Similar presentations:
Background radiation
1.
Background radiation2.
Sources of radiationNatural background radiation is due to radiation of natural
radionuclides of the Earth and cosmic radiation.
Technologically modified natural background radiation is formed from
natural sources of ionizing radiation, for example radiation scattered
in the environment of natural radionuclides.
Artificial background radiation - the global pollution of the environment
by artificial radionuclides formed in the fission of nuclei of uranium
and plutonium. This background is due to testing of nuclear
weapons, in part by emissions from nuclear power plants noble
gases, carbon, and tritium. Artificial background radiation in the
globe on average is 1-3% of natural background radiation.
3.
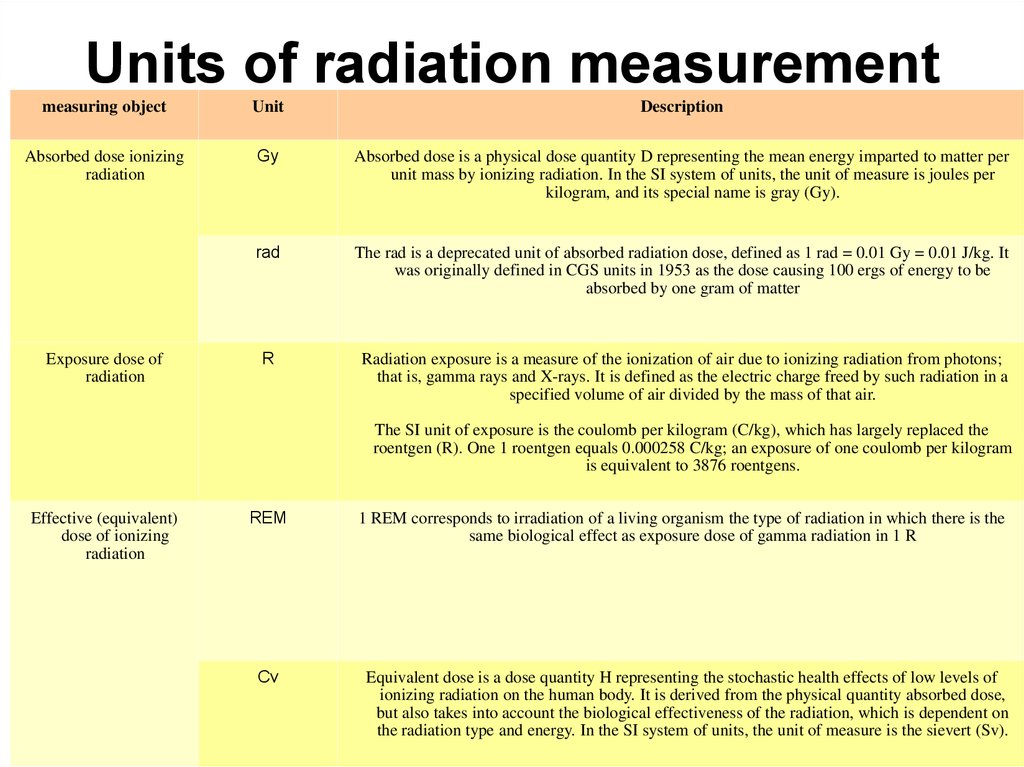
Units of radiation measurementmeasuring object
Unit
Description
Absorbed dose ionizing
radiation
Gy
Absorbed dose is a physical dose quantity D representing the mean energy imparted to matter per
unit mass by ionizing radiation. In the SI system of units, the unit of measure is joules per
kilogram, and its special name is gray (Gy).
rad
The rad is a deprecated unit of absorbed radiation dose, defined as 1 rad = 0.01 Gy = 0.01 J/kg. It
was originally defined in CGS units in 1953 as the dose causing 100 ergs of energy to be
absorbed by one gram of matter
R
Radiation exposure is a measure of the ionization of air due to ionizing radiation from photons;
that is, gamma rays and X-rays. It is defined as the electric charge freed by such radiation in a
specified volume of air divided by the mass of that air.
Exposure dose of
radiation
The SI unit of exposure is the coulomb per kilogram (C/kg), which has largely replaced the
roentgen (R). One 1 roentgen equals 0.000258 C/kg; an exposure of one coulomb per kilogram
is equivalent to 3876 roentgens.
Effective (equivalent)
dose of ionizing
radiation
REM
Cv
1 REM corresponds to irradiation of a living organism the type of radiation in which there is the
same biological effect as exposure dose of gamma radiation in 1 R
Equivalent dose is a dose quantity H representing the stochastic health effects of low levels of
ionizing radiation on the human body. It is derived from the physical quantity absorbed dose,
but also takes into account the biological effectiveness of the radiation, which is dependent on
the radiation type and energy. In the SI system of units, the unit of measure is the sievert (Sv).
4.
Radiation accidentViolation of the rules of safe operation of nuclear power installations,
equipment or device, in which there has been a release of radioactive
products or ionizing radiation provided by the project limits for their safe
operation, leading to exposure of the population and environmental
pollution.
nuclear power plant;
enterprise for nuclear fuel production, reprocessing and disposal of nuclear
waste;
research and other companies with nuclear installations and stands;
nuclear transport power systems (including space vehicles);
military facilities.
5.
International Nuclear Event ScaleThe International Nuclear and Radiological Event Scale (INES) was introduced in 1990 by the
International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) in order to enable prompt communication of safetysignificant information in case of nuclear accidents.
The scale is intended to be logarithmic, similar to the moment magnitude scale that is used to
describe the comparative magnitude of earthquakes. Each increasing level represents an accident
approximately ten times more severe than the previous level. Compared to earthquakes, where
the event intensity can be quantitatively evaluated, the level of severity of a man-made disaster,
such as a nuclear accident, is more subject to interpretation. Because of the difficulty of
interpreting, the INES level of an incident is assigned well after the incident occurs. Therefore, the
scale has a very limited ability to assist in disaster-aid deployment.
As INES ratings are not assigned by a central body, high-profile nuclear incidents are sometimes
assigned INES ratings by the operator, by the formal body of the country, but also by scientific
institutes, international authorities or other experts which may lead to confusion as to the actual
severity.
A number of criteria and indicators are defined to assure coherent reporting of
nuclear events by different official authorities. There are seven nonzero levels on the
INES scale: three incident-levels and four accident-levels. There is also a level 0.
6.
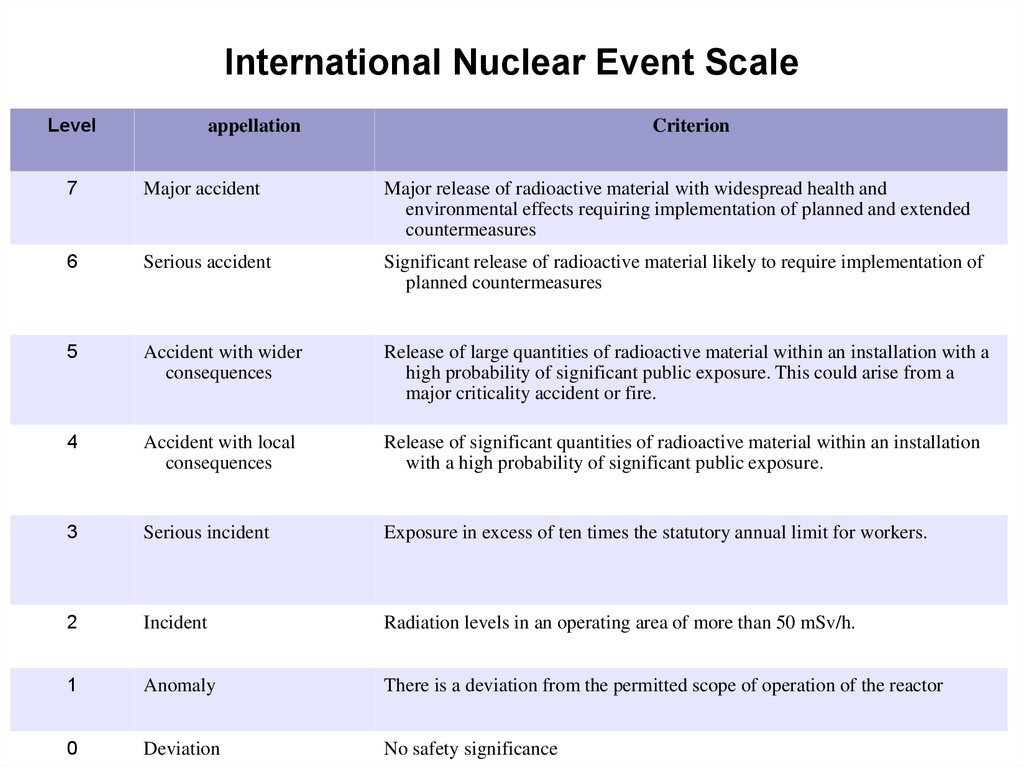
International Nuclear Event ScaleLevel
appellation
Criterion
7
Major accident
Major release of radioactive material with widespread health and
environmental effects requiring implementation of planned and extended
countermeasures
6
Serious accident
Significant release of radioactive material likely to require implementation of
planned countermeasures
5
Accident with wider
consequences
Release of large quantities of radioactive material within an installation with a
high probability of significant public exposure. This could arise from a
major criticality accident or fire.
4
Accident with local
consequences
Release of significant quantities of radioactive material within an installation
with a high probability of significant public exposure.
3
Serious incident
Exposure in excess of ten times the statutory annual limit for workers.
2
Incident
Radiation levels in an operating area of more than 50 mSv/h.
1
Anomaly
There is a deviation from the permitted scope of operation of the reactor
0
Deviation
No safety significance
7.
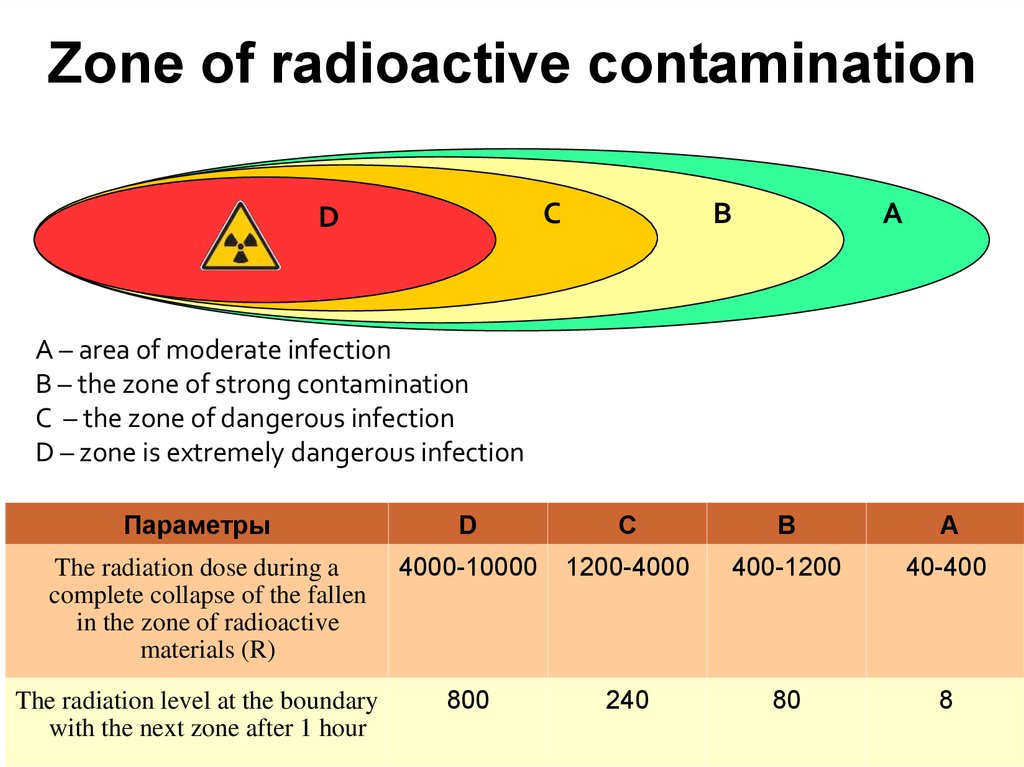
Zone of radioactive contaminationC
D
B
A
A – area of moderate infection
B – the zone of strong contamination
C – the zone of dangerous infection
D – zone is extremely dangerous infection
Параметры
The radiation dose during a
complete collapse of the fallen
in the zone of radioactive
materials (R)
The radiation level at the boundary
with the next zone after 1 hour
D
C
B
А
4000-10000
1200-4000
400-1200
40-400
800
240
80
8
8.
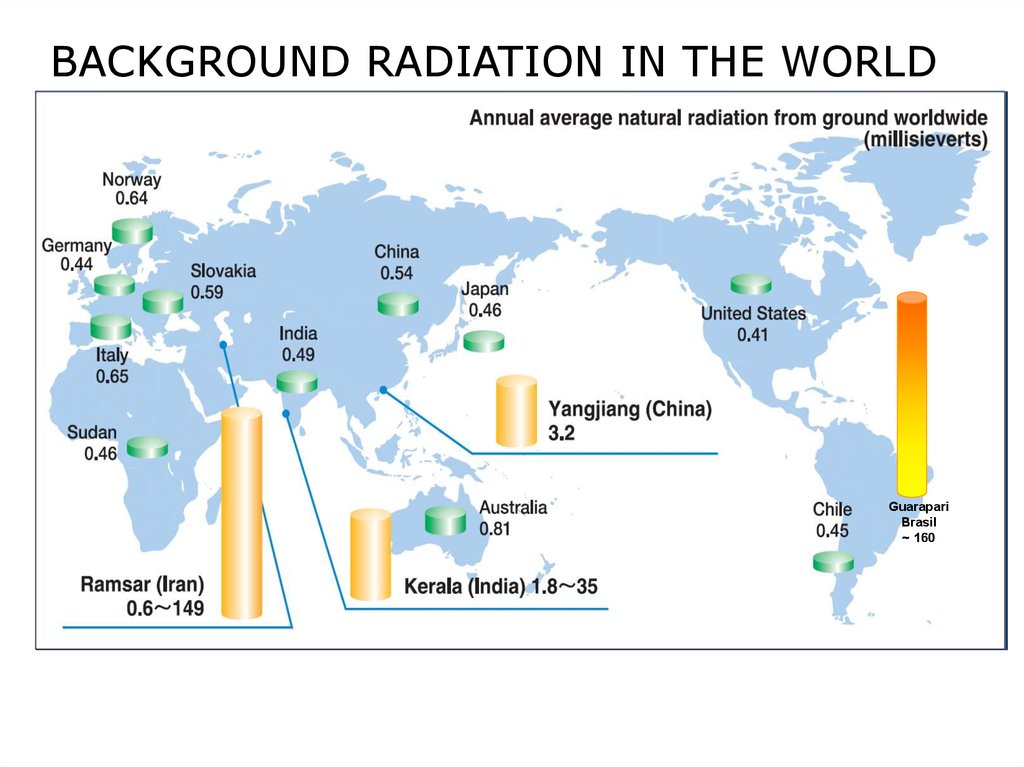
BACKGROUND RADIATION IN THE WORLDGuarapari
Brasil
~ 160
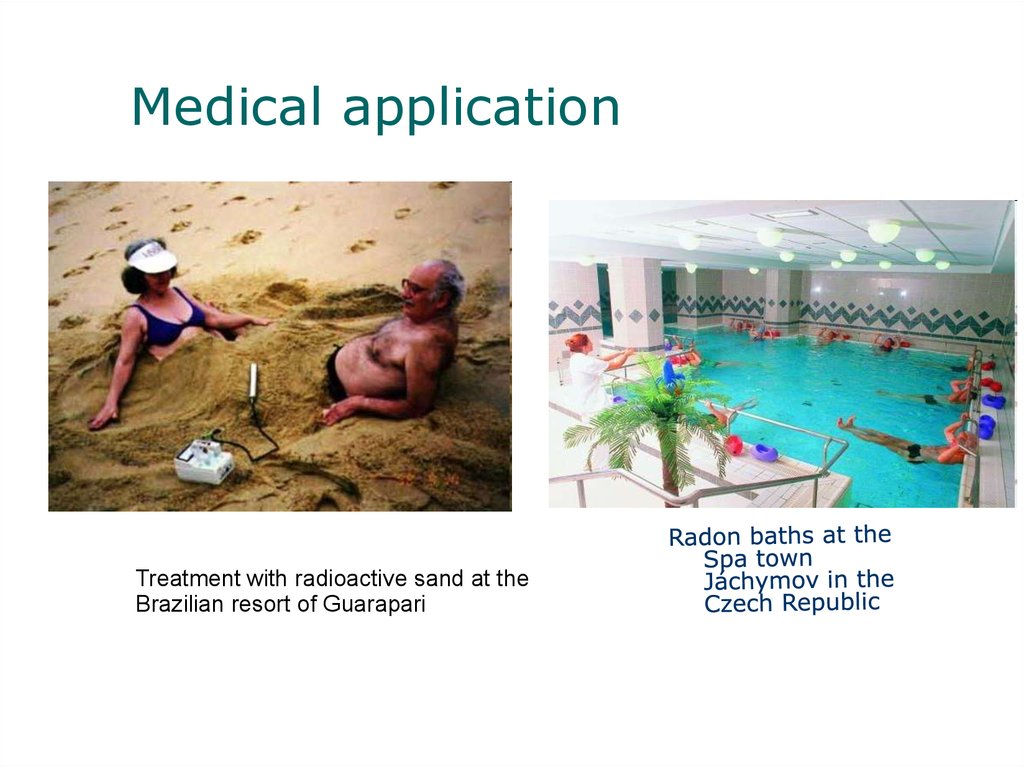
9.
Medical applicationTreatment with radioactive sand at the
Brazilian resort of Guarapari
10.
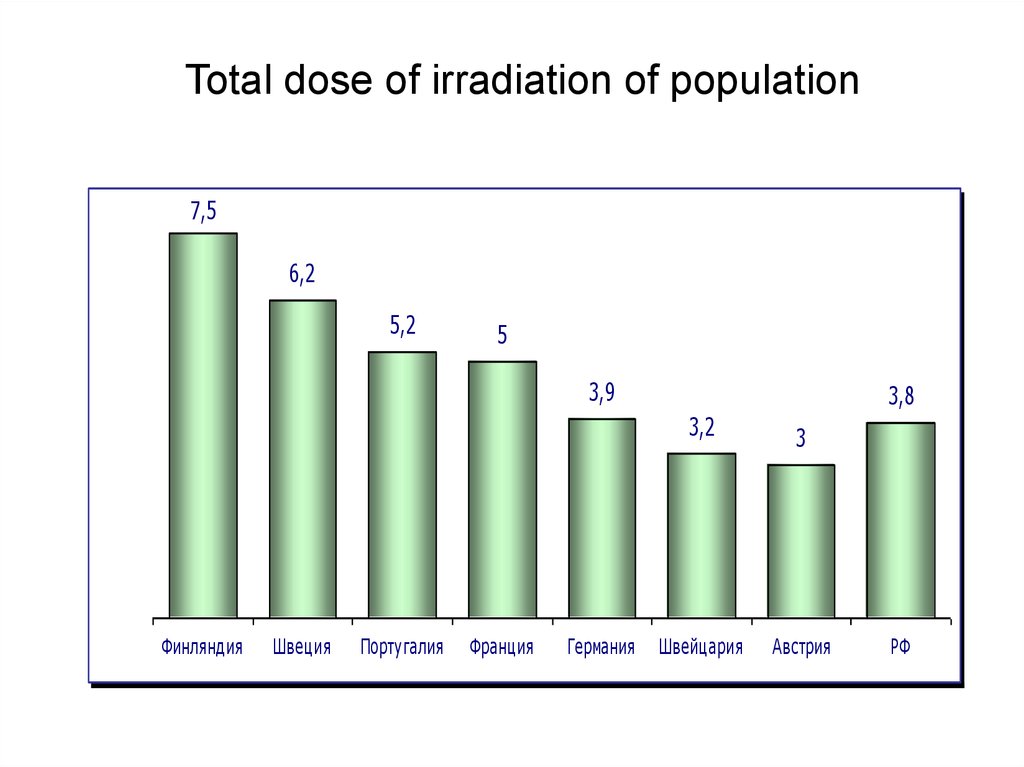
Total dose of irradiation of population7,5
6,2
5,2
5
3,9
3,8
3,2
Финляндия
Швеция
Португалия
Франция
Германия
Швейцария
3
Австрия
РФ
11.
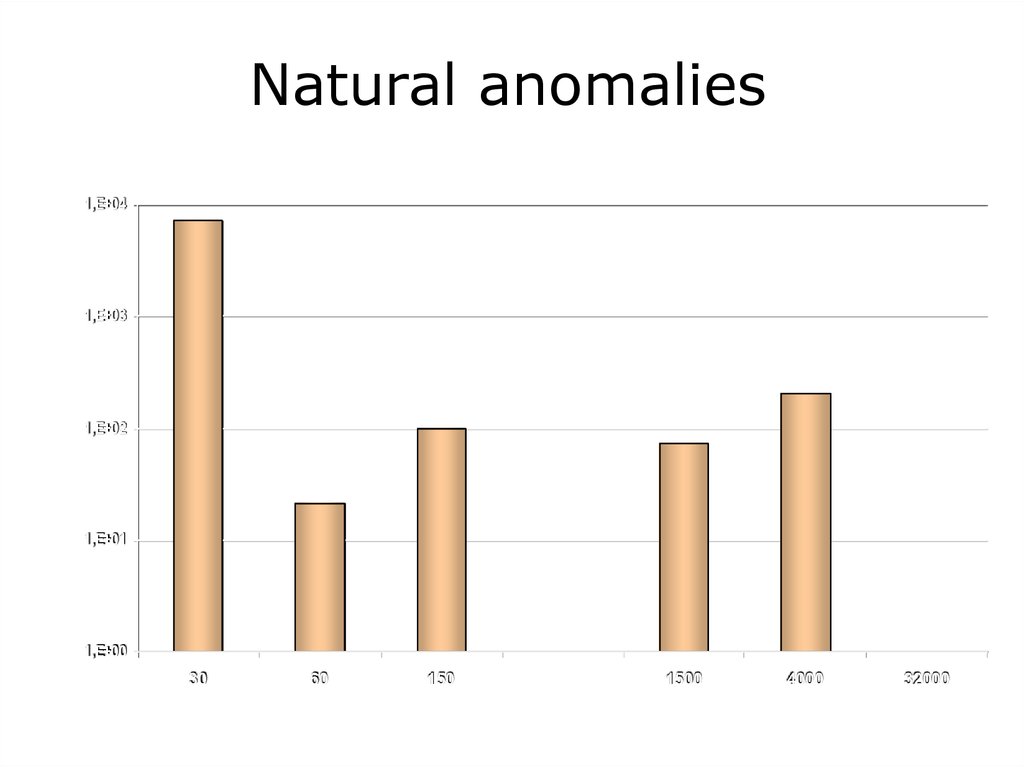
Natural anomalies1,E+04
1,E+03
1,E+02
1,E+01
1,E+00
30
60
150
1500
4000
32000
12.
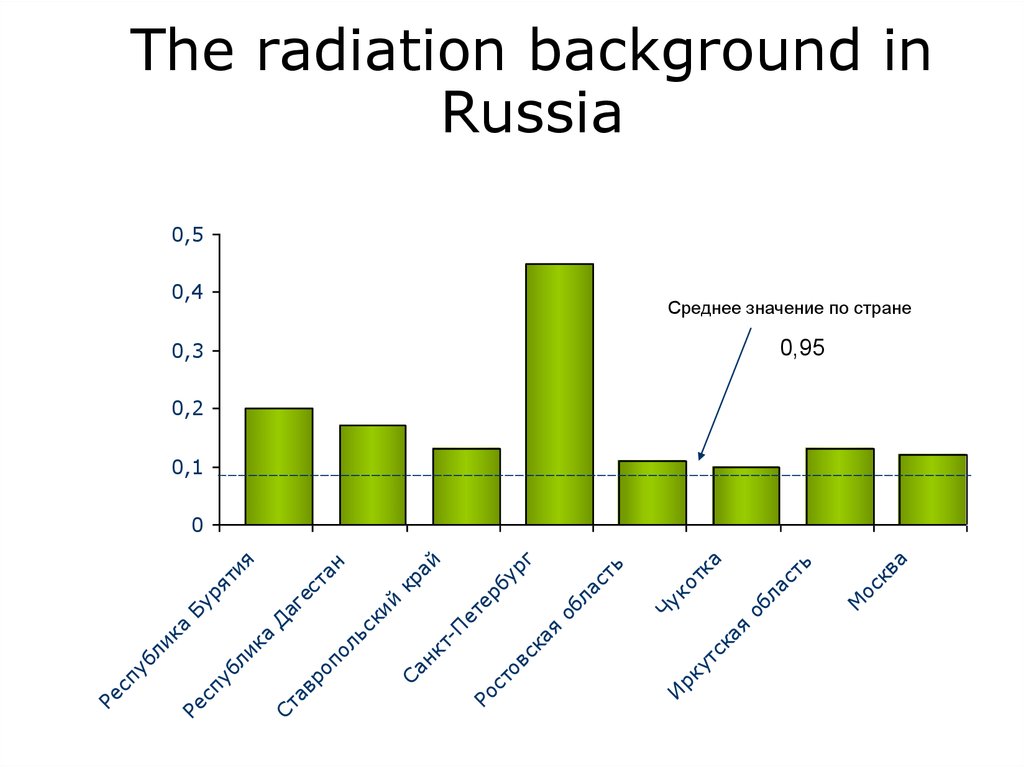
лика
ли
ка
сп
уб
сп
уб
Бу
ря
ти
я
рк
ут
с
ка
я
ос
кв
а
0,3
М
ть
от
ка
об
ла
с
Чу
к
0,4
И
Д
Ст
аг
ав
ес
ро
та
по
н
ль
ск
ий
кр
Са
ай
нк
тП
ет
Ро
ер
ст
бу
ов
рг
ск
ая
об
ла
ст
ь
Ре
Ре
The radiation background in
Russia
0,5
Среднее значение по стране
0,95
0,2
0,1
0




 physics
physics