Similar presentations:
RL Circuits. Fundamentals of Electronics
1.
RL CircuitsOEk 1115 - Fundamentals of Electronics
Lecture 10
2.
OutlineSeries RL Circuits
Parallel RL Circuits
Series-Parallel RL Circuits
3.
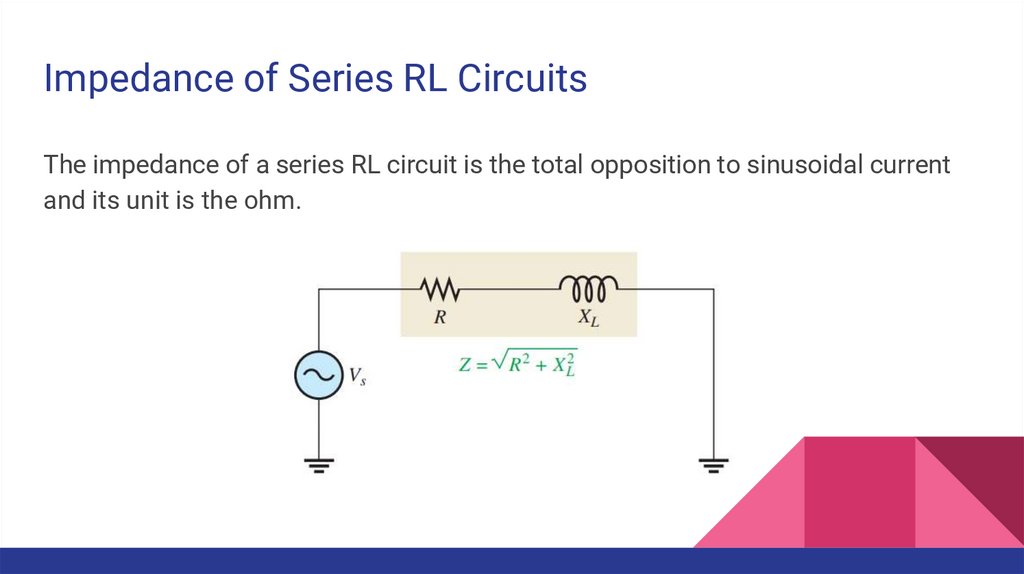
Impedance of Series RL CircuitsThe impedance of a series RL circuit is the total opposition to sinusoidal current
and its unit is the ohm.
4.
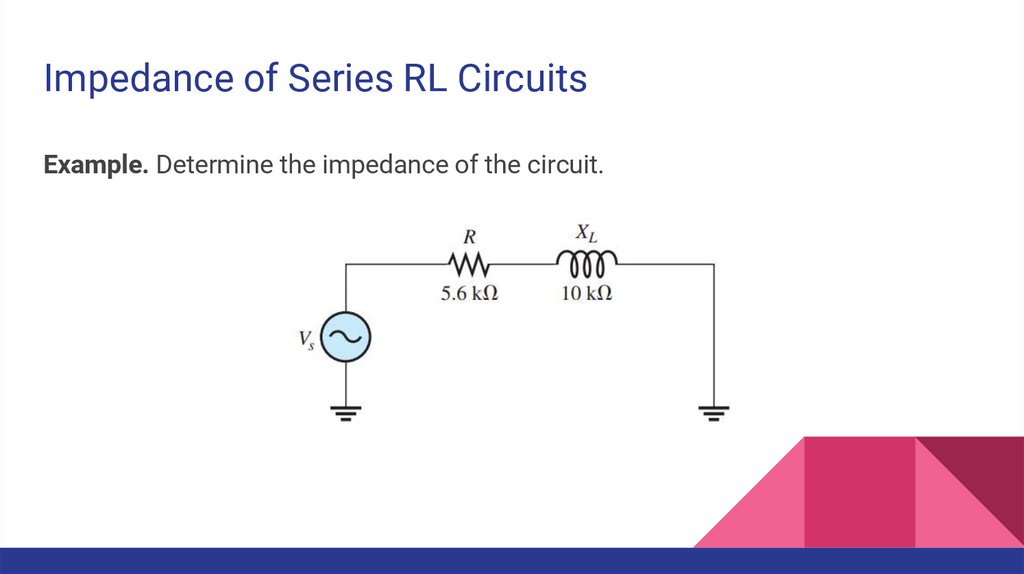
Impedance of Series RL CircuitsExample. Determine the impedance of the circuit.
5.
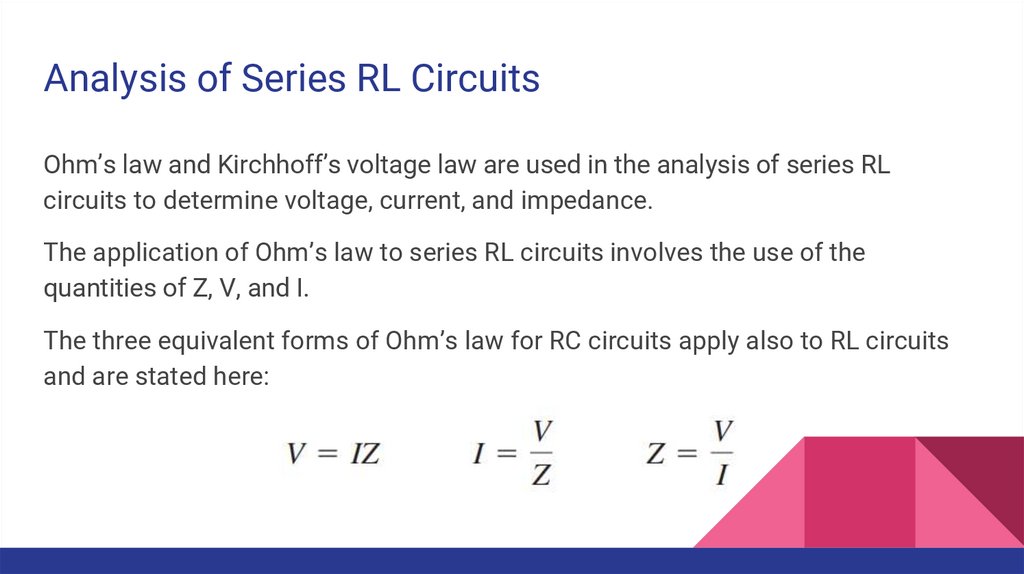
Analysis of Series RL CircuitsOhm’s law and Kirchhoff’s voltage law are used in the analysis of series RL
circuits to determine voltage, current, and impedance.
The application of Ohm’s law to series RL circuits involves the use of the
quantities of Z, V, and I.
The three equivalent forms of Ohm’s law for RC circuits apply also to RL circuits
and are stated here:
6.
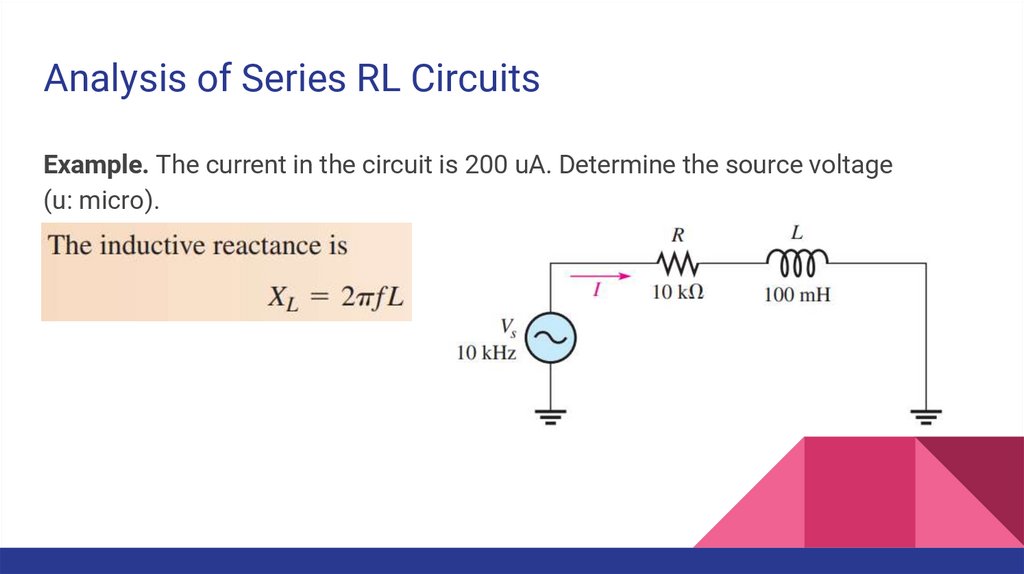
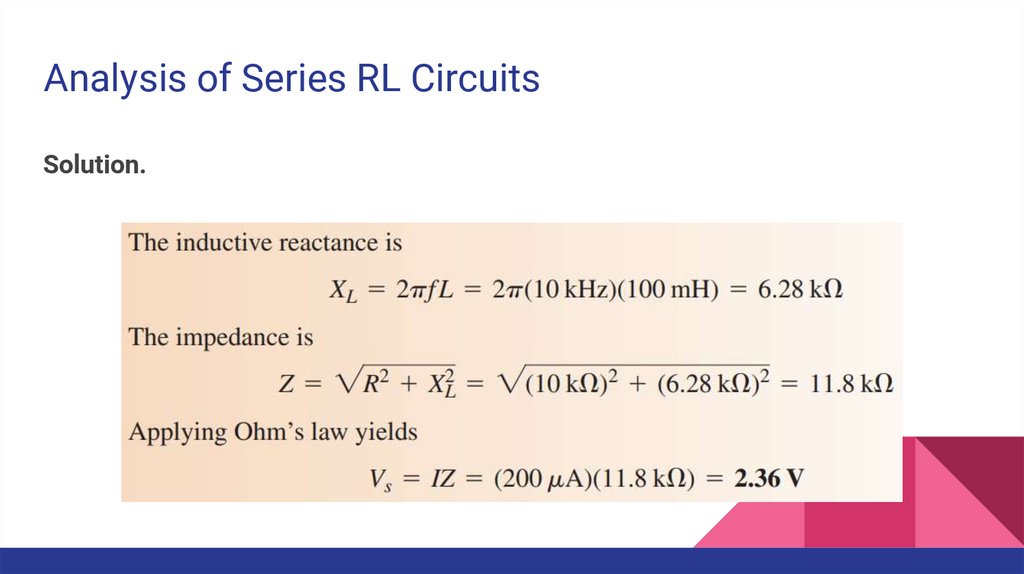
Analysis of Series RL CircuitsExample. The current in the circuit is 200 uA. Determine the source voltage
(u: micro).
7.
Analysis of Series RL CircuitsSolution.
8.
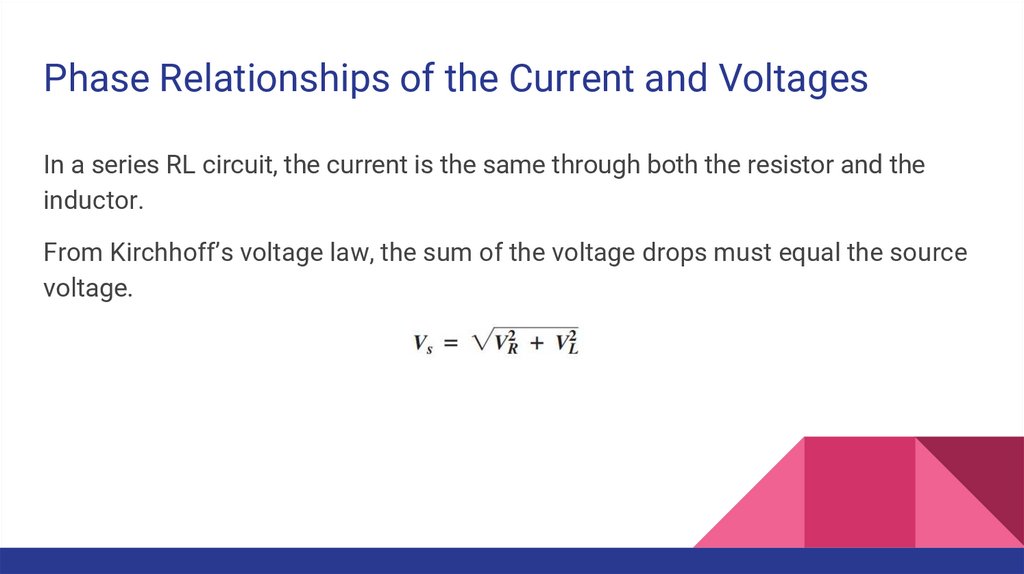
Phase Relationships of the Current and VoltagesIn a series RL circuit, the current is the same through both the resistor and the
inductor.
From Kirchhoff’s voltage law, the sum of the voltage drops must equal the source
voltage.
9.
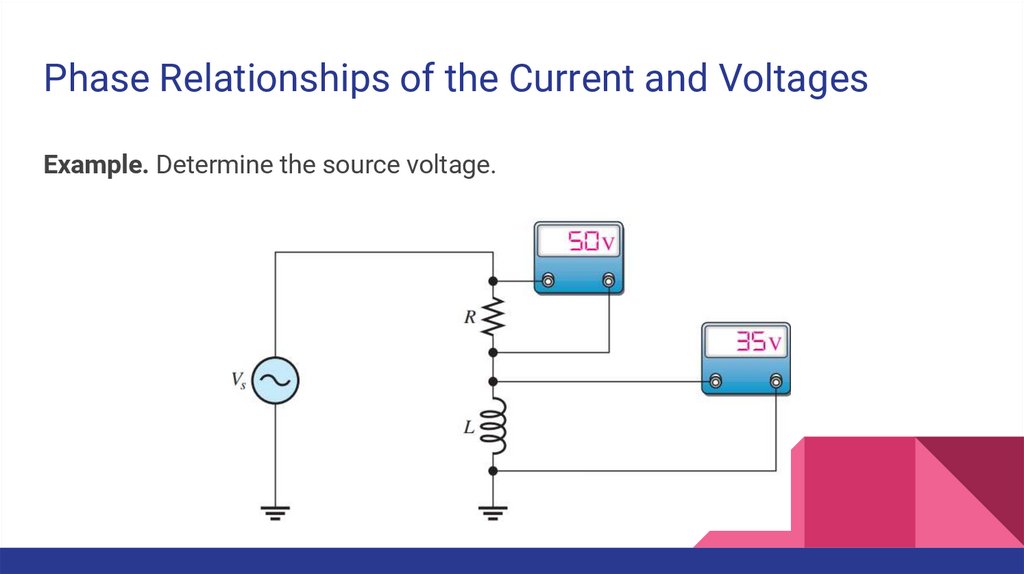
Phase Relationships of the Current and VoltagesExample. Determine the source voltage.
10.
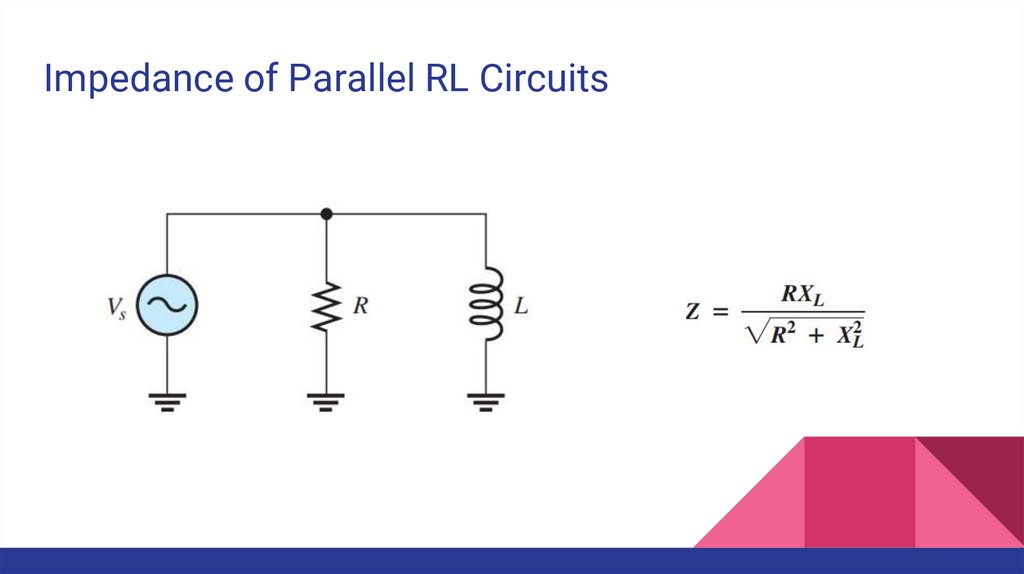
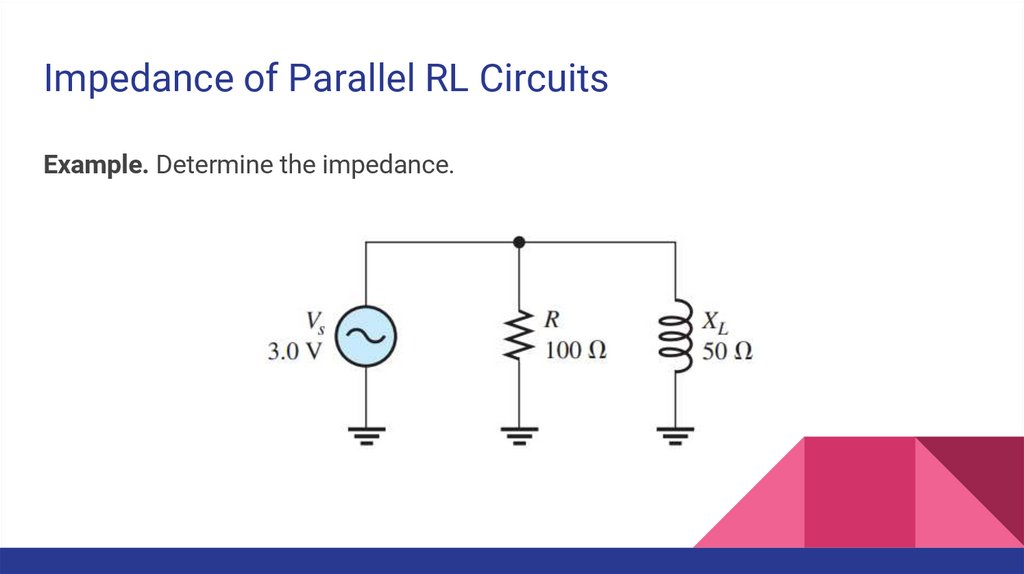
Impedance of Parallel RL Circuits11.
Impedance of Parallel RL CircuitsExample. Determine the impedance.
12.
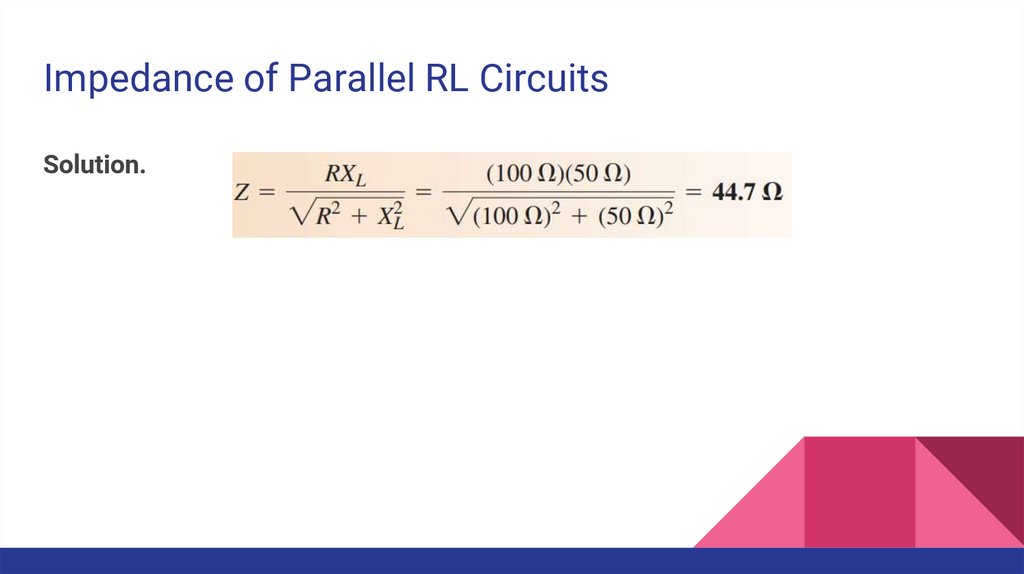
Impedance of Parallel RL CircuitsSolution.
13.
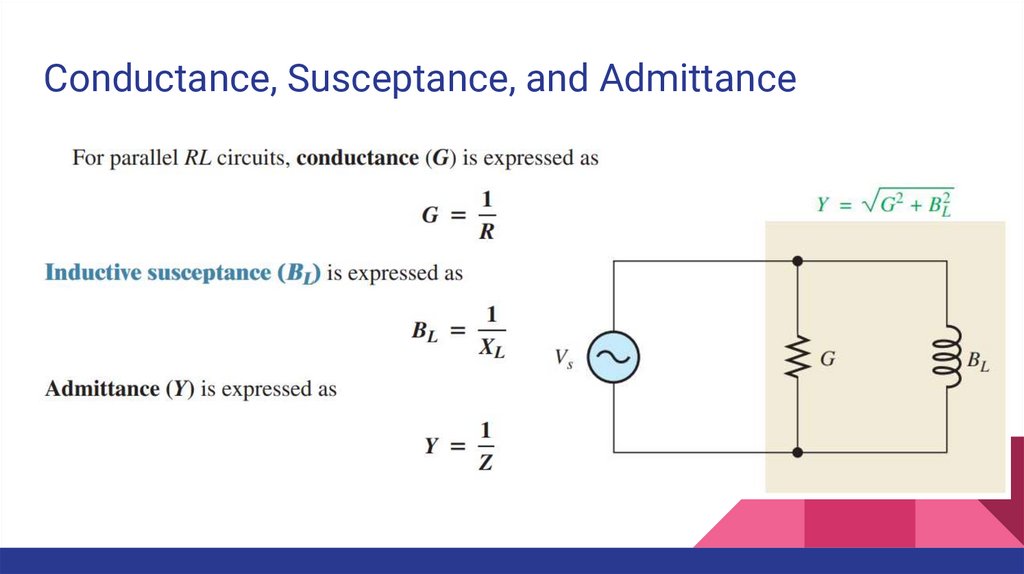
Conductance, Susceptance, and Admittance14.
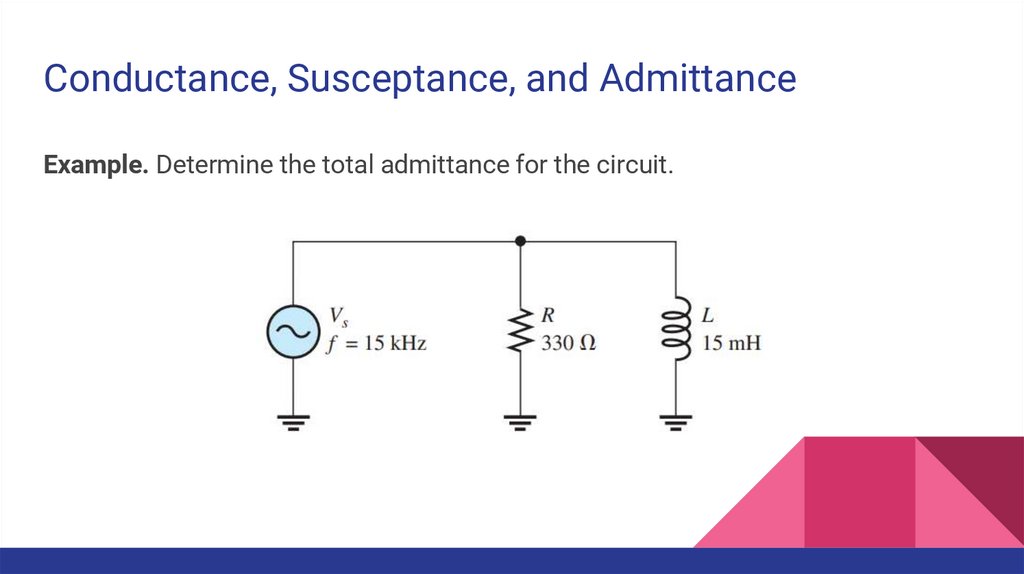
Conductance, Susceptance, and AdmittanceExample. Determine the total admittance for the circuit.
15.
Solution.16.
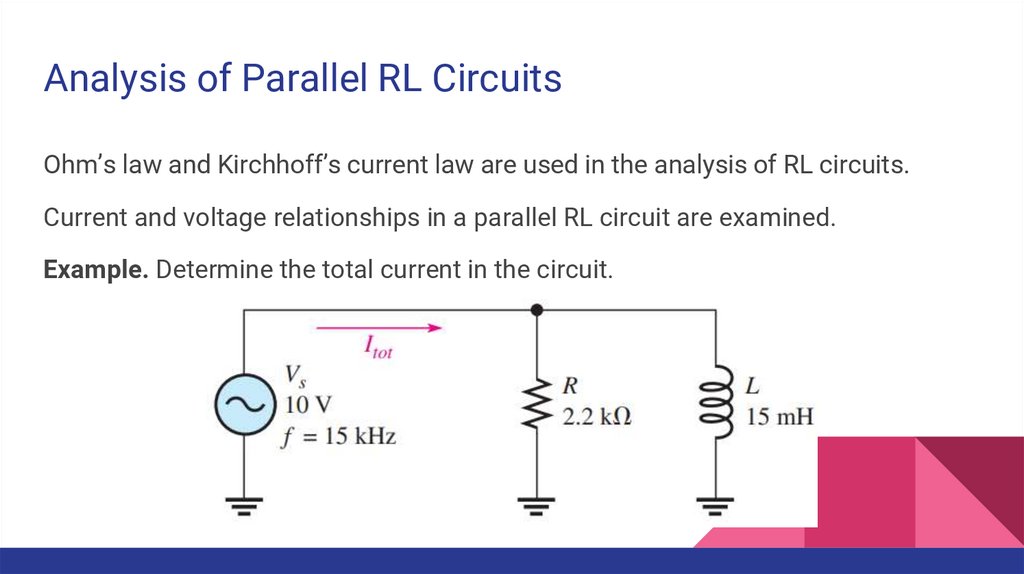
Analysis of Parallel RL CircuitsOhm’s law and Kirchhoff’s current law are used in the analysis of RL circuits.
Current and voltage relationships in a parallel RL circuit are examined.
Example. Determine the total current in the circuit.
17.
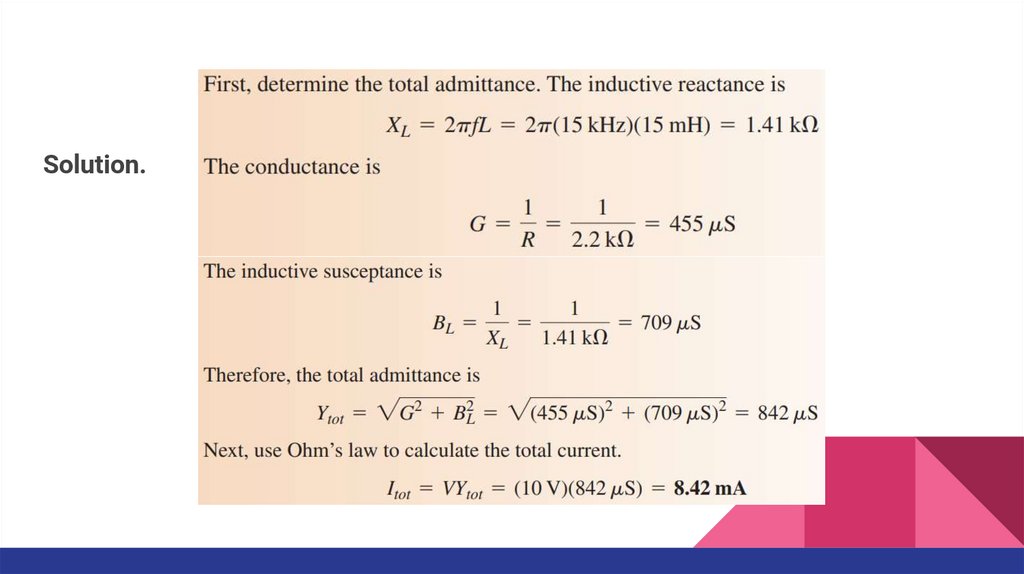
Solution.18.
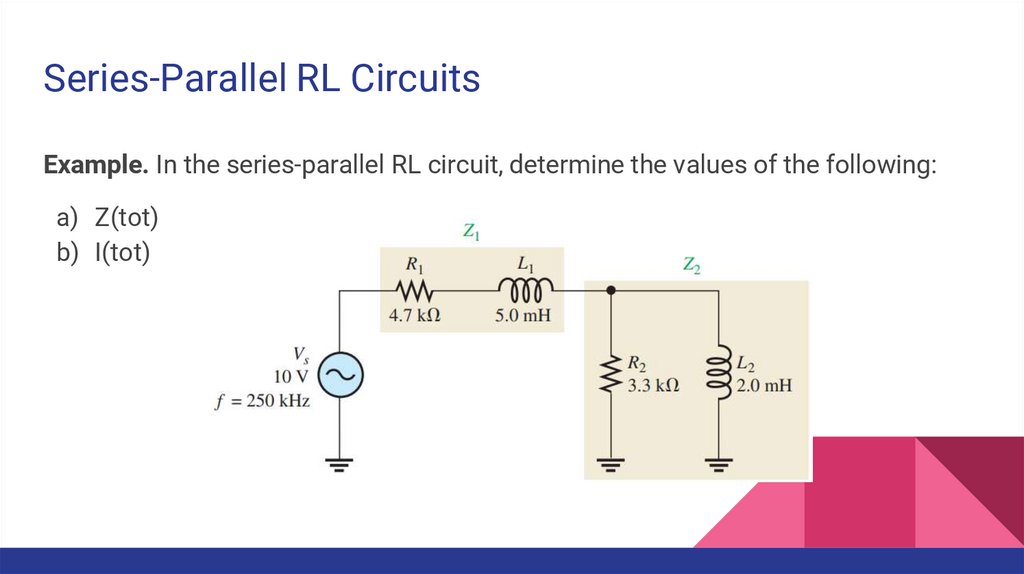
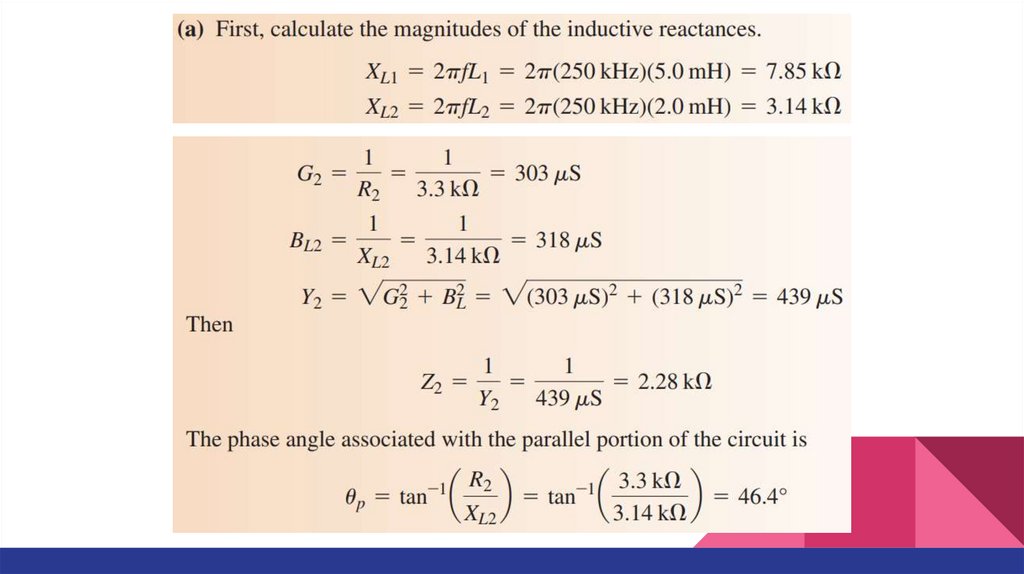
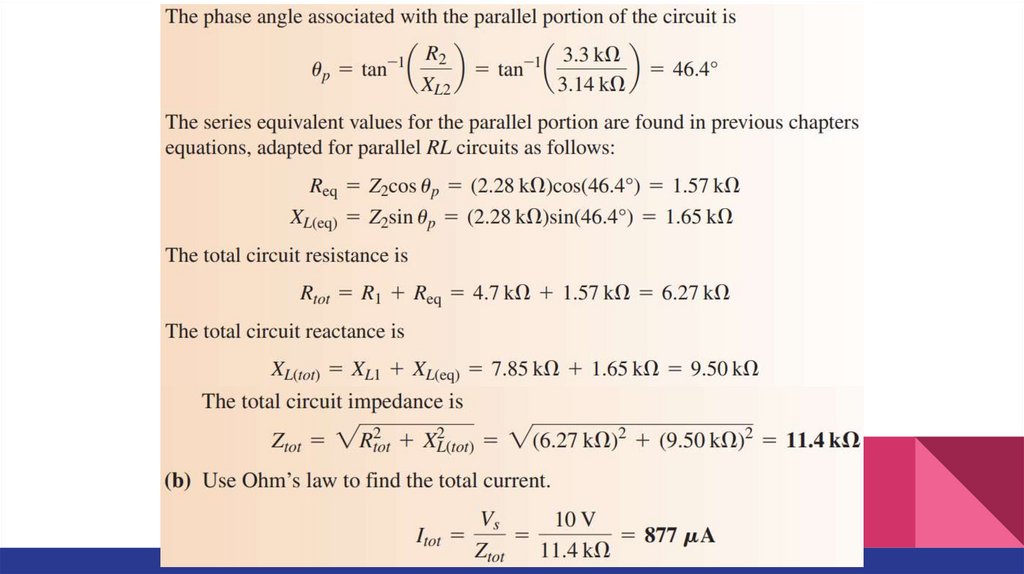
Series-Parallel RL CircuitsExample. In the series-parallel RL circuit, determine the values of the following:
a) Z(tot)
b) I(tot)
19.
20.
21.
Q&AAny Questions?




 physics
physics








