Similar presentations:
Kazakh-American Free University
1.
Kazakh-American Free UniversityPolitical
Science
Valentina V. Gersonskaya
Autumn 2024
2.
OutlineForms of government
Autocracy
Democracy
Oligarchy
Junta
Religious government
10/19/2024
Political Science
2
3.
QuestionsWhat is the difference between monarchy and
dictatorship?
What is the difference between semiconstitutional and constitutional monarchies?
What is characteristic of subnational
monarchies?
What is bad about oligarchy?
What state has anarchy?
10/19/2024
Political Science
3
4.
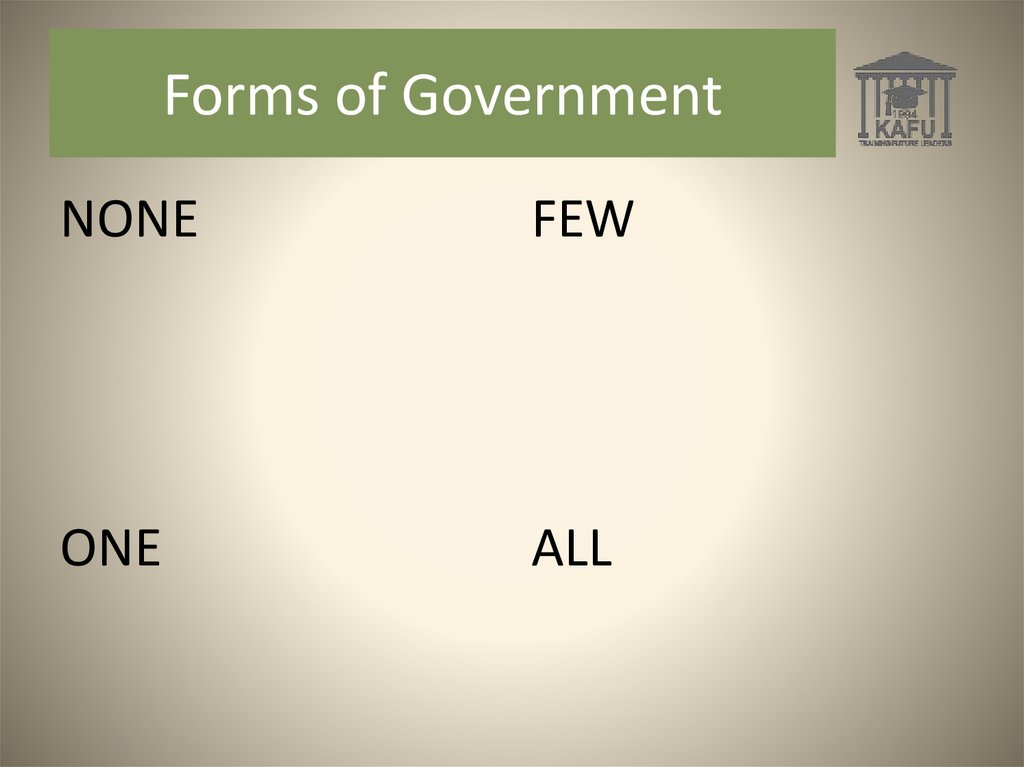
Forms of Government5.
WHO RULES ?6.
Forms of GovernmentNONE
FEW
ONE
ALL
7.
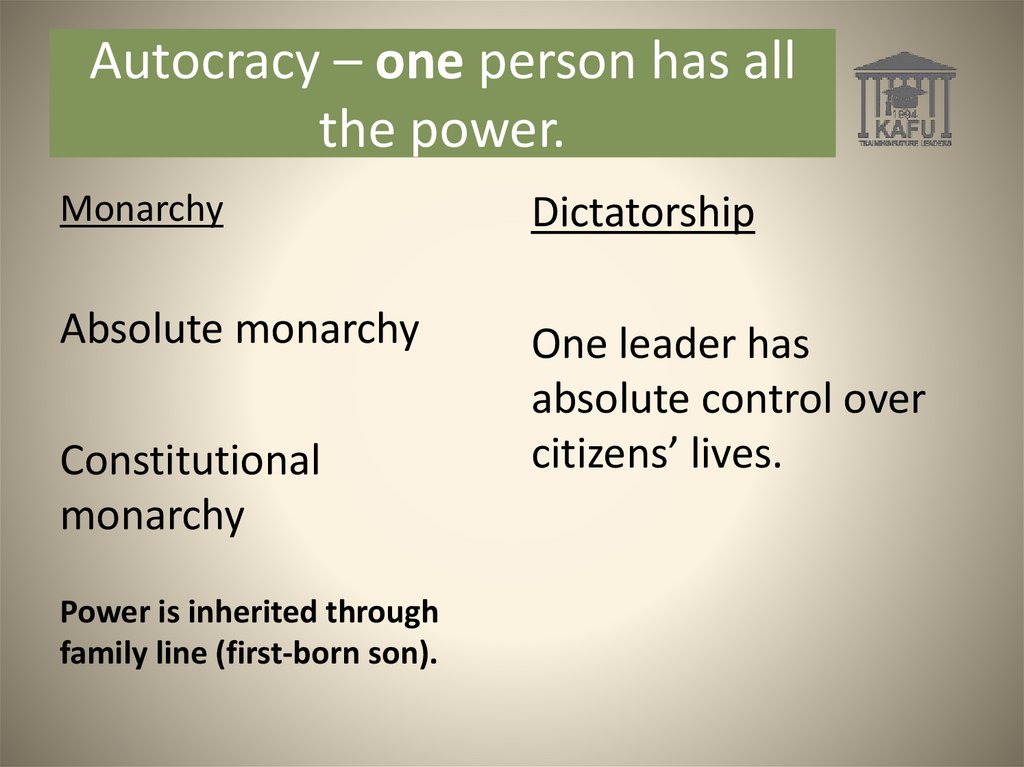
Autocracy – one person has allthe power.
Monarchy
Dictatorship
Absolute monarchy
One leader has
absolute control over
citizens’ lives.
Constitutional
monarchy
Power is inherited through
family line (first-born son).
8.
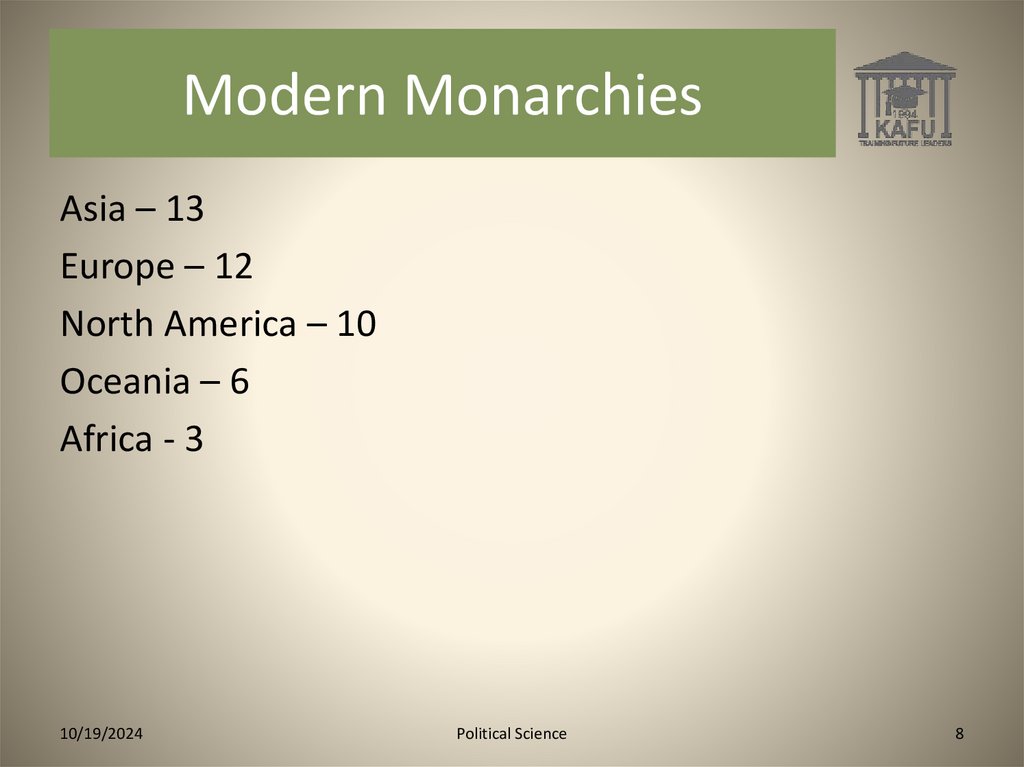
Modern MonarchiesAsia – 13
Europe – 12
North America – 10
Oceania – 6
Africa - 3
10/19/2024
Political Science
8
9.
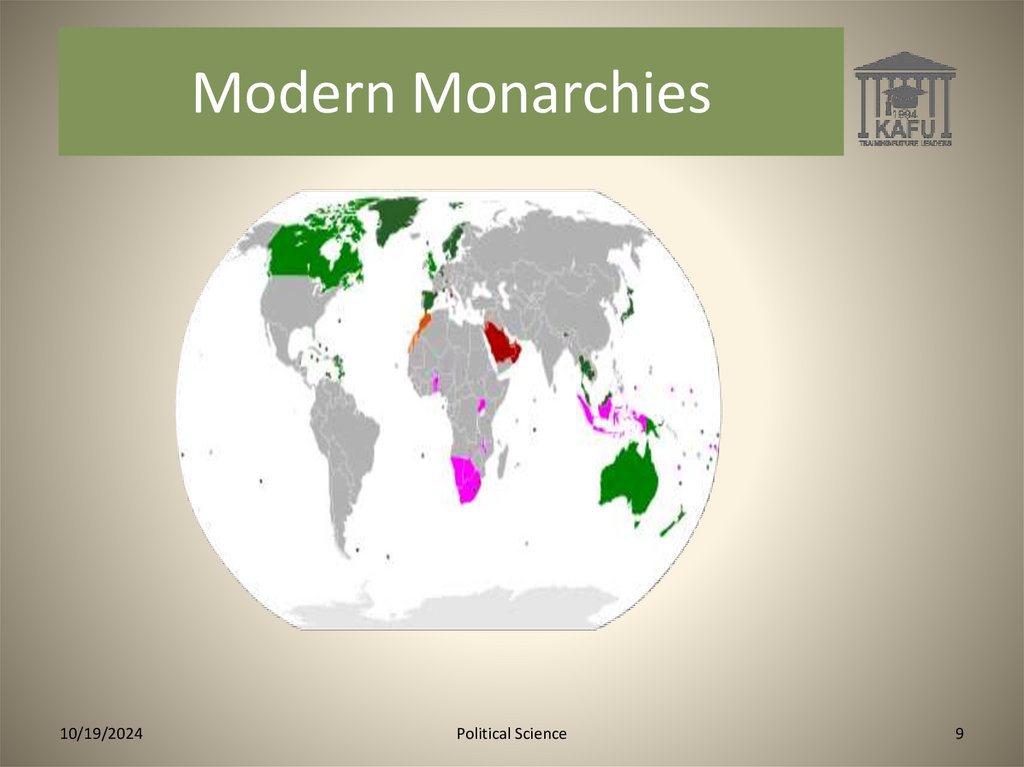
Modern Monarchies10/19/2024
Political Science
9
10.
Modern Monarchies - 44Absolute monarchy
Semi-constitutional monarchy
Constitutional monarchy
Commonwealth realms
Subnational monarchy (traditional)
10/19/2024
Political Science
10
11.
Constitutional MonarchiesWith real sovereign’s
power
With nominal power
Liechtenstein, Monaco,
Morocco, Jordan, Kuwait,
Bahrain and Bhutan
the United Kingdom and
other Commonwealth
realms, the Netherlands,
Spain, Belgium, Denmark,
Norway, Sweden, Lesotho,
Malaysia, Thailand,
Cambodia, and Japan,
10/19/2024
Political Science
11
12.
Commonwealth of Nations10/19/2024
Political Science
12
13.
Commonwealth of Nations(56 countries)
The United Kingdom of
Great Britain and Modern
Ireland
The Commonwealth of
Australia
Barbados
Antigua and Barbuda
Belize
The Commonwealth of the
Bahamas
Canada
Grenada
10/19/2024
Political Science
Jamaica
New Zealand
Santa Lucia
The Independent State of
Papua New Guinea
The Federation of Saint Kitts
and Nevis
Saint Vincent and the
Grenadines
Solomon Islands
Tuvalu
Malaisia
Mozambique…
13
14.
Commonwealth Realms -15countries
Antigua and Barbuda,
Australia, The Bahamas,
Belize, Canada, Grenada,
Jamaica, New Zealand,
Papua New Guinea, Saint
Kitts and Nevis, Saint
Lucia, Saint Vincent and
the Grenadines, Solomon
Islands, Tuvalu, and the
United Kingdom
10/19/2024
Charles III is the
Head of the State. In
14 realms he is
represented
by
governor-general.
Political Science
14
15.
The Principality of Andorra10/19/2024
Political Science
15
16.
The Principality of AndorraDiarchy – Co-princeship
The President of France
The Bishop of Urgell
• Neither Co-Prince is of Andorran descent.
• The President of France is elected by common
citizens of a foreign country (France), but not by
Andorrans as they cannot vote in the French
Presidential Elections.
• The bishop of Urgell is appointed by a foreign head
of state, the Pope.
10/19/2024
Political Science
16
17.
Democracy – power of all.Representative
Direct
Citizens
elect
leaders to represent
their rights and
interests
in
government.
Citizens are directly
involved in the work
of governing the
country.
18.
DemocracyPresidential
Parliamentary
Parliamentary vs.
Presidential Democracy
Explained
https://www.youtube.com
/watch?v=4quK60FUvkY
10/19/2024
Political Science
18
19.
Rule of Small GroupOligarchy
Junta
Small group has all
the power.
Small
group
of
military officers take
over
and
rule
country by force.
20.
OligarchyOligarchy is government of and by few at
the top who exercise power for their own
benefit.
Oligarkes (Gr.: few to rule or command)
Citizens have
government
little
involvement
in
Sparta (28 elders + two kings)
“Hunger Games”
10/19/2024
Political Science
20
21.
Types of Oligarchic Control• Military
• Social Position
• Wealth
• Religion
• Combination of several types
10/19/2024
Political Science
21
22.
Law of OligarchyRobert Michels “Political Parties”.
Gist:
• All forms of organization and government lead to
oligarchy.
• Most common in representative democracy.
• People are divided into rulers and those ruled.
• The elite is divided into decision-makers who
plan things and those who realize plans.
10/19/2024
Political Science
22
23.
Oligarchy in the 1st Gilded AgeThe USA (the 1880s - 1904)
Vast inequality
Corruption
Poverty
Hardships for most
Huge riches for a few
The way out: strict regulation of Wall Street and
encouraging Labor unions (trade unions)
10/19/2024
Political Science
23
24.
Government by organized money is just asdangerous as government by organized
mob.
Th. Roosewelt
The 2nd Gilded Age (2000 -)
10/19/2024
Political Science
24
25.
Religious Rule - TheocracyGovernment that recognizes God or a
divine being as the ultimate authority.
26.
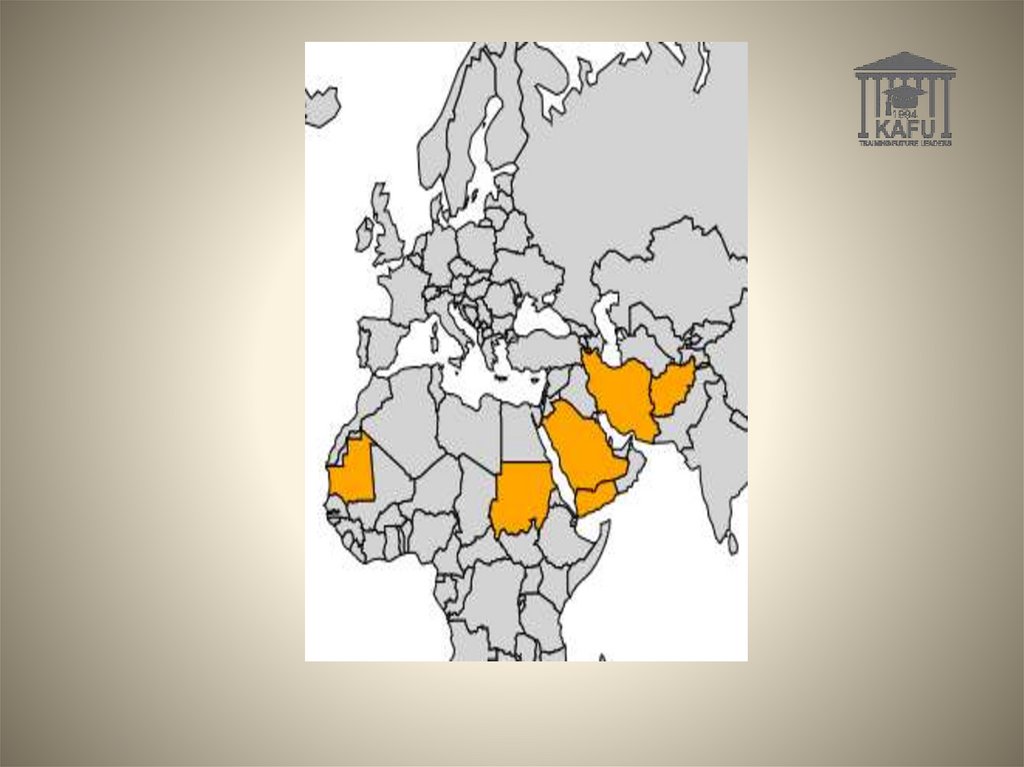
27.
Vatican CityYemen
Saudi Arabia
Sudan
Iran
Mauritania
Afghanistan
28.
Anarchy – no government and laws.29.
QuestionsWhat is the difference between monarchy and
dictatorship?
What is the difference between semiconstitutional and constitutional monarchies?
What is characteristic of subnational
monarchies?
What is bad about oligarchy?
What state has anarchy?
10/19/2024
Political Science
29
























 history
history








