Similar presentations:
Electrical injuries
1.
Electrical injuriesFirst aid
2.
Electrical injuries• Voltage=current x Resistance (V=IR)
• Increased resistance produces increased heat
• Tissue
resistance:nerve<blood<muscle<skin<tendon<fat<bone(R=heat)
• Current: flow of electrons
1.Alternating current- periodically changes its direction and
magnitute
2.Direct current- flows only in one direction
AC three times worse than DC
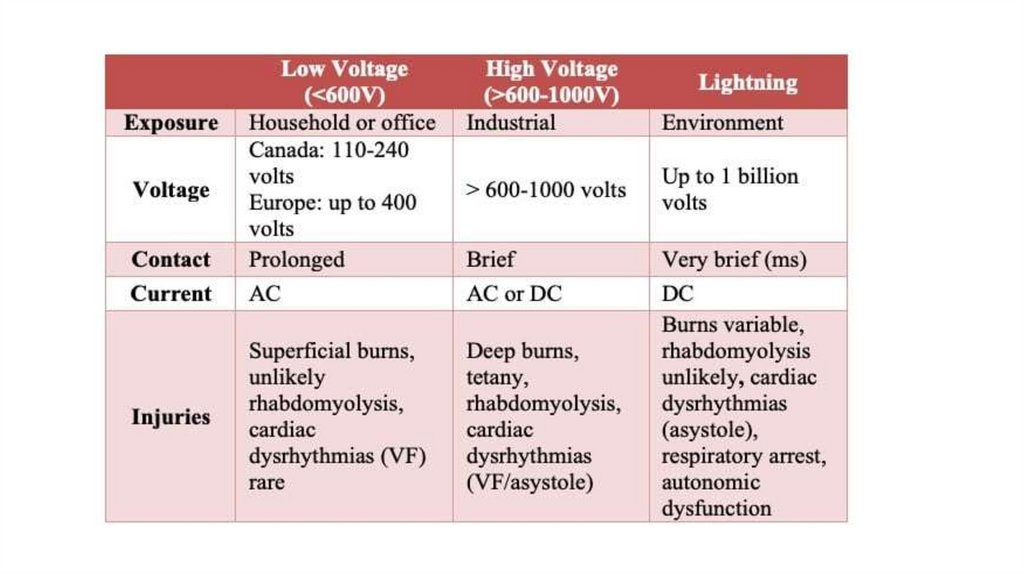
Injuries are divided into high voltage (500-1000V or higher) and low
voltage
Q= I2Rt, Q-heat generated,
3.
Electro injury depends on• Types of current
• Voltage
• Duration of exposure
• Resistance
• Pathway of current
• Predisposing factors
• Insulators
4.
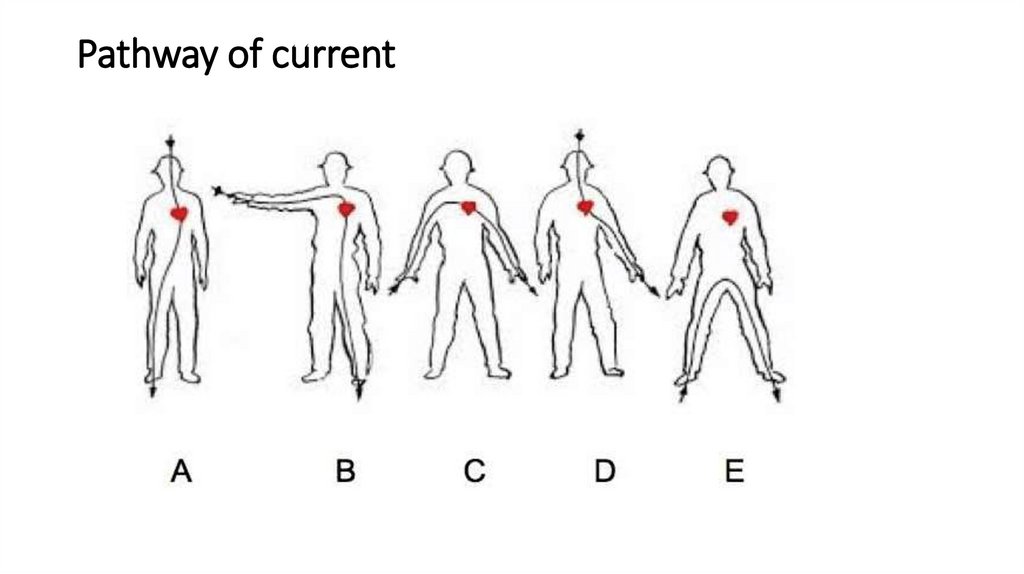
Pathway of current5.
The effect of electric current on a personElectric current,passing through the human body has a
Thermal-heat,burns
Chemical-violation of physiological functions
Biological- muscle contraction,joints dislocations etc.
Effects
Causes of Death
• Cardiac injuries
• Respiratory muscle paralysis
• CNS injuries
• Accidents
6.
7.
Low voltage injury• More common
• Burns are minor
• Half of no voltage deaths have no burns
• Low voltage AC can cause cardiac arrest,usually ventricular fibrillation
8.
High voltage• Skin burns severe
• Violent skeletal muscle contraction,throw victim
• Fractures,dislocations
• Clinical picture resembles crush injury
• High voltage AC/DC causes asystolic cardiac arrest
9.
Lightening injuries• Brief duration,passes over body,deep injury rare
• Strike types
1.Direct(most serious),look for entrance and exit wounds
2.Side flash
3.Contract strike(e.g. holding flag pole)
4.Ground current
Ruptured TM
Motor paralysis:eyes,diaphragm(hypoxia),extremity paralysis-2/3 have permanent
sequelae
Cardiac arrest:mostly asystole.
10.
Contact with eletricity• Touch tension(direct contact )
• Step voltage
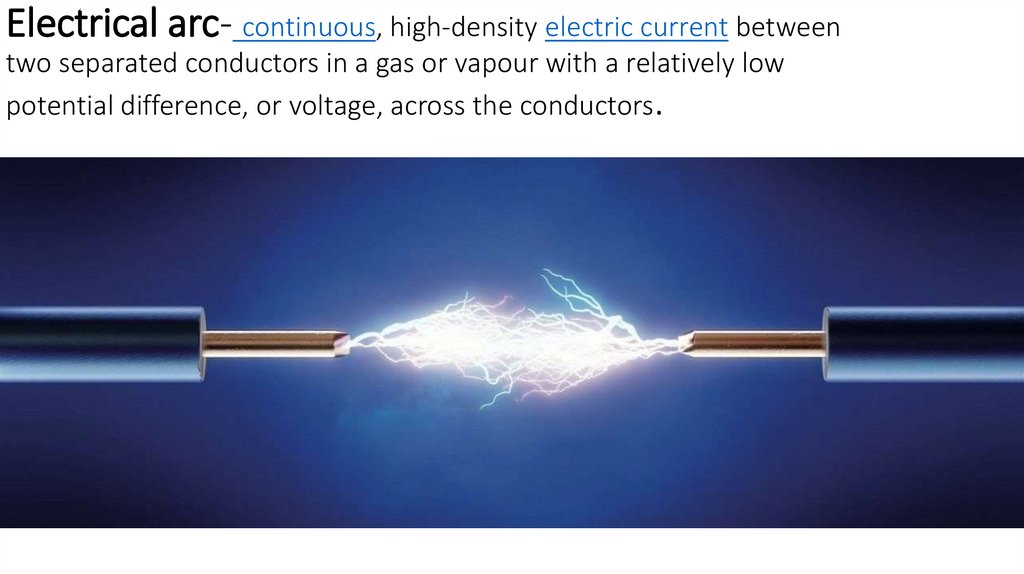
• Electrical arcs
11.
Electrical arc- continuous, high-density electric current betweentwo separated conductors in a gas or vapour with a relatively low
potential difference, or voltage, across the conductors.










 life safety
life safety








