Similar presentations:
The establishment of the phonologically relevant features
1. Problem 2 of the phonological analysis: the establishment of the phonologically relevant features.
2. Questions:
QUESTIONS:1.
2.
3.
What is the topic of my
presentation?
What kinds of irrelevant features do
you know?
Is the system of phonemes
homogeneous?
3.
• This problem is the identification of the inventory of relevantfeatures on which all phonological oppositions in the language are
based.
• Phonologically relevant feature of a phoneme is constant
distinctive feature which distinguish this phoneme from all the
other phonemes of the language.
Each allophone of a certain phoneme is characterized by definite
phonologically relevant features plus a number of irrelevant
(or incidental) features.
Phonologically irrelevent feature distinguish the allophone
from all the other allophones of the phoneme.
4.
Relevant features are affected by phonetic context.Irrelevant may be of two kinds: - indispensable (they
are always present at allophones), - incidental.
Relevant features make up the basis of the
phonological description, while irrelevant features are
redundant from the phonological point of view but still
very important for the articulation of the sounds.
5.
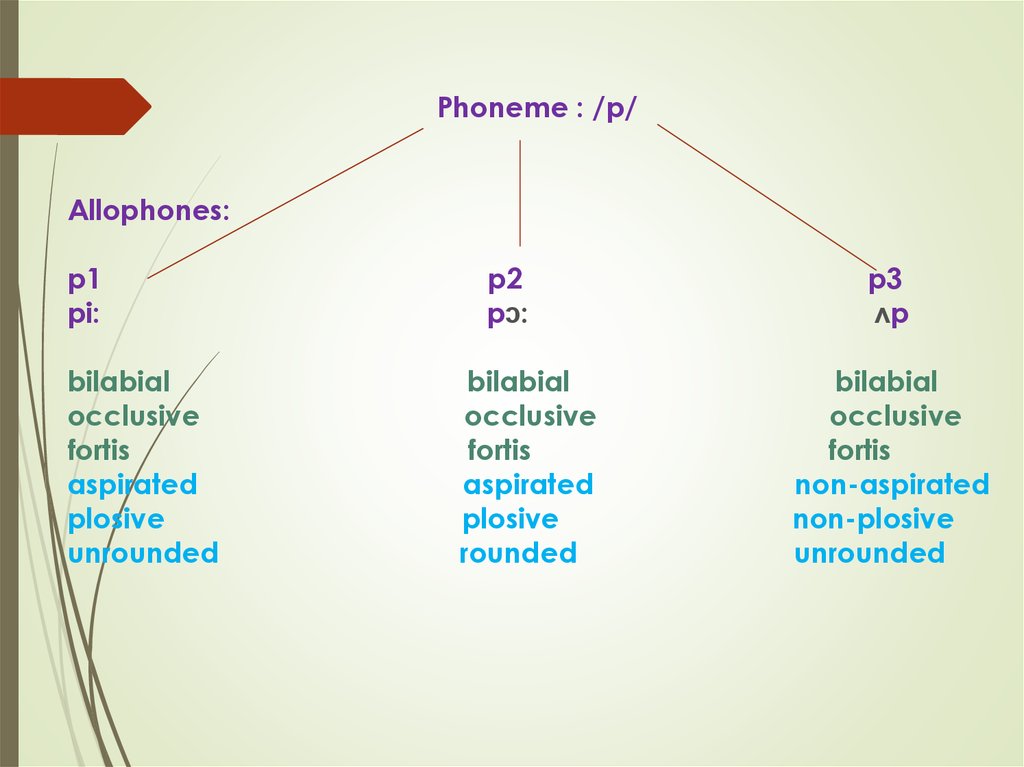
Phoneme : /р/Allophones:
p1
pi:
bilabial
occlusive
fortis
aspirated
plosive
unrounded
p2
pɔ:
bilabial
occlusive
fortis
aspirated
plosive
rounded
p3
ʌp
bilabial
occlusive
fortis
non-aspirated
non-plosive
unrounded
6. The phonologically relevant features that characterize the phoneme /p/ are, therefore, bilabial, occlusive and fortis.
Aspiration,plosiveness,labialization etc.arephonolodically irrelevant features
Phonologically irrelevant does not necessarily
mean useless for communication.
It has already been mentioned that the
aspiration /p/ helps the listener to distinguish it
from /b/
(as in pride- bride, pie –buy)
7.
The system of phonemes is not homogeneous.On the most general principle all the phonemes are divided into
vowels and consonants.
The chief difference lies in the fact that vowels have only voice while
consonants have voice and noise combined.
The difference on the articulatory level lies on the absence or
presence of obstruction that is the case of consonants various
obstruction are made. In case of vowels there is no obstruction.
8.
Relevant- the
type of obstruction (occlusive/constrictive,
plosive/fricative/affricate/nasal)
- the active organ (labial, bilabial, labiodental/lingual/glottal)
- the force of articulation, work of local cords (lenis)
Irrelevant
- two foci
- the shape of narrow (oral, nasal, lateral articulation)
- place of obstruction
- presense or absense of voice
- aspiration
- palatalisation
9. Distinctive features for English consonants: place of articulation; manner of articulation; absence/ presence of voice
Manner of articulation1.Occlusive
1.1.noise
1.1.1.plosives [b],[d],[g]; [p],[t],[k]
1.1.2.affricates [ʤ], [ʧ]
1.2.sonorants [m], [n], [ŋ]
2.Constrictive
2.1.noise [f],[v],[s],[z],[θ],[ð],[ʃ],[ʒ],[h]
2.2.sonorants
2.2.1.lateral [l]
2.2.2.medial [w],[r],[j]
10.
Place of articulation1.Labial
1.1bilabial [p],[b], [m], [w]
1.2.labio-dental [f], [v]
2.Lingual
2.1.forelingual
2.1.1.interdental [θ],[ð]
2.1.2.alveolar [t],[d],[s],[z],[n],[l]
2.1.3.post-alveolar [r]
2.1.4.palate-alveolar [ʃ],[ʒ],[ʤ], [ʧ]
2.2.medialingual [j]
2.3. backlingual [k],[g],[ŋ]
3.Glottal [h]
And so on.
11.
VowelsIn the system of English vowels the only relevant feature is
distinctions in their quality ,which are based on the slight
differences in the tongue positions when producing these
vowels.
thus, the opposition /i: - i/ is based on the following
phonologically relevant features:
high- narrow vs. high- broad , fully-front vs. front- retracted.
12.
The End.Thank you for your
attention;)











 english
english








