Similar presentations:
Essentials of Organizational Behavior
1.
Essentials of Organizational BehaviorFifteenth Edition
Chapter 6
Perception and Individual
Decision Making
Copyright © 2022, 2018, 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
2.
What is Perception?Learning Objective 6.1
• Perception: a process by which individuals
organize and interpret their sensory impressions
in order to give meaning to their environment
• The world as it is perceived is the world that is
behaviorally important
Copyright © 2022, 2018, 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
3.
Factors that Influence Perception• Factors the influence perception include
– The perceiver: your personal characteristics
– The target: characteristics of the target
– The context: situational factors
Copyright © 2022, 2018, 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
4.
Person Perception: Making JudgmentsAbout Others
Learning Objective 6.2
• Person perceptions: perceptions we form about
each other
• Attribution Theory: an attempt to explain the
ways we judge people differently, depending on
the meaning we attribute to a behavior
• Internal and External Causation
Copyright © 2022, 2018, 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
5.
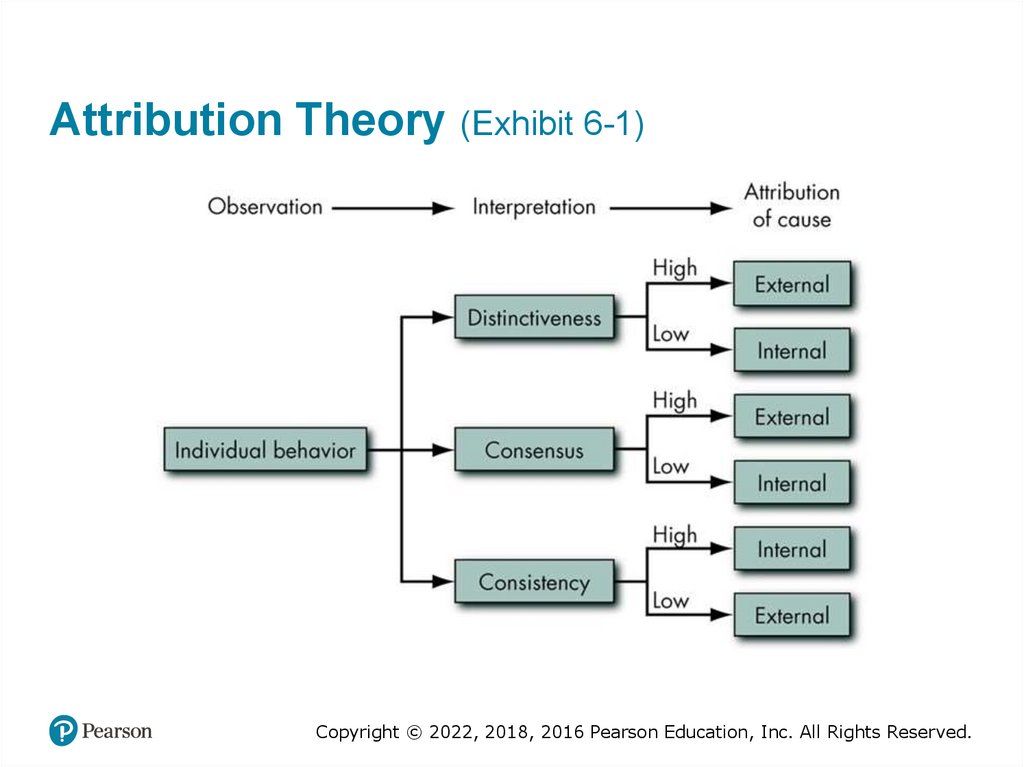
Distinctiveness, Consensus, andConsistency
• Distinctiveness – whether an individual displays
different behaviors in different situations
• Consensus – does everyone who faces a similar
situation respond in the same way as the
individual did?
• Consistency – does the person respond the same
way over time?
Copyright © 2022, 2018, 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
6.
Attribution Theory (Exhibit 6-1)Copyright © 2022, 2018, 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
7.
Errors and Biases• Fundamental attribution error:
– Tendency to underestimate the influence of external
factors and overestimate the influence of internal
factors
• Self-serving bias: occurs when individuals
overestimate their own (internal) influence on
successes and overestimate the external
influences on their failures
• Cultural differences exist
Copyright © 2022, 2018, 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
8.
Common Shortcuts in Judging Others(1 of 2)
• Selective Perception: selectively interpret based
on interests, background, and attitude
• Halo and Horns Effects: drawing a general
impression based on a single characteristic
Copyright © 2022, 2018, 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
9.
Common Shortcuts in Judging Others(2 of 2)
• Contrast Effects: our reaction is influenced by
others we have recently encountered (the context
of the observation)
• Stereotyping: judging someone on the basis of
the perception of the group to which they belong
• Threat of technological unemployment: AI taking
over jobs
Copyright © 2022, 2018, 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
10.
The Link Between Perception andDecision Making
Learning Objective 6.3
• Decision making occurs as a reaction to a
perceived problem
• Discrepancy between the current state and a desired
state
• Decisions: choices from among two or more
alternatives
Copyright © 2022, 2018, 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
11.
Decision Making in OrganizationsLearning Objective 6.4
• Approaches to decision making
– Rational decision making
– Bounded rationality
– Intuition
Copyright © 2022, 2018, 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
12.
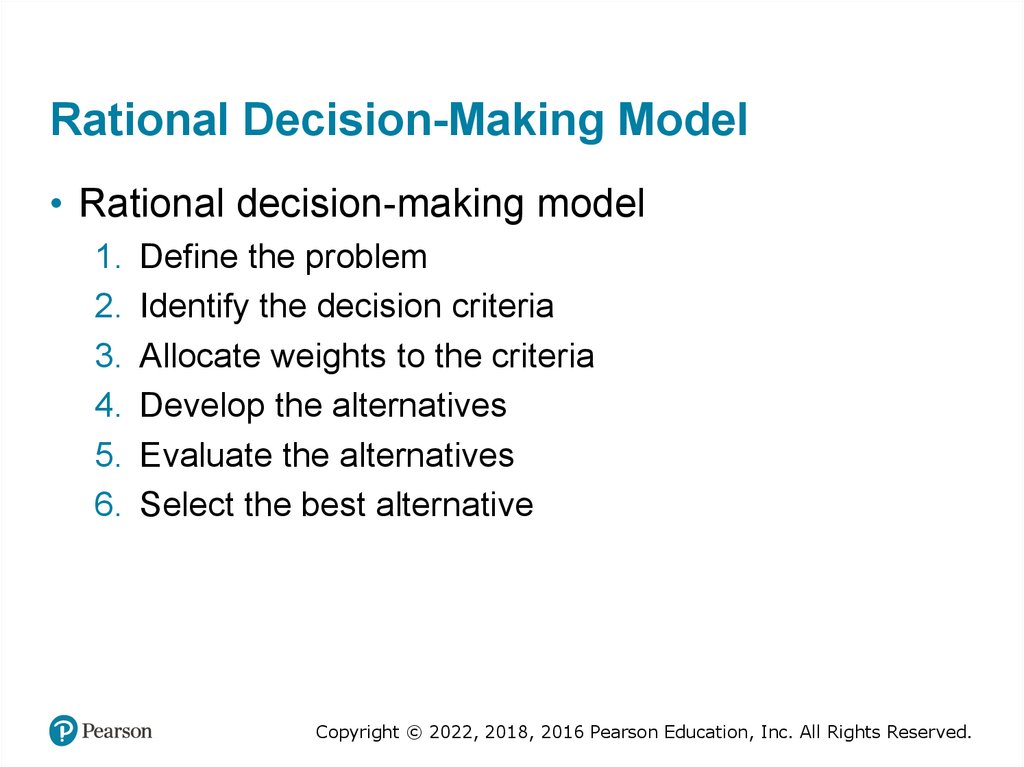
Rational Decision-Making Model• Rational decision-making model
1. Define the problem
2. Identify the decision criteria
3. Allocate weights to the criteria
4. Develop the alternatives
5. Evaluate the alternatives
6. Select the best alternative
Copyright © 2022, 2018, 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
13.
Bounded Rationality• The limited information-processing capability of
human beings makes it impossible to assimilate
and understand all the information necessary to
optimize
– People seek solutions that are satisfactory and
sufficient, rather than optimal (they “satisfice”)
• Bounded rationality is constructing simplified
models that extract the essential features from
problems without capturing all their complexity
Copyright © 2022, 2018, 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
14.
Intuition• Intuitive decision making: a non-conscious
process created out of distilled experience
– Least rational decision-making model
– Affectively charged
– Can be a powerful complement to rational analysis in
decision making
Copyright © 2022, 2018, 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
15.
Common Biases and Errors in DecisionMaking (1 of 2)
• Overconfidence Bias: a tendency to be
overconfident about our own abilities or the abilities of
others
• Anchoring Bias: a tendency to fixate on initial
information and fail to adequately adjust for
subsequent information
• Confirmation Bias: seeking out information that
reaffirms our past choices and discounting information
that contradicts past judgments
• Availability Bias: basing judgments on readily
available information
Copyright © 2022, 2018, 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
16.
Common Biases and Errors in DecisionMaking (2 of 2)
• Escalation of Commitment: staying with a
decision even when there is clear evidence that it
is wrong
• Randomness Error: our tendency to believe we
can predict the outcome of random events
• Risk Aversion: preferring a sure gain of a
moderate amount over a riskier outcome
• Hindsight Bias: believing falsely that we could
have predicted the outcome of an event after that
outcome is already known
Copyright © 2022, 2018, 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
17.
Influences on Decision Making: IndividualDifferences & Organizational Constraints
Learning Objective 6.5
• Individual differences
• Personality
• Gender
• General mental ability
• Cultural differences
Copyright © 2022, 2018, 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
18.
Organizational Constraints on DecisionMaking
• Performance evaluation systems
• Reward systems
• Formal regulations
• System-imposed time constraints
• Historical precedents
• Decision making in times of crisis
Copyright © 2022, 2018, 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
19.
Ethics in Decision Making (1 of 2)Learning Objective 6.6
• Three Ethical Decision Criteria
• Utilitarianism
– Provide the greatest good for the greatest number
• Rights
– Make decisions consistent with fundamental liberties and
privileges
• Justice
– Impose and enforce rules fairly and impartially so that there is
equal distribution of benefits and costs
Copyright © 2022, 2018, 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
20.
Ethics in Decision Making (2 of 2)• Choosing between criteria
• Behavioral ethics
– Analyzing how people actually behave when
confronted with ethical dilemmas
• Lying
– Deadly to decision making
Copyright © 2022, 2018, 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
21.
Creativity and Innovation in OrganizationsLearning Objective 6.7
• Creativity: the ability to produce novel and useful
ideas
• Helps people:
– See problems others can’t see
– Better fully understand problems
Copyright © 2022, 2018, 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
22.
Three-Stage Model of Creativity inOrganizations (Exhibit 6-4)
Copyright © 2022, 2018, 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
23.
Creative BehaviorSteps:
1. Problem formulation: identify a problem or
opportunity that requires a solution as yet
unknown
2. Information gathering: possible solutions
incubate in an individual’s mind
3. Idea generation: develop possible solutions
from relevant information and knowledge
4. Idea evaluation: evaluate potential solutions
and identify the best one
Copyright © 2022, 2018, 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
24.
Causes of Creative Behavior• Creative potential:
• Intelligence and creativity
• Personality and creativity
• Expertise and creativity
• Ethics and creativity
• Creative environment
– Motivation
– Rewards and recognition
– Jobs with clear innovative expectations
Copyright © 2022, 2018, 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
25.
Creative Outcomes (Innovation)• Creative outcomes: ideas or solutions judged to
be novel and useful by relevant stakeholders
Copyright © 2022, 2018, 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
26.
Implications for Managers• Behavior follows perception, so to influence behavior at
work, assess how people perceive their work.
• Make better decisions by recognizing perceptual biases
and decision-making errors we tend to commit.
• Adjust your decision-making approach to the national
culture you’re operating in and to the criteria your
organization values.
• Combine rational analysis with intuition.
• Try to enhance your creativity.
Copyright © 2022, 2018, 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved.





















 biology
biology








