Similar presentations:
Ethanol production and biofuels
1.
EthanolProduction
and
Biofuels
2.
Learning Objectives• Understand the two main routes for
ethanol production and the advantages
and disadvantages of each
• Understand the environmental issues
of ethanol production including those
of bioethanol fuels, and understand the
concept of carbon neutrality
• Be able to discuss biofuels in the
context of environmental issues
3.
Success Criteria• State the two main routes for ethanol
production.
• Give the advantages and
disadvantages of each of these routes
in making ethanol.
• Explain the concepts of biofuels and
carbon neutrality.
• Describe the advantages and
disadvantages of using biofuels.
4.
KeywordsHydration
Fermentation
Yeast
Batch process
Biofuel
Biogas
Gasohol
Renewable
Sustainable
Carbon neutral
5.
Uses of Ethanol6.
INDUSTRIAL PREPARATION OF ALCOHOLS1.Hydration of Ethene
Catalyst: H3PO4 or H2SO4
What are the advantages and disadvantages of
using this method to produce ethanol?
Would you drink industrial alcohol?
7.
1. Advantages of Hydration of Method8.
1. Disadvantages of Hydration of Method9.
sugarcaneCorn/maize
potatoes
Sorghum
10.
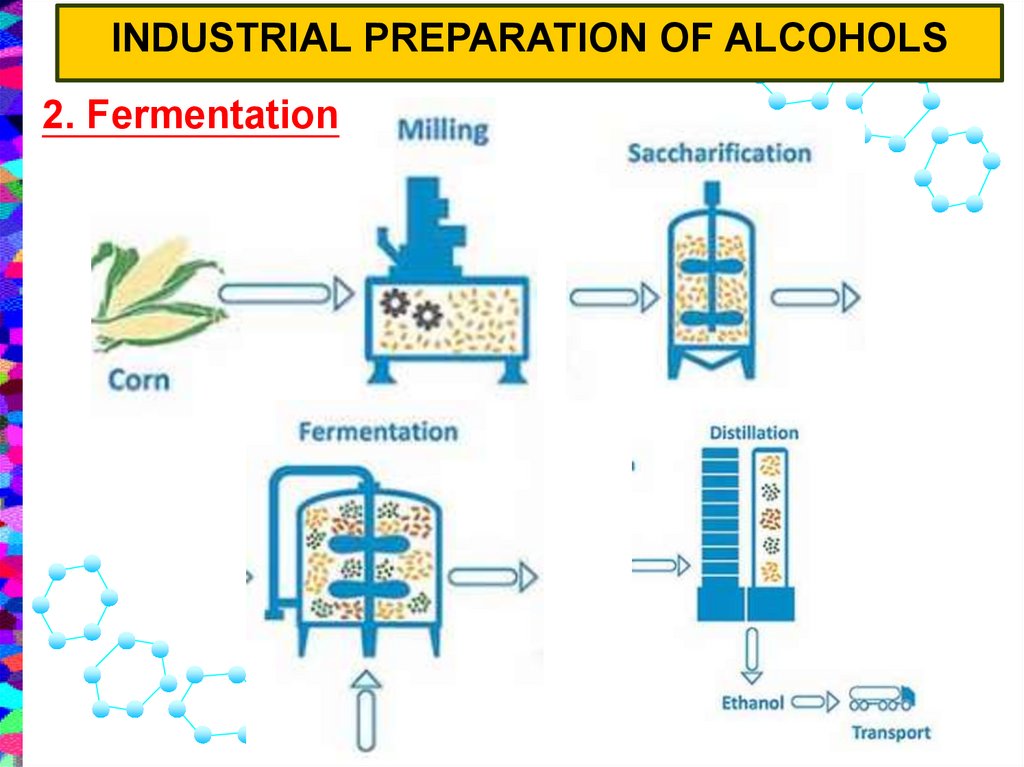
INDUSTRIAL PREPARATION OF ALCOHOLS2. Fermentation
11.
FERMENTATION OF SUGAR → ALCOHOL2. Fermentation
yeast
C6H12O6 → 2CO2 + 2C2H5OH
glucose (sugar)
ethanol
Yeast die when the alcohol concentration is too high
wine yeast approx. 12%
brewer's yeast approx 5%
special yeast approx 21%
95% alcohol can be made by distillation, but this is
the highest concentration possible by distillation as
ethanol pulls in water from the air
12.
FERMENTATION OF SUGAR → ALCOHOLFroth (CO2) produced by
yeast fermenting sugar
Producing Cider and Wine
13.
The yeast used to make bread, ferments thesugars (carbohydrates) and produces CO2
making the bread rise.
14.
Natural yeasts ferment fruit, making ethanol.Wasps eat the fruit and get drunk, that's why they're
aggressive in late summer.
15.
wine yeast approx. 12%brewer's yeast approx 5%
special yeast approx 21%
16.
Purification of EthanolEthanol is toxic to yeast above a certain
concentration. This limits the concentration of
ethanol that can be made by fermentation.
Only 15% concentration is made.
Distillation up to 95% ethanol
Further purification up to 99.5% ethanol
using a dehydrating agents.
17.
Fermentation has a number ofadvantages:
- It is a low-technology process, which
means it can be used anywhere.
- It does not use much energy.
- It uses sugar cane as a raw material,
which is a renewable resource.
18.
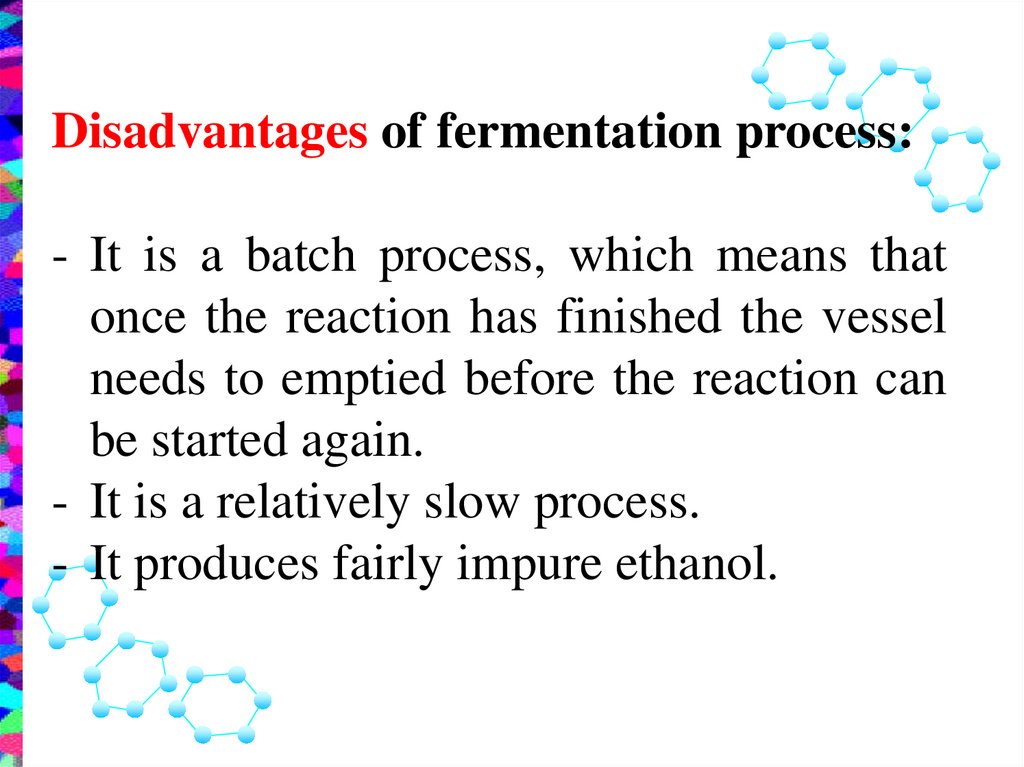
Disadvantages of fermentation process:- It is a batch process, which means that
once the reaction has finished the vessel
needs to emptied before the reaction can
be started again.
- It is a relatively slow process.
- It produces fairly impure ethanol.
19.
20.
The Fermentation Process21.
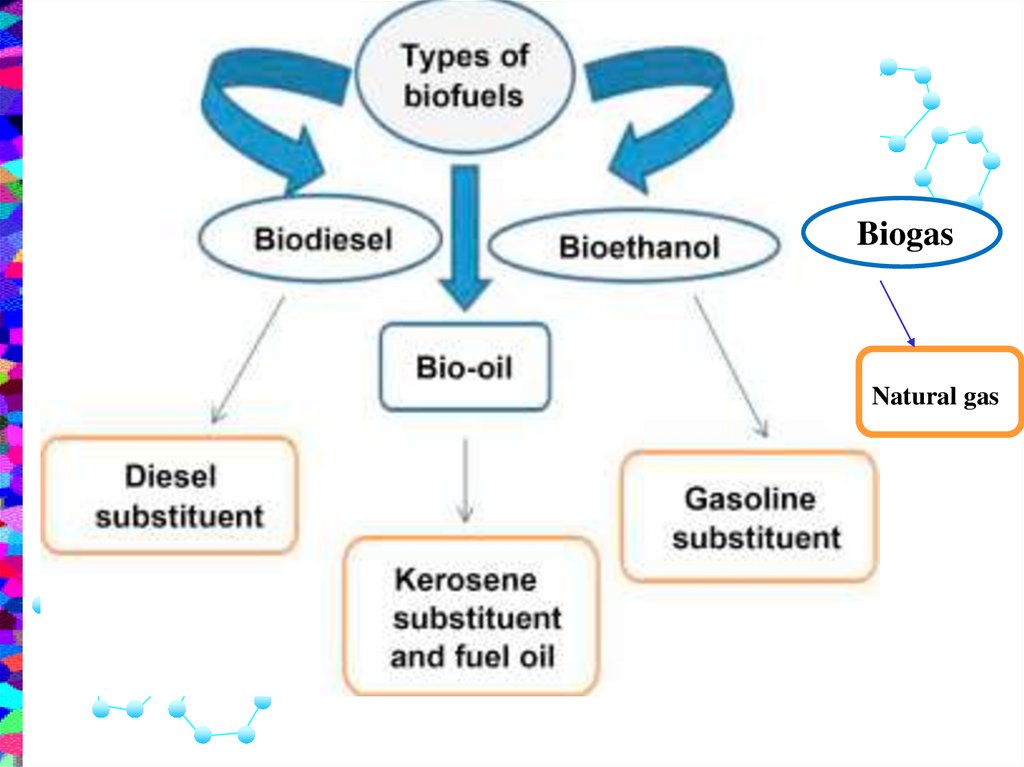
Ethanol is a BiofuelA biofuel is a fuel that is made from biomass
(remains of biological materials).
22.
BiogasNatural gas
23.
BioethanolThe ethanol can be
extracted by
distillation and then
used as a fuel for
cars.
Cars need to be
modified if they use
pure ethanol.
Whilst cars can run on
a mixture of petrol
and ethanol (called
gasohol) without
problems.
24.
BiogasBiogas is formed when bacteria breakdown plant
material or animal waste anaerobically.
Biogas mainly consists of methane so it is highly
flammable!
Millions of animals around the world produce tonnes
of faeces and urine and plants grow quickly so biogas
can be produced on a large scale!
25.
Large scale productionThis reaction is exothermic.
Generators can be built above the ground or
below.
26.
Biofuels have some advantages over fossil fuels (coal, oil and gas)and some potential drawbacks.
1) Biofuels are renewable energy sources. Unlike fossil
fuels, biofuels will not run out, so they are more
sustainable.
2) Biofuels do produce CO2 when they are burnt.
However, the CO2 produced are absorbed by plants
while growing, so biofuels are usually still classed as
carbon neutral.
27.
Topic for Debate: Are biofuels reallycarbon neutral???
28.
Biofuels have some advantages over fossil fuels (coal, oil and gas)and some potential drawbacks.
1) But one problem with switching from fossil fuels
to biofuels in transport is that petrol car engines
would have to be modified.
2) Land is used to grow crops for fuel instead of
using it to grow crops for food. If countries
start using land to grow biofuel crops instead of
food, they may be unable to feed everyone in the
country.
29.
BIOFUELS30.
Reflection• What has been learned
• What remained unclear
• What is necessary to work on



























 biology
biology








