Similar presentations:
Electricity markets. Natural monopoly model
1. Electricity markets
Natural Monopoly model2. Overview
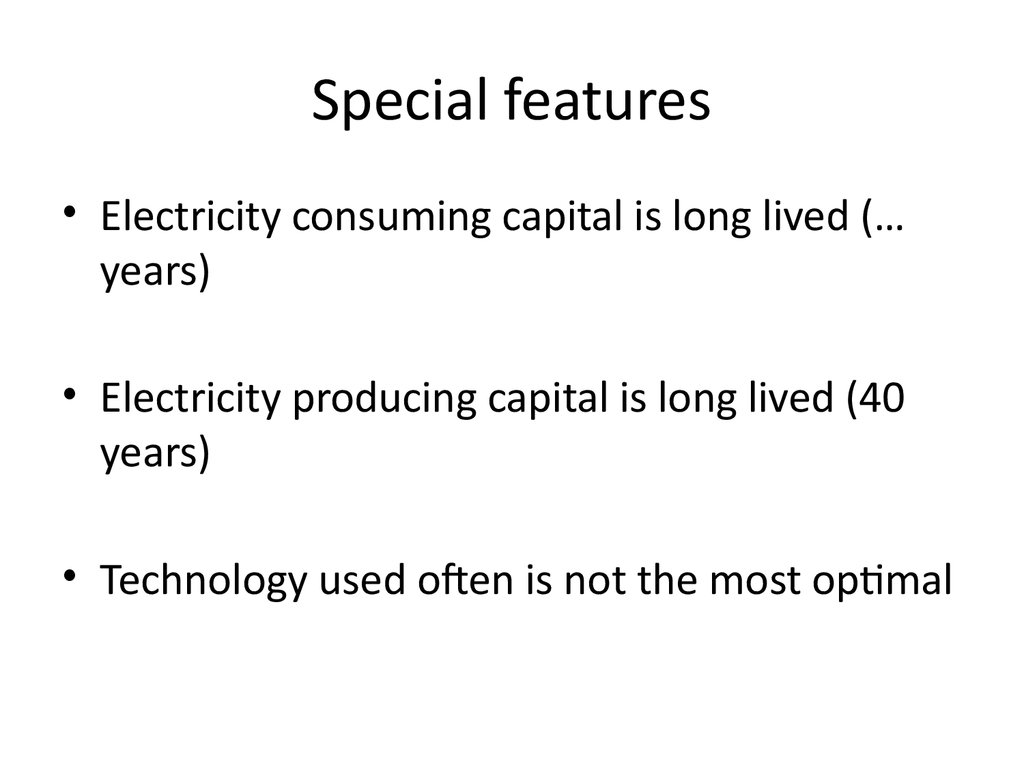
Special features
Stages of electricity production
Production function and costs
Natural monopoly
Regulation
Technological change
3. Special features
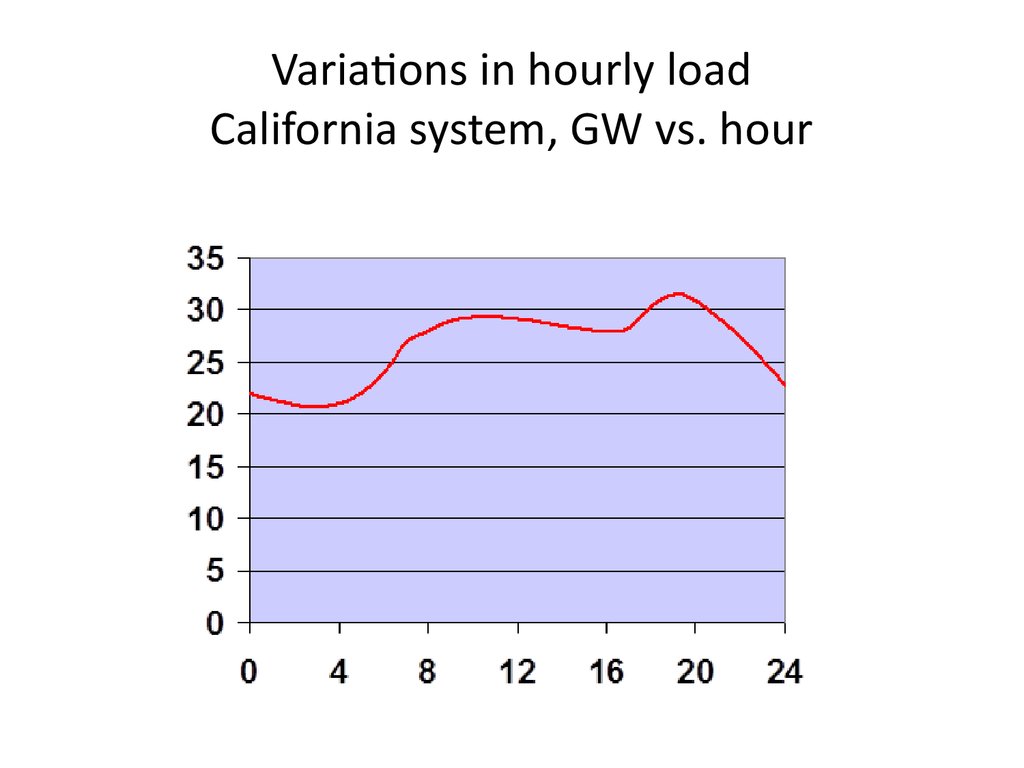
• Demand fluctuations• within the day, across seasons
• Demand = load
• Peak vs. offpeak demand
4. Variations in hourly load California system, GW vs. hour
5. Special features
• Not storable (electricity today is not asubstitute for electricity tomorrow)
6. Special features
• High costs of shortages• Blackouts or brownouts
• Capacity >= load
• “peak load problem”
7. Special features
• Electricity is a secondary source of energy• Electricity is both an output and an input with
respect to other energy products
• E.g. output with respect to …?
• E.g. input with respect to …?
• Electricity is a substitute to some of its inputs
8. Special features
• Electricity consuming capital is long lived (…years)
• Electricity producing capital is long lived (40
years)
• Technology used often is not the most optimal
9. Special features Summary
• Demand fluctuations (within the day, acrossseasons)
• Not storable (electricity today is not a
substitute for electricity tomorrow)
• High costs of shortages
• Complex relations with respect to other
energy products
10. Production process
• Generation• Transmission
• Distribution
11. Production process
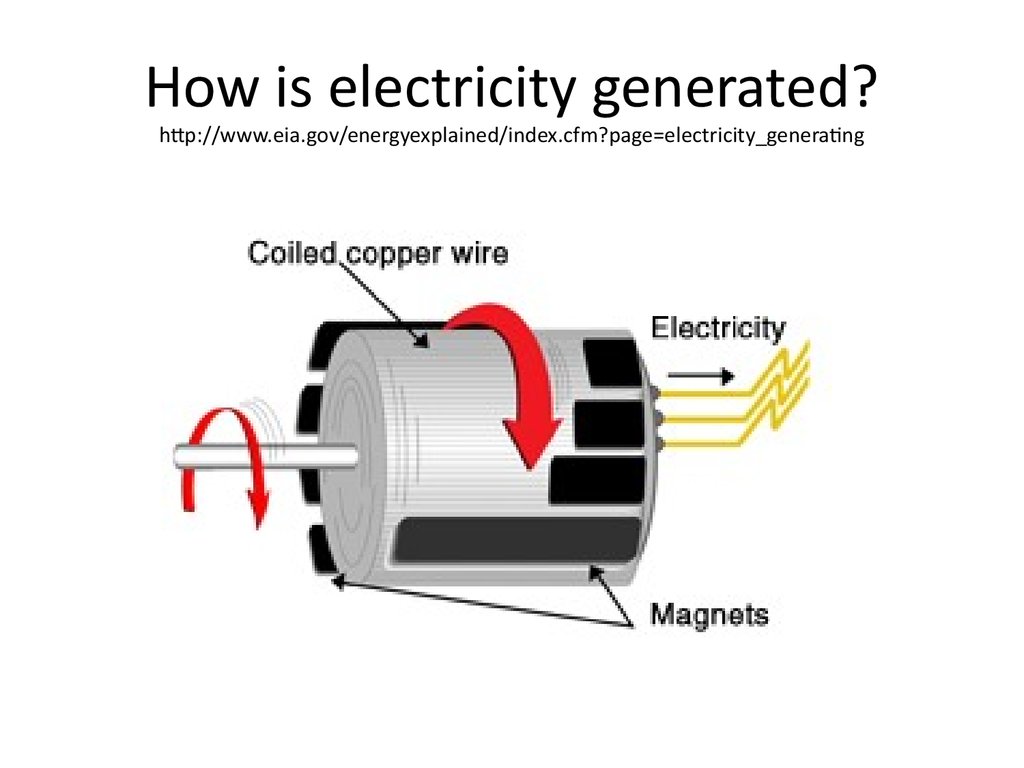
Generation
Electricity is a secondary energy source
Transformation of one energy into electricity
Mechanical power into electric power:
Hydropower and wind
Thermal (coal, gas, oil)
Solar
Nuclear
12. How is electricity generated? http://www.eia.gov/energyexplained/index.cfm?page=electricity_generating
13. Supply chain video
• https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=20Vb6hlLQSg
14. Electricity supply chain
• Generation: transformation of other energyinto electric energy
• Transmission: high voltage transport of energy
• Distribution: low voltage transport of energy
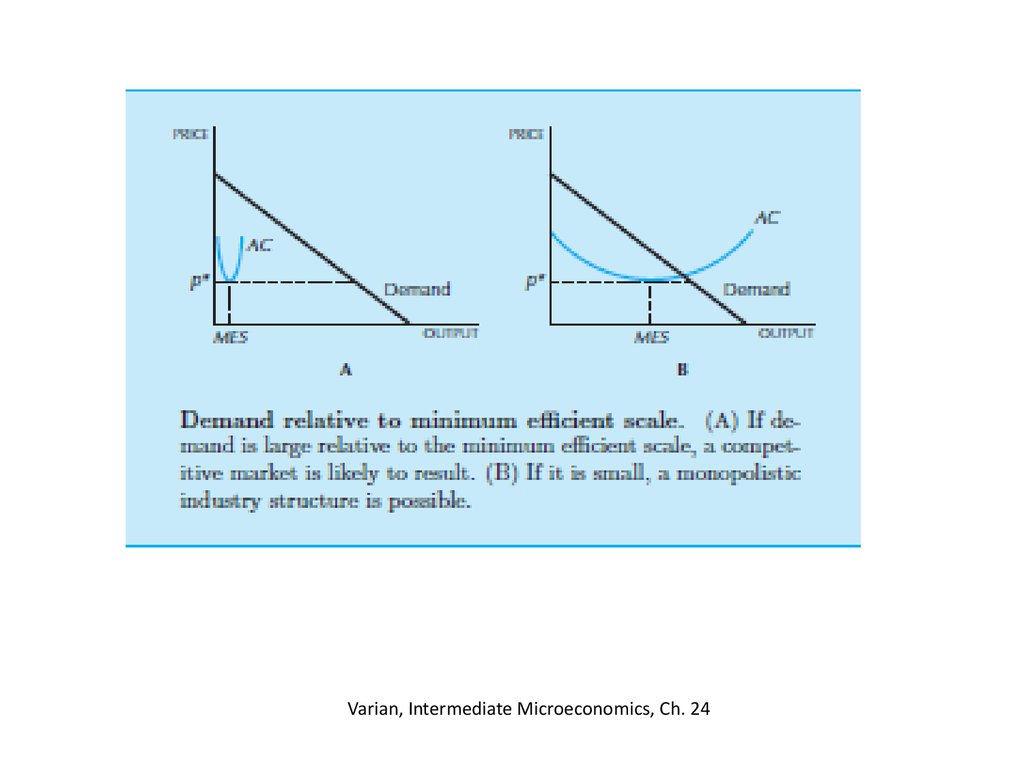
15. Minimum efficient scale
• MES is the level of output that minimizesaverage cost relative to the demand
16. Varian, Intermediate Microeconomics, Ch. 24
17. Modelling electricity markets
• High fixed cost• Low variable cost
• Average cost declines as Q grows
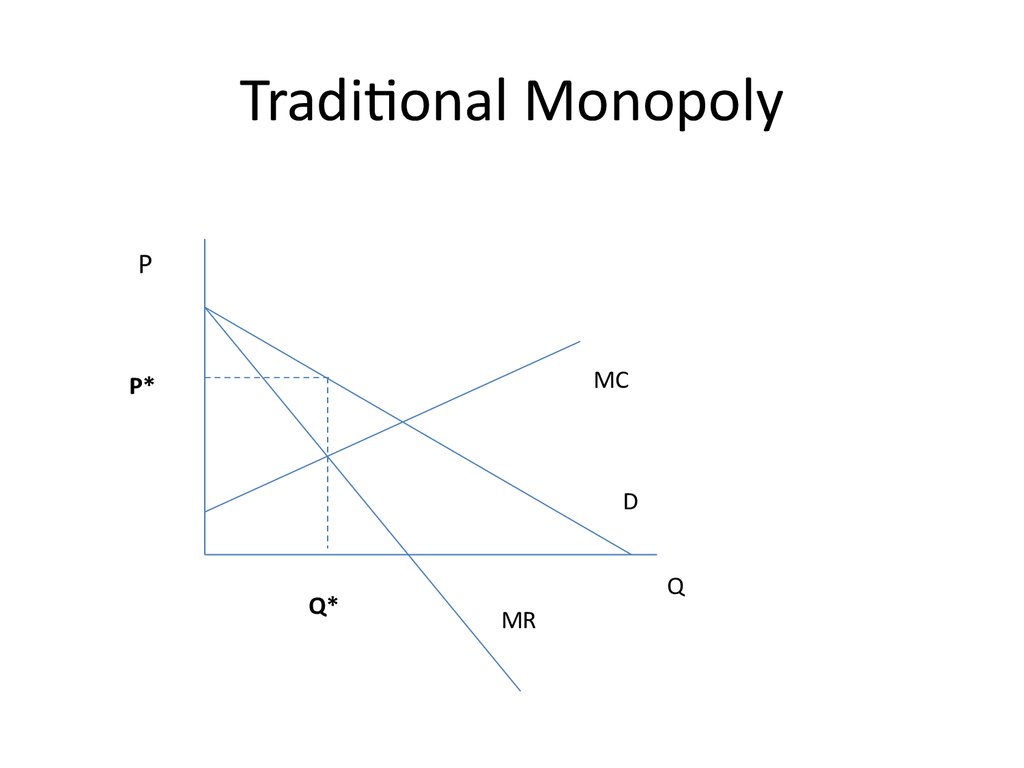
18. Traditional Monopoly
PMC
P*
D
Q*
Q
MR
19. Natural Monopoly
PD
AC
MC
Q
MR
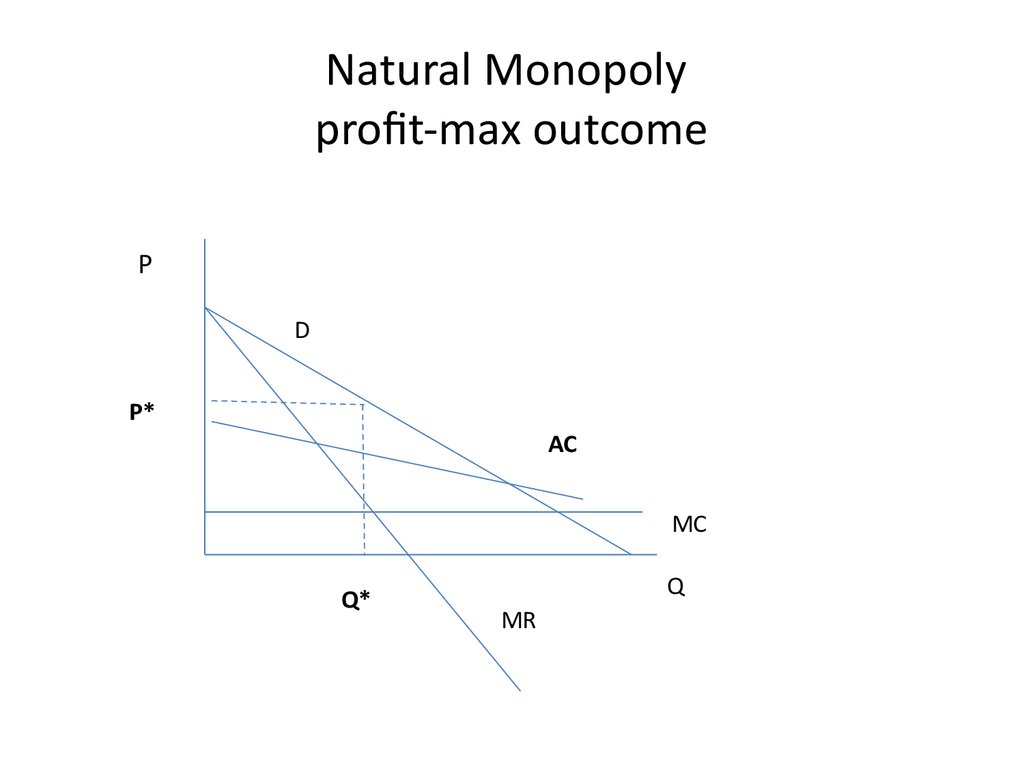
20. Natural Monopoly profit-max outcome
PD
P*
AC
MC
Q*
Q
MR
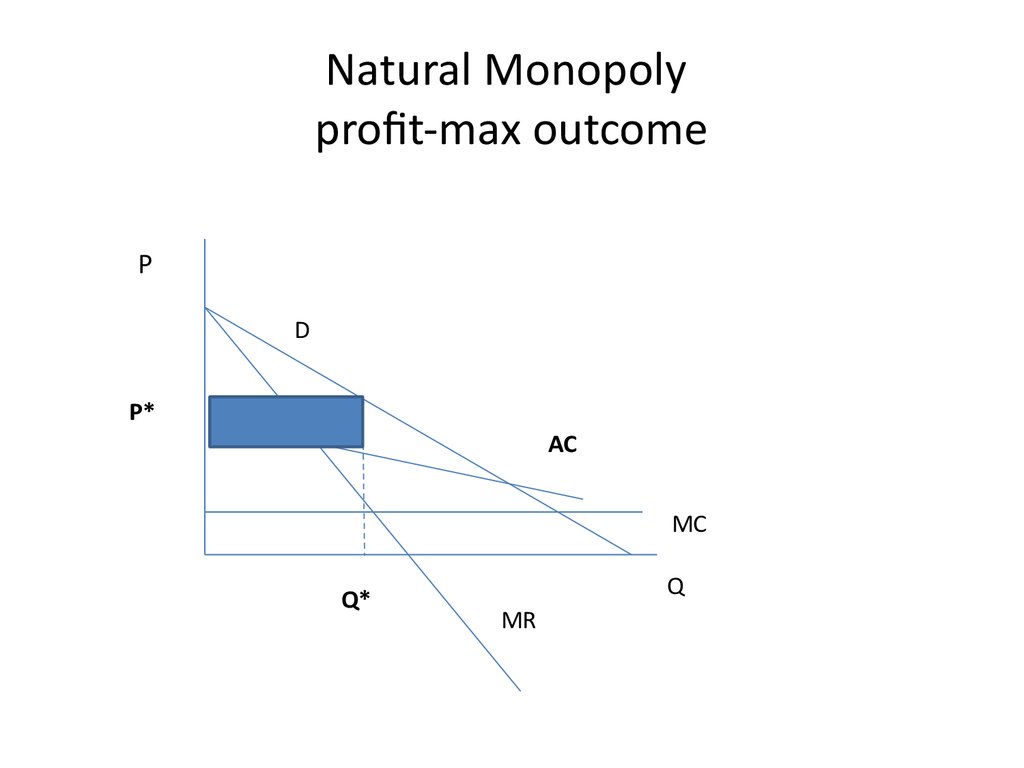
21. Natural Monopoly profit-max outcome
PD
P*
AC
MC
Q*
Q
MR
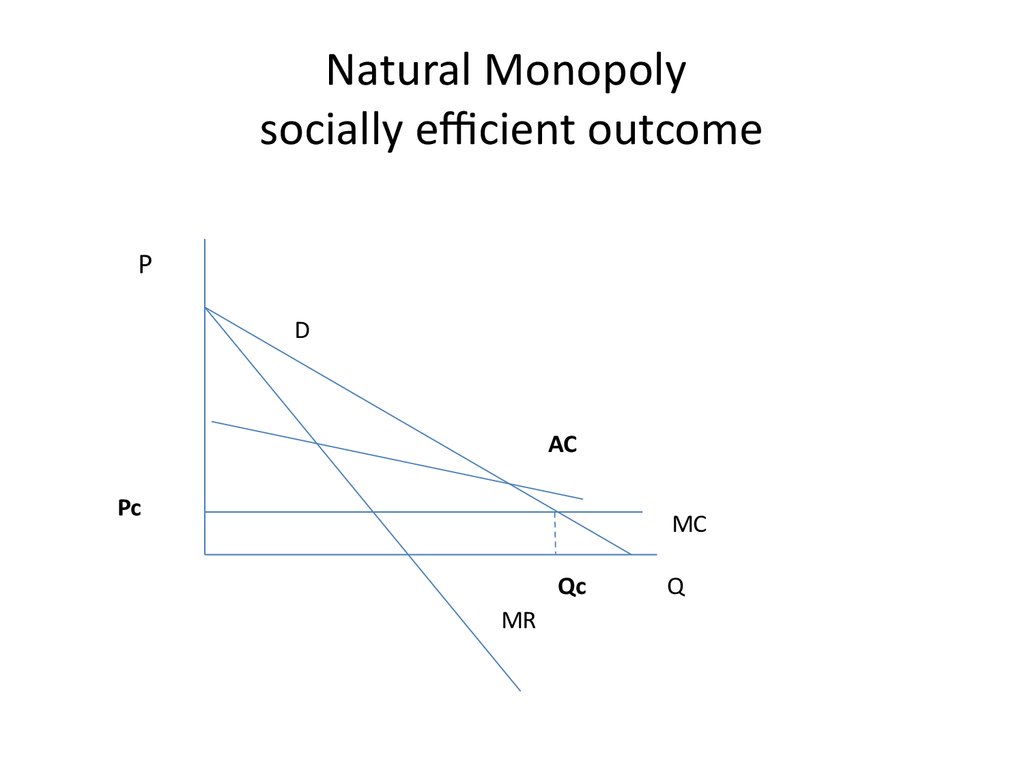
22. Natural Monopoly socially efficient outcome
PD
AC
Pc
MC
Qc
MR
Q
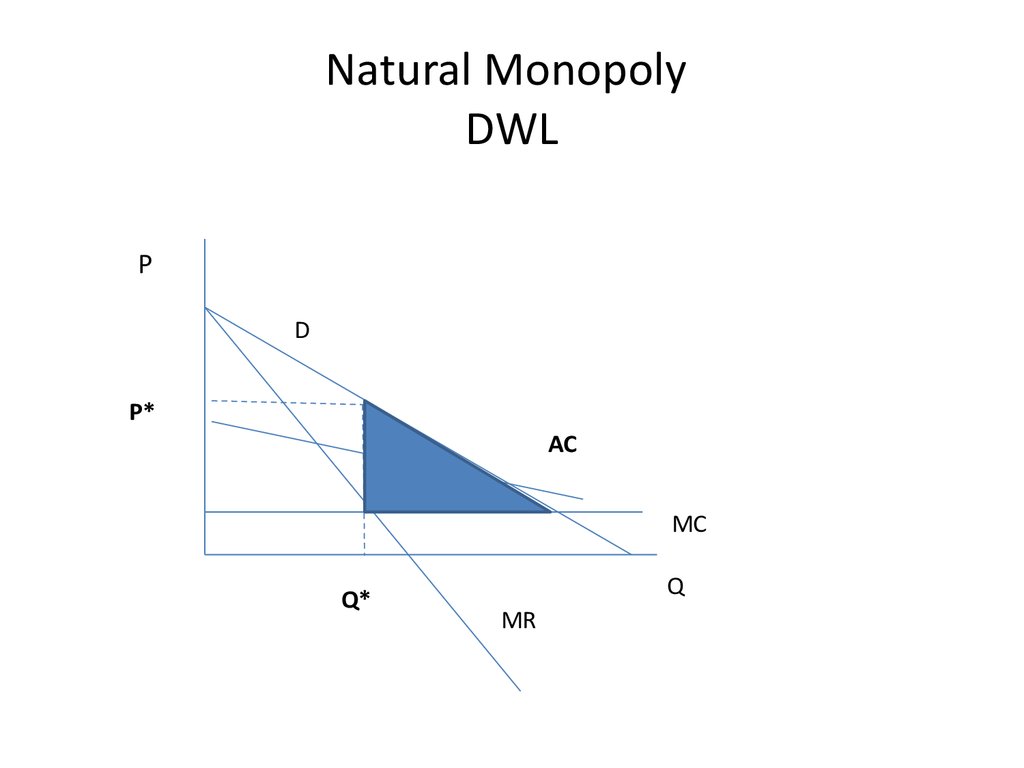
23. Natural Monopoly DWL
PD
P*
AC
MC
Q*
Q
MR
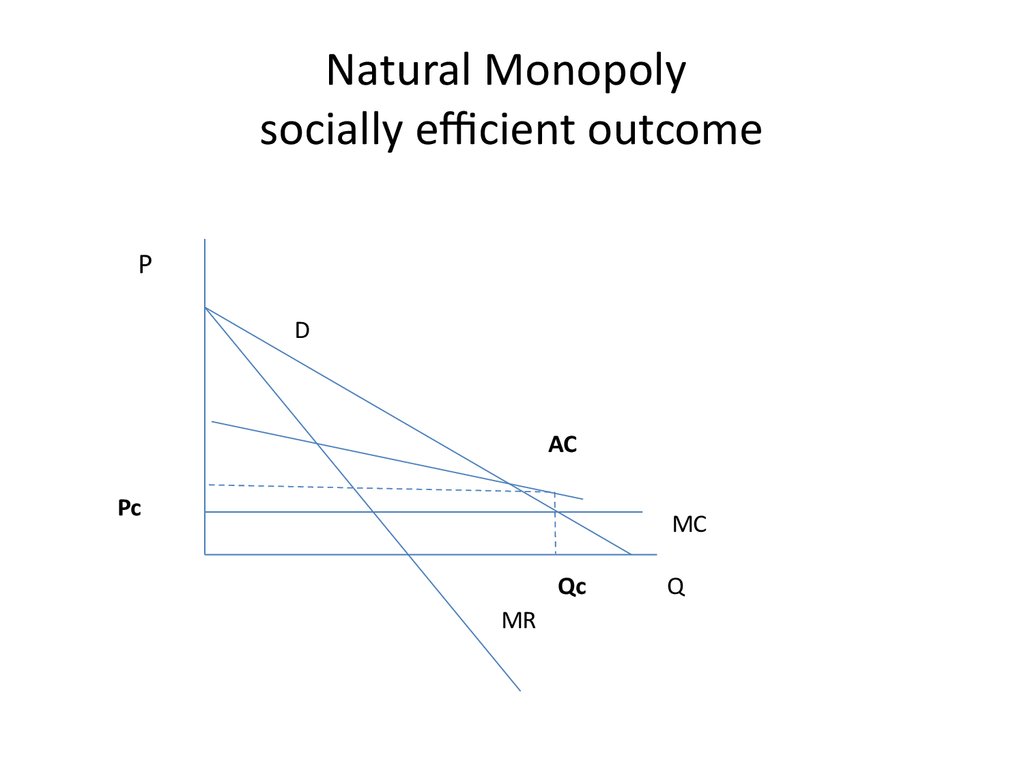
24. Natural Monopoly socially efficient outcome
PD
AC
Pc
MC
Qc
MR
Q
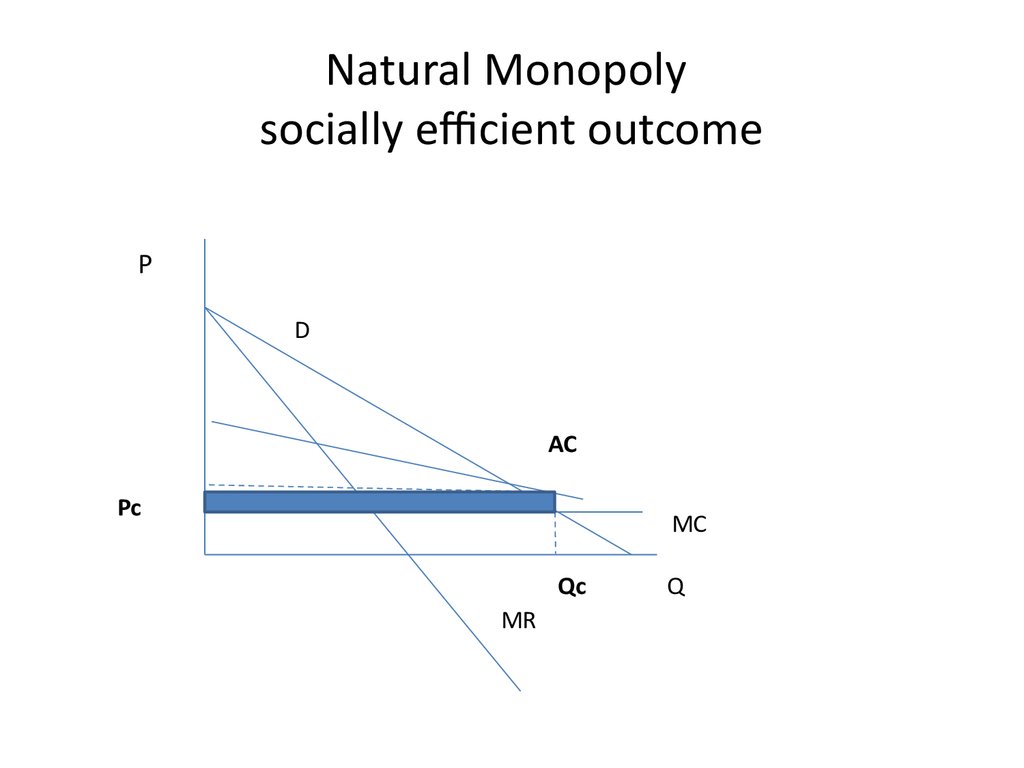
25. Natural Monopoly socially efficient outcome
PD
AC
Pc
MC
Qc
MR
Q
26. Natural Monopoly Policy
• 1. Public Ownership• 2. Private Ownership + regulation
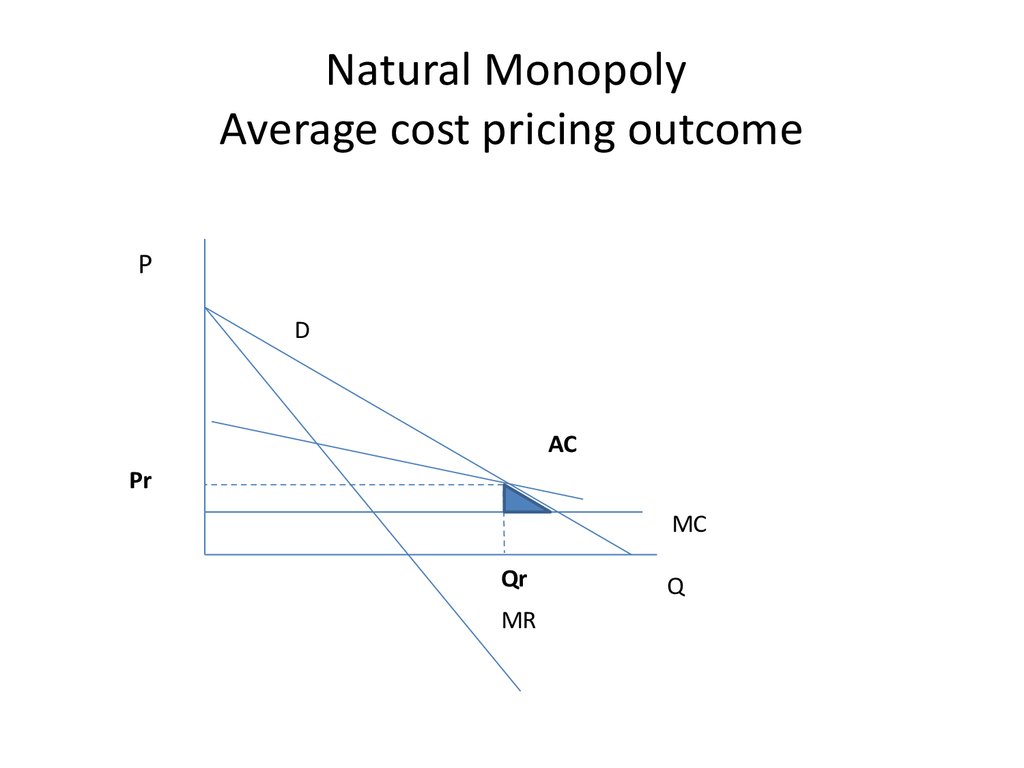
27. Natural Monopoly Average cost pricing outcome
PD
AC
Pr
MC
Qr
MR
Q
28. Differentiating peak & off-peak demand
Differentiatingpeak & off-peak demand
29. Peak & offpeak load
Peak & offpeak loadP
P
Qp
Qo
30. Which prices to charge?
• How to distribute costs among two consumergroups?
• Fixed cost? ~ “Capital cost” (Ck)
• Variable cost? ~ “Operating cost” (Cp – during
peak hours; Co – during offpeak hours)
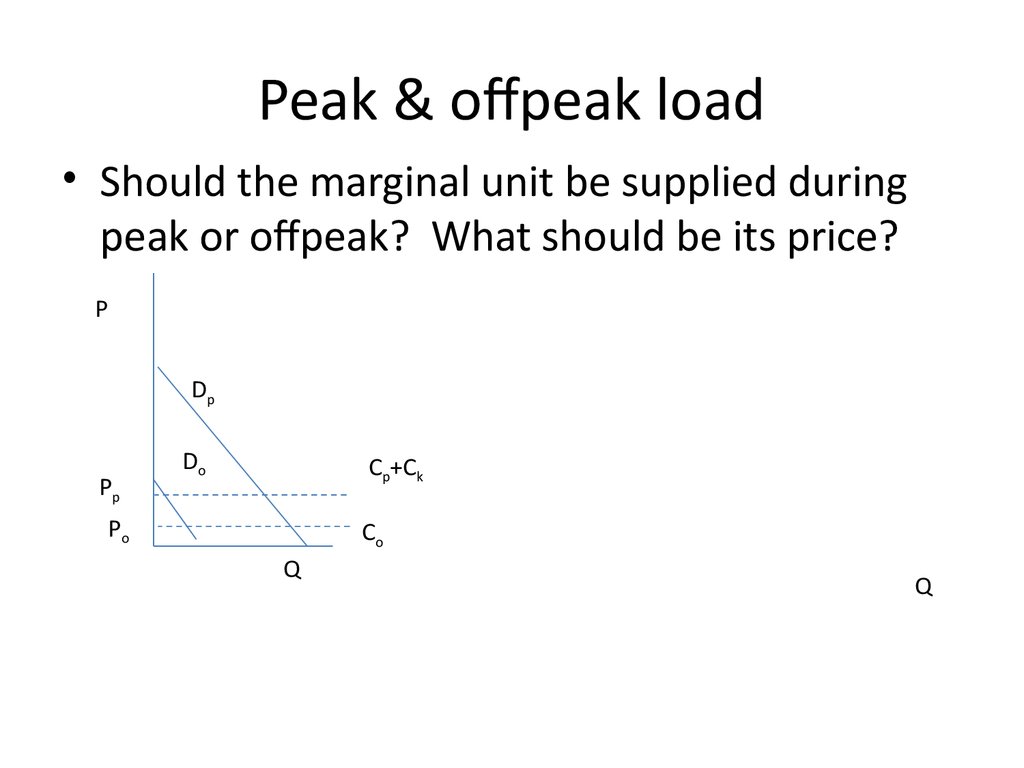
31. Peak & offpeak load
Peak & offpeak load• Should the marginal unit be supplied during
peak or offpeak? What should be its price?
P
Dp
Pp
Do
Cp+Ck
Po
Co
Q
Q
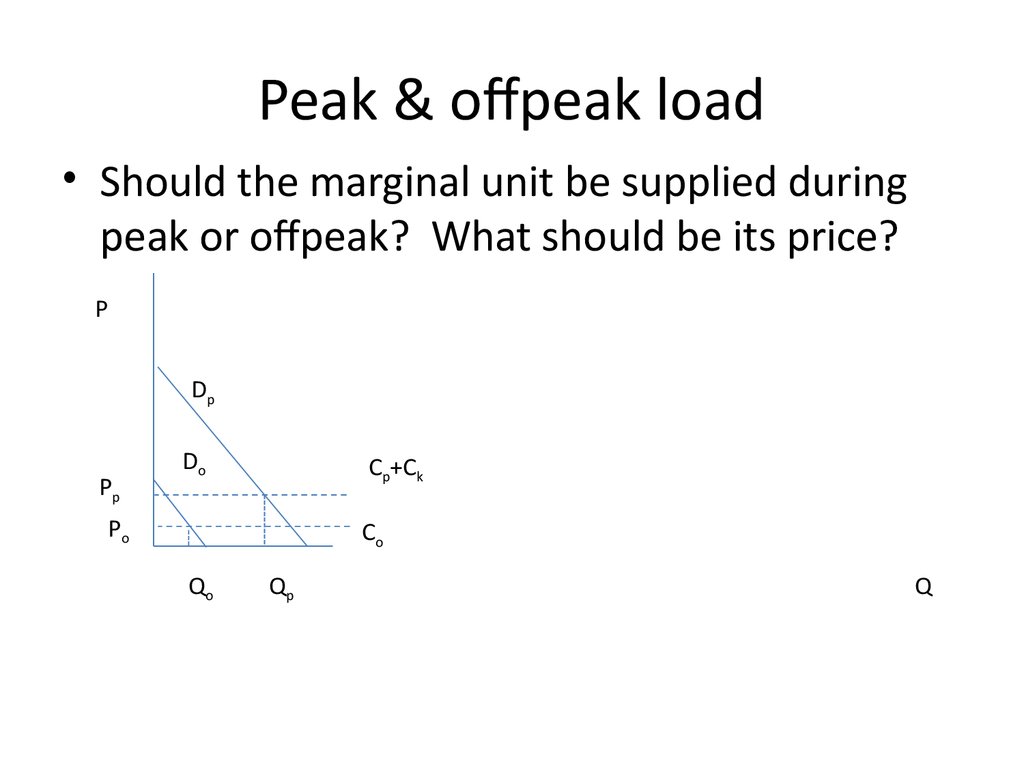
32. Peak & offpeak load
Peak & offpeak load• Should the marginal unit be supplied during
peak or offpeak? What should be its price?
P
Dp
Pp
Do
Cp+Ck
Po
Co
Qo
Qp
Q
33. Smart meters and differentiating peak & off-peak demand
Smart meters and differentiatingpeak & off-peak demand
34. Peak-load pricing
• Electricity prices in Astana:• 23:00-7:00 => 3.21 KZT/ kWh
• 7:00-23:00 => 14.52 KZT/ kWh
35. Peak-load pricing
• Summary• Peak-load pricing allows a utility to cover the
fixed cost.
• Peak-load pricing became feasible due to
advances in technology.
36. Electricity industry in Kazakhstan
37. Industry structure
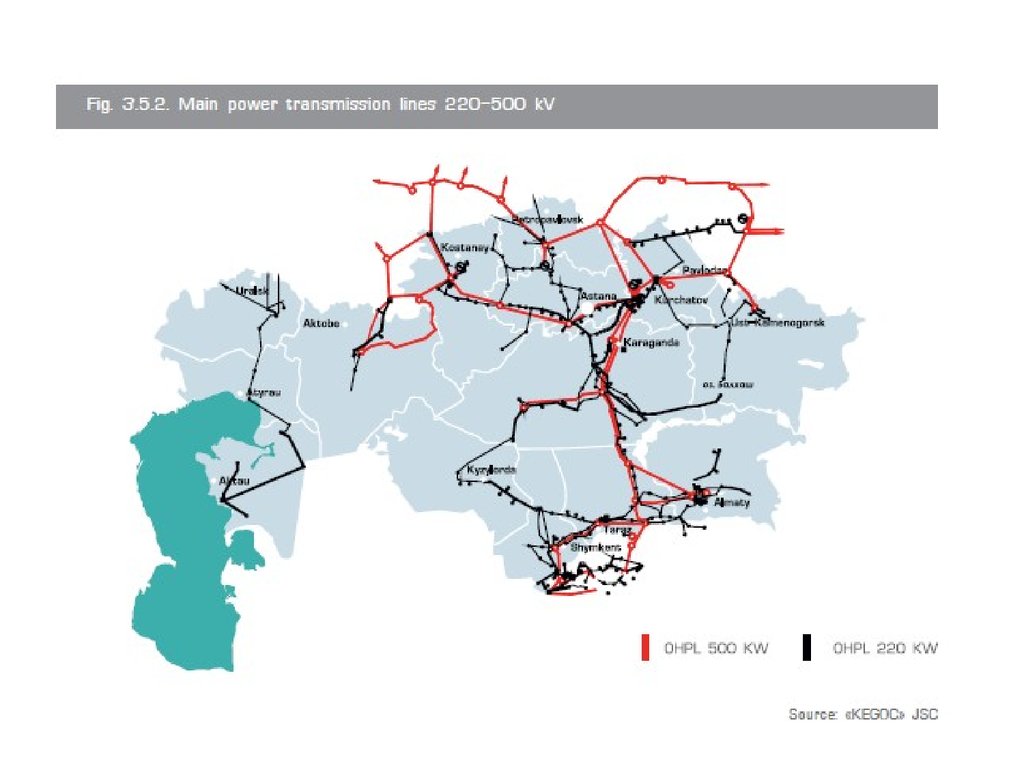
• Generation: mostly privately owned• Transmission: KEGOC, state-owned
• Distribution: 15 regional distribution
companies, state/privately owned
38.
39.
40.
41.
42.
43.
44. Review
Special features
Stages of electricity production
Production function and costs
Natural monopoly
Regulation
45. Readings
• Dahl, Ch. 4• Kazenergy pp. 274-275, 290-291, 303-305.























 economics
economics finance
finance industry
industry








