
1. Evolution: Artificial Selection
Learning Objective11.2.5.1 Explore ways to improve agricultural plants and animals using the methods of breeding.
Success Criteria
1.
Define hybrid, inbreeding and outbreeding
2.
Identify two plants and explain how they have been bred to increase certain traits (mustard plant –
cauliflower – flowers, and stems celery)
3.
Identify two animals and explain how they have been bred to increase certain traits (cow – milk,
meat)
2.
3.
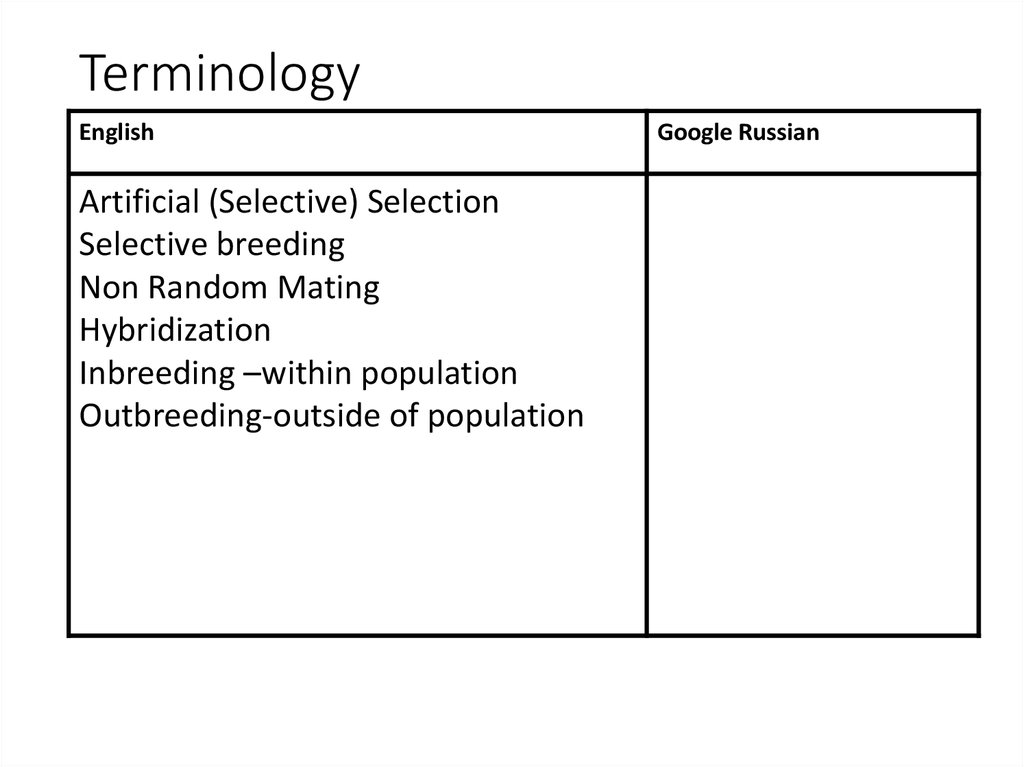
4. Terminology
EnglishArtificial (Selective) Selection
Selective breeding
Non Random Mating
Hybridization
Inbreeding –within population
Outbreeding-outside of population
Google Russian
5.
6.
7.
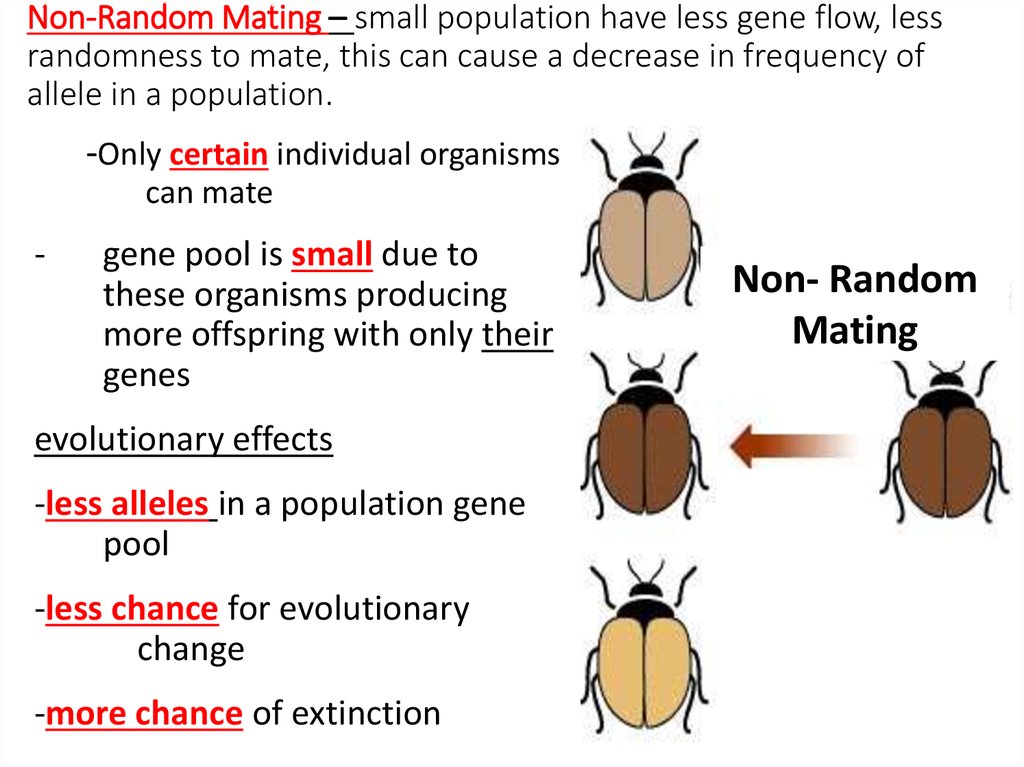
8. Non-Random Mating – small population have less gene flow, less randomness to mate, this can cause a decrease in frequency of
allele in a population.-Only certain individual organisms
can mate
-
gene pool is small due to
Random
these organisms producing
Mating
more offspring with only their
genes
Non- Random
Mating
evolutionary effects
-less alleles in a population gene
pool
-less chance for evolutionary
change
-more chance of extinction
8
9.
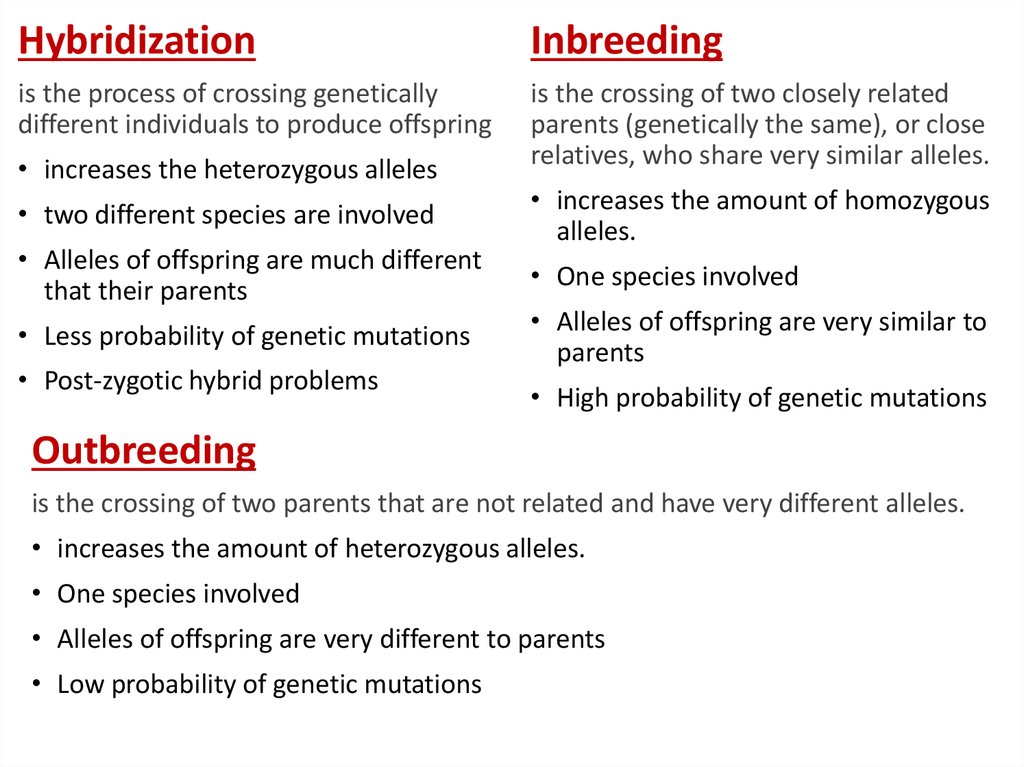
HybridizationInbreeding
is the process of crossing genetically
different individuals to produce offspring
is the crossing of two closely related
parents (genetically the same), or close
relatives, who share very similar alleles.
• increases the heterozygous alleles
• two different species are involved
• Alleles of offspring are much different
that their parents
• Less probability of genetic mutations
• Post-zygotic hybrid problems
• increases the amount of homozygous
alleles.
• One species involved
• Alleles of offspring are very similar to
parents
• High probability of genetic mutations
Outbreeding
is the crossing of two parents that are not related and have very different alleles.
• increases the amount of heterozygous alleles.
• One species involved
• Alleles of offspring are very different to parents
• Low probability of genetic mutations
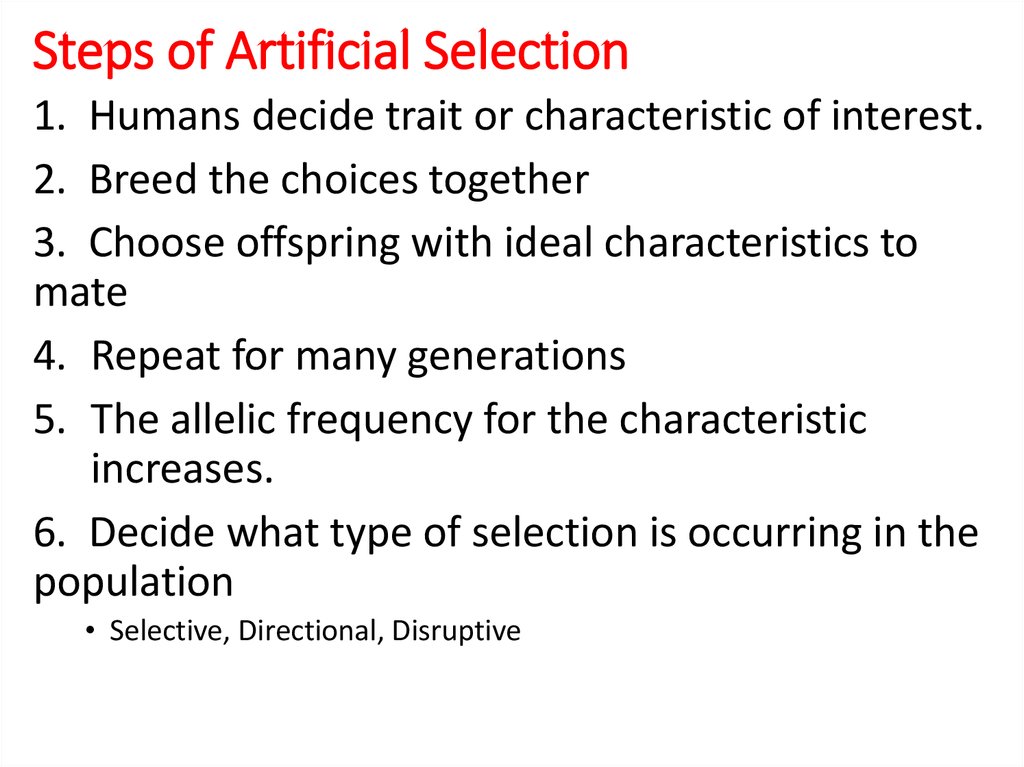
10. Steps of Artificial Selection
1. Humans decide trait or characteristic of interest.2. Breed the choices together
3. Choose offspring with ideal characteristics to
mate
4. Repeat for many generations
5. The allelic frequency for the characteristic
increases.
6. Decide what type of selection is occurring in the
population
• Selective, Directional, Disruptive
11.
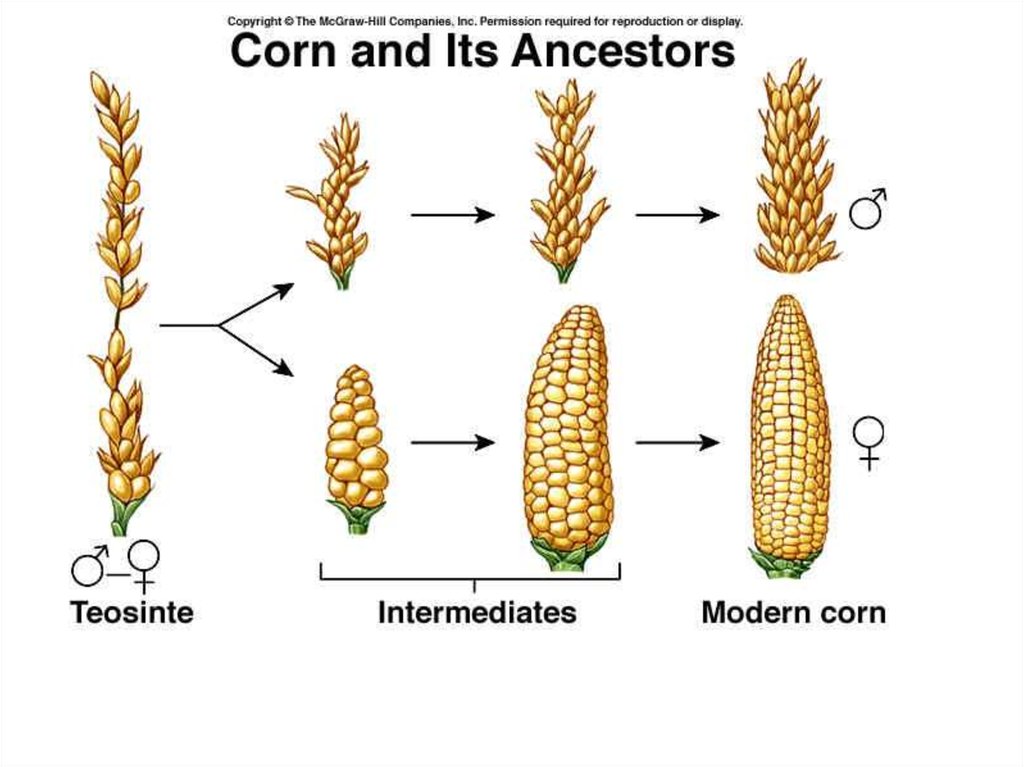
The evolution of corn by Artificial Selection12.
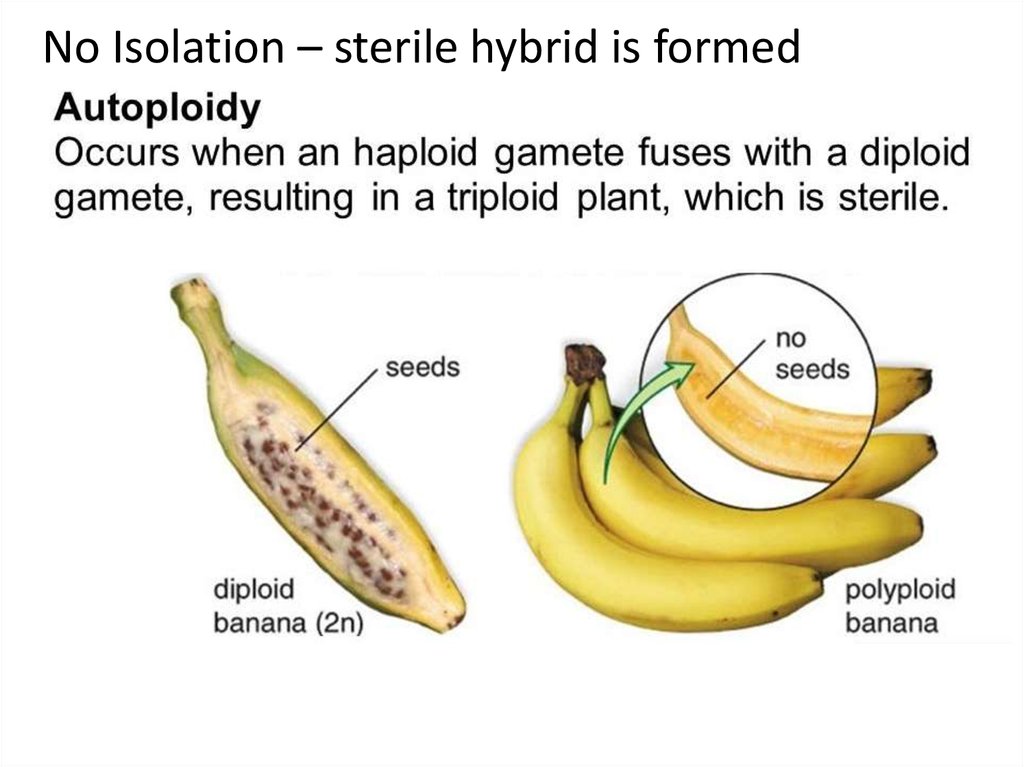
13. Artificial Selection – hybrid Banana’s that have been bred until they have no seeds. All bananas are CLONES! Low genetic
variation less success…..In contrast to natural
selection artificial selection
is intentional breeding or organisms for
certain favorable traits, or combination
of traits.
14.
No Isolation – sterile hybrid is formed15.
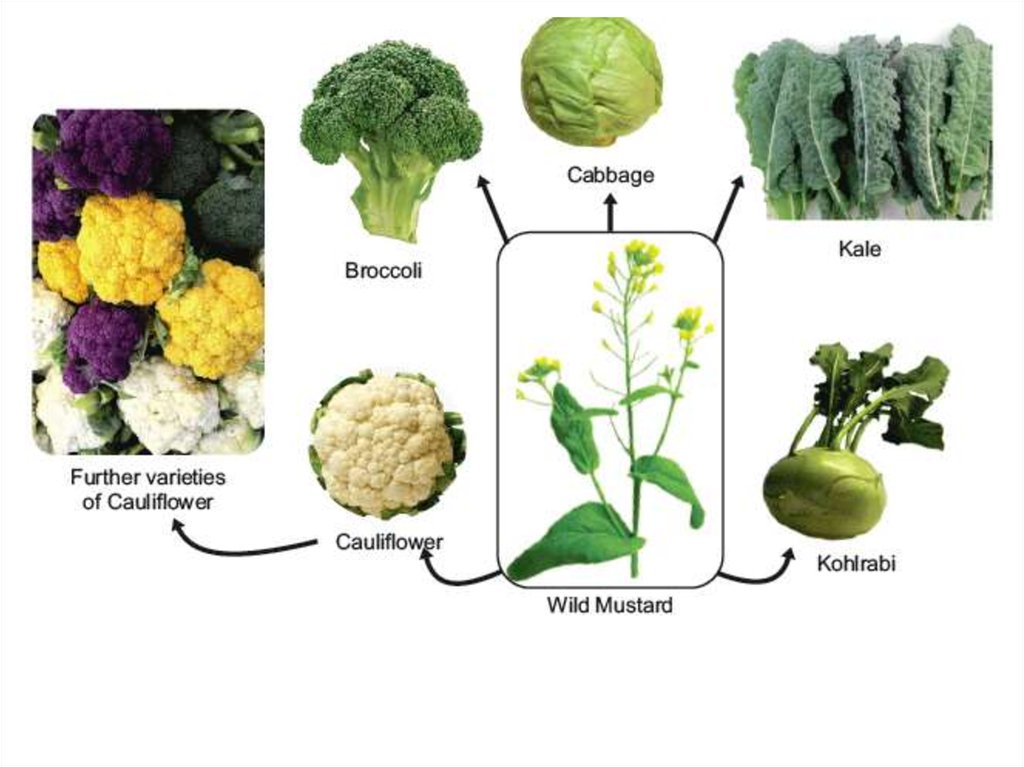
These were all created by Artificial SelectionFrom this plant.
Wild mustard
Sinapis arvensis
HOW?
16.
17.
ArtificialBroccoli: Flower
development is
suppressed
Selection
Cabbage: selection for
the terminal bud (head
only forms)
Cauliflower: flowers
are sterile
In contrast to natural selection this is the
intentional breeding or organisms for
certain favorable traits, or ombination of
traits.
Kale: selection is for
leaves only
Undomesticated
banana-lots of
seeds compared
to artificially
selected with
little to no seeds
17
18.
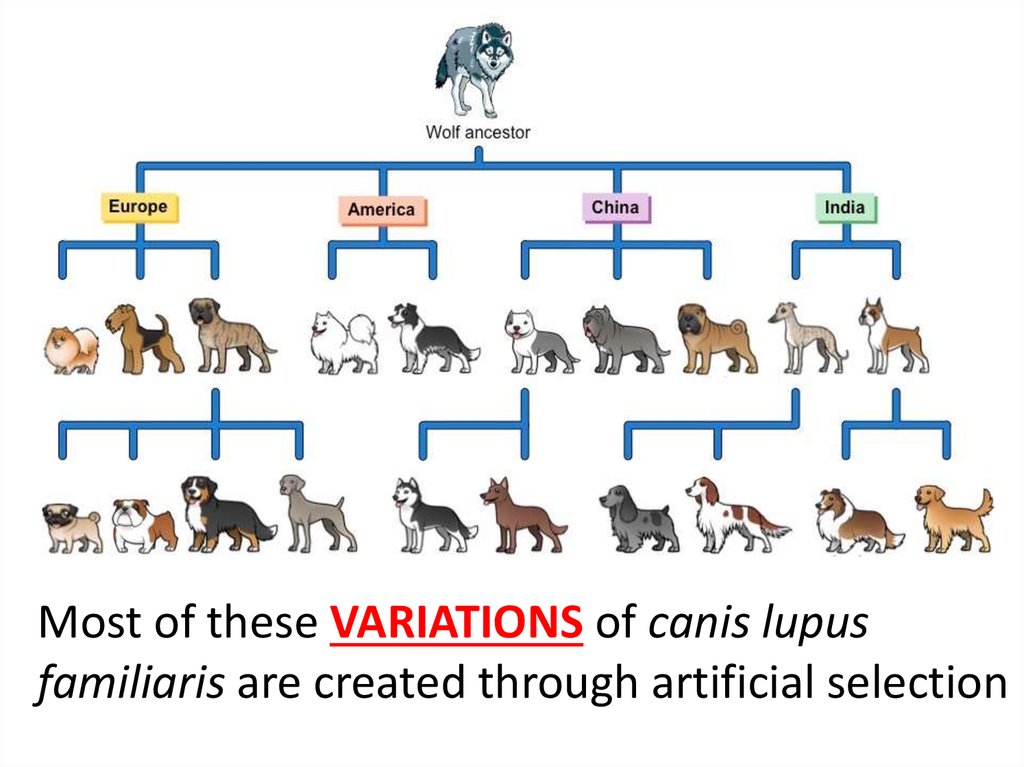
Most of these VARIATIONS of canis lupusfamiliaris are created through artificial selection
19.
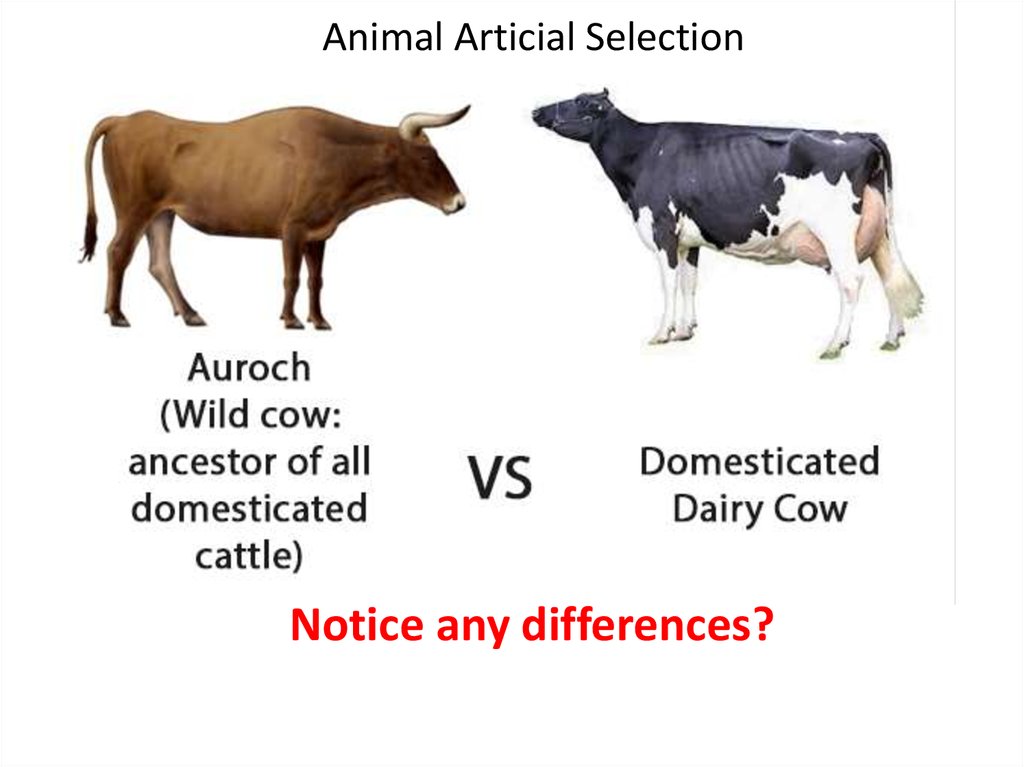
Animal Articial SelectionNotice any differences?
20.
21. Belgian Blue cattle ... they have a mutation that creates twice the muscle tissue. Calves are so big that Caesarian births are
standard.22.
1. How as artificial selection improved these cows?2. Is it an improvement that the cow would be ‘selected’ for if
released into the wild?
3. Reproductive success?
23.
What traitwas
artificially
selected for
in this cow?
24.
Success Criteria1. Define hybrid, inbreeding and outbreeding
2. Identify two plants and explain how they
have been bred to increase certain traits
(mustard plant , corn)
3. Identify two animals and explain how they
have been bred to increase certain traits (cow –
milk, meat)
25. Choose One to Investigate
11.2.5.1 Explore ways to improve agricultural plants and animals using the methods of breedingChoose One to Investigate
Crop Plants
• Wheat
• Millet
• Carrots
• Potatoes
• Broccoli
Animals
• Horses
• Sheep
• Goats
• Cattle
• Dogs
• Cats
26.
Make 1-2 slide presentation that clearlyinvestigates artificial selection
You are investigating inbreeding and hybrids as method of artificial
selection, not genetic engineering or Genetically Modified
Organisms (GMO)
Criteria
√ Name the trait that was selected.
√ Tell why the trait was selected
√ Clear use of terminology explaining the mechanism.
√ Picture of before artificial selection and after artificial
selection.
√
Work shows understanding of differences between the two
types of artificial selection.















 biology
biology








