Similar presentations:
Structure of a lesson
1. structure of a lesson
STRUCTURE OF A LESSONAnna N. Kondakova
2. Aims of today’s session:
Look at different lesson componentsShare ideas to start lessons effectively
Discuss inductive and deductive teaching
Explain rationales behind different types of
practice activities
• Self-study: Look at how different types of
lessons are organized
3. Finish these metaphors for lessons:
A good lesson is like a film because ...A good lesson is like a football match
because ...
A good lesson is like a meal because ...
A good lesson is like a symphony because
...
4.
• Every effective lesson plan should build towardthe achievement of the objective and connect
to long-term instructional goals
• “I do, we do, you do” approach
• Five Step Lesson Plan
5. 5-Step Lesson Structure
6.
Okay class, openyour books to page
321 and begin
reading the text.
When you finish, do
tasks 3 through 11.
Any questions?
7. Opening procedures may include…
• Signaling attention• Describe the goals of the lesson
• Inform students about the
knowledge and skills they will
acquire
• Explain how this information relates
to previous class, life outside class,
and bigger world
• Explain what students are
expected to do in class, including
rules and teacher expectations
• Describe the relationship of the
lesson with the forthcoming test or
exam
• Provides an opportunity to review
the previous lesson
• Helps assess knowledge and skills
relevant to the current lesson
• …
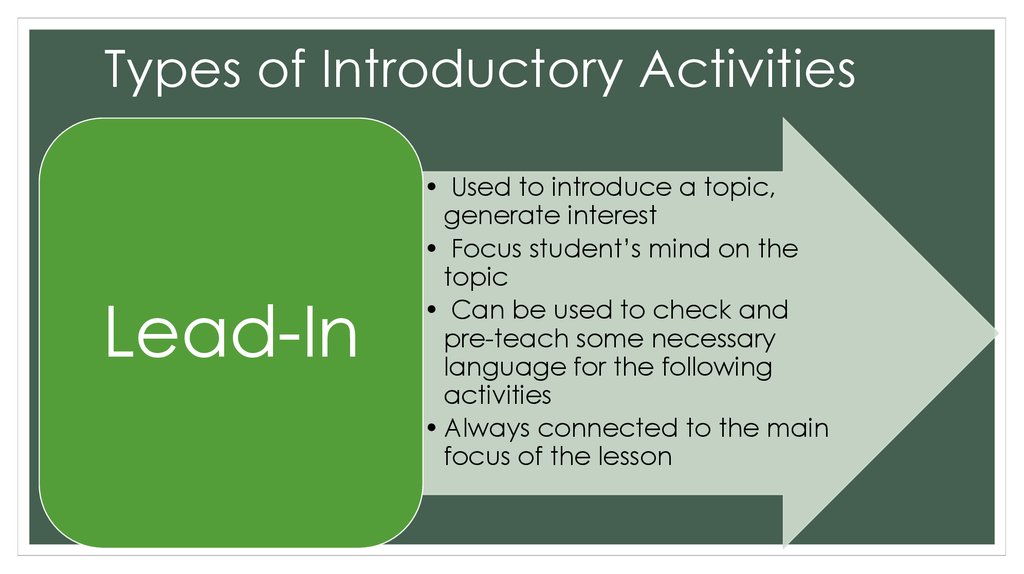
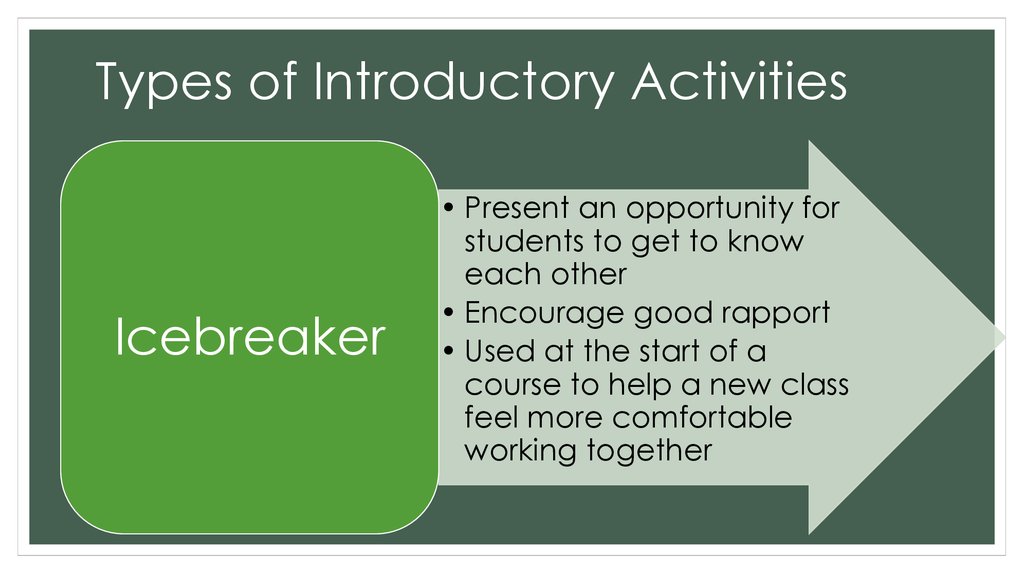
8. Types of Introductory Activities
Lead-insWarmers
Icebreakers
9. Types of Introductory Activities
Lead-In• Used to introduce a topic,
generate interest
• Focus student’s mind on the
topic
• Can be used to check and
pre-teach some necessary
language for the following
activities
• Always connected to the main
focus of the lesson
10. Types of Introductory Activities
Warmer(or warmups)
•Give class more energy at
the start of a lesson
•Encourage
communication
•Typically ‘stand alone’
activities and are outside
the main flow of the lesson
•Group-building rather then
linguistic
11. Types of Introductory Activities
Icebreaker• Present an opportunity for
students to get to know
each other
• Encourage good rapport
• Used at the start of a
course to help a new class
feel more comfortable
working together
12. Type of introductory activity?
1. Teacher gets each student to write threestatements about themselves. Two statements are
true, while one is false. Each student reads their
three statements to the class and the rest of the
class guess which statement isn’t true.
2. Teacher commands drills in a funny way (e.g.
Stand up. Sit down. Hold up your right hand. Show
me your pen….)
13.
3. Teacher puts a quote on the wall. The quotereads: “All you need is love. But a little chocolate
now and then “doesn't hurt.” Charles M. Schulz”. T
asks the students how they feel about the quote
(Do you agree or disagree with this statement?)
4. Teacher writes a long word on the board (e.g.
CONSTITUTION) and asks students to provide
words using the letters of the word on the board.
14.
5. Each student divides the sheet into foursquares. For each square, each person will
describe themselves in the form of drawings. They
could be asked to draw “favorite hobbies,”
“favorite place on earth for vacation,” “if you
were an animal, which one would you be?” and
“what are the most important things in your life?”
When everyone is finished drawing, T gathers
them together to share the drawings as a group.
15.
6. The learners are going to read a text about computers inthe lesson. The teacher asks them to change their seating
and sit down in an order based on how much they use a
computer. This requires them to move around and talk to
each other.
7. Teacher gives out several strips with sentence parts from a
text. Students have to put the sentences in the correct order
individually, in pairs or small groups. After students assemble
the scrambled sentences in order and there is a class
consensus on the correct order, T ask students what they think
the reading will be about.
16.
8. Teacher gives each learner a sheet with a seriesof 'Find someone who…' statements, e.g. 'Find
someone who has a cat'. Learners circulate around
the class and complete the statements with names.
9. Teacher puts a picture of a family on the board.
She begins by stating, “What do you see,” then asks
a more specific question, such as “What problems
do you see in this picture?” “Why is this boy sad?”
17. Three teachers’ lesson starts
THREE TEACHERS’LESSON STARTS
• What strategies of lesson opening do they use?
• What works well?
• What would you do differently?
18. Effective lesson starts
• Lesson opening should be relevant to the topic you arestudying
• Hook the students attention at once
• Consider quiet or energizing lesson starts depending on
the energy in the group
• Activate Ss experience and previous knowledge
• Think carefully about the type of lesson start and timing
• Use pictorial prompts, realia, anecdotes, personal stories
with care!
19. Instruction
INSTRUCTION20. Inductive teaching
SS are exposed to newlanguage through a
set of examples
SS have to discover
language or rule
SS apply rules in a
series of activities
•T gives SS a text to read and
respond to.
•T asks SS to identify all the
conjunctions in the text
•SS produce their own examples
to demonstrate the use of
conjunctions
21. Advantages of inductive teaching
• It is student-centered• It is authentic
• It stimulates learner autonomy
• The action of discovery helps learners retain more
information
• It fosters communication in class
• It responds better to SS needs and encourages use of
various learning strategies and styles
22. Any disadvantages?
• Can require more class-time• SS may need to be introduced into such
kind of teaching
• May not be appropriate for all SS and
especially administration
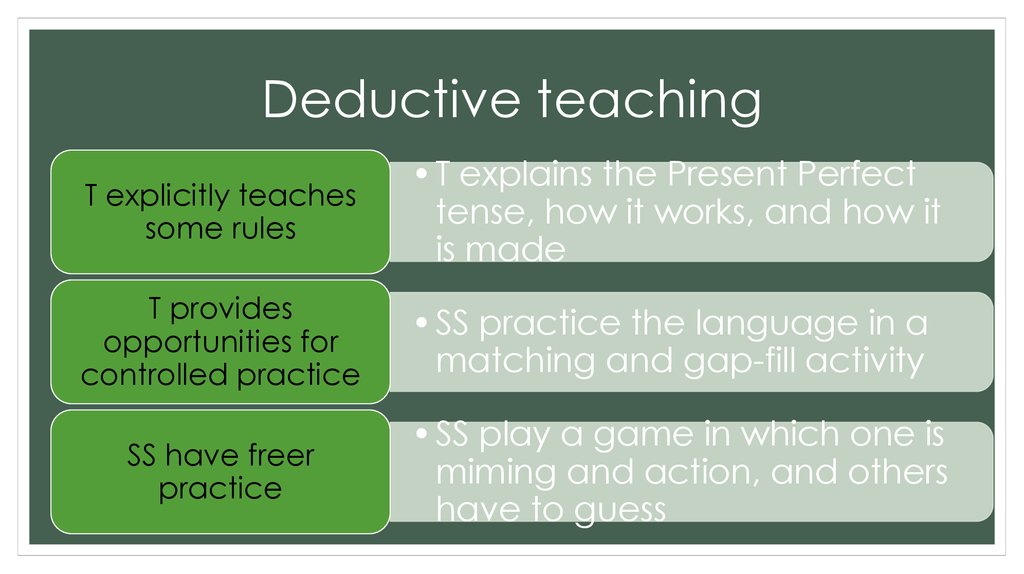
23. Deductive teaching
T explicitly teachessome rules
•T explains the Present Perfect
tense, how it works, and how it
is made
T provides
opportunities for
controlled practice
•SS practice the language in a
matching and gap-fill activity
SS have freer
practice
•SS play a game in which one is
miming and action, and others
have to guess
24. Advantages of deductive teaching
• It can meet student expectations• It is more ‘teacher-friendly’ (T controls the
input)
• A more efficient use of time
• Complies with many coursebooks and
syllabuses
25. Any disadvantages?
• It is teacher-centered• It does not provide room for learner
autonomy
• It can be boring
26. Video
• Watch two teachers presenting instructionto their learners.
• Say which is an example of inductive and
deductive teaching.
• Watch Teacher 3 – what kind of approach
is used?
27. Types of lessons
Reading skills lessons
Listening skills lessons
Writing skills lessons
Speaking skills lessons
Grammar lessons
28.
Making reading communicativehttps://www.teachingenglish.org.uk/article/makingreading-communicative
A framework for planning a listening skills lesson at
http://www.teachingenglish.org.uk/comment/18920
Planning a writing lesson
https://www.teachingenglish.org.uk/article/planning
-a-writing-lesson
29.
Planning a grammar lessonhttp://www.teachingenglish.org.uk/article/planning
-a-grammar-lesson
Improving Adult English Language Learners'
Speaking Skills
http://www.cal.org/caela/esl_resources/digests/Sp
eak.html
Stages of a speaking lesson
https://www.professorjackrichards.com/stagesspeaking-lesson/



























 english
english pedagogy
pedagogy








