Similar presentations:
Marketing strategy and customer relationships. An overview of strategic marketing
1. 1
Part OneMarketing
Strategy and
Customer
Relationships
An Overview of Strategic Marketing
2. Objectives
1. To be able to define marketing asfocused on customers
2. To identify some important marketing
terms, including target market,
marketing mix, marketing exchanges,
and marketing environment
3. To become aware of the marketing
concept and marketing orientation
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
1 | 2
3. Objectives (cont’d)
4. To understand the importance ofbuilding customer relationships
5. To learn about the process of
marketing management
6. To recognize the role of marketing in
our society
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
1 | 3
4. Chapter Outline
Defining Marketing
Understanding the Marketing Concept
Managing Customer Relationships
Value-Driven Marketing
Marketing Management
The Importance of Marketing in Our
Global Economy
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
1 | 4
5. Marketing
• Importance of marketing– Financial success depends on marketing
ability
– Finance, operations, accounting, design,
etc. will not really matter if there is not
sufficient demand for products and
services
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
1 | 5
6. Defining Marketing
• Marketing– The process of creating, distributing,
promoting, and pricing goods, services,
and ideas to facilitate satisfying exchange
relationships with customers in a dynamic
environment
– Meeting needs profitably
– Should result in a customer who is ready
to buy
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
1 | 6
7. Defining Marketing
• Customer needs– Ebay
– IKEA
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
1 | 7
8. Defining Marketing
• Marketing decisions–
–
–
–
–
–
What features to design into a product
What prices to offer customers
Where to sell products
How much to spend on advertising
Wording on packaging
Design of packaging
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
1 | 8
9. Defining Marketing
• A person can obtain a product in one offour ways:
–
–
–
–
Self produce
Steal
Beg
purchase
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
1 | 9
10. Defining Marketing
• Customers– The purchasers of organizations’ products;
the focal point of all marketing activities
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
1 | 10
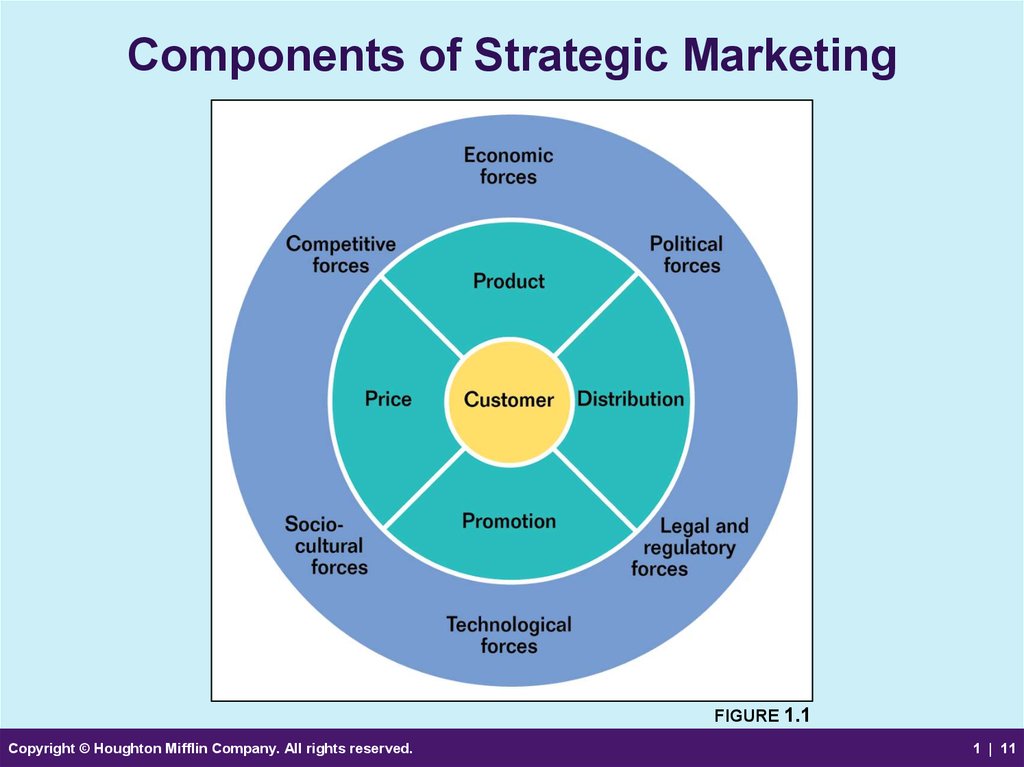
11. Components of Strategic Marketing
FIGURE 1.1Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
1 | 11
12. Marketing Focuses on Customers
• Target Market– A specific group of customers on whom an
organization focuses its marketing efforts
Large or small customer groups
Single or multiple product markets
Single or multiple products
Local to global markets
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
1 | 12
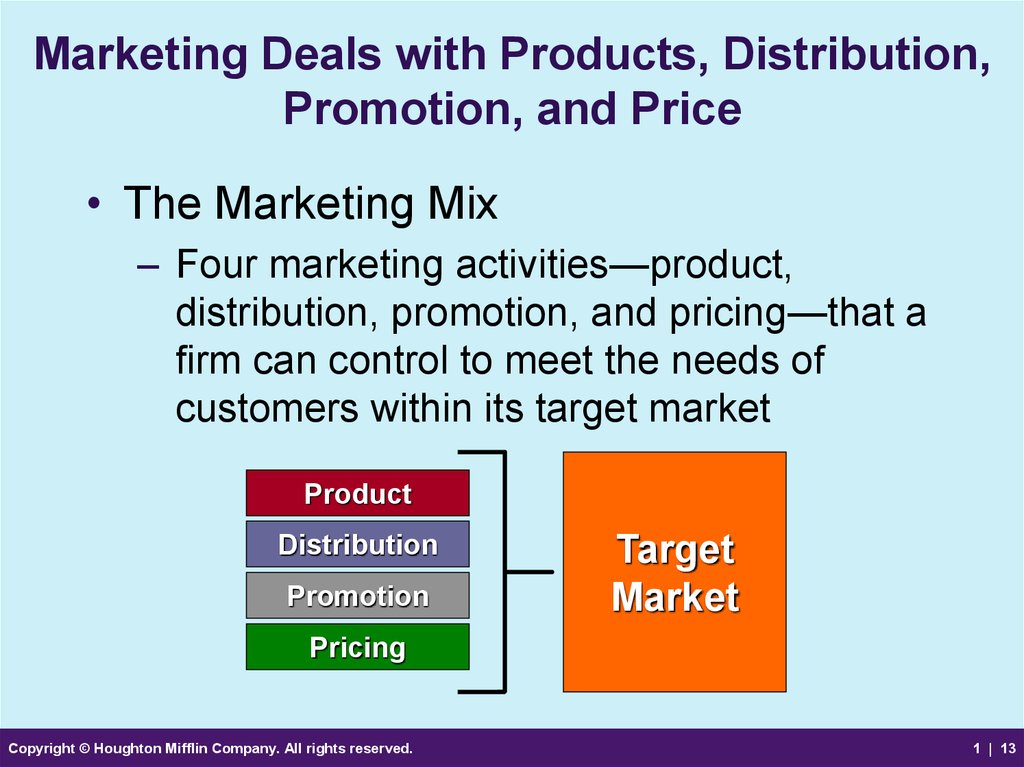
13. Marketing Deals with Products, Distribution, Promotion, and Price
• The Marketing Mix– Four marketing activities—product,
distribution, promotion, and pricing—that a
firm can control to meet the needs of
customers within its target market
Product
Distribution
Promotion
Target
Market
Pricing
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
1 | 13
14. Marketing Mix Variables
ProductDistribution
Goods, services, or ideas that satisfy
customer needs
The ready, convenient, and timely
availability of products
Promotion
Activities that inform customers about
the organization and its products
Pricing
Decisions and actions that establish
pricing objectives and policies and set
product prices
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
1 | 14
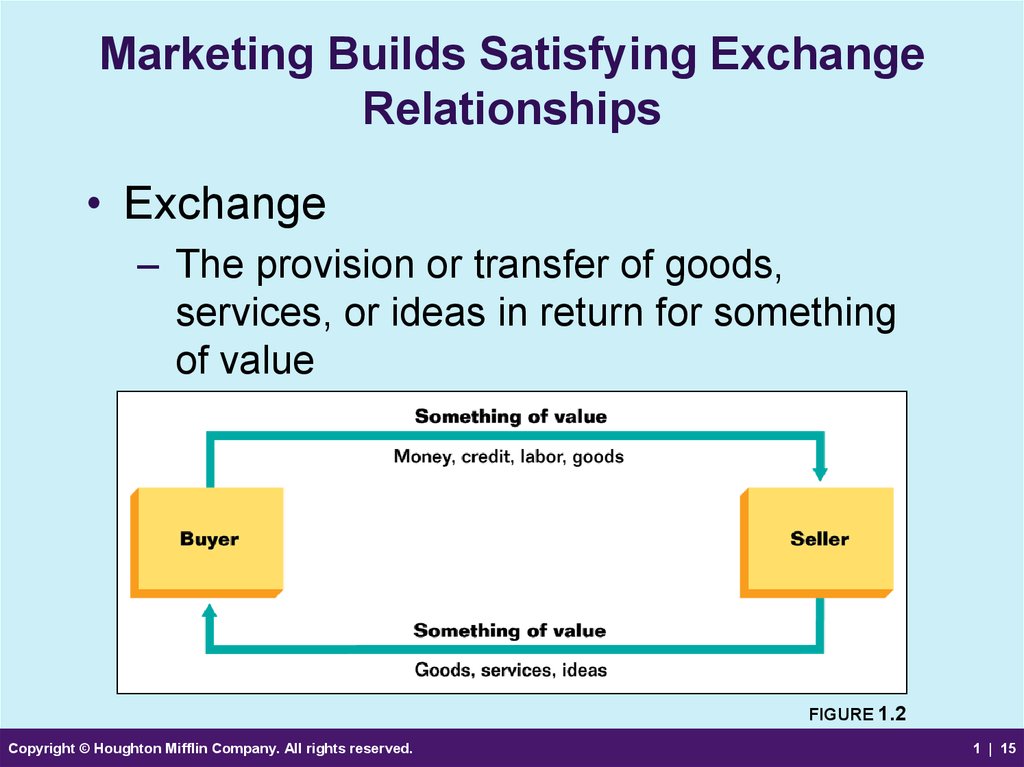
15. Marketing Builds Satisfying Exchange Relationships
• Exchange– The provision or transfer of goods,
services, or ideas in return for something
of value
FIGURE 1.2
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
1 | 15
16. Marketing Builds Satisfying Exchange Relationships (cont’d)
• Exchange Conditions– Two or more participants have something of value
that the other party desires.
– Exchange provides mutual benefit/satisfaction.
– Each party has confidence in the exchange value
of the other party’s offering.
– Each party must meet the expectations of the
exchange to become trusted by the other parties.
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
1 | 16
17. Marketing Builds Satisfying Exchange Relationships (cont’d)
• Exchange forms–
–
–
–
Business firm wants purchases
Political candidate wants votes
Church wants active members
Social-action group wants passionate adoption of
some cause
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
1 | 17
18. Marketing Occurs in a Dynamic Environment
• Marketing Concept– A philosophy that an organization should
try to satisfy customers’ needs through a
coordinated set of activities that also
allows the organization to achieve its goals
– Against the “selling concept”, which
focuses on the needs of the seller
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
1 | 18
19. Marketing Occurs in a Dynamic Environment
• Marketing Concept– Customer satisfaction
• Analysis of customers’ current and long-term
needs
• Analysis of competitors’ capabilities
• Integration of firm’s resources
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
1 | 19
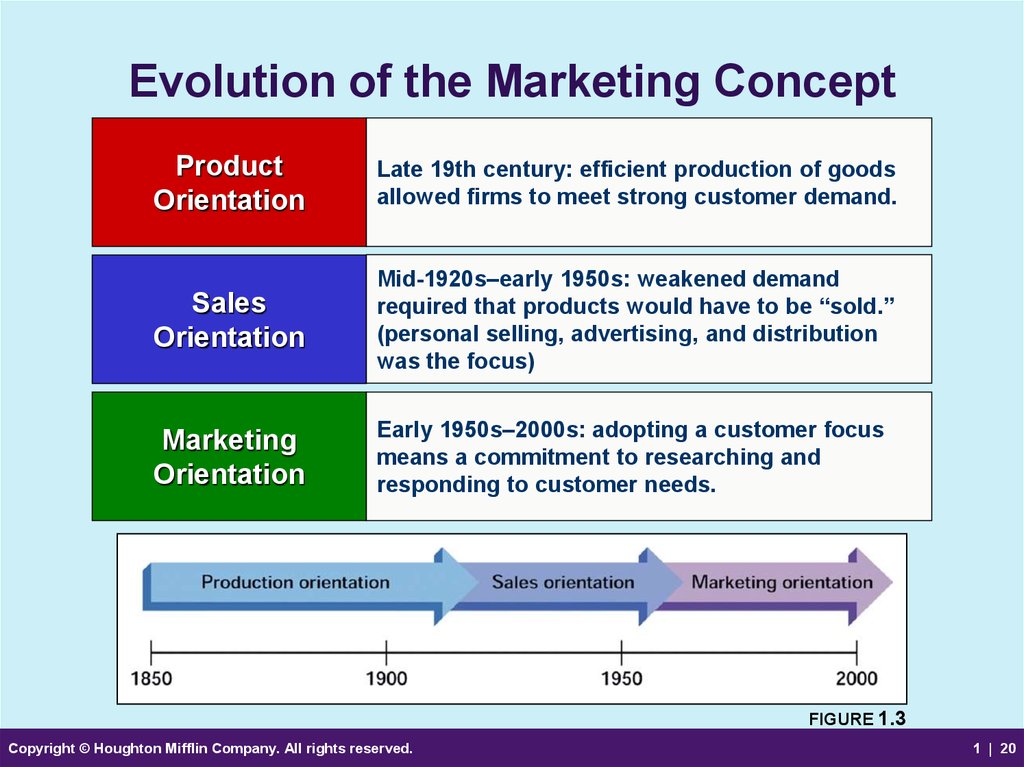
20. Evolution of the Marketing Concept
ProductOrientation
Late 19th century: efficient production of goods
allowed firms to meet strong customer demand.
Sales
Orientation
Mid-1920s–early 1950s: weakened demand
required that products would have to be “sold.”
(personal selling, advertising, and distribution
was the focus)
Marketing
Orientation
Early 1950s–2000s: adopting a customer focus
means a commitment to researching and
responding to customer needs.
FIGURE 1.3
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
1 | 20
21. Implementing the Marketing Concept
• Becoming marketing oriented requires– Establishing an information system to discover
customers’ needs and using the information to
create satisfying products.
– Coordinating all marketing activities by
restructuring the organization.
– Obtaining the support of all managerial
and staff levels in the organization.
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
1 | 21
22. Managing Customer Relationships
• Relationship Marketing– Establishing long-term, mutually satisfying
buyer-seller relationships allowing for
cooperation and mutual dependency
• Increased value of customer (loyalty) over time
results in increased profitability.
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
1 | 22
23. Managing Customer Relationships (cont’d)
• Customer Relationship Management(CRM)
– Using information about customers to
create marketing strategies that develop
and sustain desirable customer
relationships
• Identifying buying-behavior
patterns of customers
• Using behavioral
information to focus on
the most profitable
customers
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
1 | 23
24. Value-Driven Marketing
• Value– A customer’s subjective assessment of benefits
relative to the costs in determining the worth of a
product
• Customer value = customer benefits – customer costs
– Customer benefits
• Anything desired by the customer that is received in an
exchange
– Customer costs
• Anything a customer gives up in an exchange for
benefits
– Monetary price of the benefit
– Search costs (time and effort) to locate the product
– Risks associated with the exchange
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
1 | 24
25. Marketing Management
• Marketing Management– The process of planning, organizing,
implementing, and controlling marketing activities
to facilitate exchanges effectively and efficiently
– Effectiveness
• The degree to which an exchange
helps an organization achieve its
objectives
– Efficiency
• The process of minimizing the
resources an organization must
spend to achieve a specific level
of desired exchanges
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
1 | 25
26. Marketing Management (cont’d)
• Planning– Assessing opportunities and resources
– Determining marketing objectives
– Developing a marketing strategy and plans for
implementation and control
• How, when and by whom are marketing activities
performed?
• Organizing
– Developing the internal structure of the marketing
unit
• Functions, products, regions, customer types
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
1 | 26
27. Marketing Management (cont’d)
• Implementation– Coordinating marketing activities
– Motivating marketing personnel
– Developing effective internal communications
within the unit
• Control
– Establishing performance standards
– Comparing actual performance to established
standards
– Reducing the difference between desired and
actual performance
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
1 | 27
28. Effective Marketing Control Process
• Provides for quick detectionof differences in planned
and actual performance
• Accurately monitors
activities and is flexible
enough to accommodate changes
• Incurs low process costs relative to the
costs of a “no-control” situation
• Is understandable by both managers
and subordinates.
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
1 | 28
29. The Importance of Marketing in Our Global Economy
• Marketing costs consume a sizableportion of buyers’ dollars
• Marketing is used in nonprofit
organizations
• Marketing is important to business and
the economy
• Marketing fuels our
global economy
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
1 | 29
30. The Importance of Marketing in Our Global Economy (cont’d)
• Marketing knowledge enhancesconsumer awareness
• Marketing connects people through
technology
• Socially responsible marketing can
promote the welfare of customers and
society
• Marketing offers many exciting career
prospects
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
1 | 30
31. After reviewing this chapter you should:
• Be able to define marketing as focusedon customers.
• Know the meaning of important
marketing terms, including target
market, marketing mix, marketing
exchanges, and marketing environment.
• Be more aware of the marketing
concept and marketing orientation.
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
1 | 31
32. After reviewing this chapter you should:
• Understand the importance of buildingcustomer relationships.
• Have learned about the process of
marketing management.
• Recognize the important role of
marketing in our society.
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
1 | 32


























 marketing
marketing








