Similar presentations:
A Brief on Potatoes in India
1.
A Brief on Potatoes in Indiawww.indianpotato.com
2.
Agriculture and Potatoes In IndiaOverview
• Agriculture, including allied activities, contributes almost 17% of the GDP
• Agriculture accounts for 58% of total employment in the country.
• The Indian food processing industry accounts for 32% of the country’s total food market, one of the
largest industries in India and is ranked fifth in terms of production, consumption, export and expected
growth.
Most likely, potato reached the Indian southern coast as food aboard Portuguese ship during later part
of 16th century. The first written mention of potato in India occurs in 1615 Edward Terry’s account of a
lavish banquet hosted by Mughal Emperor Jehangir, in honour of the British Ambassador Thomas Roe
Potato cultivation in the country remained restricted before independence due to non-availability of
locally adapted varieties and technologies for growing potato under sub-tropical Indian climatic
condition
ICAR-Central Potato Research Institute, Shimla was established in August 1949 . The major
outcome of the scheme is 32.6 fold increase in production, 9.3 fold increase in area and 3.5
fold increase in yield during last seven decades
www.indianpotato.com
3.
Potatoes In IndiaOverview
• India is the second largest annual producer of potato after China. In 2022-23, India produced
60.14 million tonnes from 2.3million ha area (DOAFW, Government of India)
• Current share of potato to agricultural GDP is 2.86% out of 1.32% cultivable area
• Potato contribution to Indian economy can be clearly realized by its Gross Production Value of
USD 676 Billion for the year 2022-23 with more than 20-fold increase in the last six decades
(Source: fao.org)
• Contribution of potato in agricultural GDP from unit area of cultivable land is about 3.7 times
higher than rice and 5.4 times higher than wheat
India will be the most populous country in the world by 2050 with about
1.67 billion population.
Diversification and utilization of horticultural crops, majorly potato, would
be the most important strategy to ensure food and nutritional security of
the burgeoning population
www.indianpotato.com
4.
Potatoes In IndiaDrivers of growth
• The stagnating growth rates of cereals’ productivity, Steep rise in per capita consumption of pulses, edible oil, fruits,
vegetables, milk, sugar and non-vegetarian food in the regime of steadily rising population is bound to put pressure on
existing cultivable land.
• Cultivable land is expected to remain more or less constant in the next 40 years, the role of crops like potato having
higher production potential per unit land and time will become imperative.
• In this context potato crop has very high probability of making crucial contribution to the future national food security
agenda
The perceived changes in Indian socio-economics in the medium and long term are expected to enhance per capita food
consumption of fresh potatoes.
Potato is an important ingredient of most of the fast foods in organised as well as unorganised sector
Rapid rate of urbanization
Faster rise of number of nuclear families,
Higher disposable incomes on account of fast economic growth.
Rapid increase in the number of working women
Ability of potato to produce highest nutrition and dry matter on per unit area and time basis, among major crops
www.indianpotato.com
5.
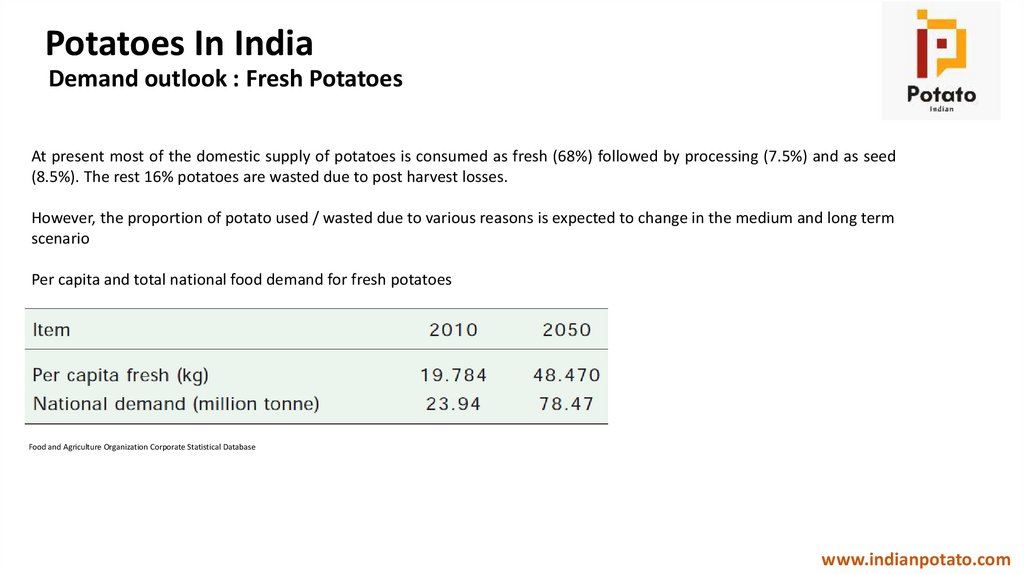
Potatoes In IndiaDemand outlook : Fresh Potatoes
At present most of the domestic supply of potatoes is consumed as fresh (68%) followed by processing (7.5%) and as seed
(8.5%). The rest 16% potatoes are wasted due to post harvest losses.
However, the proportion of potato used / wasted due to various reasons is expected to change in the medium and long term
scenario
Per capita and total national food demand for fresh potatoes
Food and Agriculture Organization Corporate Statistical Database
www.indianpotato.com
6.
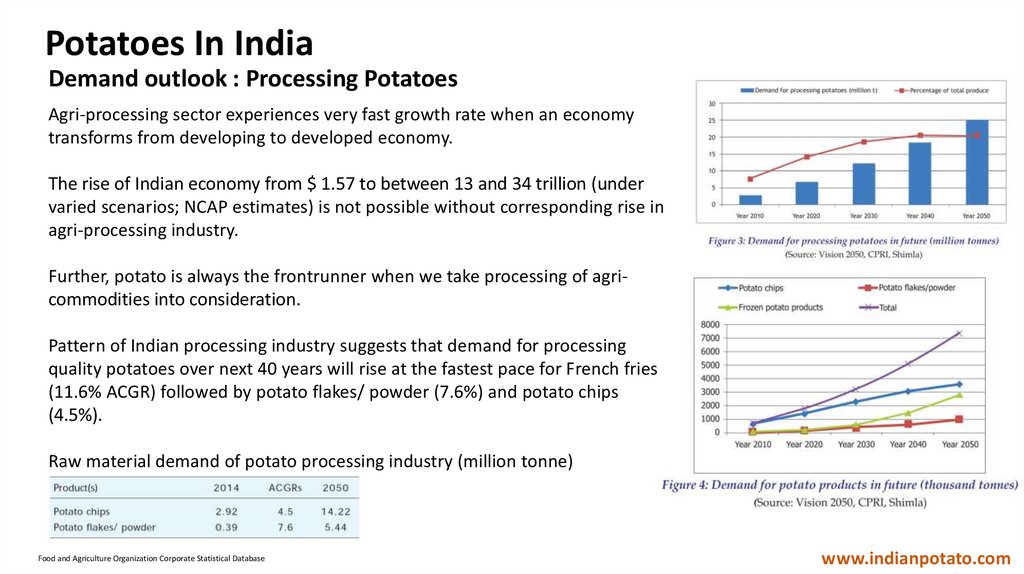
Potatoes In IndiaDemand outlook : Processing Potatoes
Agri-processing sector experiences very fast growth rate when an economy
transforms from developing to developed economy.
The rise of Indian economy from $ 1.57 to between 13 and 34 trillion (under
varied scenarios; NCAP estimates) is not possible without corresponding rise in
agri-processing industry.
Further, potato is always the frontrunner when we take processing of agricommodities into consideration.
Pattern of Indian processing industry suggests that demand for processing
quality potatoes over next 40 years will rise at the fastest pace for French fries
(11.6% ACGR) followed by potato flakes/ powder (7.6%) and potato chips
(4.5%).
Raw material demand of potato processing industry (million tonne)
Food and Agriculture Organization Corporate Statistical Database
www.indianpotato.com
7.
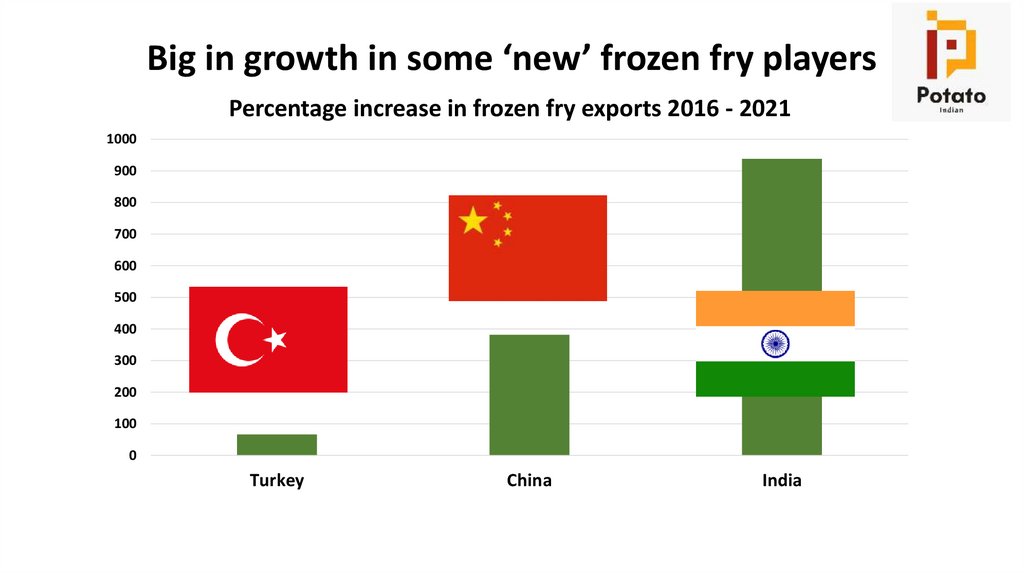
Big in growth in some ‘new’ frozen fry playersPercentage increase in frozen fry exports 2016 - 2021
1000
900
800
700
600
500
400
300
200
100
0
Turkey
China
India
8.
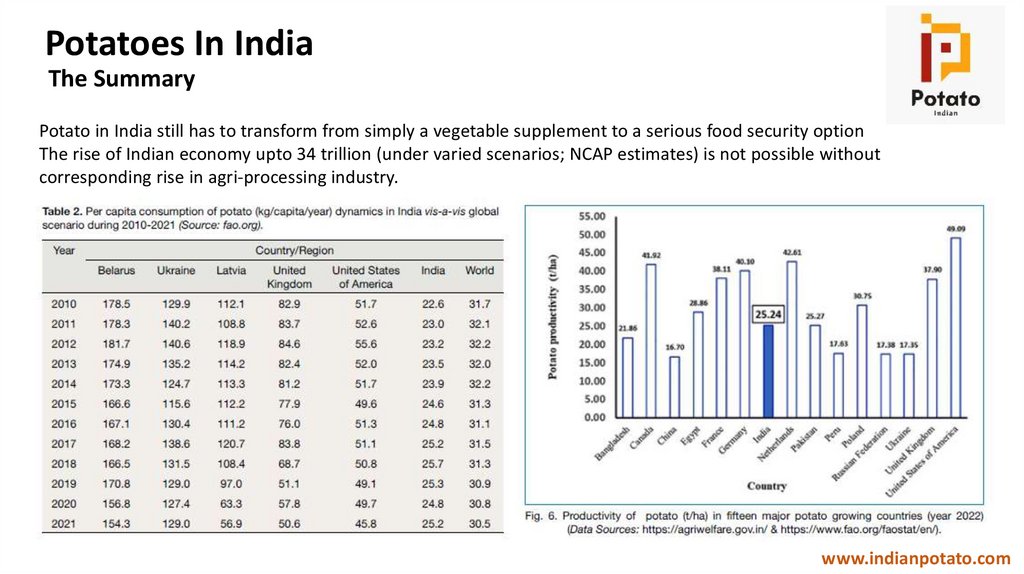
Potatoes In IndiaThe Summary
Potato in India still has to transform from simply a vegetable supplement to a serious food security option
The rise of Indian economy upto 34 trillion (under varied scenarios; NCAP estimates) is not possible without
corresponding rise in agri-processing industry.
www.indianpotato.com
9.
Visit for latest updateson Indian Potato
www.indianpotato.com






 biology
biology








