Similar presentations:
Product decisions
1.
2.
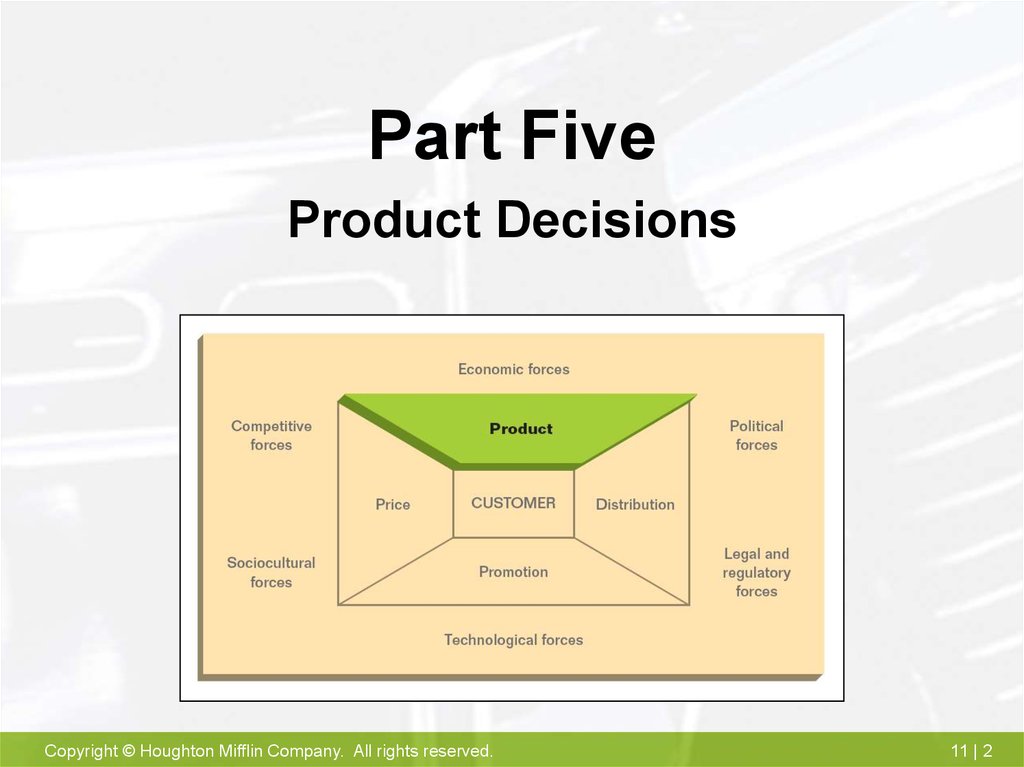
Part FiveProduct Decisions
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
11 | 2
3. Chapter 11 Product Concepts
4. Objectives
• Understand the concept of a product• Explain how to classify products
• Examine concepts of product: item, line,
and mix and how they are connected
• Understand product life cycle and impact
on marketing strategies
• Describe product adoption process
• Understand why products fail/succeed
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
11 | 4
5. What Is A Product?
• Good- Tangible physical entity• Service- Intangible result of the application
of human and mechanical efforts to people
or objects
• Idea- Concept, philosophy, image, or issue
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
11 | 5
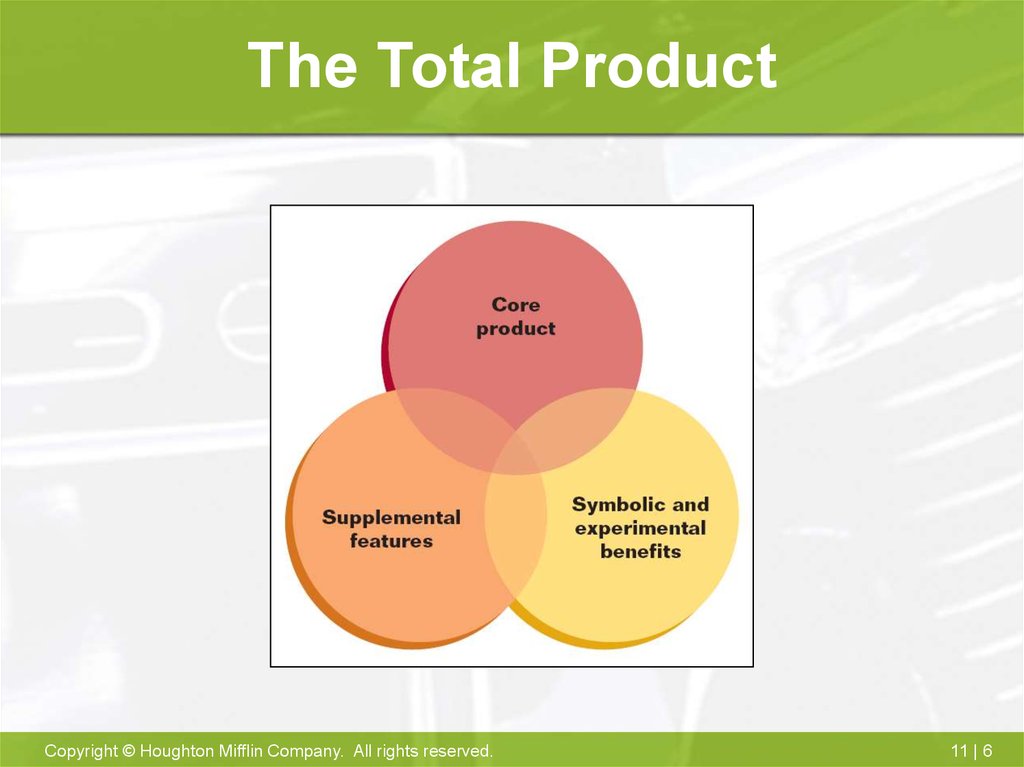
6. The Total Product
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.11 | 6
7. Product Characteristics
• Fundamental utility• Supplemental features
–
–
–
–
Installation
Delivery
Training
Financing
• Symbolic meaning
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
11 | 7
8. Classifying Products
• Consumer- products purchased to satisfypersonal and family needs
• Business- products brought to use in an
organization’s operations, to resell, or to
make other products
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
11 | 8
9. Convenience Products
Relatively inexpensive, frequently purchaseditems for which buyers exert only minimal
purchasing effort
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
11 | 9
10. Convenience Product Strategy Implications
Retail outlets
Low per-unit gross margins
Little promotion effort
Packaging important
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
11 | 10
11. Shopping Products
Items for which buyers are willing toexpend considerable effort in planning
and making purchases
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
11 | 11
12. Shopping Product Marketing Implications
• No brand loyalty• Fewer retail outlets than convenience
• Lower inventory turnover
• Higher gross margins
• Personal selling
• Channel member cooperation
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
11 | 12
13. Specialty Products
Items with unique characteristics thatbuyers are willing to expend considerable
effort to obtain.
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
11 | 13
14. Specialty Product Marketing Implications
• Limited retail outlets• Lower inventory turnover
• High gross margins
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
11 | 14
15. Unsought Products
Products purchased to solve a suddenproblem, products of which customers
are unaware, and products that people
do no necessarily think of buying.
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
11 | 15
16. Unsought Products Marketing Implications
Build trust with consumer by:• Recognizable brand
• Superior performance
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
11 | 16
17. Business Products
Installations- facilities & nonportable equipment
Accessory equipment- not part of final product
Raw materials- natural materials part of product
Component parts- finished items ready for
assembly or need little processing
• Process materials-used in production but not
identifiable
• MRO supplies-maintenance, repair, and
operating items not part of final product
• Services-intangible products in operations
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
11 | 17
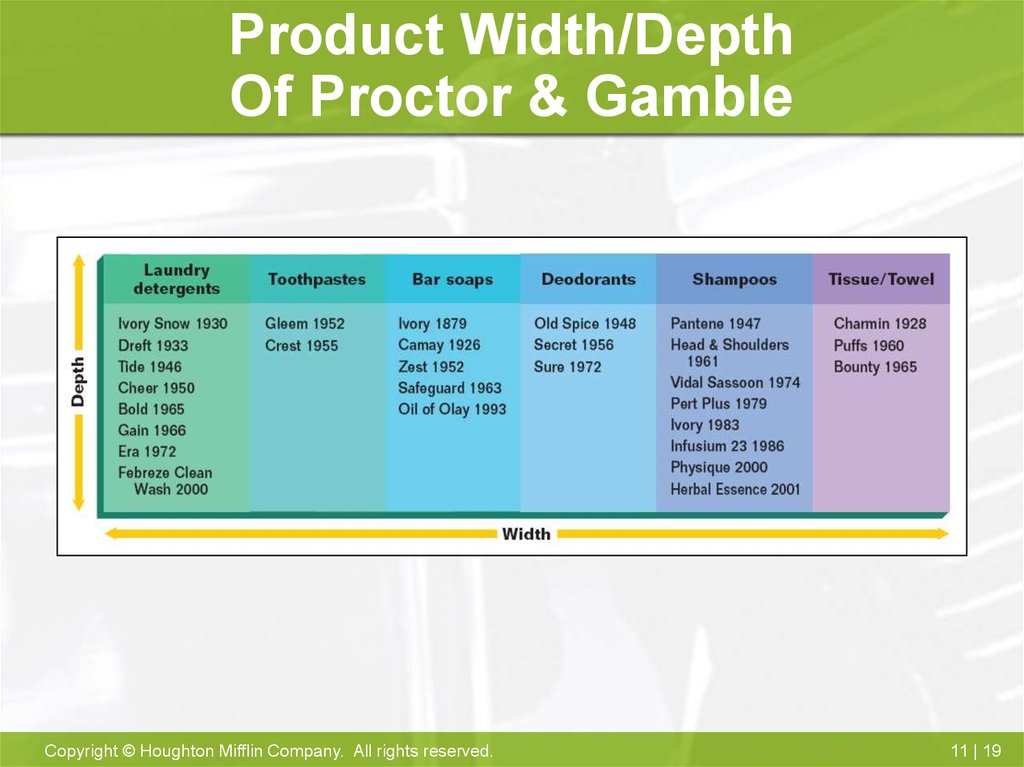
18. Product Line And Product Mix
• Item- specific version of product• Line- closely related items viewed as a unit
• Mix- total group of products
• Width of mix- number to lines
• Depth of mix- number of different products
in line
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
11 | 18
19. Product Width/Depth Of Proctor & Gamble
Product Width/DepthOf Proctor & Gamble
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
11 | 19
20. Product Life Cycle
The progression of a product throughfour stages: introduction, growth,
maturity, and decline.
Windows Product Life Cycle Policy
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
11 | 20
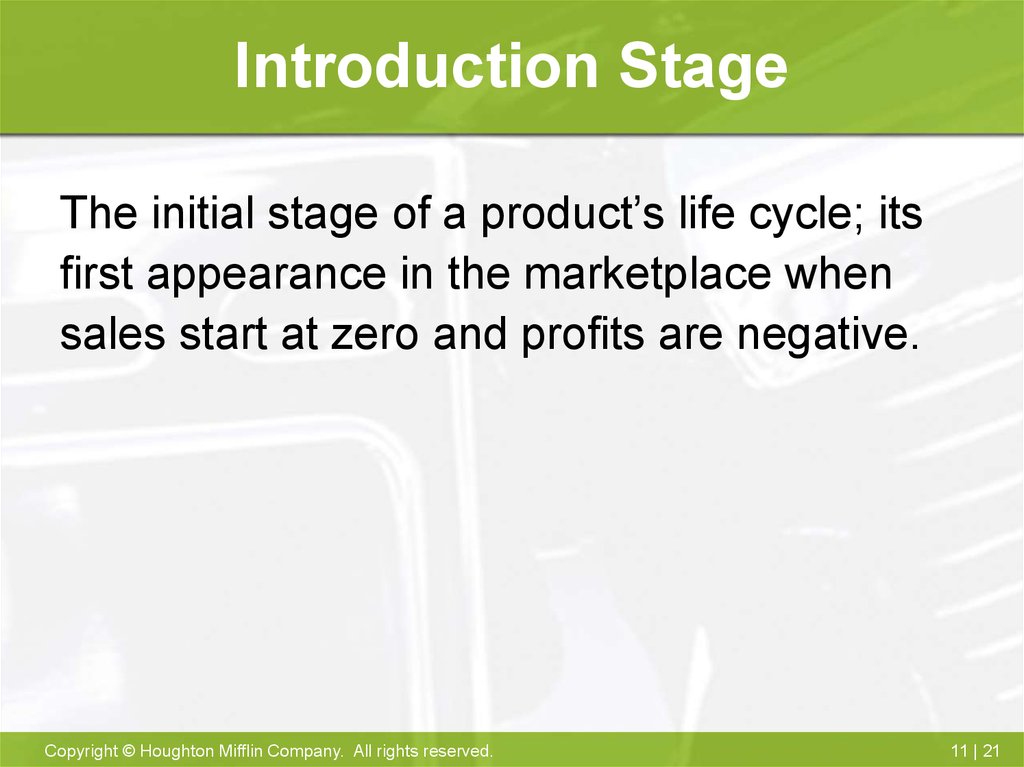
21. Introduction Stage
The initial stage of a product’s life cycle; itsfirst appearance in the marketplace when
sales start at zero and profits are negative.
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
11 | 21
22. Introductory Stage
• Risk of failure high• Buyers must be made aware of:
– Features
– Uses
– Advantages
• Sellers lack
– Resources
– Technological knowledge
– Marketing know-how
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
11 | 22
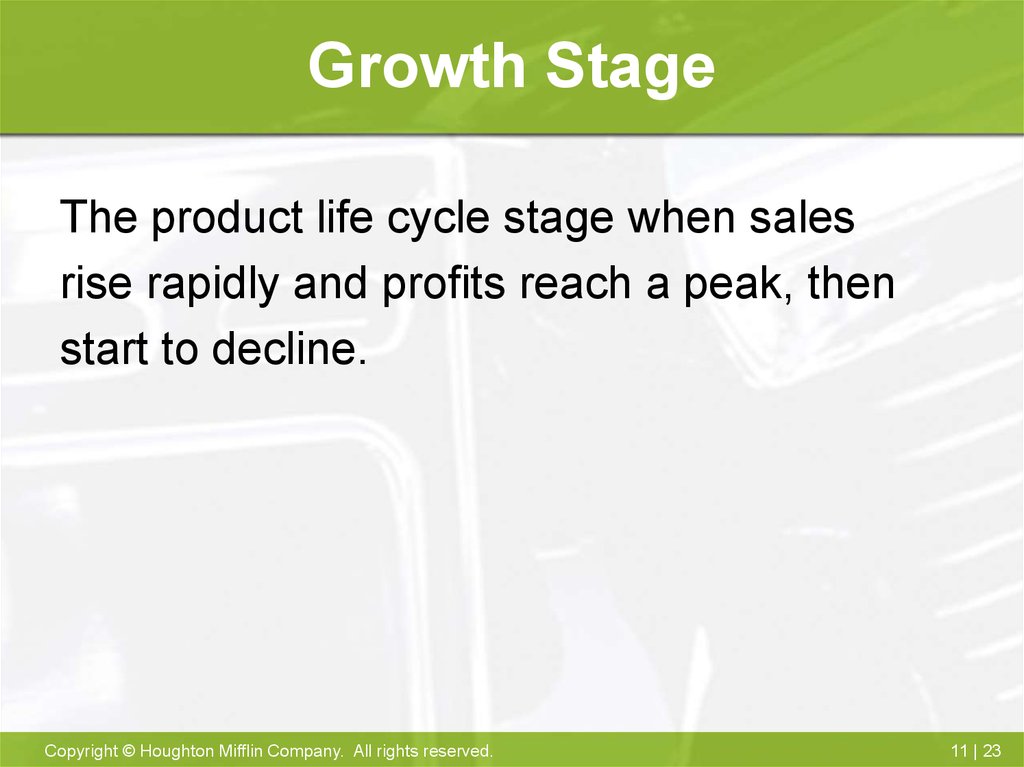
23. Growth Stage
The product life cycle stage when salesrise rapidly and profits reach a peak, then
start to decline.
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
11 | 23
24. Growth Stage
• Sales rise rapidly• Profits peak
• Starts to decline
• Competitors react
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
11 | 24
25. Growth Stage Marketing Strategy
• Encourage brand loyalty- stressbrand benefits
• Strengthen market share
• Emphasize product’s benefits
• Aggressive pricing
• Analyze production position
• Efficient distribution system
• Promotion costs drop as % of sales
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
11 | 25
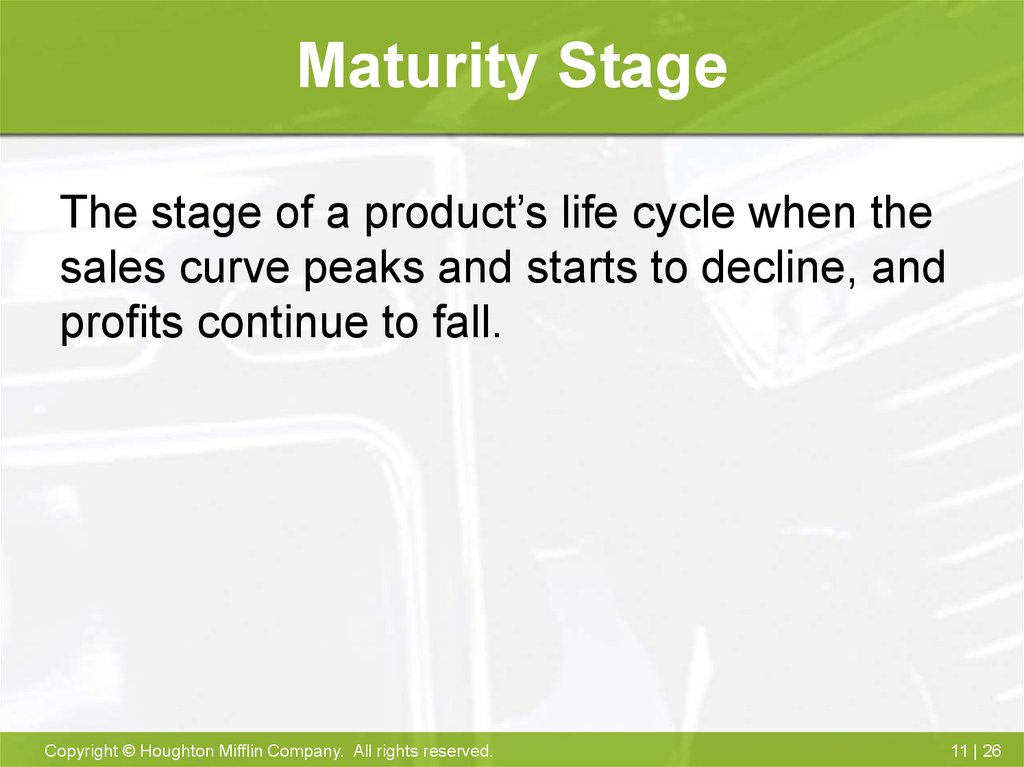
26. Maturity Stage
The stage of a product’s life cycle when thesales curve peaks and starts to decline, and
profits continue to fall.
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
11 | 26
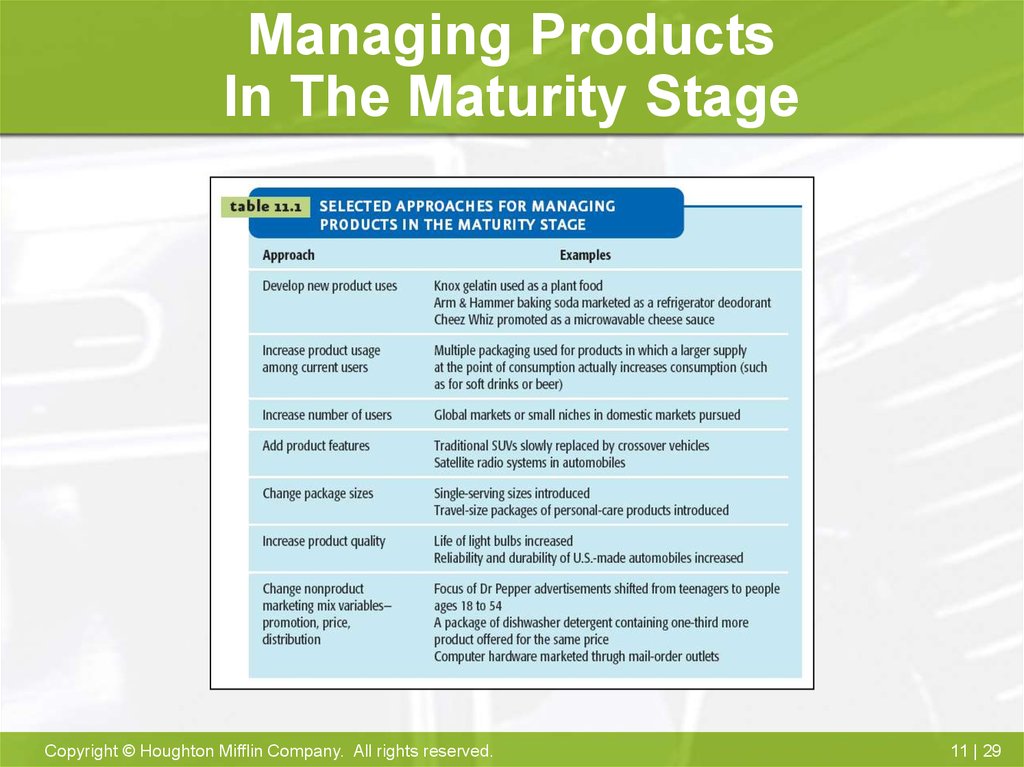
27. Maturity Stage Marketing Strategy
• Intense competition• Emphasize improvements and differences
• Advertising and dealer-oriented promotion
• Global expansion
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
11 | 27
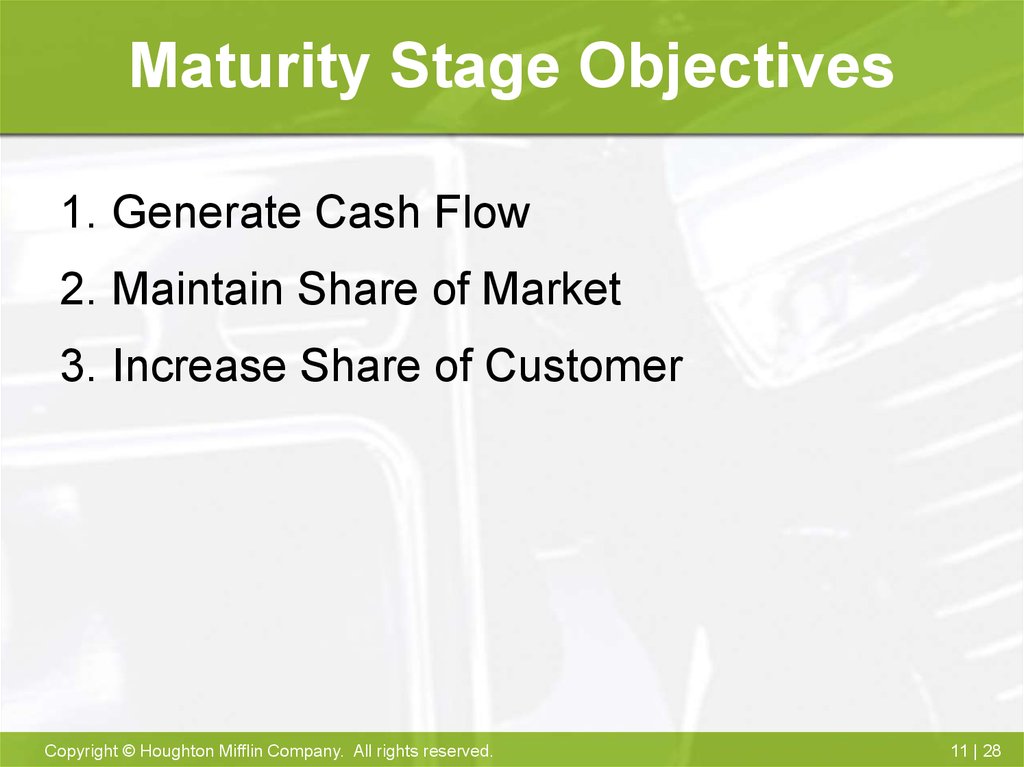
28. Maturity Stage Objectives
1. Generate Cash Flow2. Maintain Share of Market
3. Increase Share of Customer
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
11 | 28
29. Managing Products In The Maturity Stage
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.11 | 29
30. Decline Stage
The stage of a product’s life cycle whensales fall rapidly.
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
11 | 30
31. Decline Stage Marketing Strategy
Eliminate/reposition items
Cut promotion
Eliminate marginal distributors
Plan for phase out
Approaches
– Harvesting
– Divesting
Nike Product Life Cycle
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
11 | 31
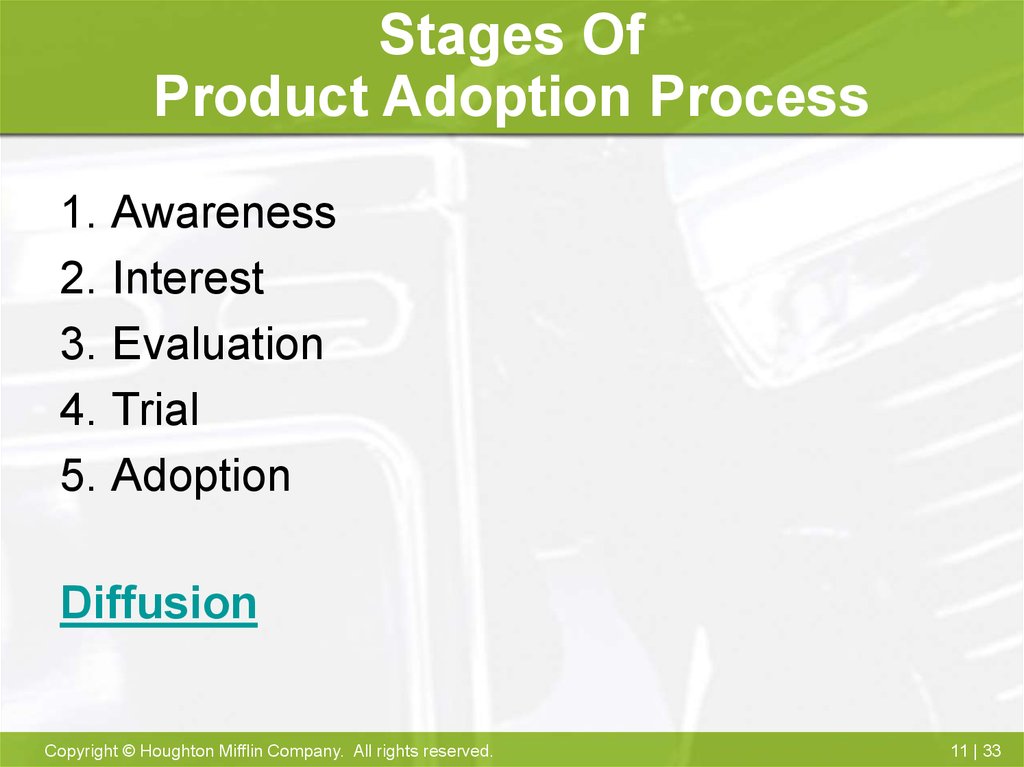
32. Product Adoption Process
The five-stage process of buyer acceptanceof a product: awareness, interest, evaluation,
trial, and adoption.
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
11 | 32
33. Stages Of Product Adoption Process
1.2.
3.
4.
5.
Awareness
Interest
Evaluation
Trial
Adoption
Diffusion
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
11 | 33
34. Most New Ideas Have Their Skeptics
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.11 | 34
35. Adopter Categories
Innovators- first adoptersEarly Adopters- careful choosers
Early Majority- deliberate and cautious
Late Majority- skeptics who only adopt
when necessary
Laggards- distrust new products
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
11 | 35
36. Product Adopter Categories
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.11 | 36
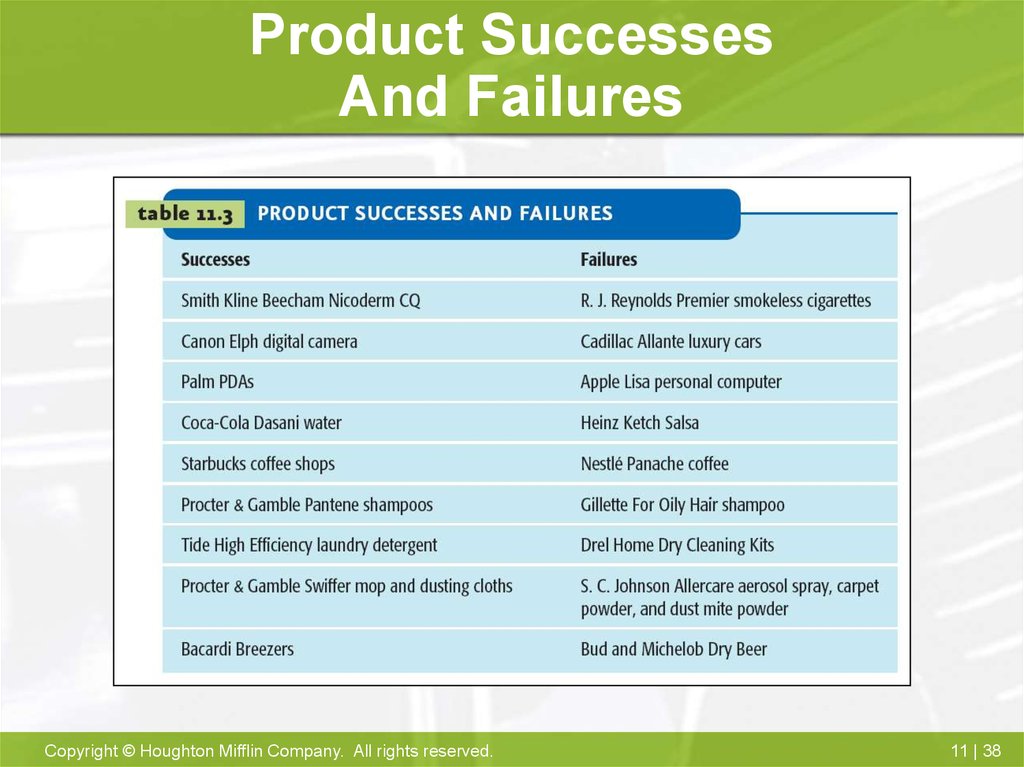
37. Why Some Products Fail/Succeed
Failure to match product to needs
Failure to send right message
Technical/design problems
Poor timing
Overestimate market
Ineffective promotion
Insufficient distribution
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
11 | 37
38. Product Successes And Failures
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.11 | 38



























 marketing
marketing








