Similar presentations:
Explore 1: Laundry Machine. Electricity – Potential Dividers
1.
Recording NoticeThis lesson is
being recorded
2.
King’s Interhigh Logo3.
Explore 1: Laundry MachineElectricity – Potential Dividers
4.
ObjectiveUnderstand how the potential along a uniform current-carrying
wire varies with the distance along it.
Understand the principles of a potential divider circuit and
understand how to calculate potential differences and
resistances in such a circuit.
Be able to analyse potential divider circuits where one
resistance is variable including thermistors and light dependent
resistors (LDRs).
5.
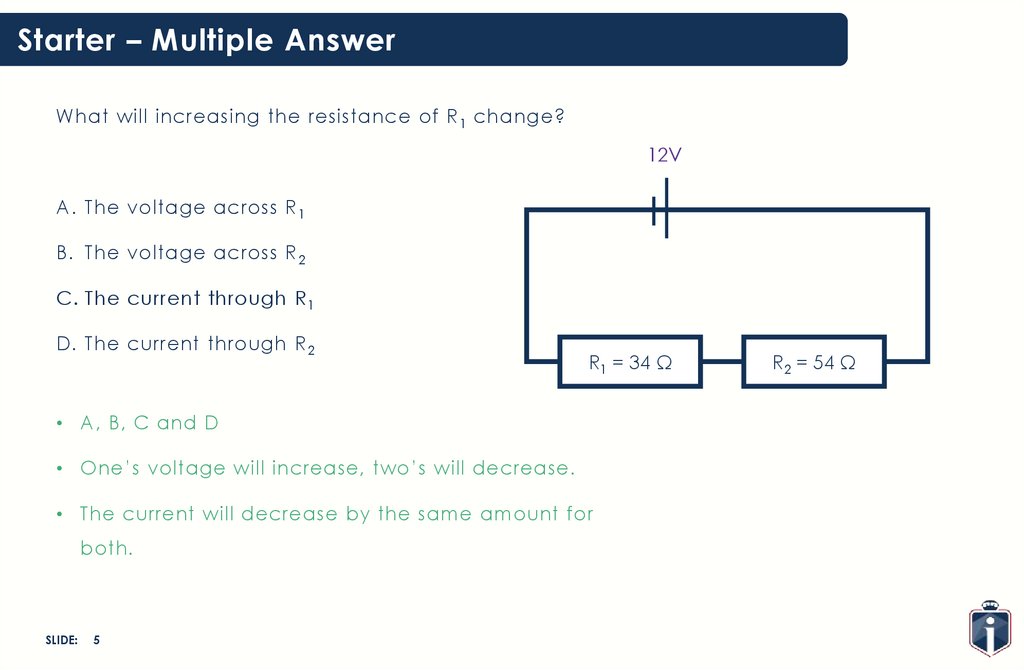
Starter – Multiple AnswerWhat will increasing the resistance of R 1 change?
12V
A. The voltage across R 1
B. The voltage across R 2
C. The current through R 1
D. The current through R 2
R1 = 34 Ω
• A, B, C and D
• One’s voltage will increase, two’s will decrease.
• The current will decrease by the same amount for
both.
SLIDE:
5
R2 = 54 Ω
6.
Activity: Washing line missionYour mission is to design an automatic
washing line.
It must sense:
• Heat
• Rain (lack of)
• Sunshine
To put the laundry out it must be:
• Dry
• Sunny and/or warm
Thermistor
SLIDE:
6
LDR
Moisture detector
7.
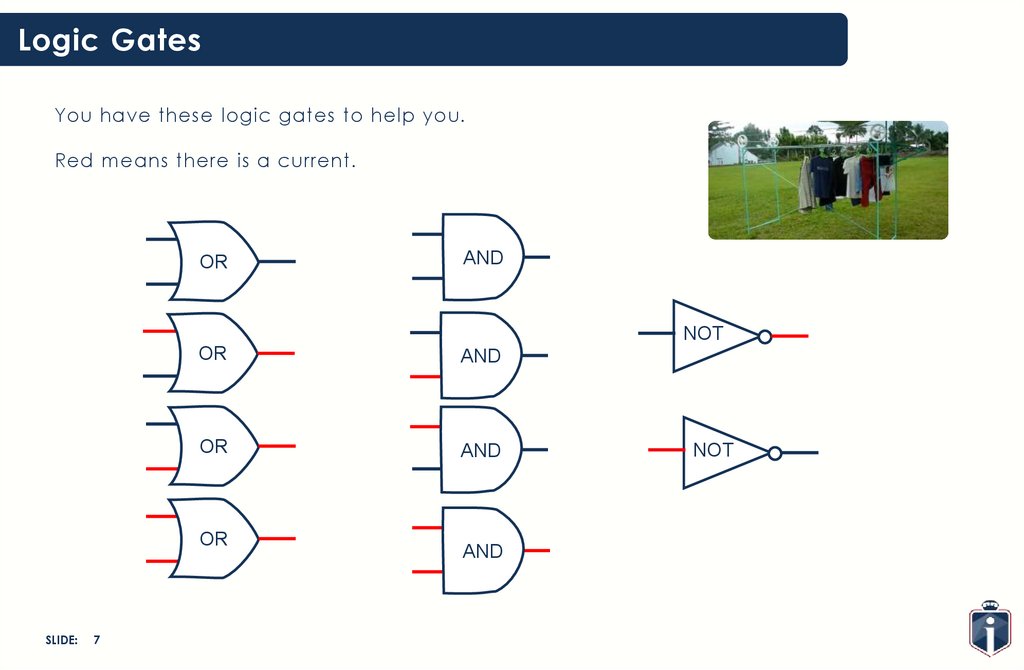
Logic GatesYou have these logic gates to help you.
Red means there is a current.
OR
AND
T
NOT
AND
OR
AND
OR
SLIDE:
7
AND
NOT
T
OR
8.
Blank slide to draw on in BreakoutsSLIDE:
8
9.
SLIDE:9
Out?
OR
Sunny
AND
Warm
M
Rain
Solution
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
1
1
1
0
0
0
1
0
1
0
1
1
0
0
1
1
1
0
10.
PlenaryFill in the blanks
1
• A potential divider is a part of a circuit with two components.
2
• Typically, one component is variable
resistor.
• The other is often a thermistor or a LDR. 3
• Together they control an output voltage.
4
SLIDE:
10
11.
ObjectiveUnderstand how the potential along a uniform current-carrying
wire varies with the distance along it.
Understand the principles of a potential divider circuit and
understand how to calculate potential differences and
resistances in such a circuit.
Be able to analyse potential divider circuits where one
resistance is variable including thermistors and light dependent
resistors (LDRs).
SLIDE:
11
12.
Explore 2: Exam Practice IElectricity – Potential Dividers
13.
ObjectiveUnderstand how the potential along a uniform current-carrying
wire varies with the distance along it.
Understand the principles of a potential divider circuit and
understand how to calculate potential differences and
resistances in such a circuit.
Be able to analyse potential divider circuits where one
resistance is variable including thermistors and light dependent
resistors (LDRs).
14.
StarterWrite any points or questions you have relating to potential dividers.
Points
SLIDE:
14
Questions
15.
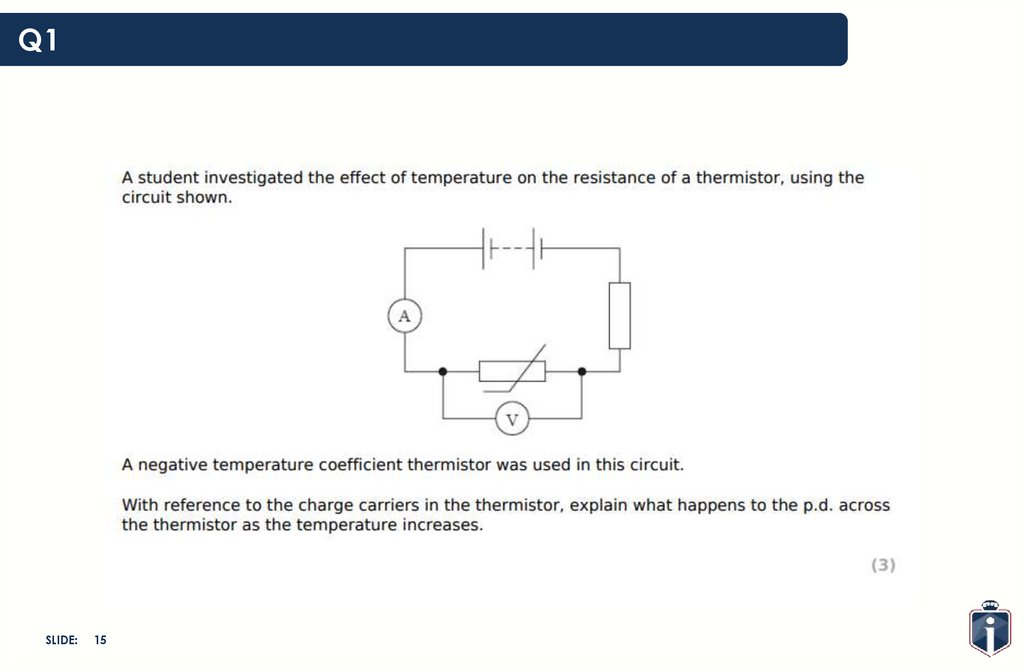
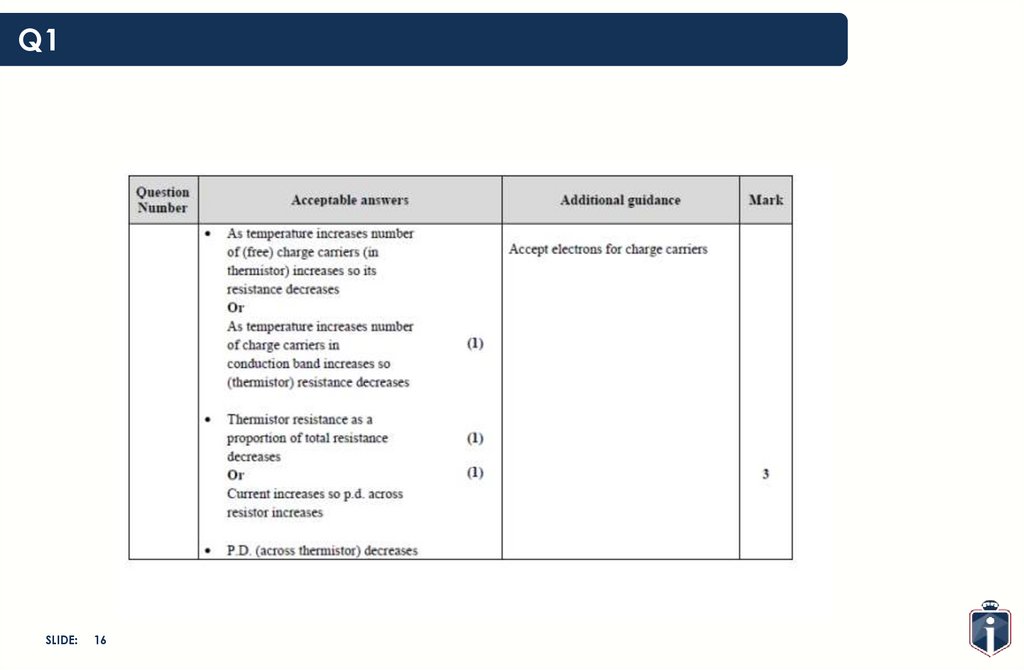
Q1SLIDE:
15
16.
Q1SLIDE:
16
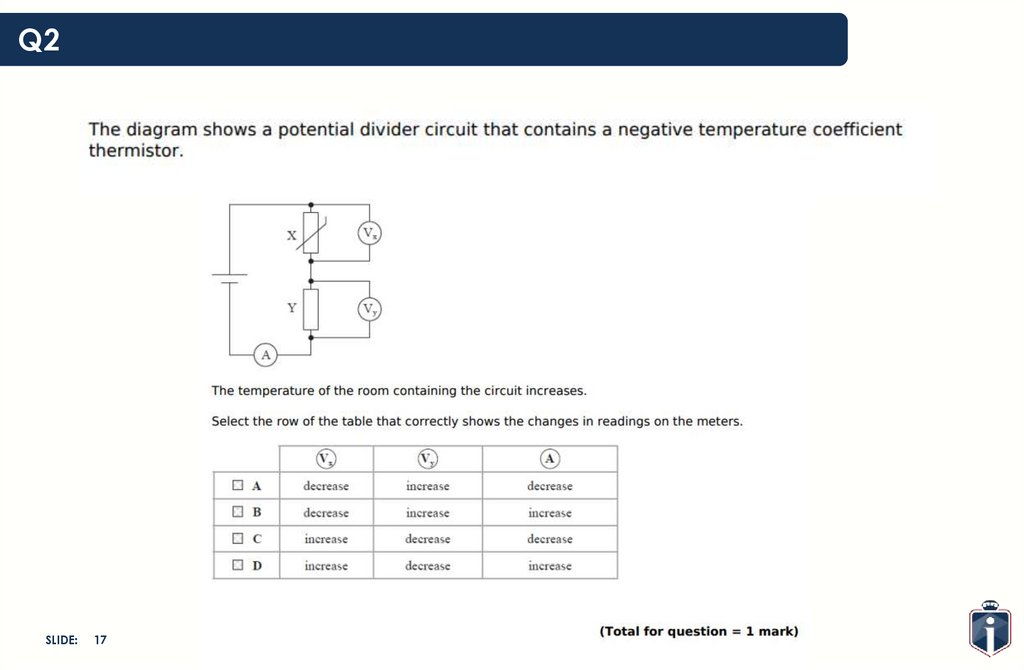
17.
Q2SLIDE:
17
18.
Q2SLIDE:
18
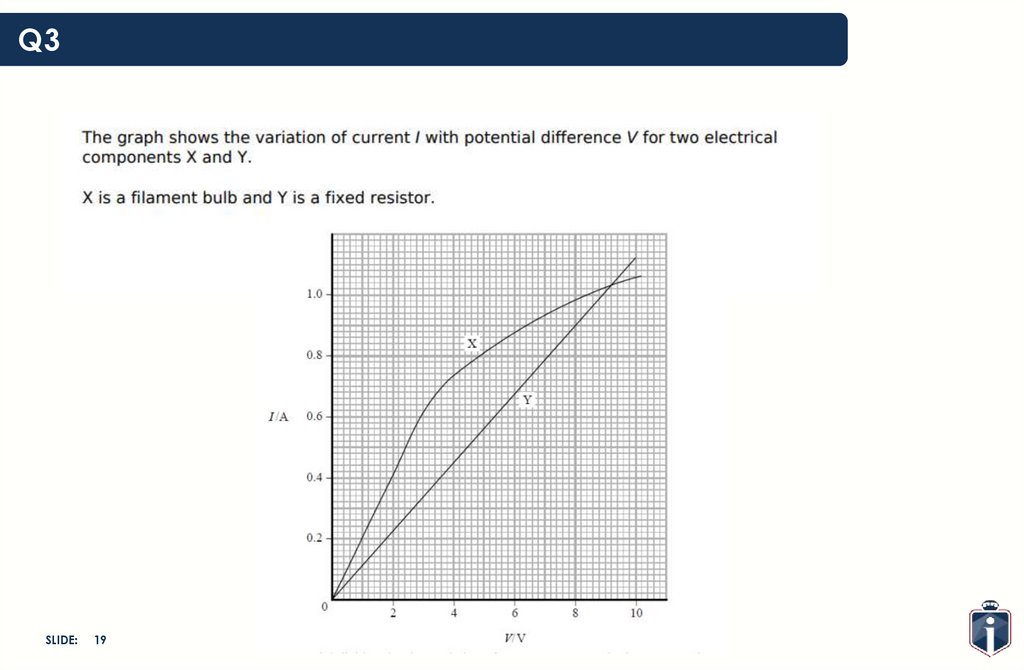
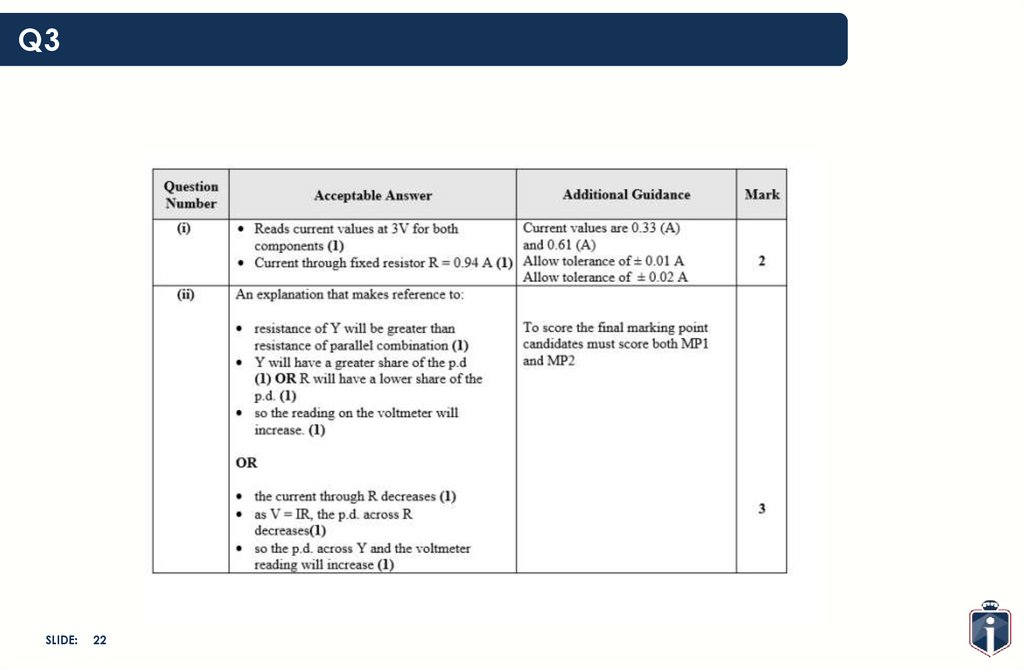
19.
Q3SLIDE:
19
20.
Q3SLIDE:
20
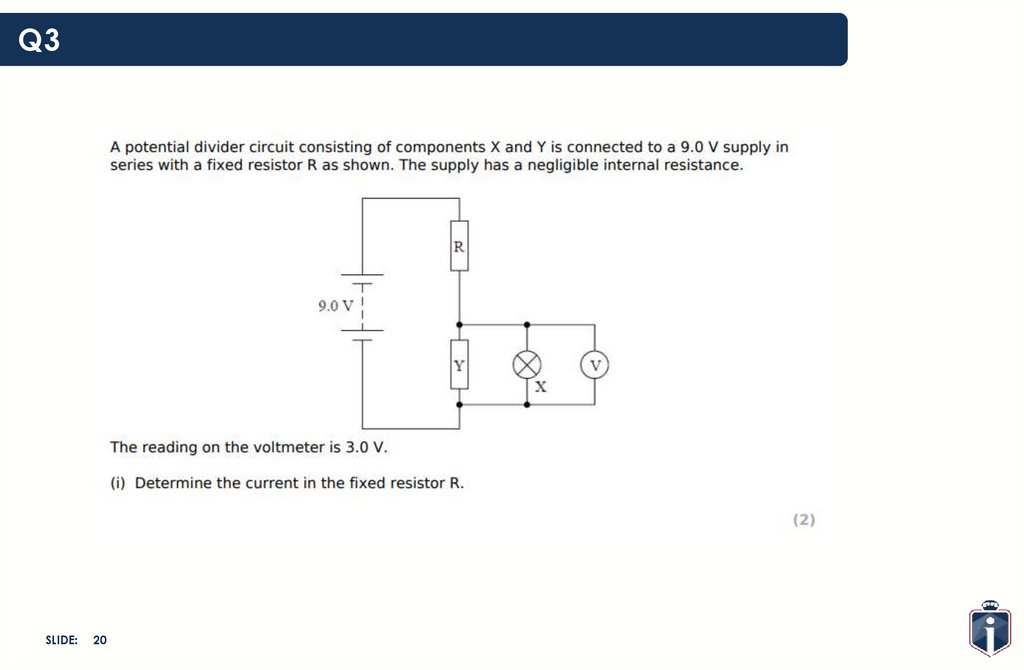
21.
Q3SLIDE:
21
22.
Q3SLIDE:
22
23.
PlenaryPlay taboo with words and phrases related to this topic….
SLIDE:
23
24.
ObjectiveUnderstand how the potential along a uniform current-carrying
wire varies with the distance along it.
Understand the principles of a potential divider circuit and
understand how to calculate potential differences and
resistances in such a circuit.
Be able to analyse potential divider circuits where one
resistance is variable including thermistors and light dependent
resistors (LDRs).
SLIDE:
24
25.
Explore 3: PracticalElectricity – Potential Dividers
26.
ObjectiveBuild a virtual potential divider.
SLIDE:
26
27.
StarterWhy are potential dividers useful?
What two things do they allow you to do?
• They allow a device to work automatically
and respond to an outside stimulus, like
temperature.
• You can set the conditions for the response
action: example - at what temperature the
heating comes on
SLIDE:
27
28.
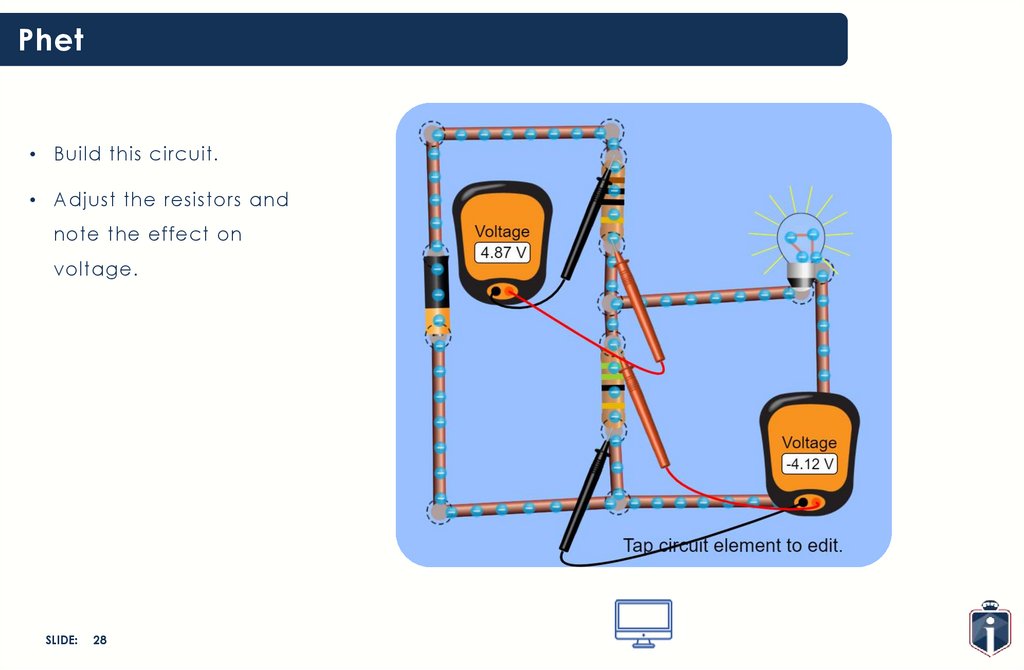
Phet• Build this circuit.
• Adjust the resistors and
note the effect on
voltage.
SLIDE:
28
29.
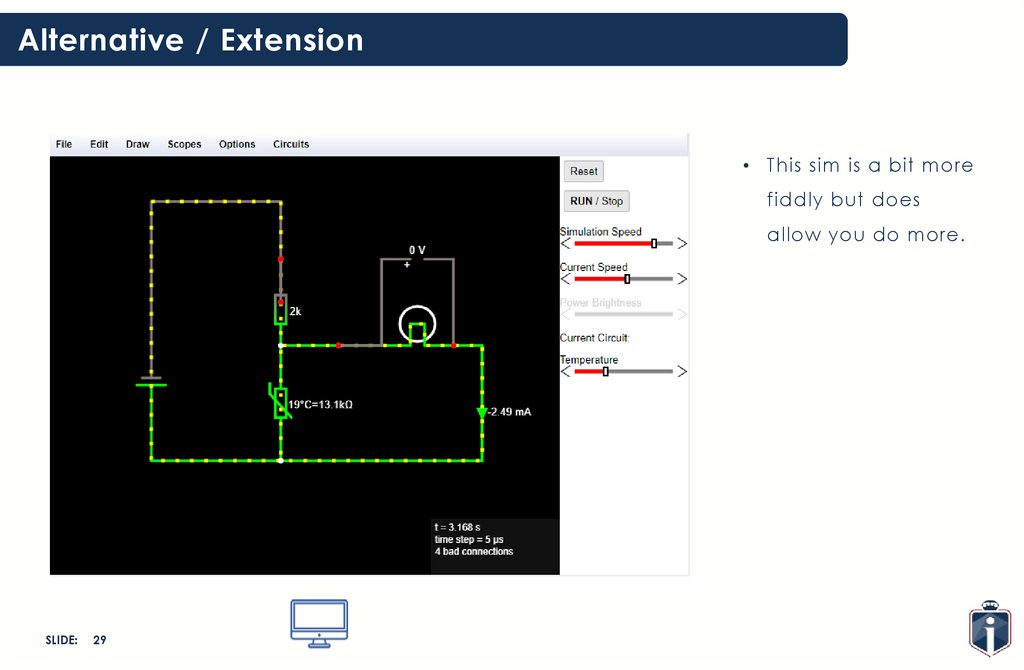
Alternative / Extension• This sim is a bit more
fiddly but does
allow you do more.
SLIDE:
29
30.
PlenaryWatch the 6.45 min onwards.
How is its metaphor useful for
Potential Dividers?
• The more one step drops the
marble the less height there is
for the other component.
Electric Circuits: Basics of the voltage and current laws
9.47 min
SLIDE:
30
31.
ObjectiveUnderstand how the potential along a uniform current-carrying
wire varies with the distance along it.
Understand the principles of a potential divider circuit and
understand how to calculate potential differences and
resistances in such a circuit.
Be able to analyse potential divider circuits where one
resistance is variable including thermistors and light dependent
resistors (LDRs).
SLIDE:
31
32.
Explore 4: Exam Practice IIElectricity – Potential Dividers
33.
ObjectiveUnderstand how the potential along a uniform current-carrying
wire varies with the distance along it.
Understand the principles of a potential divider circuit and
understand how to calculate potential differences and
resistances in such a circuit.
Be able to analyse potential divider circuits where one
resistance is variable including thermistors and light dependent
resistors (LDRs).
SLIDE:
33
34.
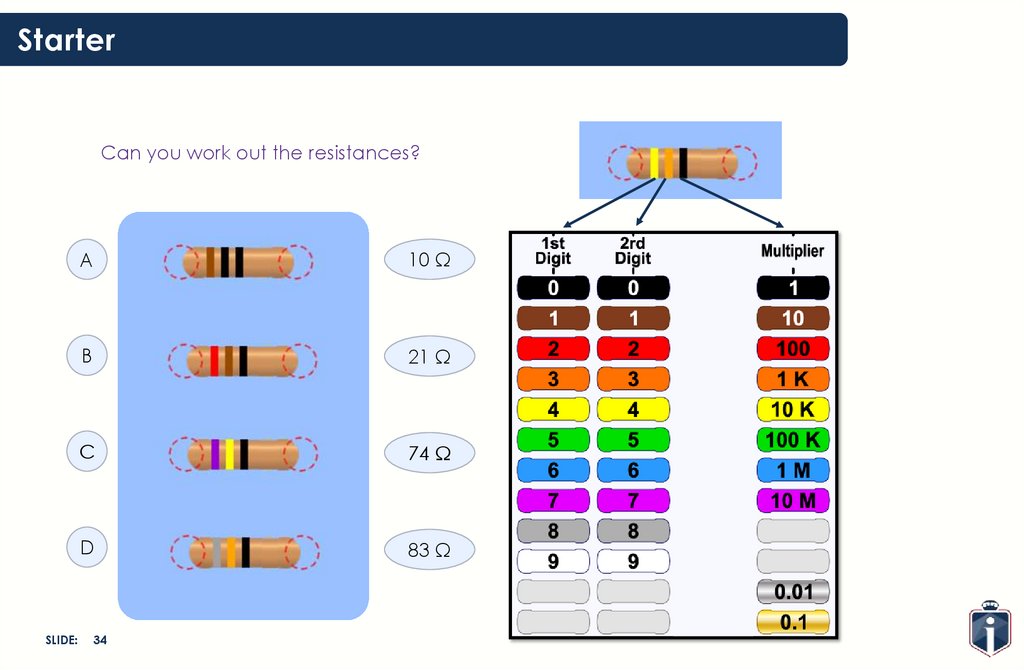
StarterCan you work out the resistances?
SLIDE:
A
10 Ω
B
21 Ω
C
74 Ω
D
83 Ω
34
35.
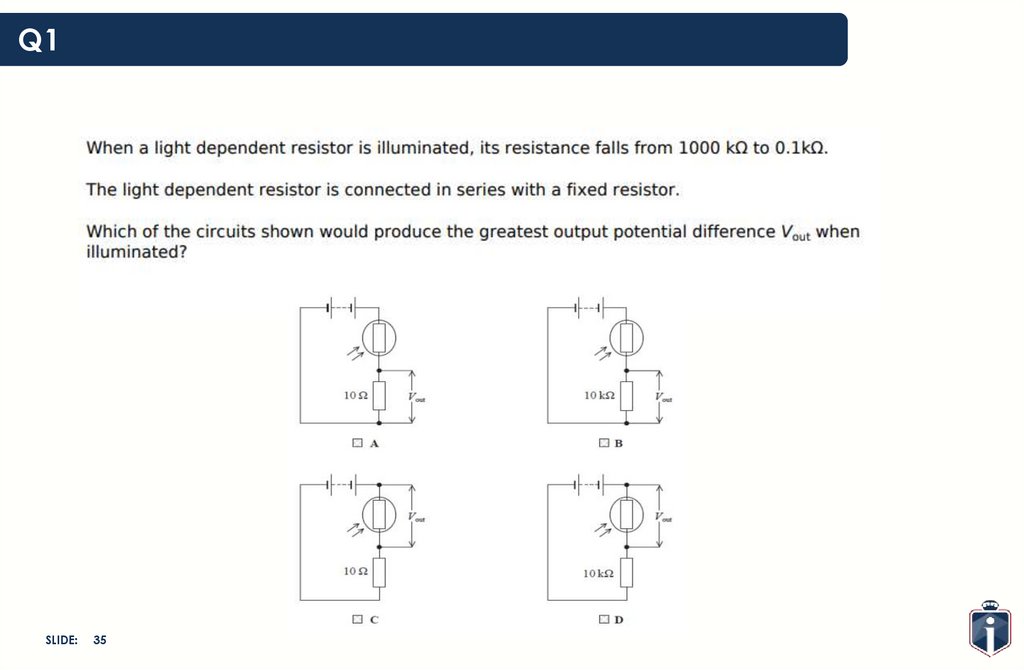
Q1SLIDE:
35
36.
Q1SLIDE:
36
37.
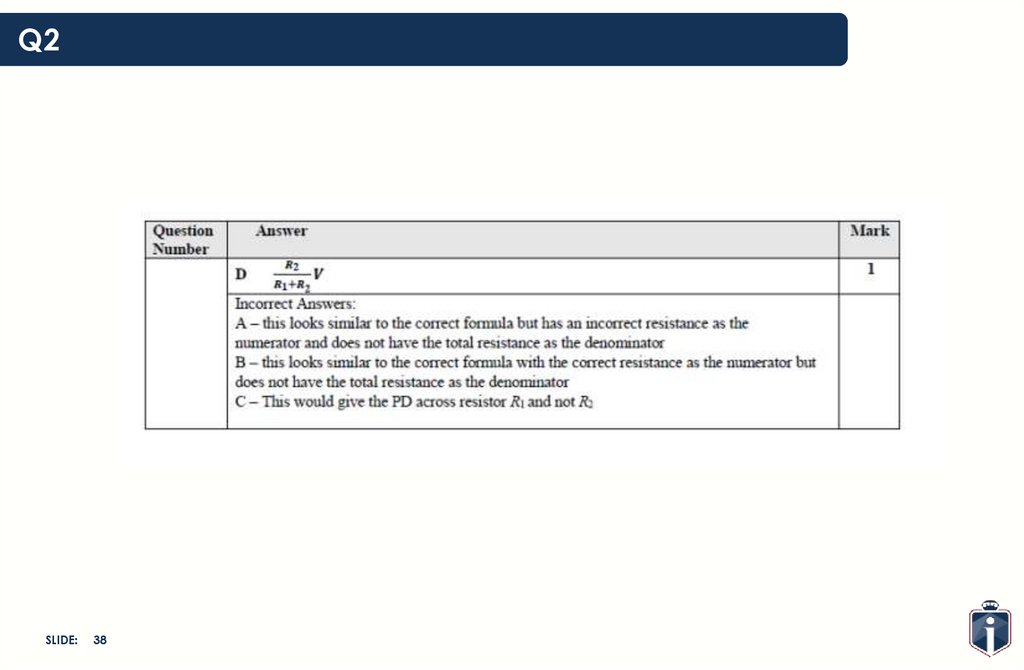
Q2SLIDE:
37
38.
Q2SLIDE:
38
39.
Q3SLIDE:
39
40.
Q3SLIDE:
40
41.
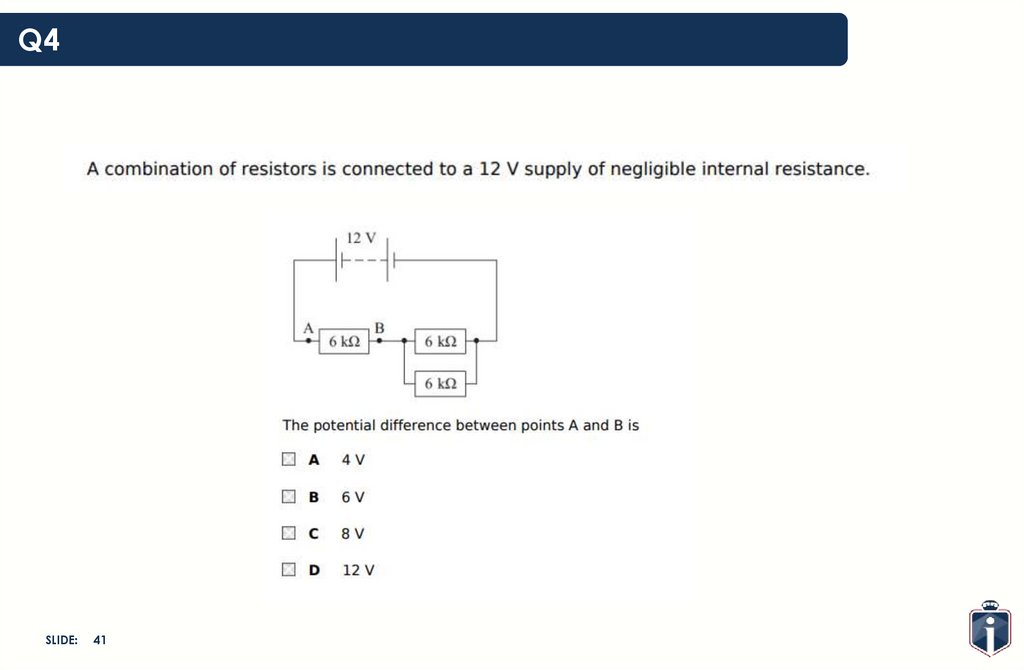
Q4SLIDE:
41
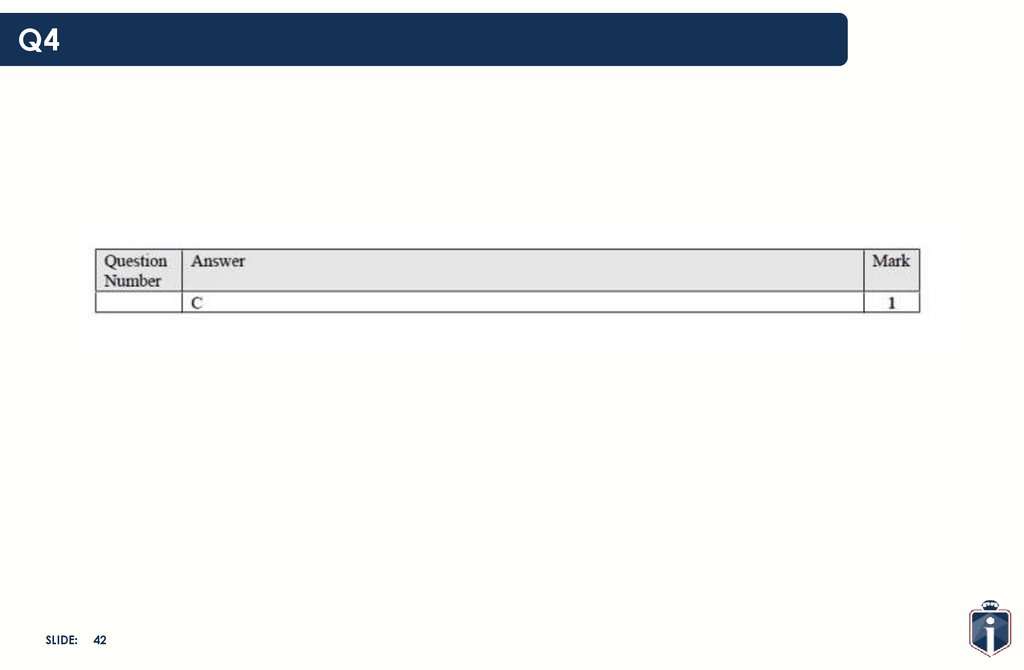
42.
Q4SLIDE:
42
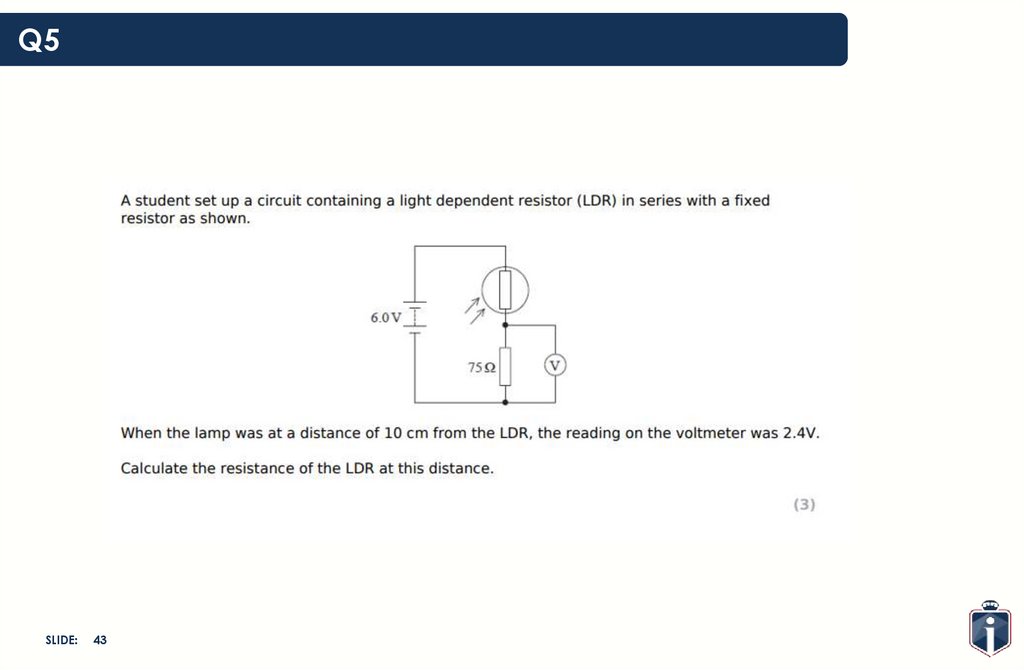
43.
Q5SLIDE:
43
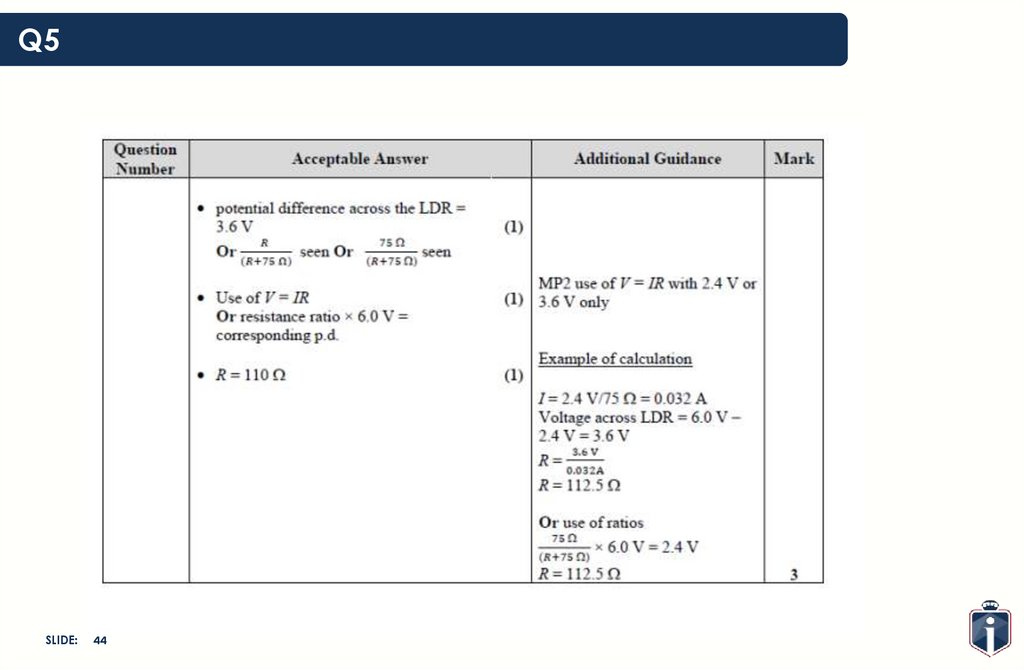
44.
Q5SLIDE:
44
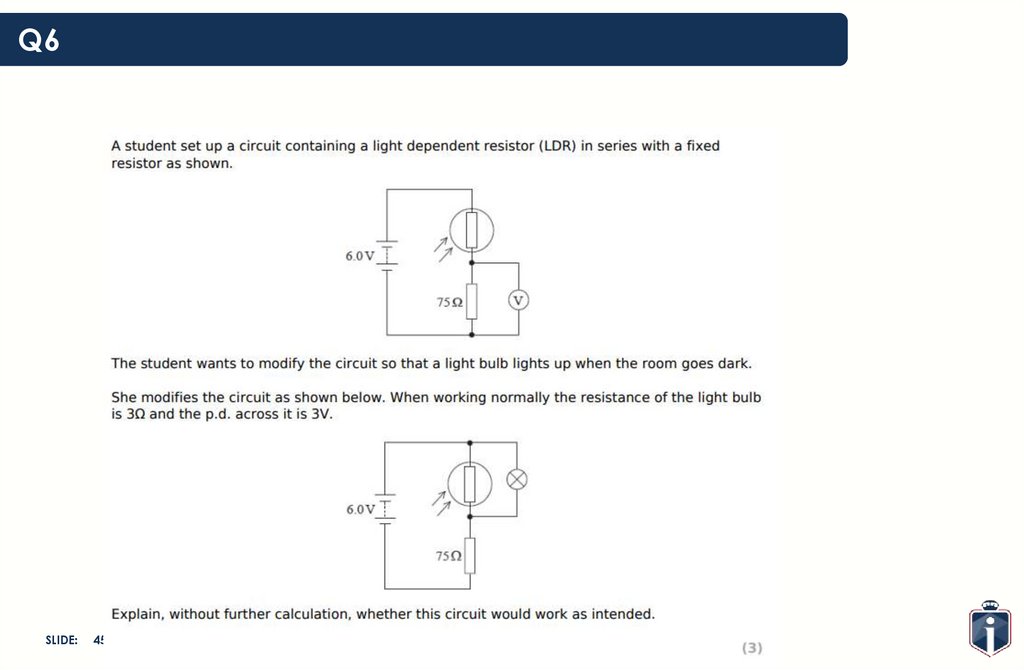
45.
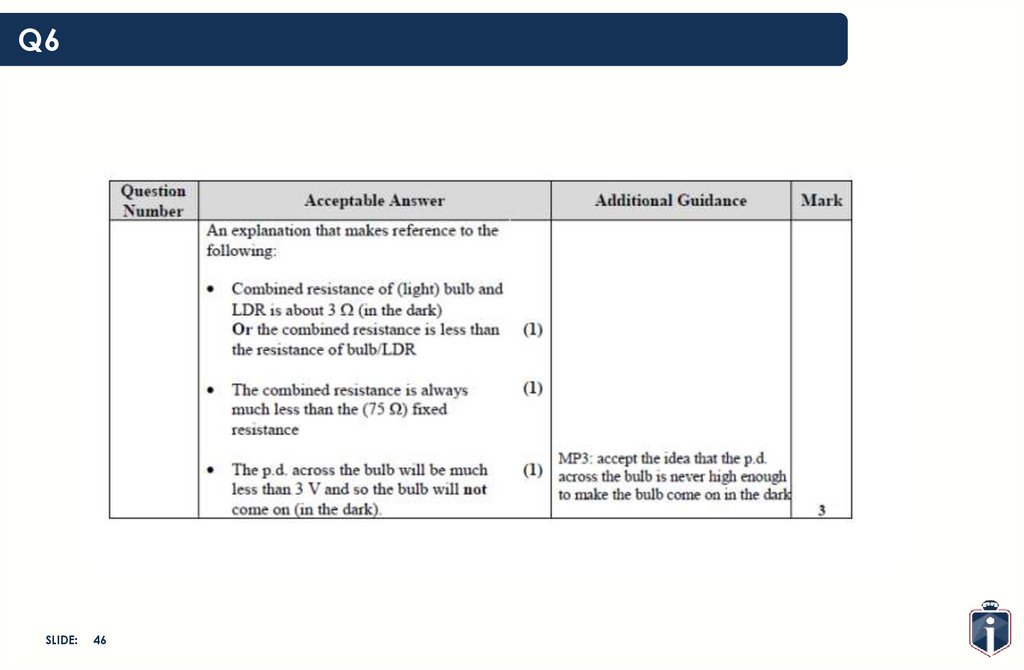
Q6SLIDE:
45
46.
Q6SLIDE:
46
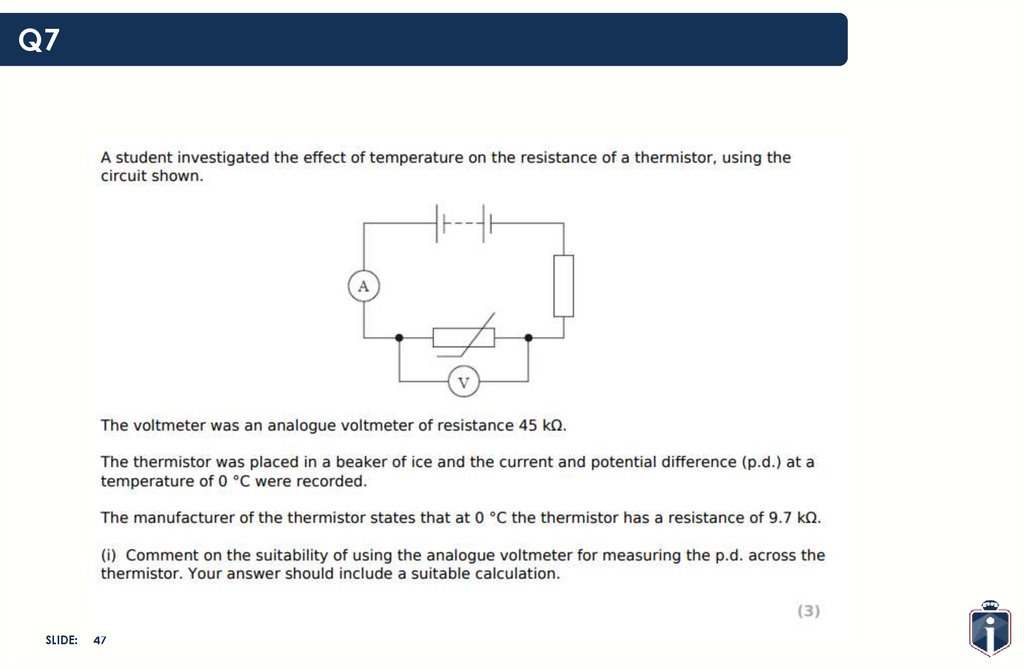
47.
Q7SLIDE:
47
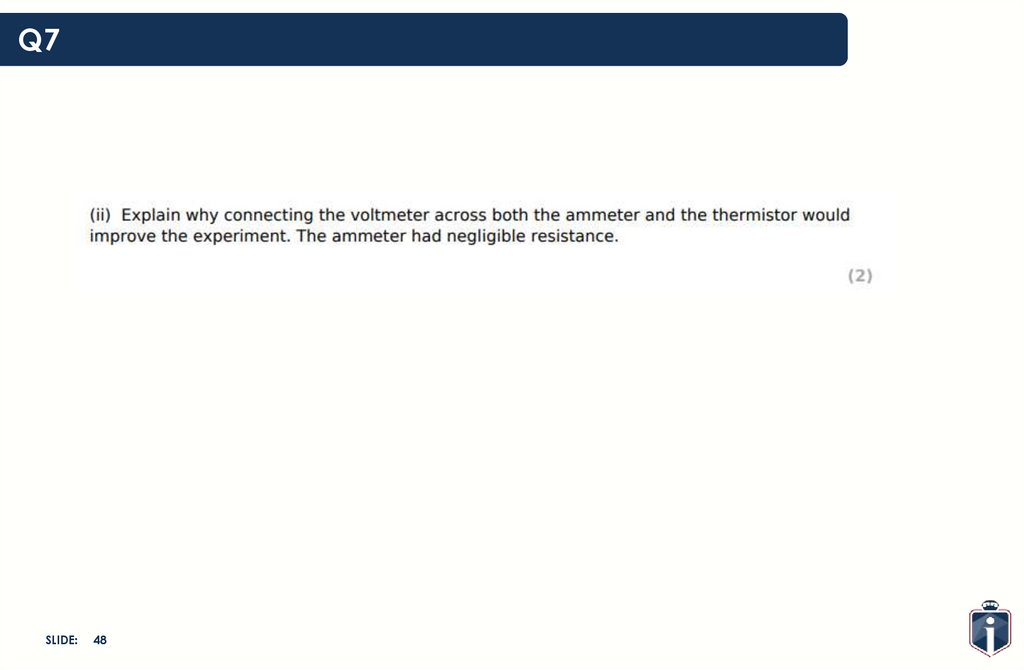
48.
Q7SLIDE:
48
49.
Q7SLIDE:
49
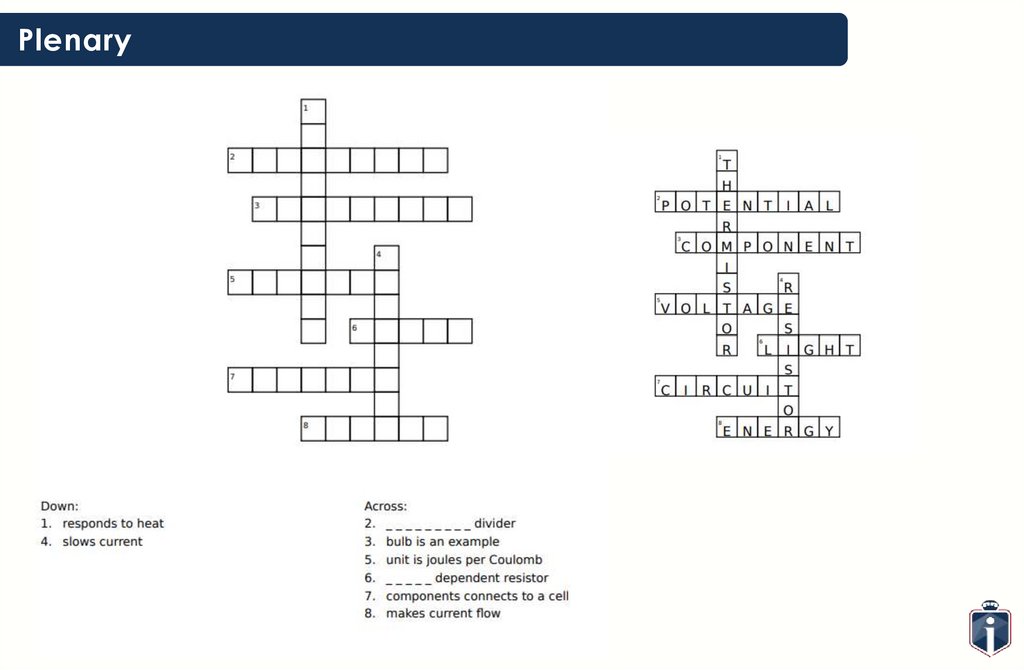
50.
PlenarySLIDE:
50
51.
ObjectiveUnderstand how the potential along a uniform current-carrying
wire varies with the distance along it.
Understand the principles of a potential divider circuit and
understand how to calculate potential differences and
resistances in such a circuit.
Be able to analyse potential divider circuits where one
resistance is variable including thermistors and light dependent
resistors (LDRs).
SLIDE:
51
52.
Lesson complete!See you next lesson




























 electronics
electronics








