Similar presentations:
Introduction to Sociology
1.
Lecture 1Introduction to
Sociology
Aigul Zhanadilova, Senior lecturer Ph.D candidate in sociology
2.
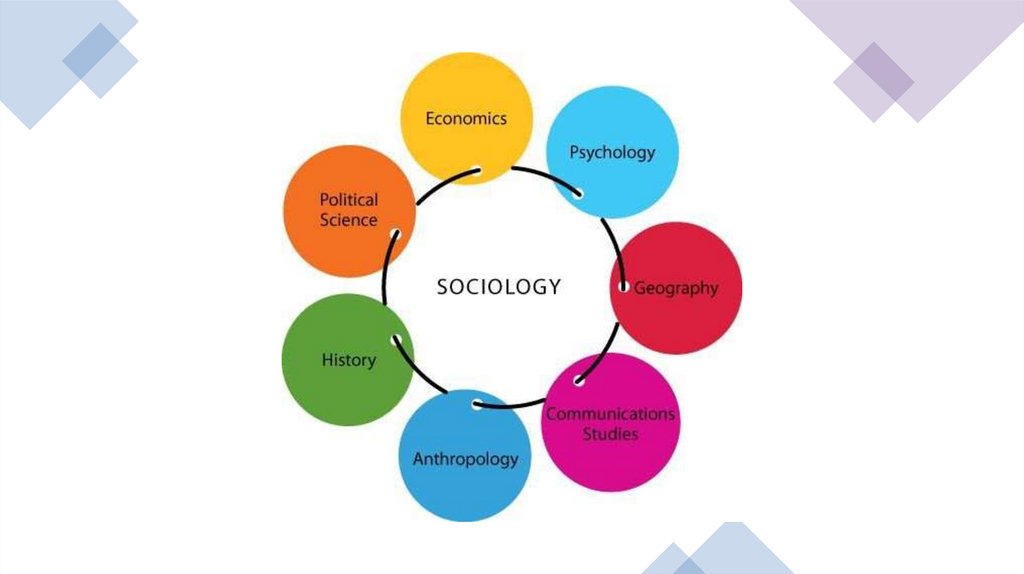
Content• Sociology
• Sociological Imagination
• Founding fathers of
• Glossary
3.
What is sociology?● Sociology is the scientific study of human life,
social groups, whole societies and the human
world as such.
● Sociology, a social science that studies human
societies, their interactions, and the processes that
preserve and change them.
4.
Comte introduced the term “Sociology” for thefirst time in his famous work “Positive
Philosophy” at about 1839.
5.
1.Emile Durkheim defines sociology as the “science ofsocial institutions”.
2. Small defines sociology as the “science of social
relations”.
3. Kingsley Davis says that “sociology is a general
science of society”.
4. Park regards sociology as the “science of collective
behaviour”.
5. Jones defines sociology as the “study of man in
relationship to men”.
6.
• Sociology demonstrates the need to take a much broader view of our ownlives in order to explain why we act as we do.
• Its major concern is society, and hence it is popularly known as the
“science of society”.
• Study social relationships, their specific forms, varieties and patterning. We
study how the relations combine, how they build up smaller or greater
systems, and how they respond to changes and changing demands or needs.
7.
Do you love to drinkcoffee?
Sociological imagination - The essence of the sociological
imagination lies in the ability to see and analyze social
phenomena not only from an individual perspective, but
also taking into account their social context and impact
on society as a whole.
8.
The sociologicalimagination
rights and environmental
destruction
1.social interaction
5. contemporary debates
about globalization,
international fair trade,
human
-symbolic value
4. social and economic
development
-the simple act
worldwide social
influences and
communications
2.why these differences
exist
3. complicated set of
social and economic
relationships
-tolerate the consumption
9.
10.
G. Bajoit has gathered the human conceptions that form thebasis of sociological theories in 4 main groups:
Human is a needy creature by nature. Therefore, he tries to feel safe
by living in solidarity with his peers.
Human is a opportunistic, calculating, egoistic, trying to maximize
their interests.
Human is a structure that can be exploited, alienated, and blinded by
a false consciousness.
Human is a solidarist, insistent, selfless being, trying to get rid of the
yoke of domination, capable of being effective on society and
reproducing it by acting together, even if he is crushed under the
"sacred weights".
11.
• Social structure is not like a physical structure, such as a building, which existsindependently of human actions.
12.
13.
Emergence of SociologySociology has had a fourfold origin:
• political philosophy,
• philosophy of history,
• biological theories of evolution
• and the movements for social and political reforms
14.
15.
How can sociology help us in our lives? Or Uses ofsociology
The significant aspects of sociology:
1.Sociology studies society in a scientific way.
2. Sociological research provides practical help in assessing the results of policy
initiatives.
3. Sociology has drawn our attention to the intrinsic worth and dignity of man.
4. Sociology gives us an awareness of cultural difference that allows us to see the
social world from many perspectives.
5.Sociology can provide us with self enlightenment – increased self understanding.
6.Sociologists concern themselves directly with practical matters as professionals.
7. The study of society is of paramount importance in solving social problems
16.
17.
Special sociological theories and directionsare the sociology
sociology of
the family,
sociology of
labor,
sociology of
free time,
sociology of
culture,
sociology of
science,
sociology of
education,
sociology of
social-class
relations,
sociology of
national
relations,
sociology of
politics,
sociology of
religion,
sociology of
morality,
sociology of
organizations,
sociology of
conflict, etc.
18.
Glossary terms:Sociology, object of sociology, functions of sociology,
social institutions, social relations, collective behavior,
sociological imagination, symbolic value, social
interaction, sociological study, social structure, physical
structure
















 english
english








