Similar presentations:
Discrete Math
1.
• Discrete Math1
2.
Chapter 1.1Logical Form, Logical Equivalence and
Conditional Statements
2
3.
34.
45.
56.
67.
78.
89.
910.
1011.
1112.
1213.
1314.
1415.
1516.
1617.
1718.
1819.
1920.
2021.
2122.
2223.
2324.
2425.
2526.
2627.
Chapter 1.2Digital Logical Circuits and Number Systems
27
28.
2829.
2930.
3031.
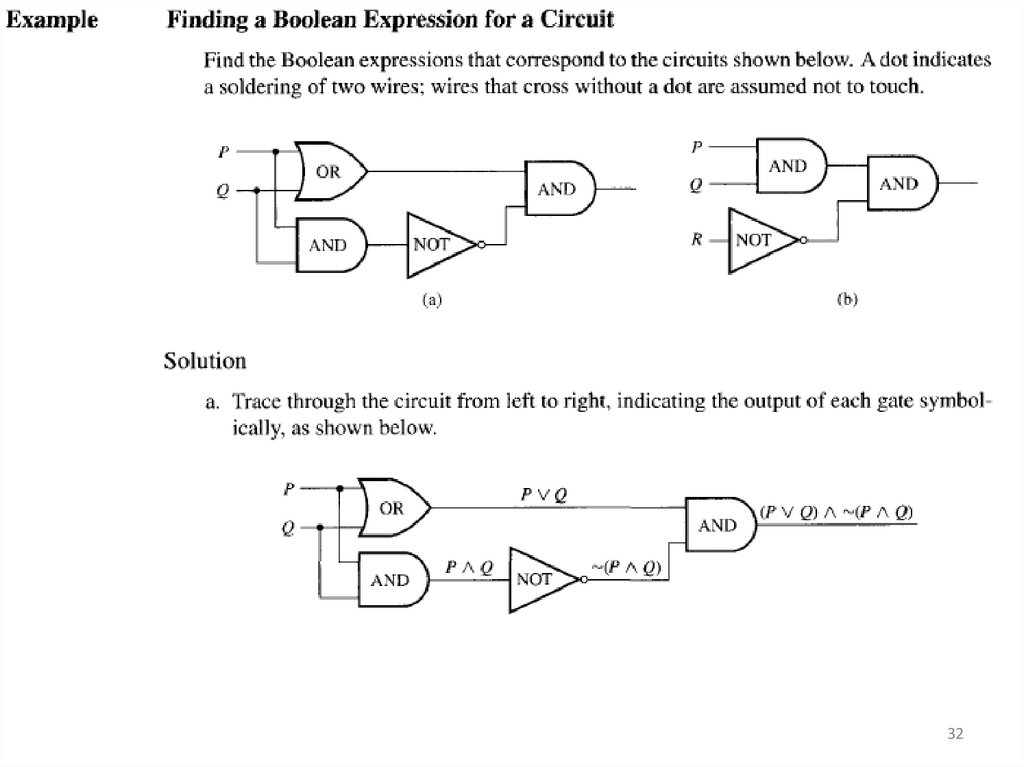
3132.
3233.
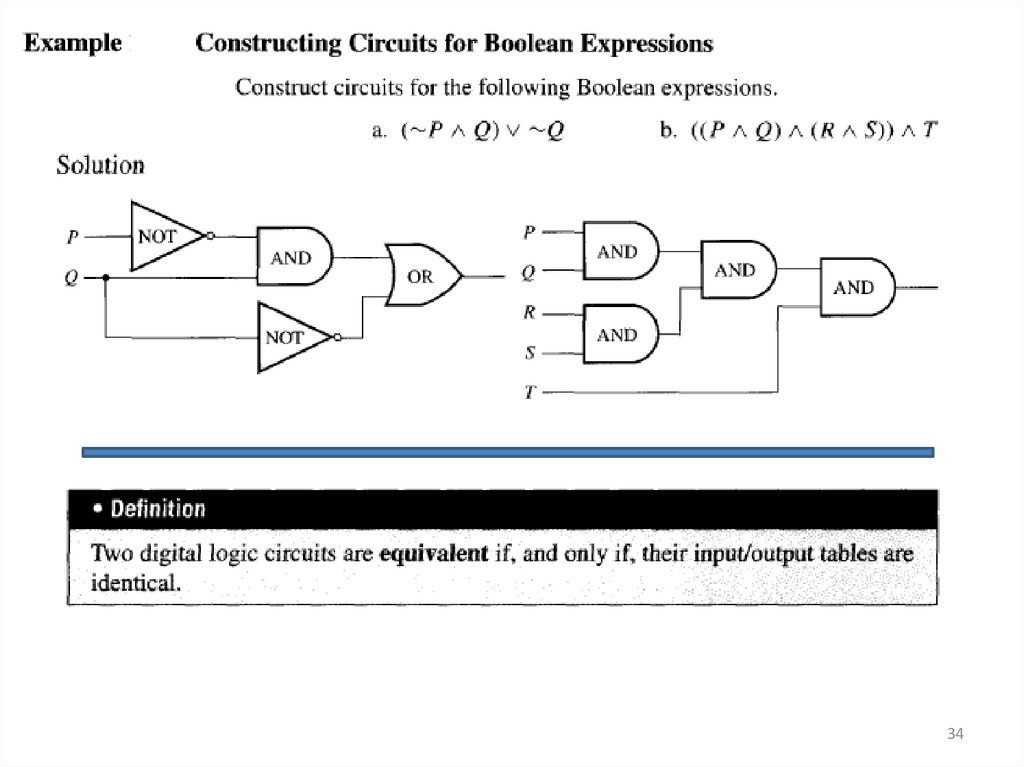
3334.
3435.
3536.
3637.
3738.
3839.
3940.
4041.
4142.
Chapter 2Predicates and Quantifiers
42
43.
4344.
4445.
4546.
4647.
4748.
4849.
4950.
5051.
5152.
5253.
5354.
5455.
5556.
5657.
5758.
5859.
5960.
6061.
6162.
6263.
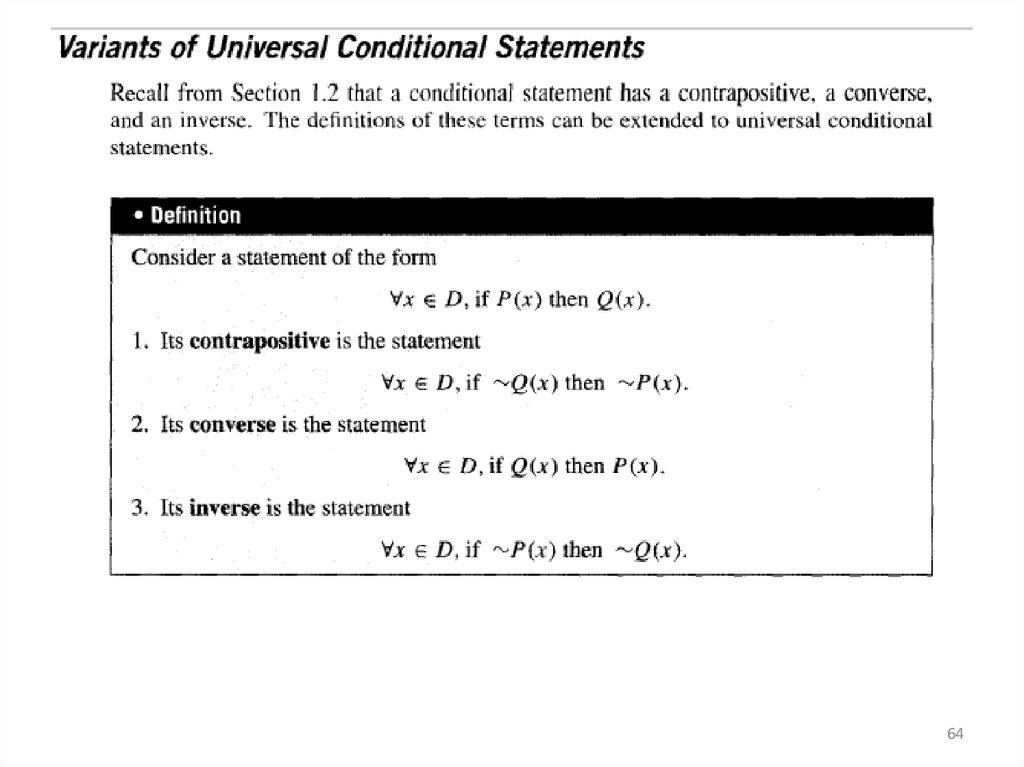
6364.
6465.
6566.
6667.
6768.
6869.
6970.
7071.
7172.
Example 1:72
73.
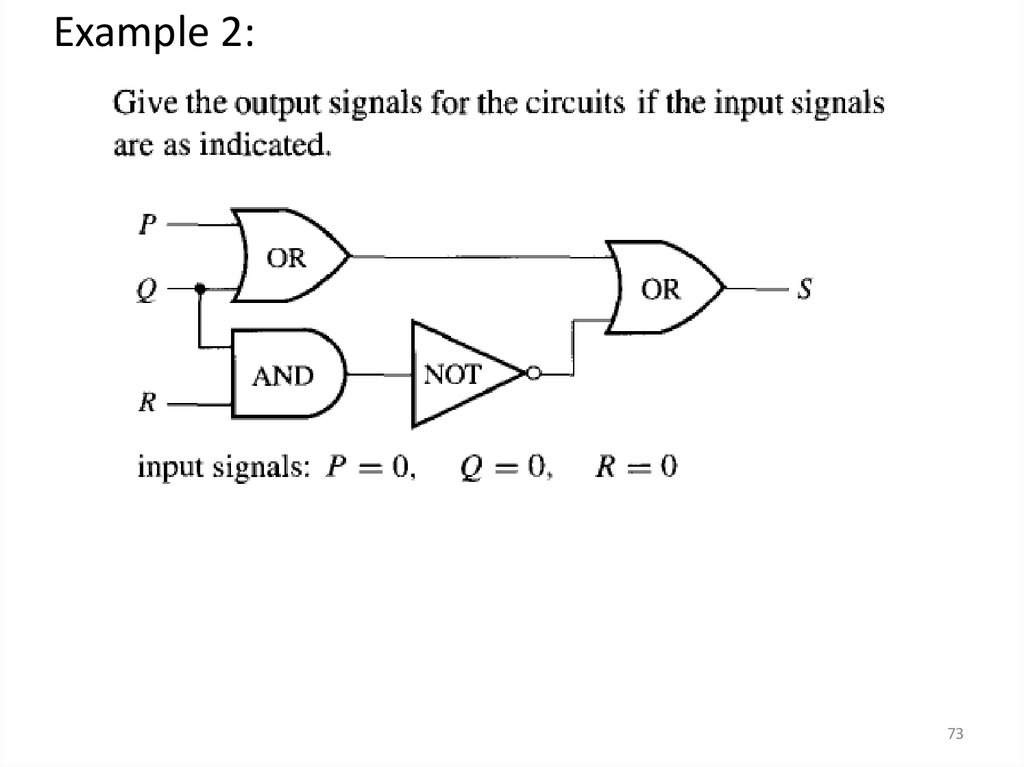
Example 2:73
74.
Example 3:74
75.
Example 4:Show that circuits in a) and b) produce the same output table,
and same boolean expressions.
75
76.
Example 5:Show that circuits in a) and b) produce the same output table,
and same boolean expressions.
76
77.
Example 6:77
78.
Example 7:Show that circuits in a) and b) produce the same output table,
and same boolean expressions.
78
79.
Example 8:Verify the logical equivalences given below.
79
80.
Example 9:80
81.
Examples 10,11:81
82.
Example 12:82
83.
Example 13:83
84.
Example 14:84
85.
Example 15:85
86.
Example 16:86
87.
Example 17:87
88.
Example 18:88
89.
Example 19:89
90.
Example 20:90
91.
Example 21:91
92.
Example 22:92
93.
Example 23:93
94.
Example 24:94
95.
Example 25:95
96.
Example 26:96
97.
Example 27:97
98.
Example 28:98
99.
Example 29:99































































































 mathematics
mathematics








