Similar presentations:
The noun (lecture 3)
1.
Lecture 3:THE NOUN
2.
Plan:1. General characteristics of the
Noun as a part of speech.
2. Number.
3. Case.
4. The problem of gender in modern
English.
3.
4.
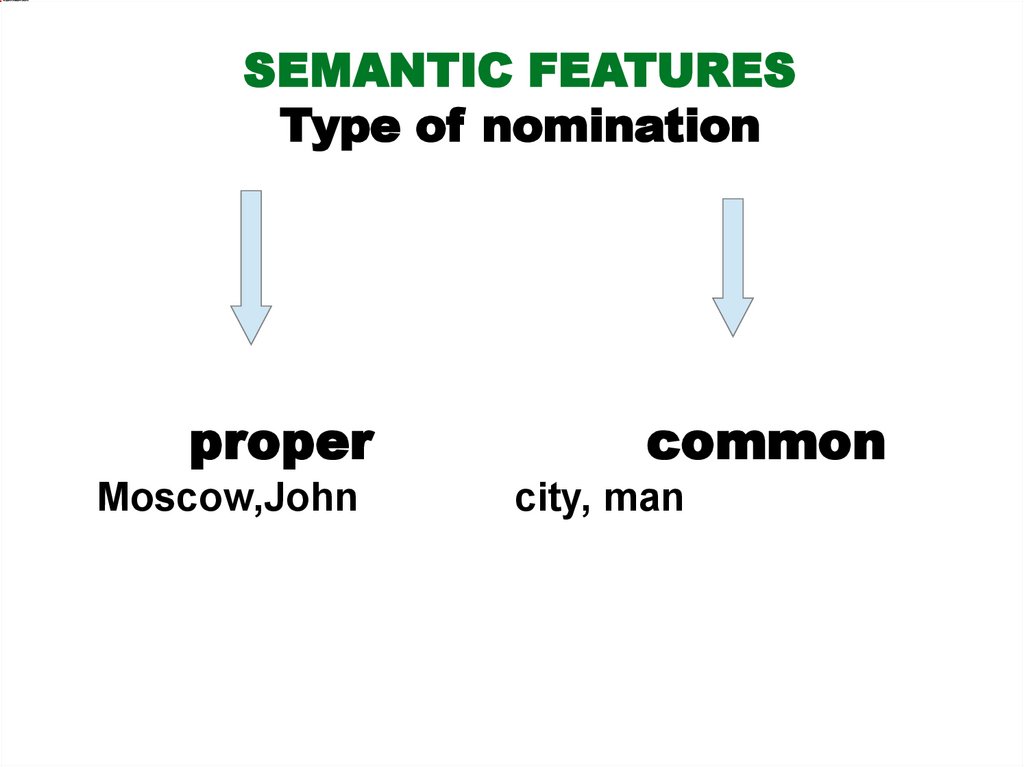
SEMANTIC FEATURESType of nomination
proper
Moscow,John
common
city, man
5.
6.
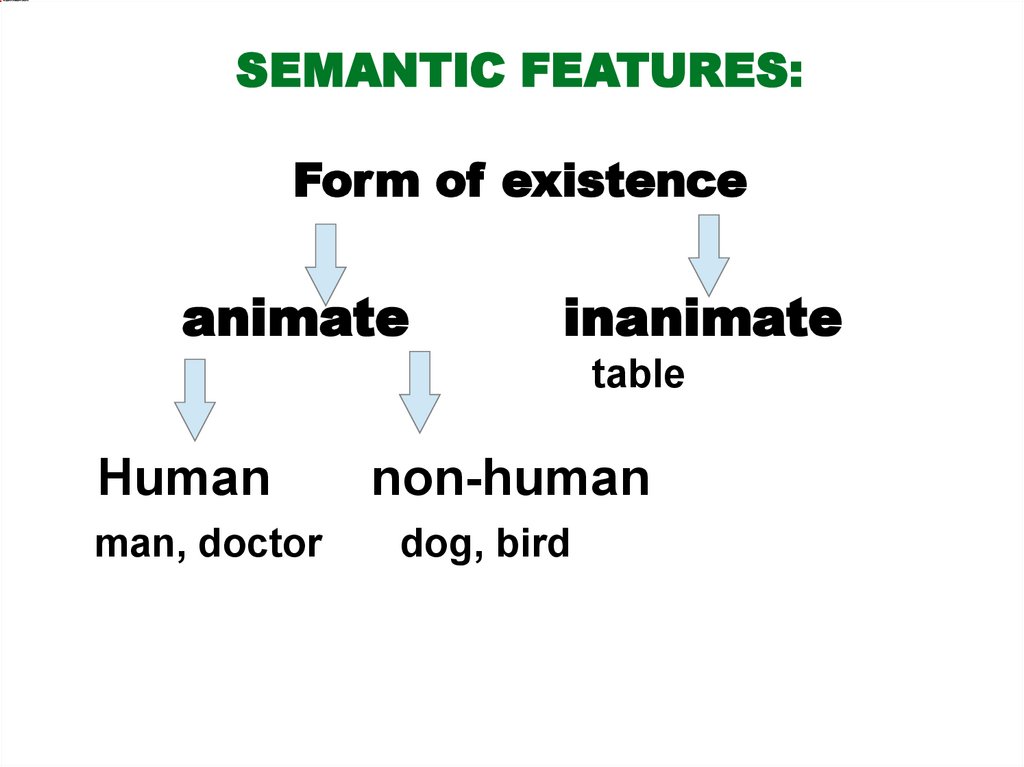
SEMANTIC FEATURES:Form of existence
animate
inanimate
table
Human
non-human
man, doctor
dog, bird
7.
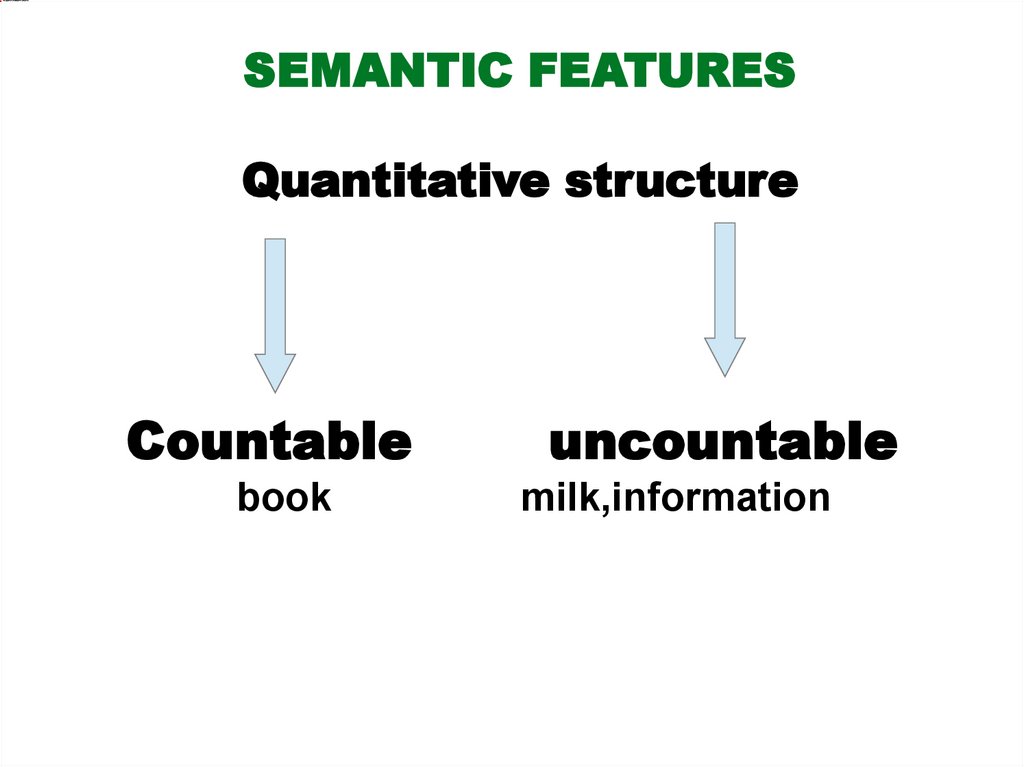
SEMANTIC FEATURESQuantitative structure
Countable
book
uncountable
milk,information
8.
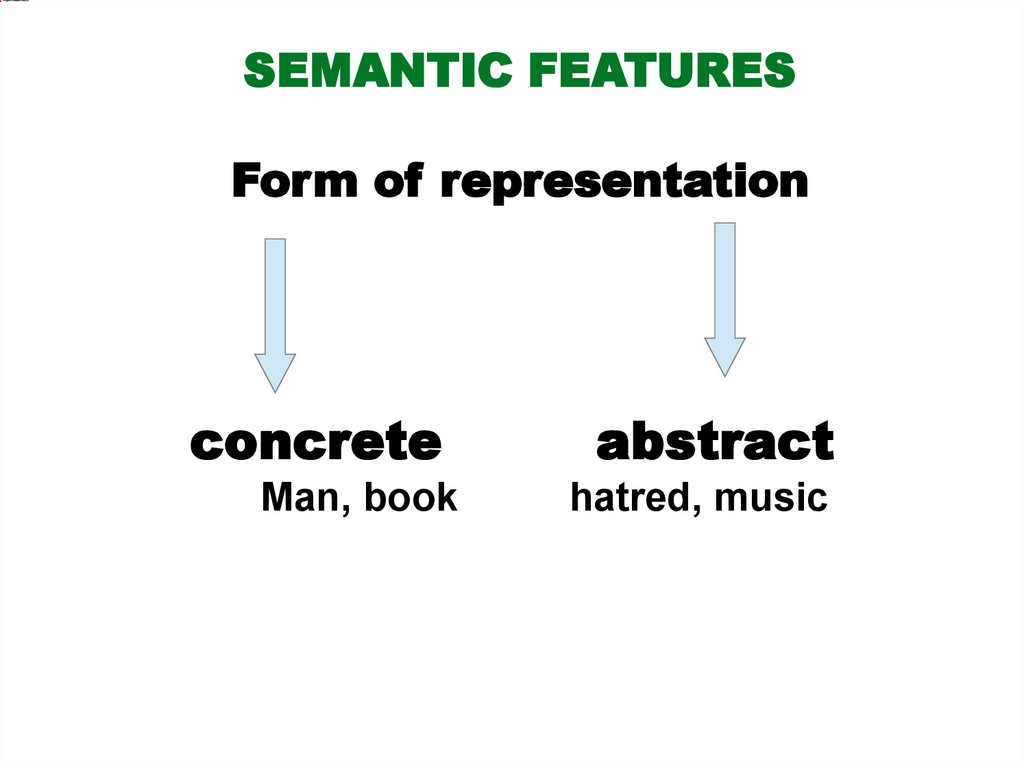
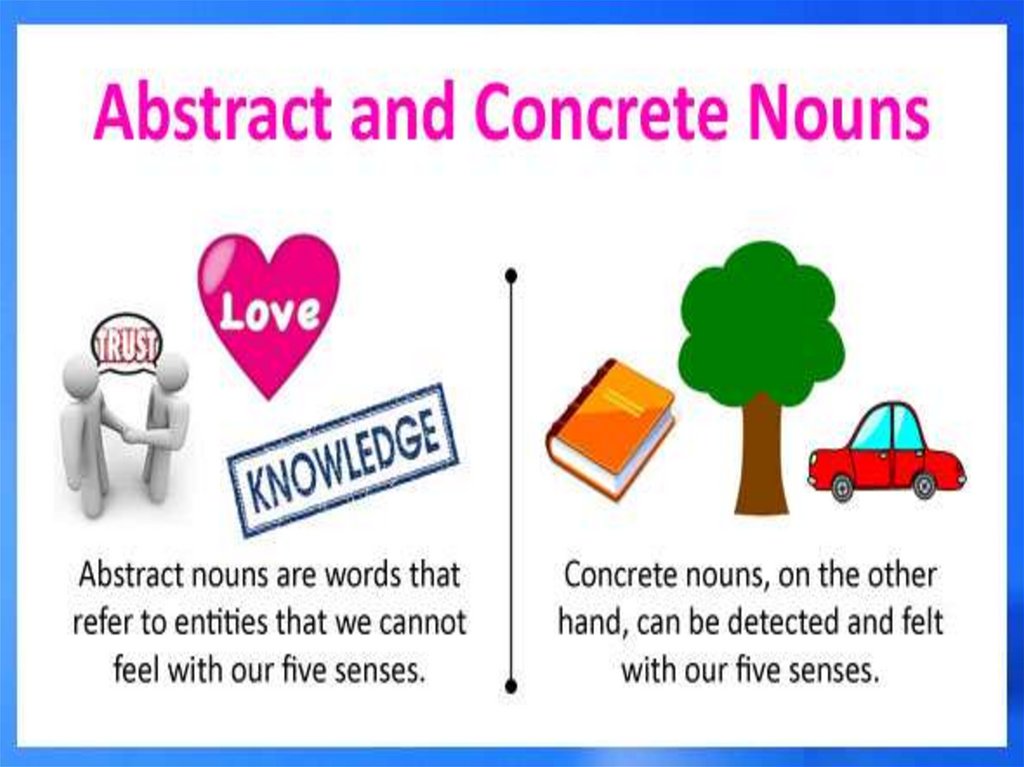
SEMANTIC FEATURESForm of representation
concrete
abstract
Man, book
hatred, music
9.
10.
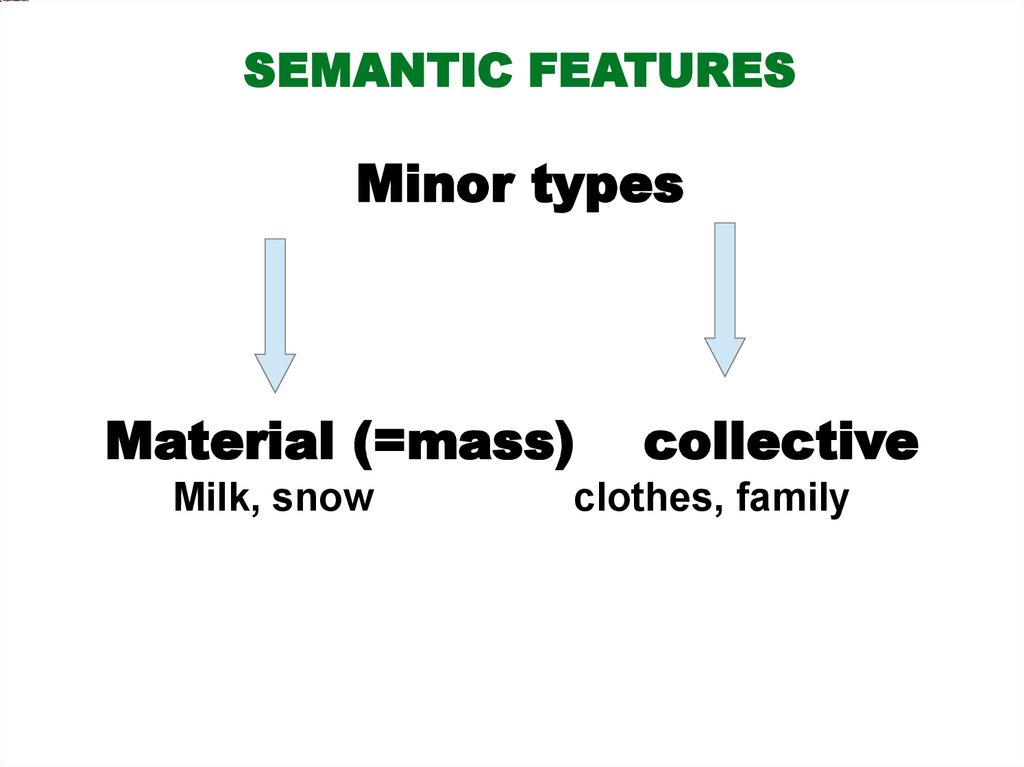
SEMANTIC FEATURESMinor types
Material (=mass)
Milk, snow
collective
clothes, family
11.
12.
Morphological features:According to morphemic structure:
•Simple (pen)
•Derived (dark/ness)
•Compound (armchair)
•Composite (sister-in-law, forget-me-not)
13.
Morphological features:(grammatical categories):
•Number (Sg/Pl)
•Case (Common/possessive)
14.
Syntactic features:Perform
functions!!!
ALL
syntactic
The only exception – predicate (but it can
be a predicative:
He is (a teacher).
15.
Distributional features:Can be combined with almost
ALL parts of speech:
A pen (article)
A summer dress (a noun)
the boy reads
(a verb).
A clever boy (adjective)
Two boys (numeral)
The seat behind (adverb)
16.
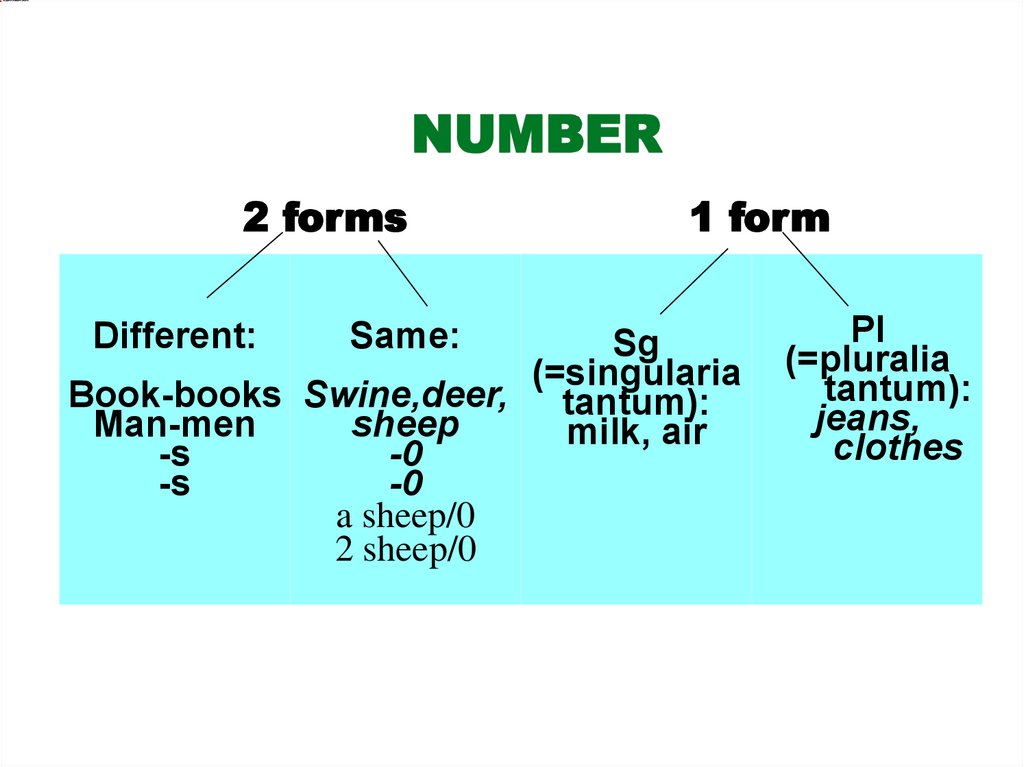
NUMBER2 forms
Different:
Same:
1 form
Sg
(=singularia
Book-books Swine,deer, tantum):
Man-men
sheep
milk, air
-s
-0
-s
-0
a sheep/0
2 sheep/0
Pl
(=pluralia
tantum):
jeans,
clothes
17.
Lexicalization of the inflection:a)book/0 (= 1 object)
book/s (= more than 1 object)
=> “-s” is an INFLECTION
b)snow/0 ( an uncountable notion)
snow/s
-a great amount of smth.
-stylistic colouring
18.
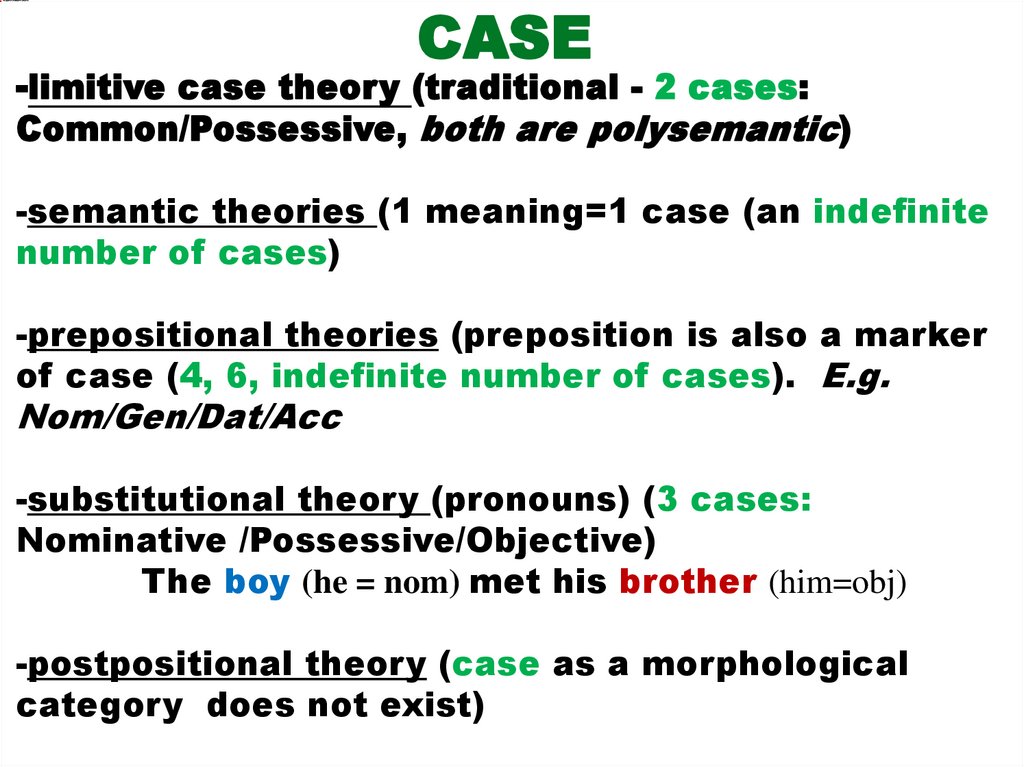
CASE-limitive case theory (traditional - 2 cases:
Common/Possessive, both are polysemantic)
-semantic theories (1 meaning=1 case (an indefinite
number of cases)
-prepositional theories (preposition is also a marker
of case (4, 6, indefinite number of cases). E.g.
Nom/Gen/Dat/Acc
-substitutional theory (pronouns) (3 cases:
Nominative /Possessive/Objective)
The boy (he = nom) met his brother (him=obj)
-postpositional theory (case as a morphological
category does not exist)
19.
CASE-postpositional theory
-’s
The (Queen of England) ’s residence
The (Oxford professor of poetry)’s lecture
(it’s a syntactic phenomenon , -s is a postposition,
but not an inflection of ONE word.
-So the noun itself is not marked morphologically;
-So case as a morphological category does not
exist at all.)
‘Group genitive’
(belongs to syntactic level !!!!)
20.
THE PROBLEM OF GENDERLEXICAL MEANS
DERIVATIONAL MEANS
Boy- girl
Cock- hen
He-cat – she-cat
Waiter –waitress
Lion – lioness
Compare:
учитель-ница, Lehrer-in
!!! But no MORHOLOGICAL means
(inflections)
=> Gender as a MORHOLOGICAL
category does not exist now.












 english
english








