Similar presentations:
Tale about the analysis of the production
1.
Tale about the analysis of the production2
2.
Phase 1Phase 2
Phase 3
Total production or output
irrationa
l
rationa
l of output
The
production
as some function of
the level
irrational
depending on one variable input factor in the production while
maintaining all other inputs constant
increasing yield
point of inflection
Goal: to understand the
negative
yield of
decreasing yield
productivity
of factors
production and its influence on
the production function
Consider a production system with two variable
inputsпроизводства
One variable input
3.
Production function with twovariable inputs:
Q f (C,
L)
Капитал Труд
4.
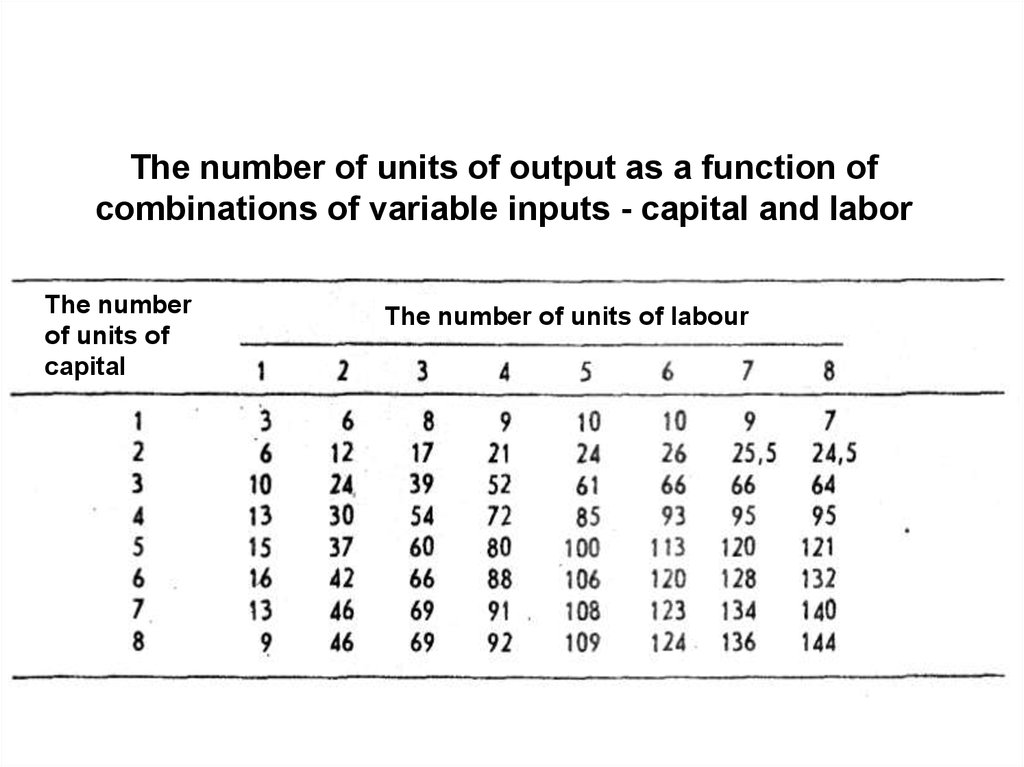
The number of units of output as a function ofcombinations of variable inputs - capital and labor
The number
of units of
capital
The number of units of labour
5.
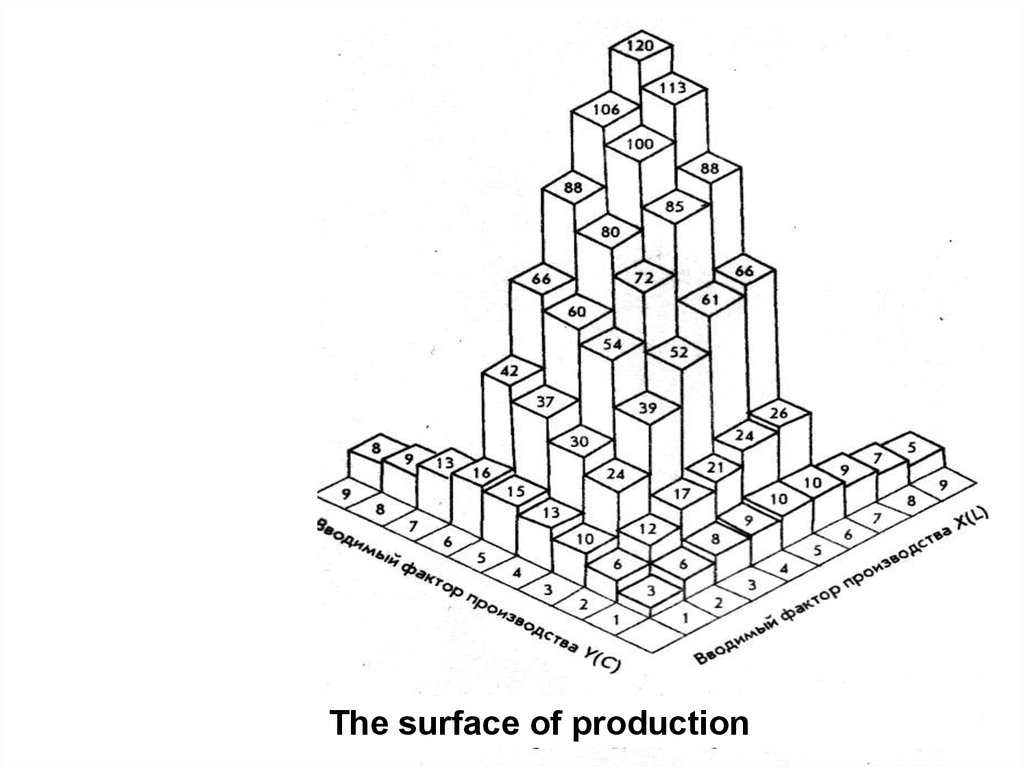
The surface of production6.
Option AOutput
factor of
production
Input factor
of
production
Option B
Input factor
of
production
Input factor
of
production
Output
factor of
production
Input factor
of
production
The surface of production formed by continuous production
functions
7.
Option AOutput
factor of
production
Input factor
of
production
Option B
Input factor
of
production
Input factor
of
production
Output
factor of
production
Input factor
of
production
The surface of production formed by continuous production
functions
8.
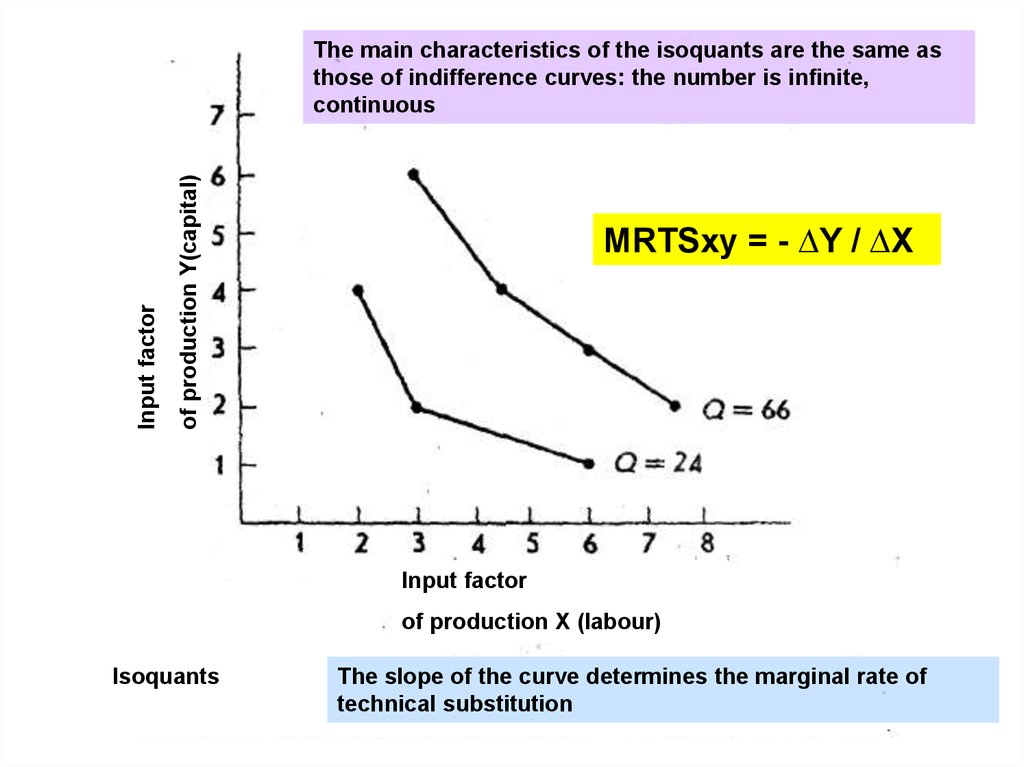
of production Y(capital)Input factor
The main characteristics of the isoquants are the same as
those of indifference curves: the number is infinite,
continuous
MRTSxy = - ∆Y / ∆X
Input factor
of production X (labour)
Isoquants
The slope of the curve determines the marginal rate of
technical substitution
9.
Amount of capitalAmount of capital
Quantity of labour
Option A
Quantity of labour
Option B
Economic decisions formed by isoquant curves
10.
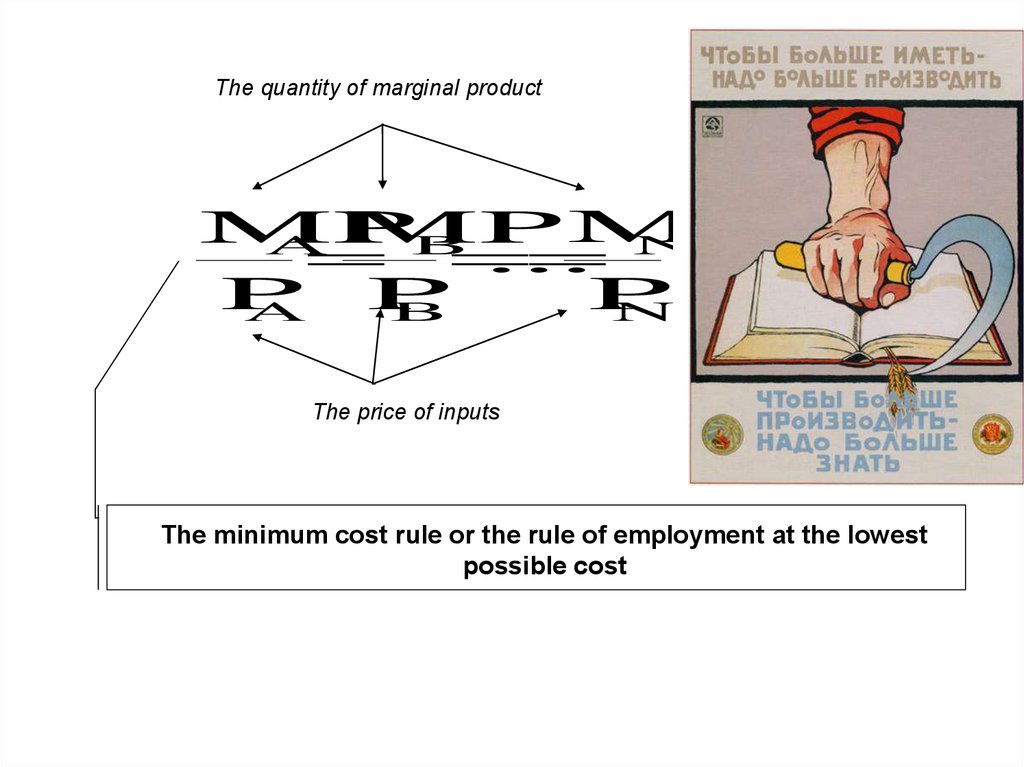
The rule of minimum cost11.
The quantity of marginal productMP
MP
N
A MP
B
...
P
P
P
A
B
N
The price of inputs
The minimum cost rule or the rule of employment at the lowest
possible cost
12.
А => С: ∆С * МРс = ∆L * MPLLet’s devide both parts by(-∆L * МРс) :
- ∆С /∆L = - MPL / МРс
LC
= - MPL / МРс
=> The slope of the isoquant indicates not
only the rate of technical substitution of
labor and capital, but also the ratio of the
marginal product of labor and marginal
product of capital
of production Y(capital)
Input factor
- ∆С /∆L = MRTS LC => MRTS
Input factor
of production X (labour)
13.
TC = L * PL + C * PCThe slope of isocost:
Isocosts shows the combination of required factors
predetermined
money
∆С / purchased
∆ L = (- TC using
/ Pc) : a(TC
/ PL) = ( - TC /amount
Pc)* (PLof
/TC)
= - PL / Pc
Isocost is always a tangent to some isoquant: =>
the balance point (the slopes of the isoquant and isocost is
equal):
of production Y(capital)
Input factor
- MPL / МРс = - PL / Pc => MPL / PL = МРс / Pc
The resulting equation for
The minimum cost rule
Input factor
of production X (labour)
14.
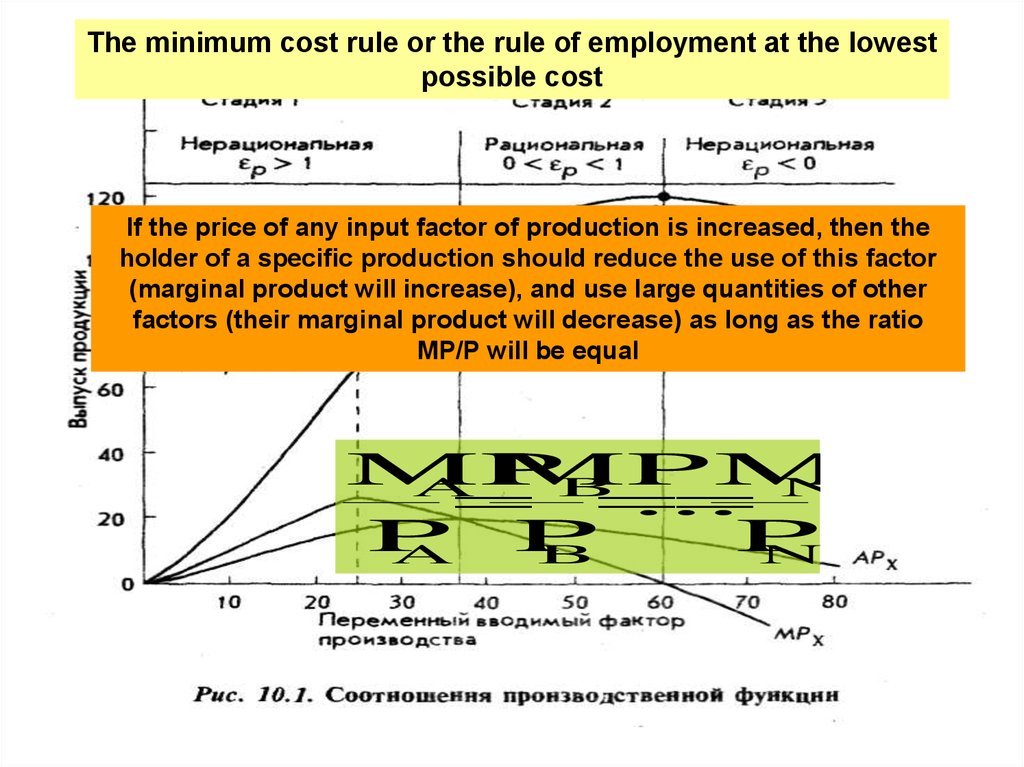
The minimum cost rule or the rule of employment at the lowestpossible cost
If the price of any input factor of production is increased, then the
holder of a specific production should reduce the use of this factor
(marginal product will increase), and use large quantities of other
factors (their marginal product will decrease) as long as the ratio
MP/P will be equal
MP
MP
A MP
B
...
N
P
P
P
A
B
N









 industry
industry








