Similar presentations:
Types of Health Care Organizations. The organization of work in these medical personnel
1. Types of Health Care Organizations The organization of work in these medical personnel
Astana Medicine UniversityThe Department of the Introduction
to the Clinic
Types of Health Care
Organizations
The organization of work in
these medical personnel
Prepared by:Erkinova Malika
131 group
General Medicine faculty
2. Outlines
IntroductionClassification of health care agencies:
1- classification by length of stay
2- classification by type of services
3- classification by type of ownership
Health care system in Kazakhstan
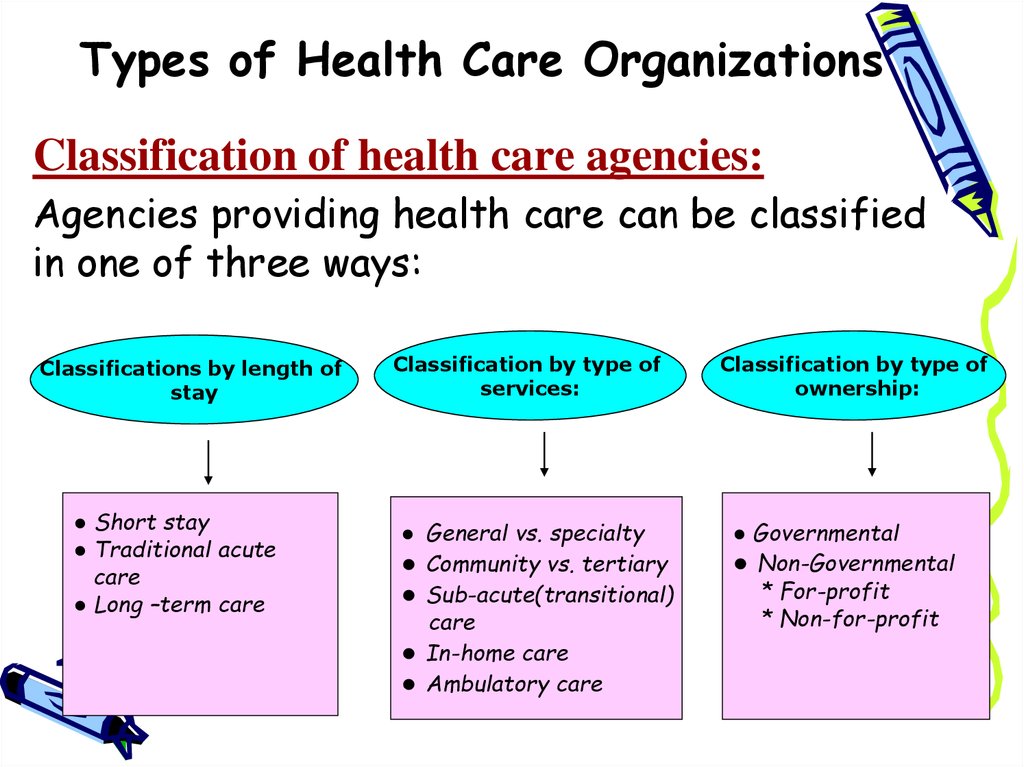
3. Types of Health Care Organizations
Classification of health care agencies:Agencies providing health care can be classified
in one of three ways:
Classifications by length of
stay
● Short stay
● Traditional acute
care
● Long –term care
Classification by type of
services:
● General vs. specialty
● Community vs. tertiary
● Sub-acute(transitional)
care
● In-home care
● Ambulatory care
Classification by type of
ownership:
● Governmental
● Non-Governmental
* For-profit
* Non-for-profit
4. Types of Health Care Organizations
Classification according to length ofstay:
1) Sort-stay facilities:
● Which provide services to patients/clients
who are suffering from acute conditions that
require less than 24 hrs of care.
● Short stay may take place in separate units in a
hospital, or in short –stay centers.
5. Types of Health Care Organizations
2) Traditional acute care:● It takes place in the hospital.
● It includes patients staying more than 24 hrs but fewer
than 30 days.
3) Long term care :
● Which include those agencies that offering
services to patients with major rehabilitation needs,
chronic diseases, functional losses, or
mental illness.
● The average length of stay extends from
several months to years.
6. Types of Health Care Organizations
Classification by type of service:1) General hospital:
● Which offers medical, surgical. Obstetric,
emergency, and diagnostic as well as
laboratory services.
7. Types of Health Care Organizations
2) Specialty hospital:● Which offers only a particular type of care.
such as:
- psychiatric hospitals
- women's hospitals
- children's hospitals
● Specialty hospitals tend to be less common
than general hospitals
8. Types of Health Care Organizations
3) Community hospital:● Which provides those services
provided in the general hospital but
for specific community.
9. Types of Health Care Organizations
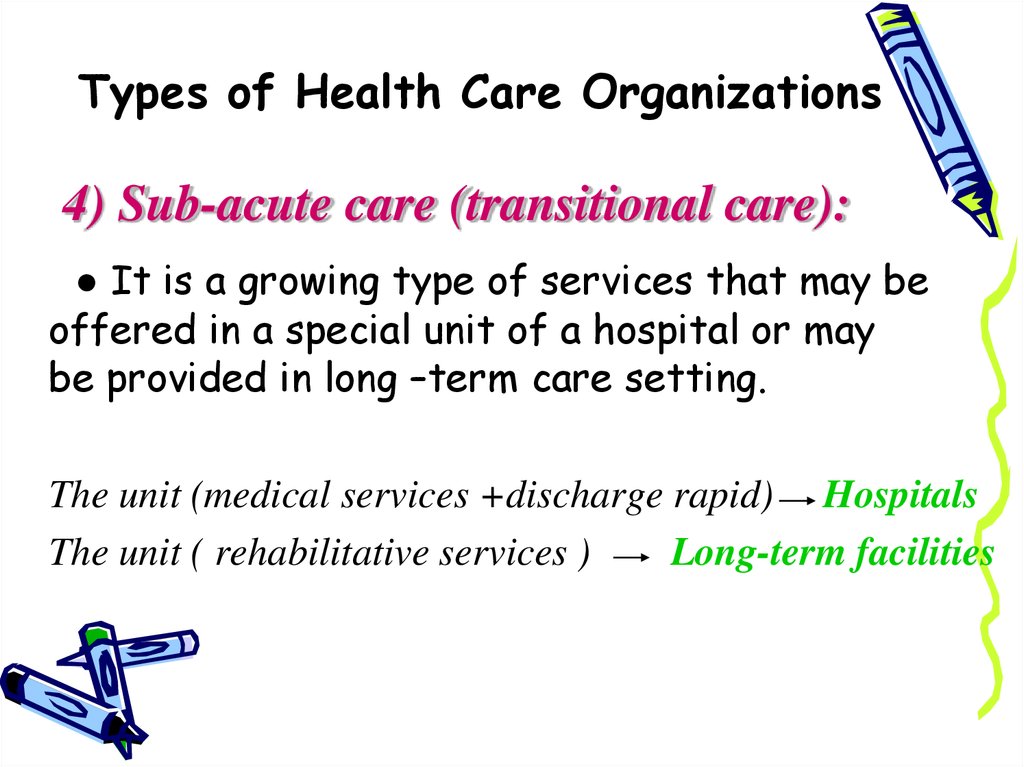
4) Sub-acute care (transitional care):● It is a growing type of services that may be
offered in a special unit of a hospital or may
be provided in long –term care setting.
The unit (medical services +discharge rapid) Hospitals
The unit ( rehabilitative services )
Long-term facilities
10. Types of Health Care Organizations
6) In-home services:●Which are provided in the community health
care agencies, by health care professional
including nurses, physical therapists, social
workers, and home health care aid.
● this care may be:
1) Short–term: teaching and monitoring
after hospitalization
2) Intermediate-term: to assist an
individual until self-care is possible
3) Long-term: for those with ongoing
health problems
11. Types of Health Care Organizations
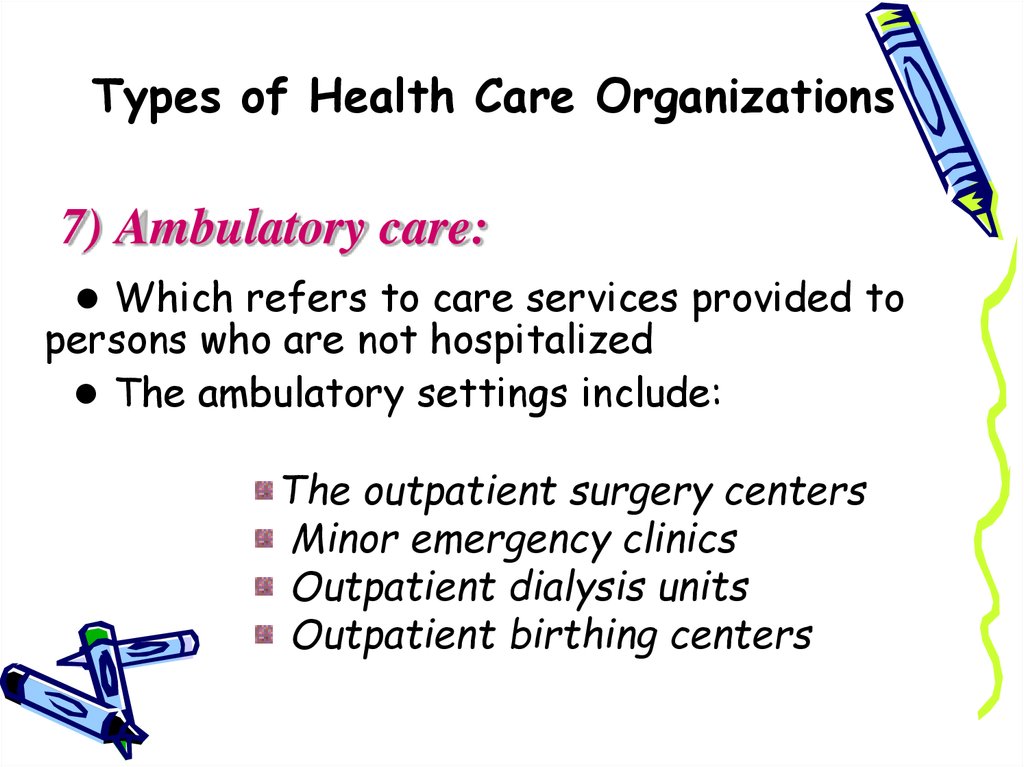
7) Ambulatory care:● Which refers to care services provided to
persons who are not hospitalized
● The ambulatory settings include:
The outpatient surgery centers
Minor emergency clinics
Outpatient dialysis units
Outpatient birthing centers
12. Types of Health Care Organizations
Classification by ownership1) Governmental Organizations:
Owned, administered, and controlled by
government
Provide free care for patients
May offer private accommodation for
free-paying patient
13. Types of Health Care Organizations
The governmental hospital are owned by:abcde-
The Ministry of Health
The University
Military personnel
Health insurance organization
Health care organization
14. Types of Health Care Organizations
2) Non-Governmental Organizations:For-profit agencies (PRIVATE):
owned, operated, and controlled by
individuals, groups, or private organizations.
15. Types of Health Care Organizations
Non-for-profit agencies (Voluntaryhealth agencies):
● Owned and operated by non-profit groups or
organizations (e.g. religious bodies &
community boards)
● The original capital costs are obtained in a
variety of ways (e.g. through donation)
16.
The essential difference between the health care system in Kazakhstan is to maintain a highdegree of centralization of management, preserving many features of free medicine that
existed in the Soviet Union. However, the development of various forms of ownership:
government agencies, state-owned utilities, which combine to provide free medical care to
the various types of paid medical services; Finally, private clinics, as being the state order
for medical care, and working offline.
Establish a regional tertiary care centers. For example, in Astana and Almaty deployed
cardiology centers with cardiovascular surgery, hematology Children's Center in
Karaganda. Their task is to focus high-tech kinds of medical care and to make them as
accessible as possible to the population.
17.
Each division has established a mandatory procedure for the staff and patients of the internal rulesof the division, which provides patients with adherence to treatment and protective modes: sleep and
rest, diet, systematic observation and care, the implementation of medical procedures, and so on. D.
Approximate internal rules of the therapeutic department
6-7 hour ascent, body temperature measurement
7 - 8:00 Toilet
8 - 10:00 Breakfast
10 - 12:00 Bypass doctors
12 - 14 per hour Performing prescribing
14 - 15 h Lunch
15-17 hour quiet hours (rest)
17-18 hour walks, visiting relatives
18-19 hour measurement of body temperature
19 - 20 hour Dinner
20 - 22 hour Free time
22 hour bedtime
18.
Emergency room or emergency department are in every hospital where there are inpatient units fortreatment of patients.
Emergency room (office) for:
- Primary nursing and medical examination of incoming patients in order to establish a preliminary
diagnosis at admission;
- Sanitizing newly admitted patients;
- Preventing the spread of nosocomial infection by creating a health filter;
- Emergency, if necessary - emergency medical care of admissions;
- Compelling differential diagnostic action to implement triage and referral to relevant department or
hospital (hospitalization) or other medical institutions (denial of admission to this hospital)
19.
Practical skills, which must hold a nurse working in the emergency departmentIn the case of the sudden death of a patient nurse must actively participate in resuscitation:
• It must be able to establish the breath of the patient using the device AMBU. The effectiveness of breathing
depends on the proper installation of the patient's head to adhere to the lower jaw;
• be able to quickly remove the electrocardiogram;
• be able to work with a defibrillator;
• know where the drugs used in emergency situations, be able to quickly open the vials, to recruit and to introduce
drugs, knowing that for the provision of resuscitation initially released only 5 minutes;
• Know what medication is best to introduce what syringes; for example, intracardiac adrenaline conveniently
administered long needle connected to a syringe with a capacity of 20 ml, and the treatment of hypoglycemic
coma need to work with two such syringes and always together, one gaining glucose, and the other introduces
her intravenously. During resuscitation, many of manipulation and must be carried out carefully, without
error and virtually be brought to automaticity (intravenous injection, electrocardiogram, and more).
Therefore, starting the duty, it is necessary to carefully check what medicines are available and where they are
(it is desirable to have a first aid kit, where the order are necessary for intensive care medicine); to see in what
condition the electrocardiograph, sufficient amount of paper in it.

















 medicine
medicine








