Similar presentations:
Transmission Media
1.
Chapter 7Transmission Media
長庚大學資訊工程學系 陳仁暉 副教授
Tel: (03) 211-8800 Ext: 5990
Email: jhchen@mail.cgu.edu.tw
URL: http://www.csie.cgu.edu.tw/~jhchen
Copyright © NDSL, Chang Gung University. Permission required for reproduction or display.
2.
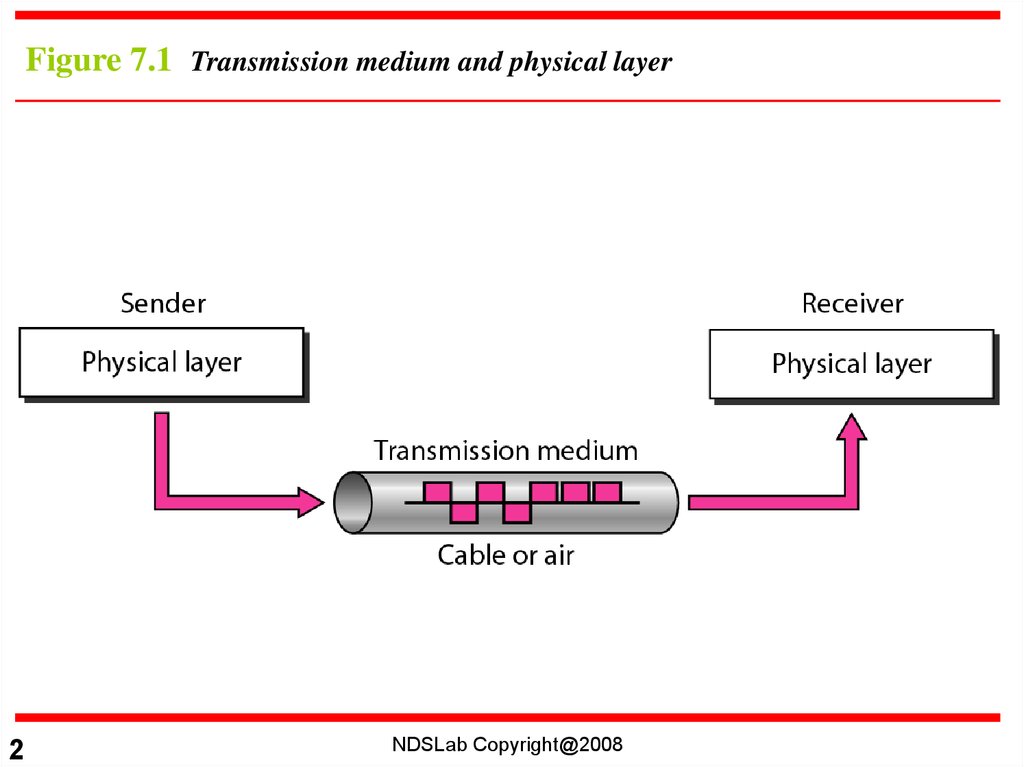
Figure 7.1 Transmission medium and physical layer2
NDSLab Copyright@2008
3.
Transmission Media• By definition
– Broadly defined as anything that can carry information
from a source to a destination.
– e.g., air, twisted-pair cable, coaxial cable, fiber-optic
cable, conductor, and so on.
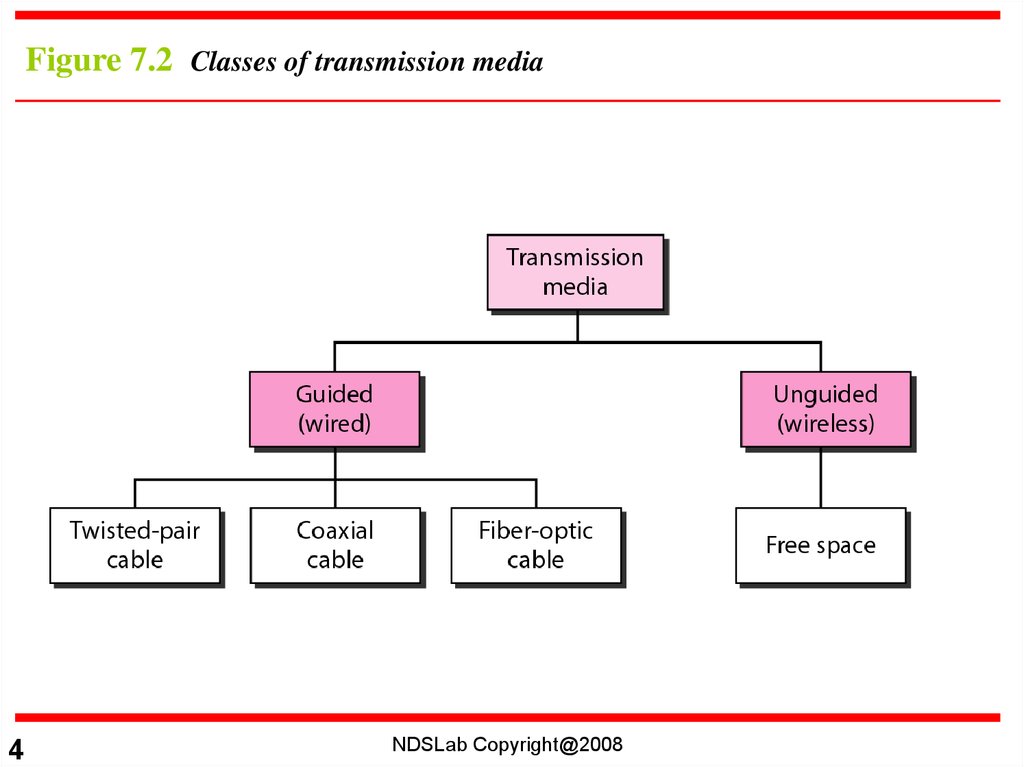
• Guided media
– Provide a conduit from one device to another, include
twisted-pair cable, coaxial cable, and fiber-optic
cable.
3
NDSLab Copyright@2008
4.
Figure 7.2 Classes of transmission media4
NDSLab Copyright@2008
5.
7-1 GUIDED MEDIAGuided media, which are those that provide a conduit
from one device to another, include twisted-pair cable,
coaxial cable, and fiber-optic cable.
Topics discussed in this section:
Twisted-Pair Cable
Coaxial Cable
Fiber-Optic Cable
5
NDSLab Copyright@2008
6.
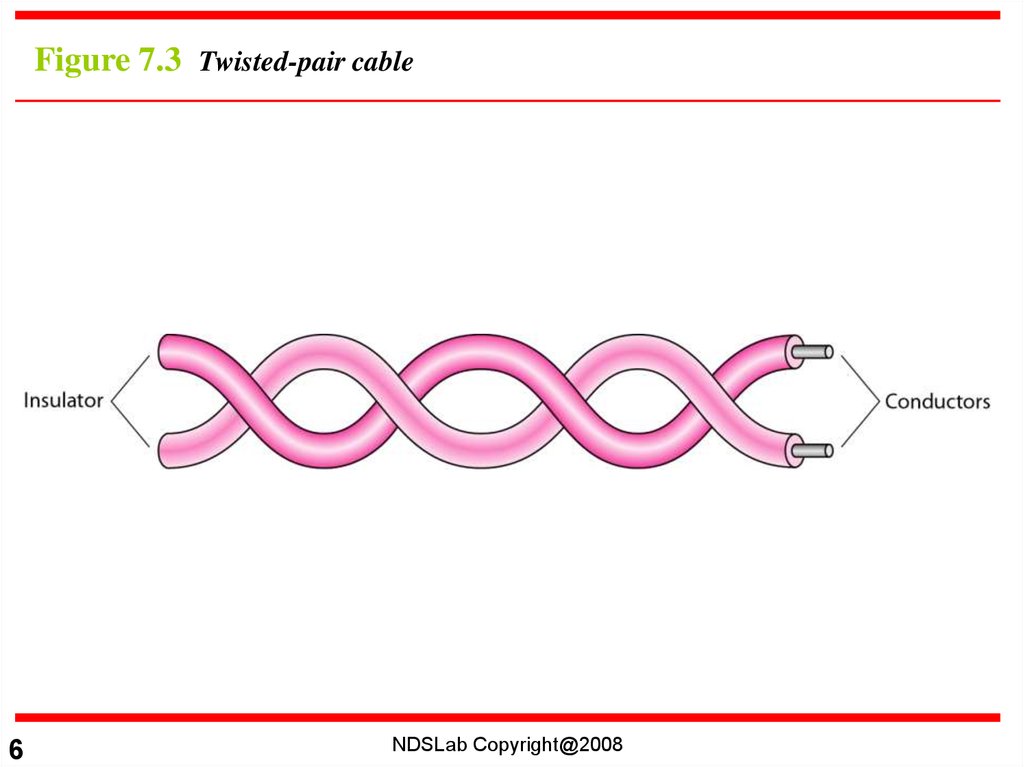
Figure 7.3 Twisted-pair cable6
NDSLab Copyright@2008
7.
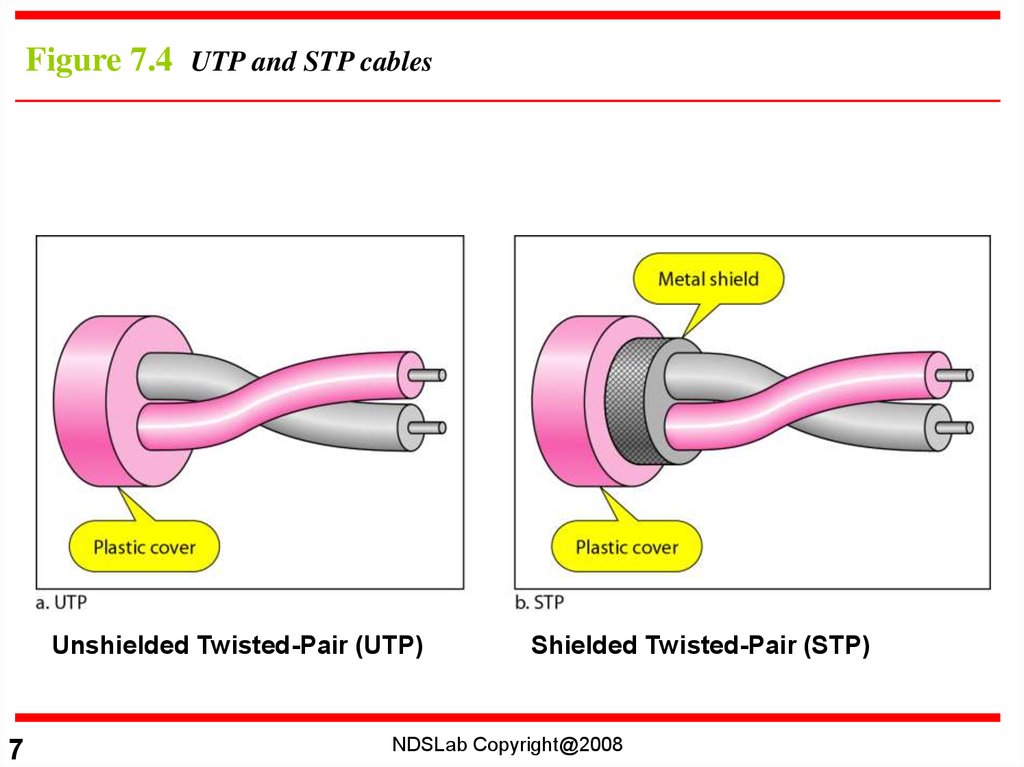
Figure 7.4 UTP and STP cablesUnshielded Twisted-Pair (UTP)
7
Shielded Twisted-Pair (STP)
NDSLab Copyright@2008
8.
Unshielded vs Shielded Twisted-Pair Cable• Unshielded twisted-pair (UTP)
• Shielded twisted-pair (STP)
– Has a metal foil or braided-mesh covering that encases
each pair of insulated conductors.
• Category
– Electronic Industries Association (EIA) has developed
standards to classify unshielded twisted-pair cable into
seven categories. Table 7.1 shows these categories.
• Connectors
– Most common UTP connector is RJ-45 (RJ stands for
registered jack).
8
NDSLab Copyright@2008
9.
Table 7.1 Categories of unshielded twisted-pair cables9
NDSLab Copyright@2008
10.
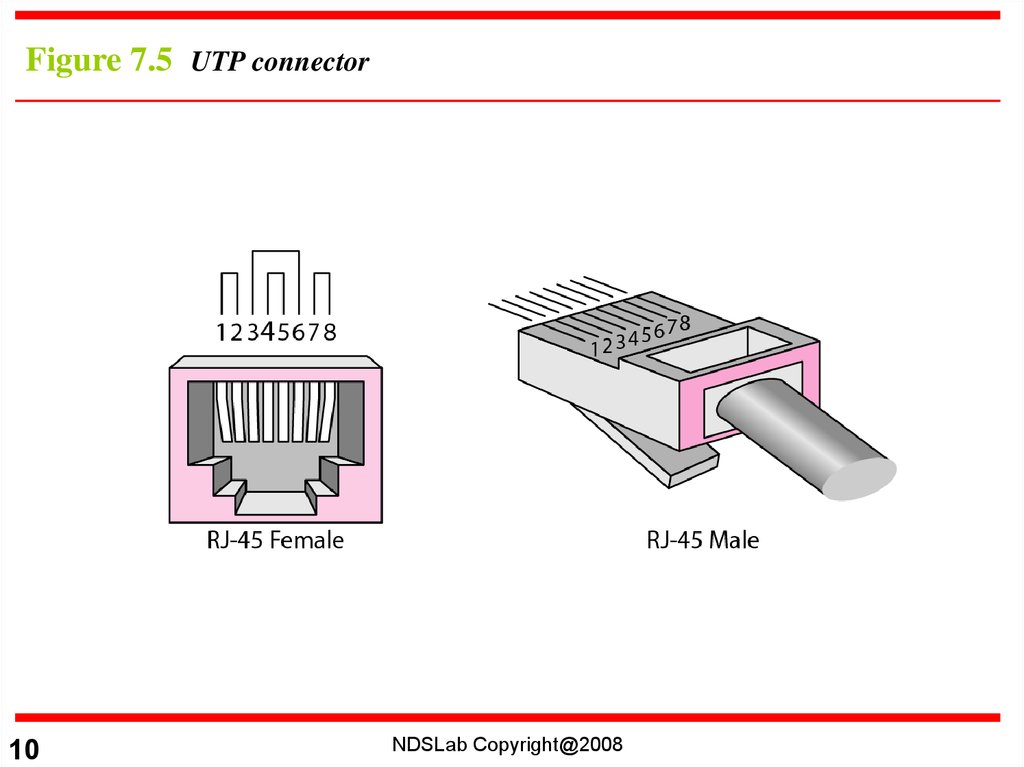
Figure 7.5 UTP connector10
NDSLab Copyright@2008
11.
Figure 7.6 UTP performanceGauge is a measure of the thickness of the wire.
11
NDSLab Copyright@2008
12.
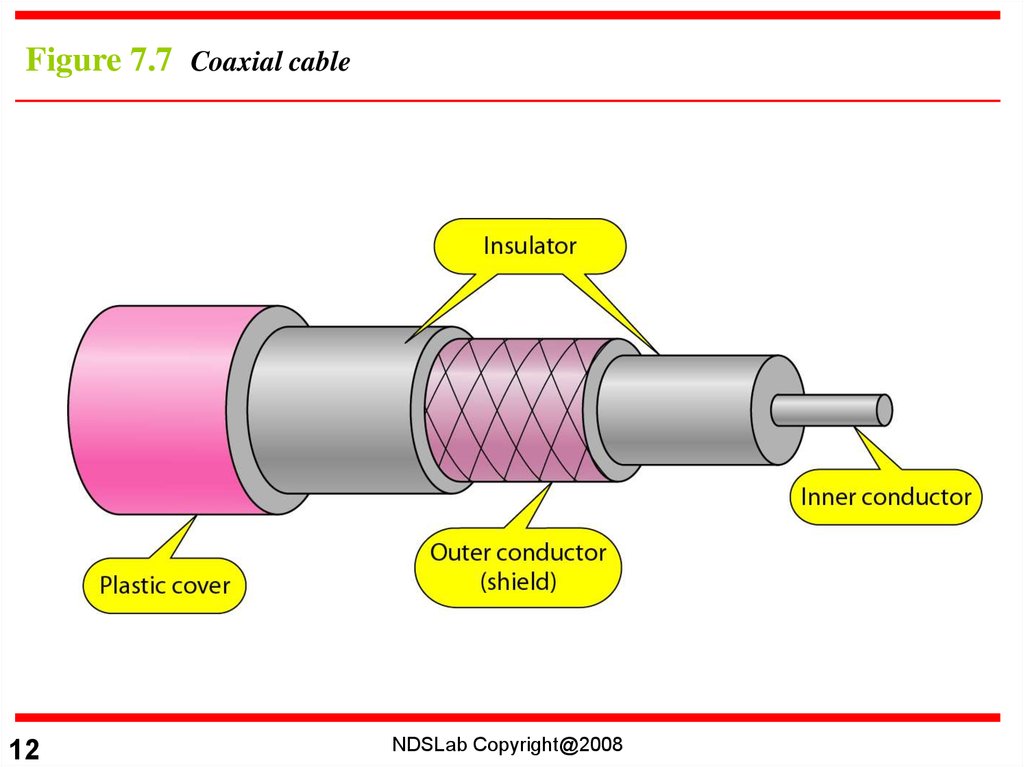
Figure 7.7 Coaxial cable12
NDSLab Copyright@2008
13.
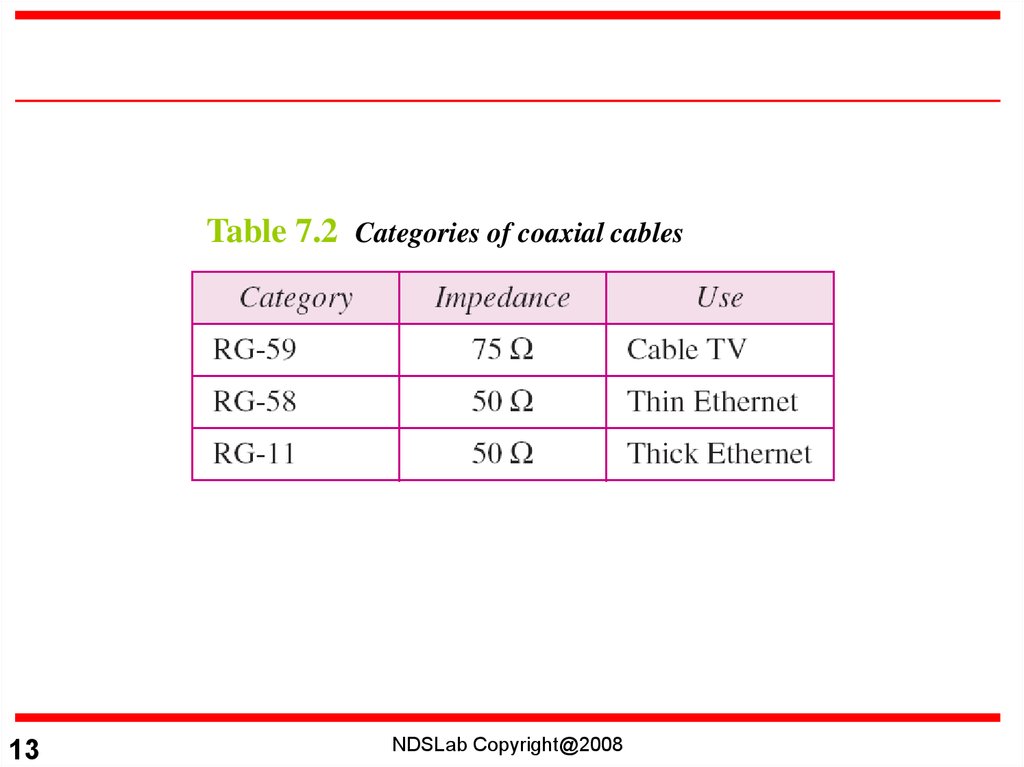
Table 7.2 Categories of coaxial cables13
NDSLab Copyright@2008
14.
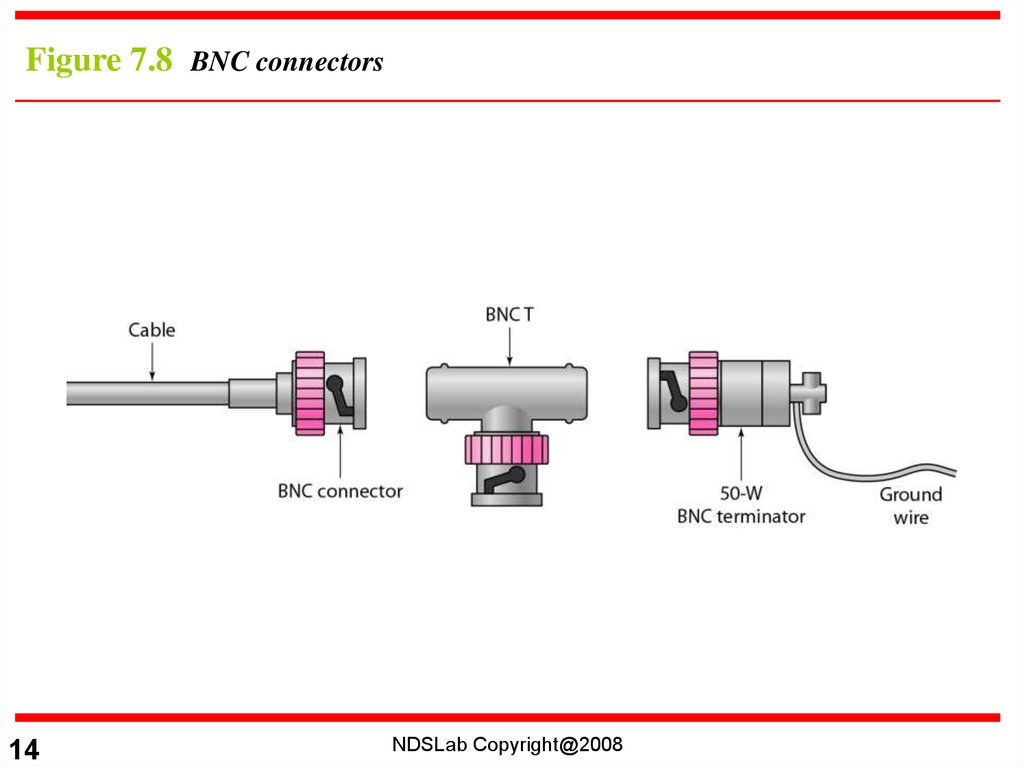
Figure 7.8 BNC connectors14
NDSLab Copyright@2008
15.
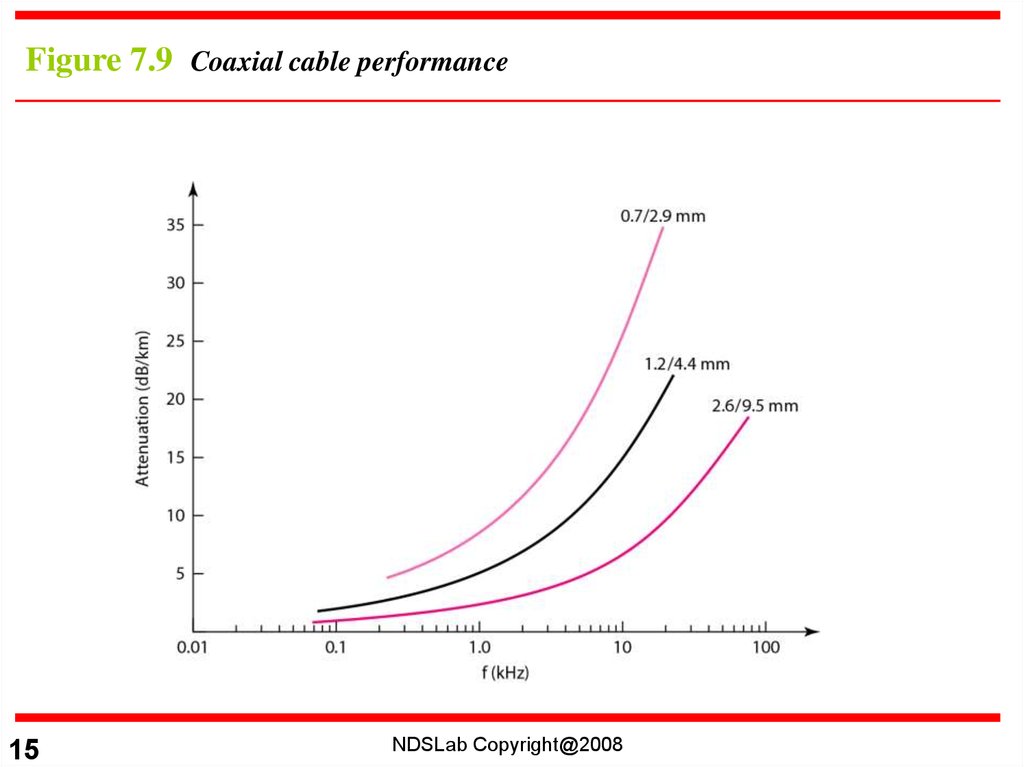
Figure 7.9 Coaxial cable performance15
NDSLab Copyright@2008
16.
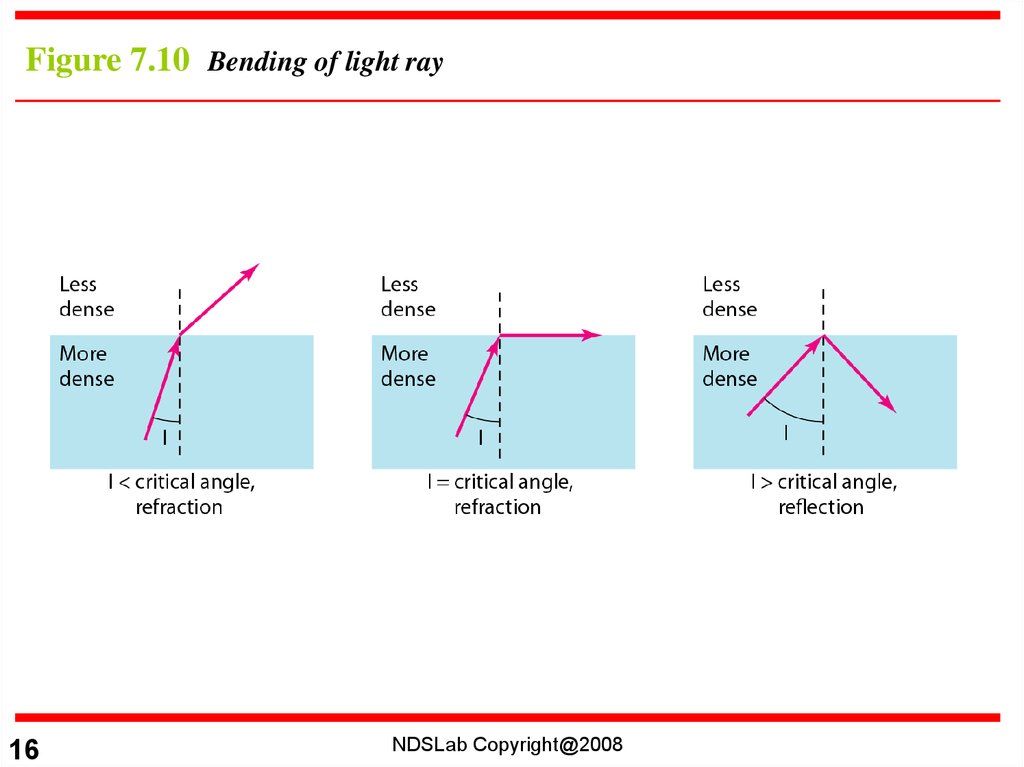
Figure 7.10 Bending of light ray16
NDSLab Copyright@2008
17.
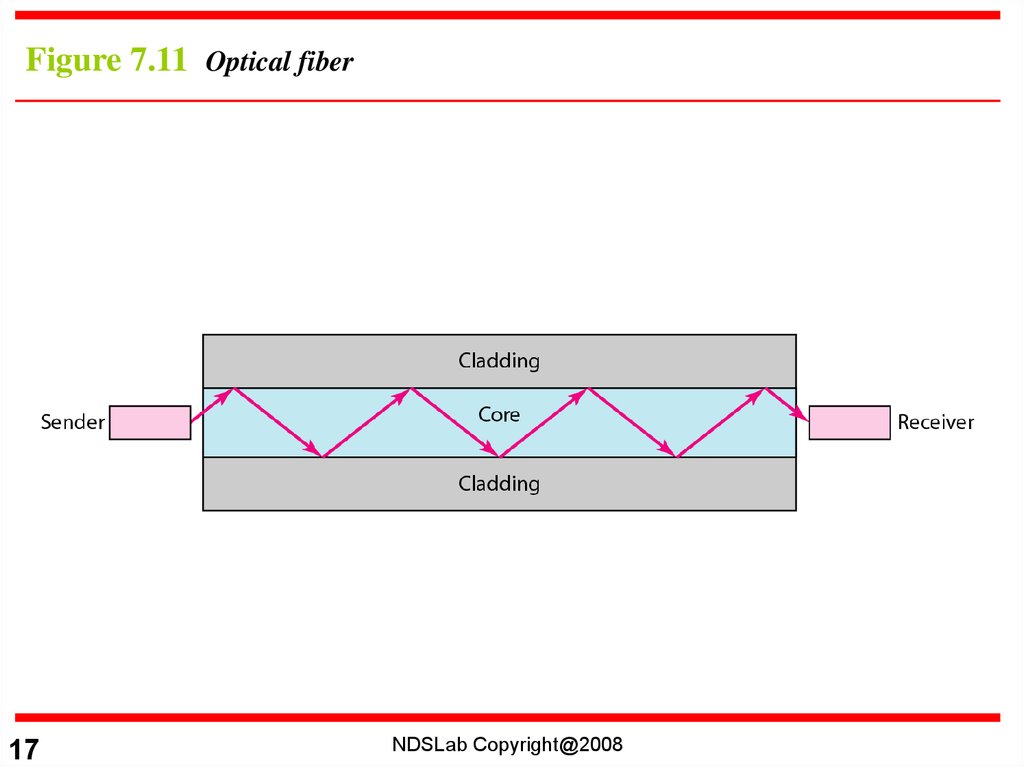
Figure 7.11 Optical fiber17
NDSLab Copyright@2008
18.
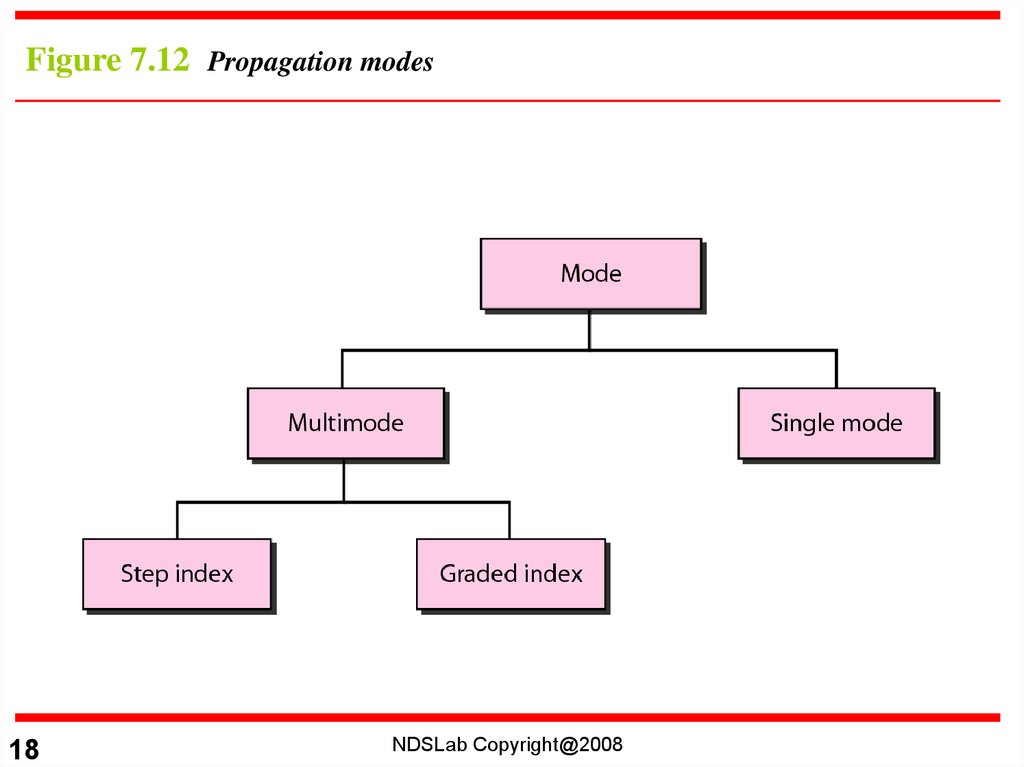
Figure 7.12 Propagation modes18
NDSLab Copyright@2008
19.
Figure 7.13 Modes19
NDSLab Copyright@2008
20.
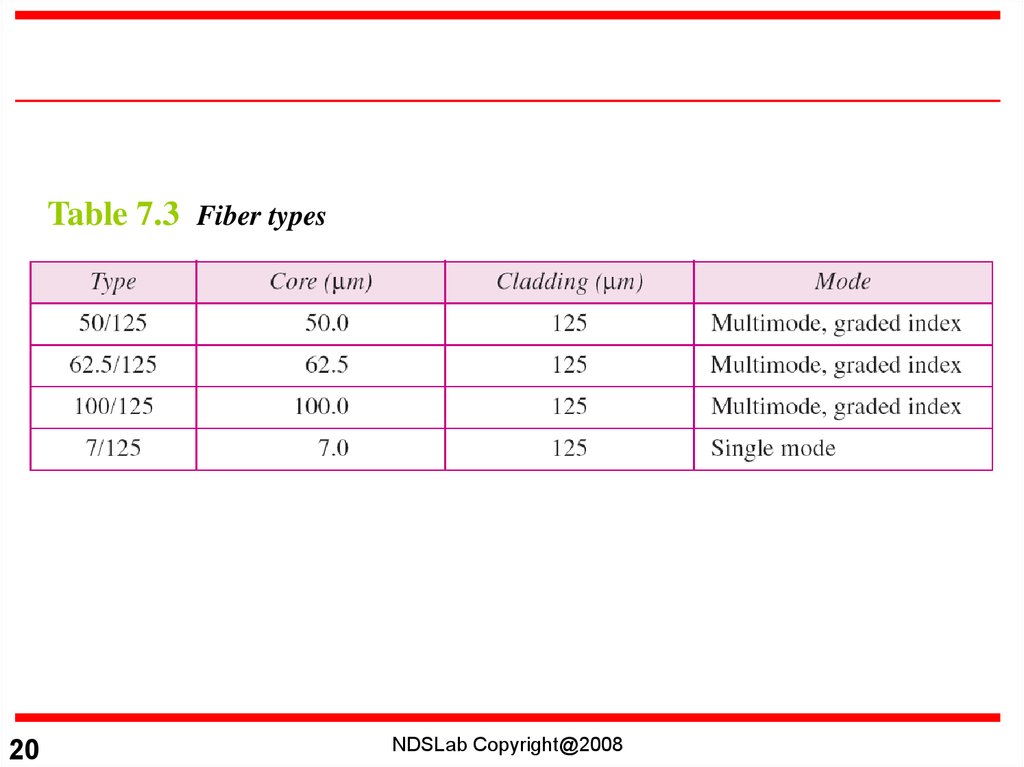
Table 7.3 Fiber types20
NDSLab Copyright@2008
21.
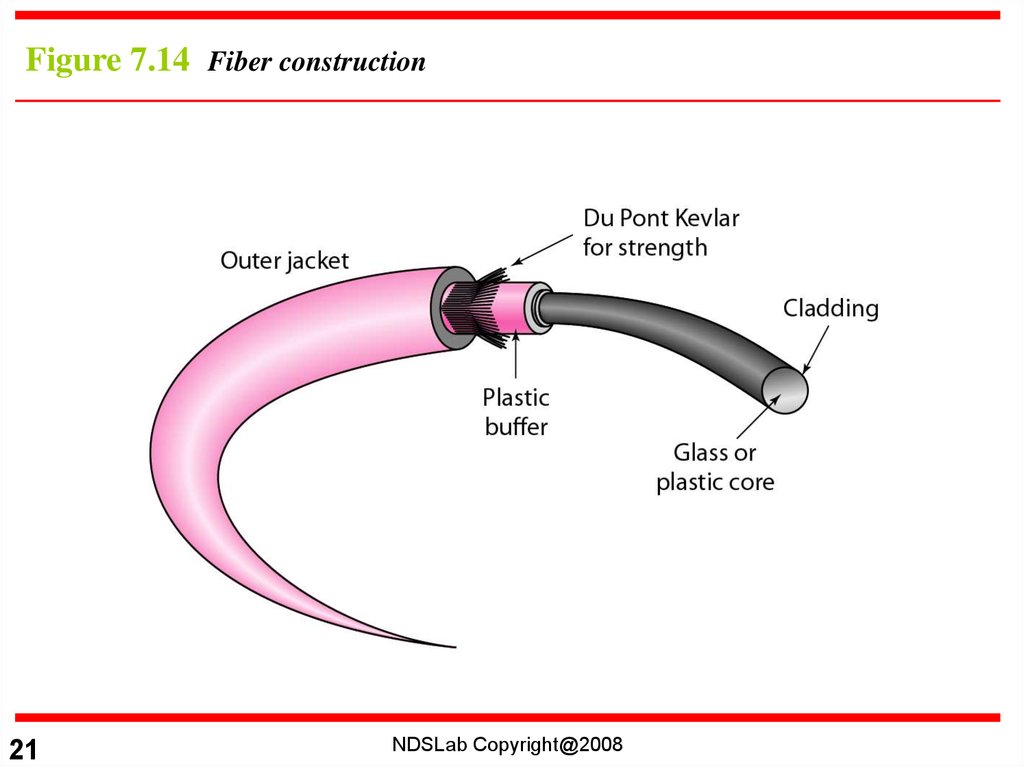
Figure 7.14 Fiber construction21
NDSLab Copyright@2008
22.
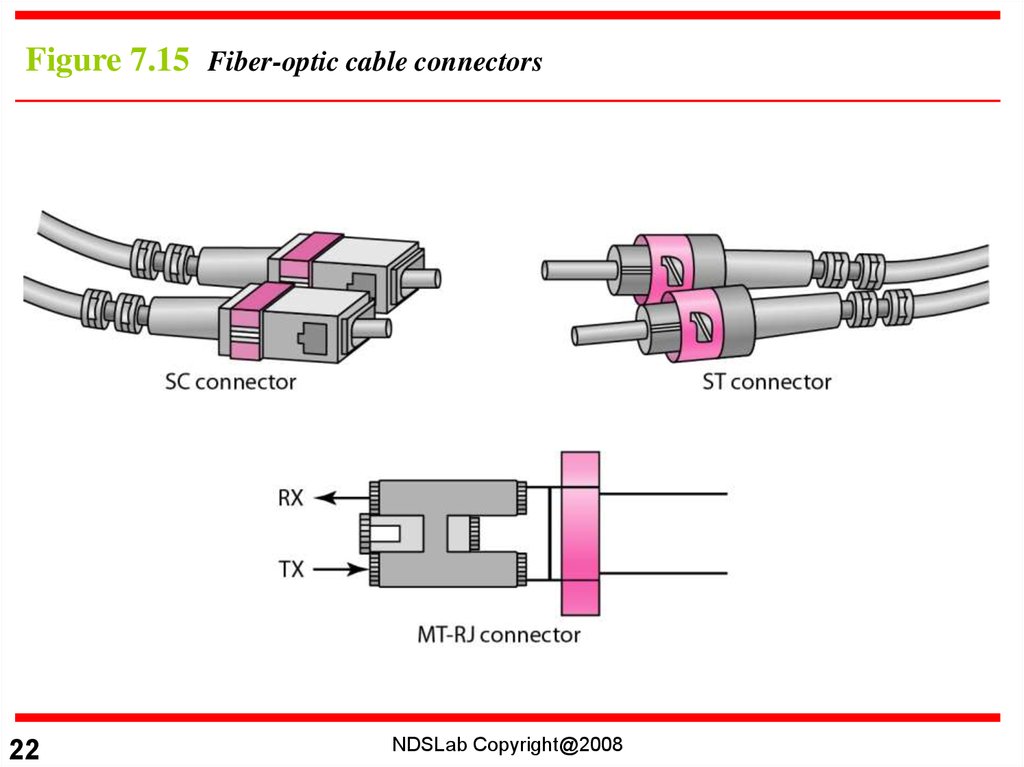
Figure 7.15 Fiber-optic cable connectors22
NDSLab Copyright@2008
23.
Figure 7.16 Optical fiber performance23
NDSLab Copyright@2008
24.
7-2 UNGUIDED MEDIA: WIRELESSUnguided media transport electromagnetic waves
without using a physical conductor. This type of
communication is often referred to as wireless
communication.
Topics discussed in this section:
Radio Waves
Microwaves
Infrared
24
NDSLab Copyright@2008
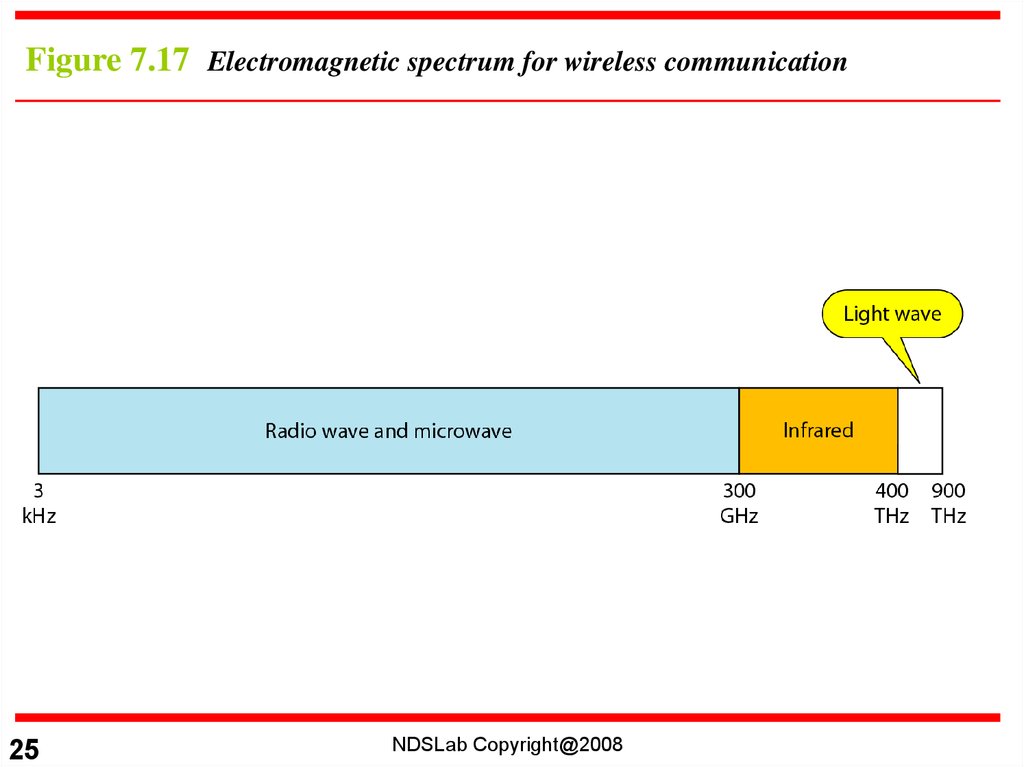
25.
Figure 7.17 Electromagnetic spectrum for wireless communication25
NDSLab Copyright@2008
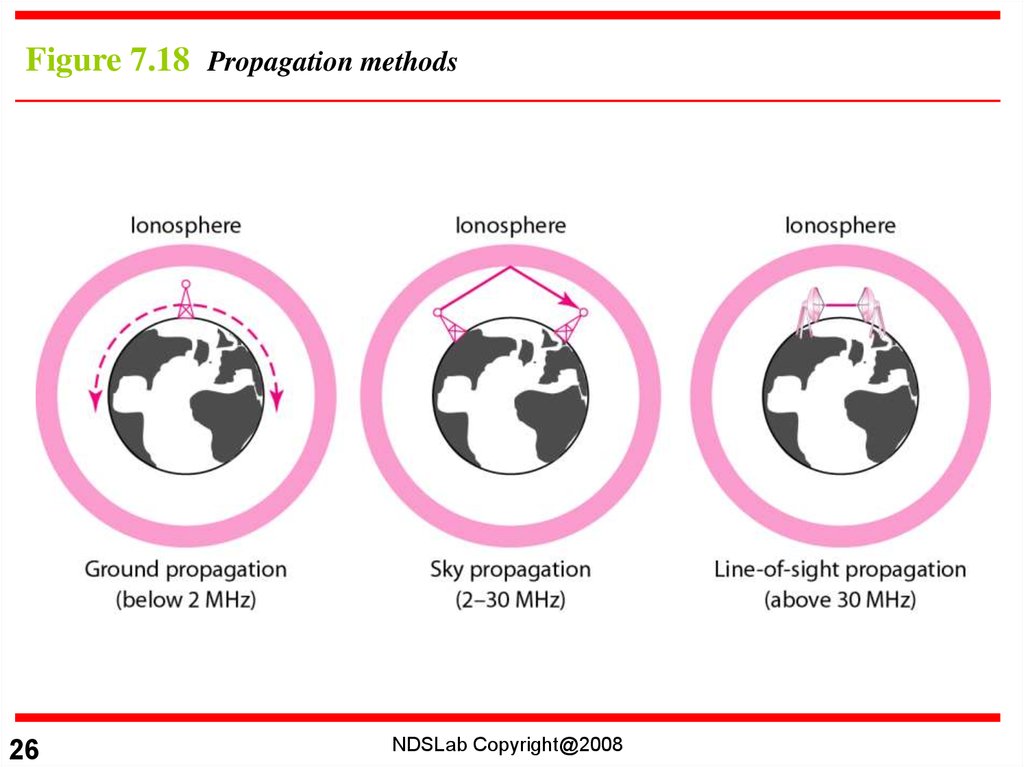
26.
Figure 7.18 Propagation methods26
NDSLab Copyright@2008
27.
Table 7.4 Bands27
NDSLab Copyright@2008
28.
Figure 7.19 Wireless transmission waves28
NDSLab Copyright@2008
29.
Figure 7.20 Omnidirectional antenna29
NDSLab Copyright@2008
30.
NoteRadio waves are used for multicast
communications, such as radio and
television, and paging systems.
30
NDSLab Copyright@2008
31.
Figure 7.21 Unidirectional antennas31
NDSLab Copyright@2008
32.
NoteMicrowaves are used for unicast
communication such as cellular
telephones, satellite networks,
and wireless LANs.
32
NDSLab Copyright@2008
33.
NoteInfrared signals can be used for shortrange communication in a closed area
using line-of-sight propagation.
33
NDSLab Copyright@2008















 physics
physics




