Similar presentations:
Phosphorus and its compounds (lecture 4)
1.
Phosphorus and its compounds:phosphoric acid.(wet and
furnace processes). Sulfur and
its compounds: sulfuric acid
Zhumashev Adil
2.
Agenda1. Raw materials for phosphoric acid production
2. Economic importance and applications
3. Manufacture of phosphoric acid (wet process)
4. Manufacture of phosphoric acid (furnace process)
5. Sulfur in nature
6. Sulfuric acid
3.
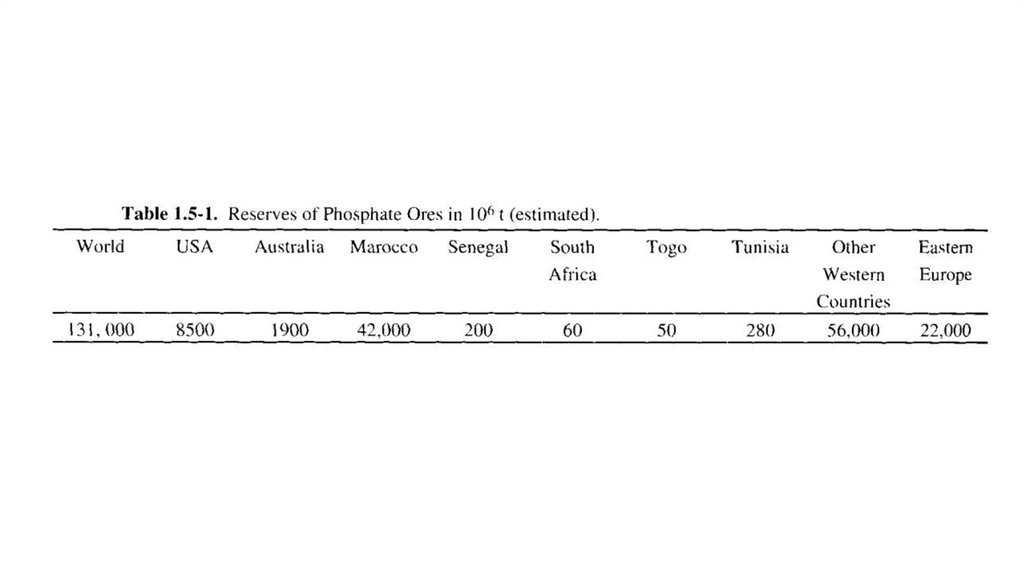
Raw materials for phosphoric acid productionThe most important group of minerals used in manufacturing
phosphoric acid is apatites, which has formula
4.
The commercially most important of these are the fluoroapatite.The aluminum phosphate deposits in Africa and South America
and guano are much less important. Phosphate ores, especially
sedimentary apatites, are widely distributed. There are massive
beds particularly in the USA and Africa. The estimated phosphate
content of these reserves is many tens of millions of tons, which
at the rate of present exploitation is sufficient for over 100 and up
to 1000 years.
5.
6.
Economic importance and applicationsPhosphoric acid is produced both by the digestion of apatite with
sulfuric acid (wet-process phosphoric acid) and by combustion of
phosphorus (“furnace phosphoric acid”). Most (> 75%) of the
mined apatite is utilized in the manufacture of phosphoric acid.
The proportion of furnace acid is decreasing in favor of the wet
process acid, of phosphoric acid manufactured by phosphorus
combustion. The use of furnace acid for fertilizer production,
previously usual in the USA, has almost ceased. In those
application areas in which high purity phosphoric acid is required
(e.g. phosphates from detergents) post-purified wet-process acid
is being increasingly used.
7.
By far the most important product produced from phosphoric acid is fertilizers. Morethan 90% of the wet-process acid is utilized in the USA in this sector compared with
50% in the Federal Republic of Germany. Other applications include:
- Phosphates for detergents (declining strongly)
- Industrial cleaning agents
- Water treatment agents
- Nutrition supplements for animal feedstuffs
- Flame-retarding agents
Phosphoric acid is directly used in the treatment of metals. For applications in the
food sector, furnace acid is generally used. Phosphates for washing powders are
manufactured from both furnace acid and purified wet-process acid.
8.
Manufacture of phosphoric acid (wet process)The wet process is a method for producing phosphoric acid and involves intricate chemical reactions when apatite reacts
with sulfuric acid. This method is widely employed in industries, particularly in fertilizer production. Here is a more detailed
description of the wet process:
Raw Material Preparation:
The process begins with the preparation of raw materials. Apatite, a natural mineral containing phosphate compounds, is typically the
primary source of phosphorus.
Digestion:
Apatite undergoes digestion with concentrated sulfuric acid (H₂SO₄). During this reaction, various phosphate compounds are formed,
including phosphoric acid (H₃PO₄).
Solution Formation:
The reaction mixture usually contains phosphoric acid and other compounds. A solution is formed from this mixture, containing di- and
tri-basic phosphoric acids.
Product Treatment:
The solution goes through a series of treatments to remove non-phosphorus impurities. Treatment stages may involve filtration,
precipitation, and other methods to obtain a purer product.
Final Concentration:
After purification, the phosphoric acid solution undergoes a concentration process to achieve the desired concentration of phosphoric
acid in the final product.
Application:
The resulting phosphoric acid, produced through the wet process, is commonly used in fertilizer production and various other chemical
and industrial applications.
9.
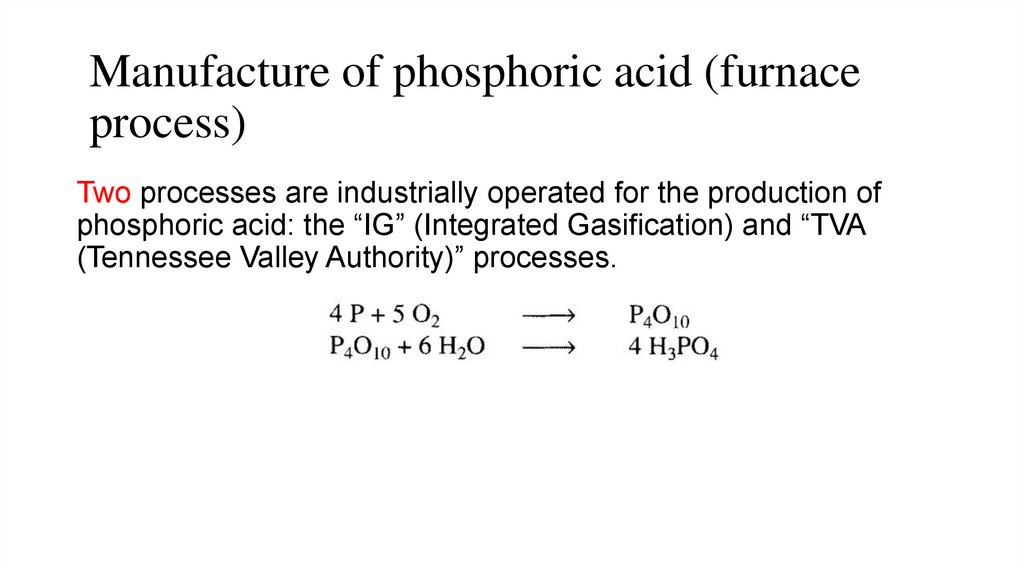
Manufacture of phosphoric acid (furnaceprocess)
Two processes are industrially operated for the production of
phosphoric acid: the “IG” (Integrated Gasification) and “TVA
(Tennessee Valley Authority)” processes.
10.
In the TVA process, combustion and absorption occur in separatetowers, while in the IG process, both processes take place in a
single tower. In the IG process, the tower walls are protected
from the hot phosphorus flame by pumped phosphoric acid. This
pumped phosphoric acid serves the dual purpose of removing
the heat of reaction by circulating through a heat exchanger and
providing the water needed for phosphoric acid formation. The
acid produced is then extracted from the pumped phosphoric
acid.
11.
Sulfur in natureSulfur is widely distributed in the Earth's crust. Elemental sulfur is
found in sedimentary deposits, forming domed structures within
rock salt, gypsum, and limestone.
12.
Sulfur exists in non-elemental forms within sulfates, such asgypsum, and sulfidic ores, including iron pyrites, as well as
sulfides of copper, zinc, lead, nickel, and cobalt. Fossil fuels also
contain sulfur, where it can be found in natural gas and crude oil,
bonded to both hydrogen and carbon. In coal, sulfur exists in the
form of inorganic and organic sulfides. The significance of sulfur
deposits in natural gas and crude oil as sources of sulfur
compounds is on the rise.
13.
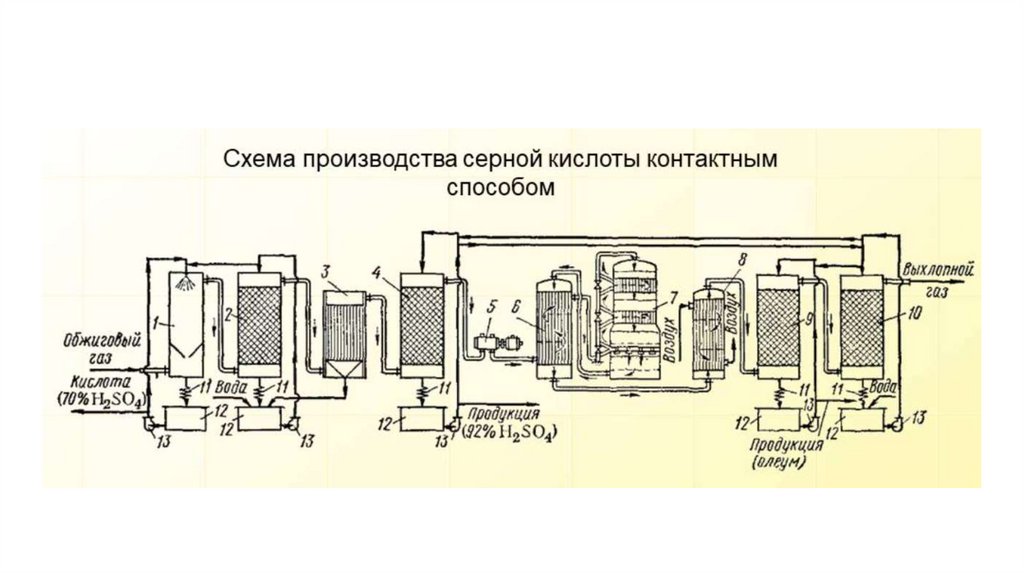
Sulfuric acidSulfuric acid plays a crucial role in numerous processes, being
one of the primary inorganic materials. Historically, it has served
as an indicator for the strength of the chemical industry in a
particular country. However, in recent times, various large-scale
processes have been modified to operate without relying on
sulfuric acid.
14.
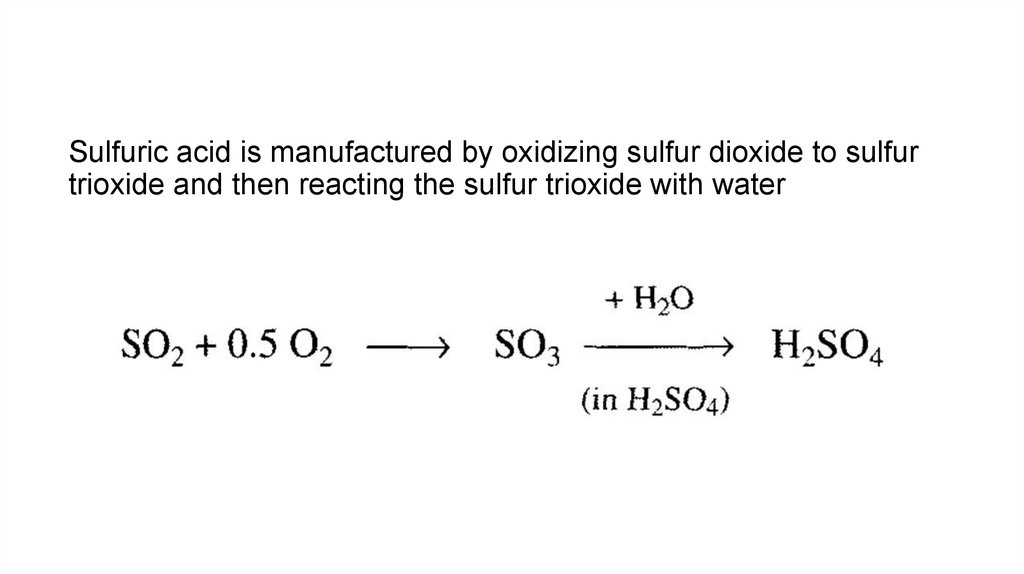
Sulfuric acid is manufactured by oxidizing sulfur dioxide to sulfurtrioxide and then reacting the sulfur trioxide with water
15.
16.
Sulfuric acid, being a crucial product in the chemical industry,finds applications across various sectors. Globally, 65% of
sulfuric acid is used in the manufacturing of phosphorus and
nitrogen fertilizers, whereas in Western Europe, only 31% is
employed for this purpose. In the Federal Republic of Germany,
approximately 90% of the produced sulfuric acid is utilized within
the chemical industry.
17.
In the petrochemical industry, sulfuric acid plays a role inprocesses such as the alkylation of isoalkanes with alkenes.
Within the broader chemical industry, it is used in the production
of inorganic chemicals (e.g., hydrofluoric acid, chromic acid,
aluminum sulfate) and organic products (e.g., dyes, explosives,
isocyanates, soaps, detergents, fibers, and pharmaceuticals).
Sulfuric acid also contributes to the manufacturing of titanium
oxide pigments, extraction processes for uranium and copper,
steel pickling, and is essential in battery production.













 chemistry
chemistry








