Similar presentations:
Markets and consumer behavior
1.
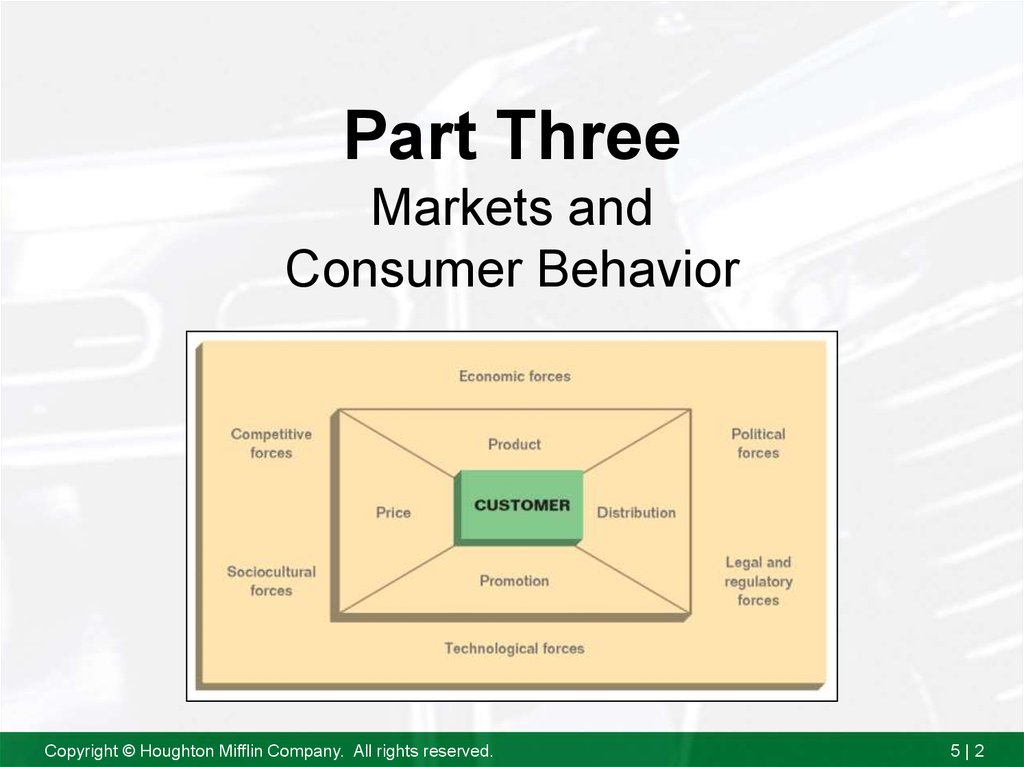
2. Part Three Markets and Consumer Behavior
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.5|2
3. Chapter 5 Consumer Buying Behavior
4. Objectives
• Understand consumers’ level of involvementwith product & describe consumer problemsolving processes
• Recognize stages of consumer buying
decision process
• Explore situational influences of consumer
buying process
• Understand psychological influences of
consumer buying process
• Examine social influences of consumer
buying process
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
5|4
5. Types Of Markets
1) Consumer2) Business
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
5|5
6. Consumer Market
Purchasers and household members whointend to consume or benefit from the
purchased products and do not buy
products to make products.
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
5|6
7. Buying Behavior
The decision processes and acts of peopleinvolved in buying and using products.
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
5|7
8. Consumer Buying Behavior
The decision processes and purchasingactivities of people who purchase products
for personal or household use and not for
business purposes.
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
5|8
9. Level Of Involvement
An individual’s intensity of interest in aproduct and the importance of the product
for that person.
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
5|9
10. Levels Of Involvement
EnduringSituational
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
5 | 10
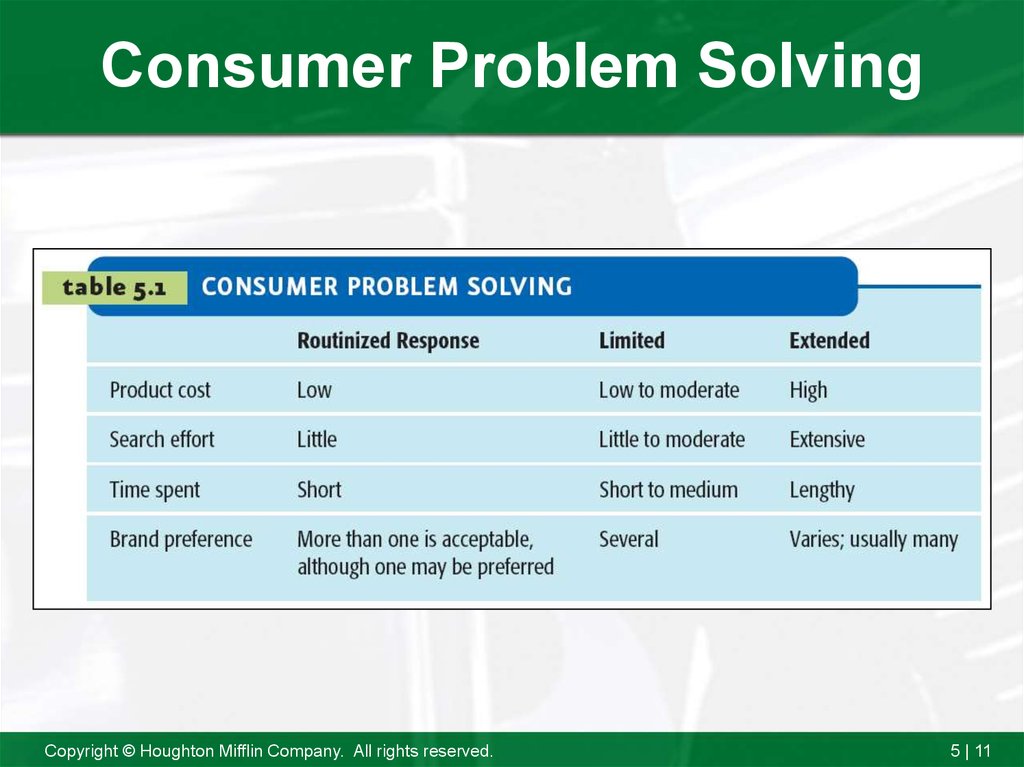
11. Consumer Problem Solving
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.5 | 11
12. Routinized Response Behavior
The consumer problem-solving processused when purchasing frequently
purchased, low-cost items needing very
little search-and-decision effort.
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
5 | 12
13. Limited Problem Solving
The consumer problem-solving processemployed when buying occasionally or
when they need to obtain information
about an unfamiliar brand in a familiar
product category.
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
5 | 13
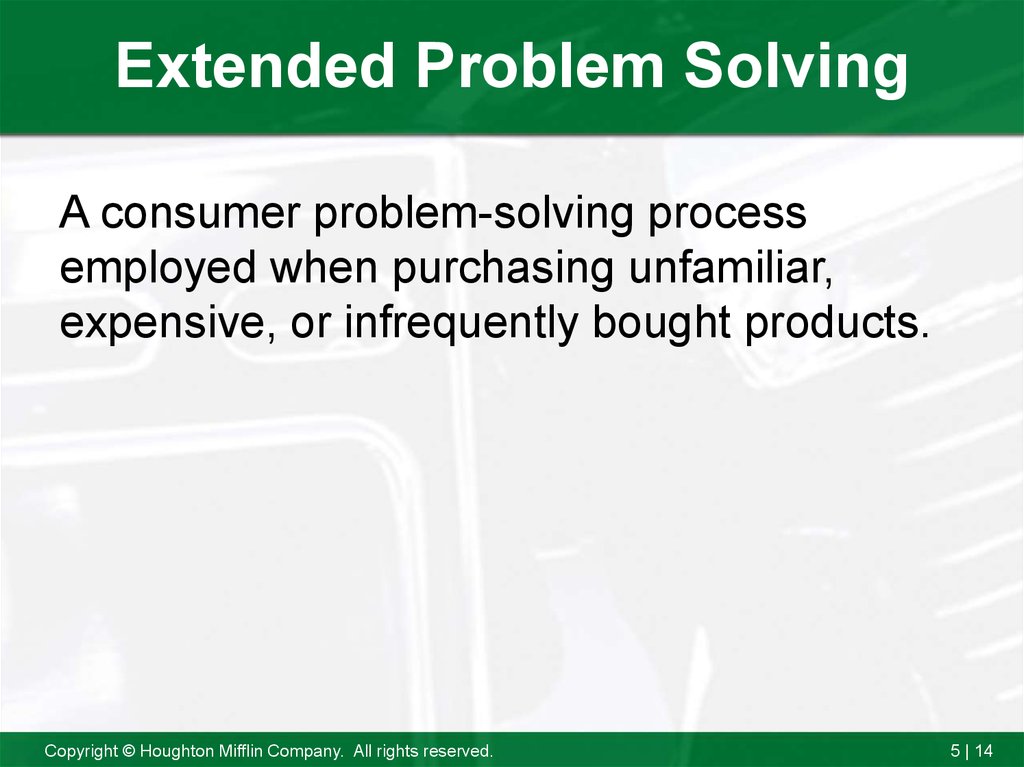
14. Extended Problem Solving
A consumer problem-solving processemployed when purchasing unfamiliar,
expensive, or infrequently bought products.
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
5 | 14
15. Impulse Buying
An unplanned buying behavior resultingfrom a powerful urge to buy something
immediately.
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
5 | 15
16. Consumer Buying Decision Process
A five-stage purchase decision process thatincludes problem recognition, information
search, evaluation of alternatives, purchase,
and postpurchase evaluation.
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
5 | 16
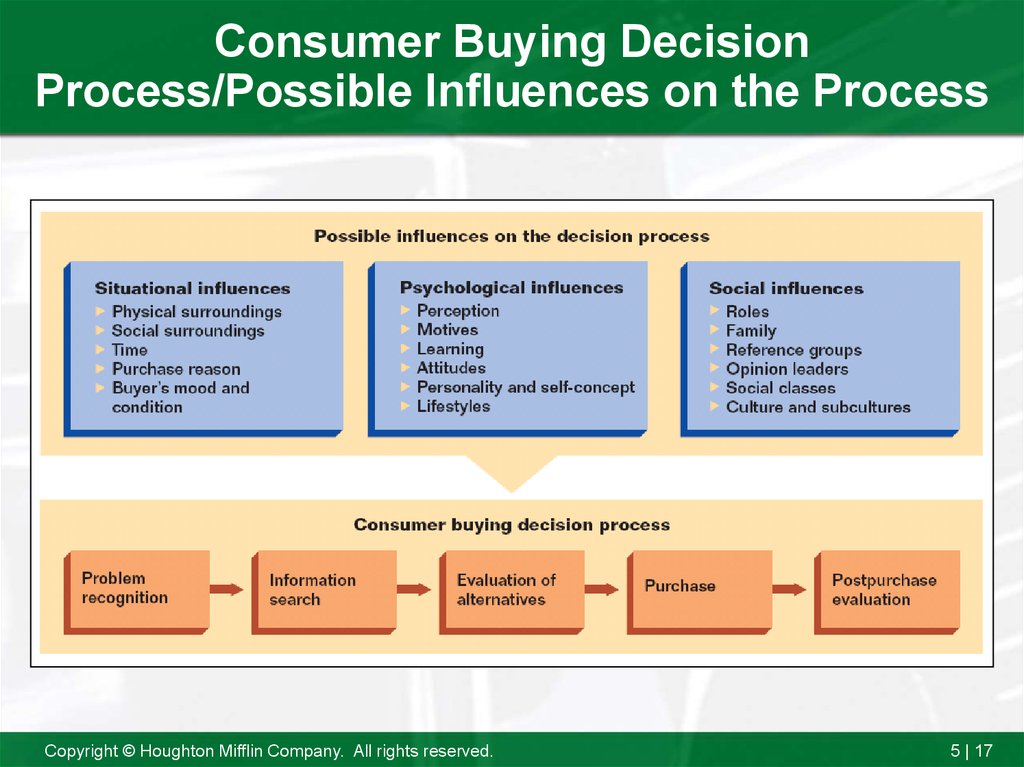
17. Consumer Buying Decision Process/Possible Influences on the Process
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.5 | 17
18. Problem Recognition
Difference between desired state andactual condition.
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
5 | 18
19. Aspects Of Information Search
• Internal Search• External Search
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
5 | 19
20. Internal Search
An information search in which buyerssearch their memories for information about
their products that might solve their problem.
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
5 | 20
21. External Search
An information search in which buyers seekinformation from sources other than memory.
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
5 | 21
22. Evaluation Of Alternatives
Consideration SetEvaluative Criteria
Framing Alternatives
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
5 | 22
23. Cognitive Dissonance
A buyer’s doubts shortly after apurchase about whether the decision
was the right one.
Sample ads of cognitive dissonance
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
5 | 23
24. Situational Influences
Influences resulting from circumstances, time,and location that affect the consumer buying
decision process.
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
5 | 24
25. Categories Of Situational Factors
Physical SurroundingsSocial Surroundings
Time Perspective
Reason For Purchase
Buyer’s Mood/Condition
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
5 | 25
26. Psychological Influences
Factors that in part determine people’sgeneral behavior, thus influencing their
behavior as consumers.
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
5 | 26
27. Types Of Perception
Information InputsSelective Exposure
Selective Distortion
Selective Retention
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
5 | 27
28. Motives
An internal energizing force thatdirects a person’s behavior toward
satisfying needs or achieving goals.
Motive for buying organic foods
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
5 | 28
29. Maslow’s Hierarchy Of Needs
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.5 | 29
30. Sources Of Learning
Behavior ConsequencesInformation Processing
Experience
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
5 | 30
31. Attitude
An individual’s enduring evaluation offeelings about and behavioral tendencies
toward an object or idea.
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
5 | 31
32. Components Of Attitude
Cognitive- knowledge or informationAffective- feelings or emotions
Behavioral- actions regarding object
or idea
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
5 | 32
33. Personality And Self-Concept
• Personality – internal traits andbehavioral tendencies
• Self-Concept – perception or view
of oneself
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
5 | 33
34. Lifestyle
An individual’s pattern of living expressedthrough activities, interests, and opinions.
Consumer lifestyles
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
5 | 34
35. Lifestyle Affected By:
• Age• Education
• Income
• Social Class
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
5 | 35
36. Role
Actions and activities that a person in aparticular position is supposed to perform
based on expectations of the individual
and surrounding persons.
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
5 | 36
37. Consumer Socialization
The process through which a personacquires the knowledge and skills to
function as a consumer.
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
5 | 37
38. Types Of Family Decisionmaking
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.5 | 38
39. Reference Group
A group that a person identifies withso strongly that he or she adopts the
values, attitudes, and behavior of
group members.
Volvo and women’s market
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
5 | 39
40. Types Of Reference Groups
1. Membership2. Aspirational
3. Disassociative
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
5 | 40
41. Opinion Leader
A member of an informal group who providesinformation about a specific topic to other
group members.
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
5 | 41
42. Examples Of Opinion Leaders And Topics
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.5 | 42
43. Social Class
An open group of individuals with similarsocial rank.
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
5 | 43
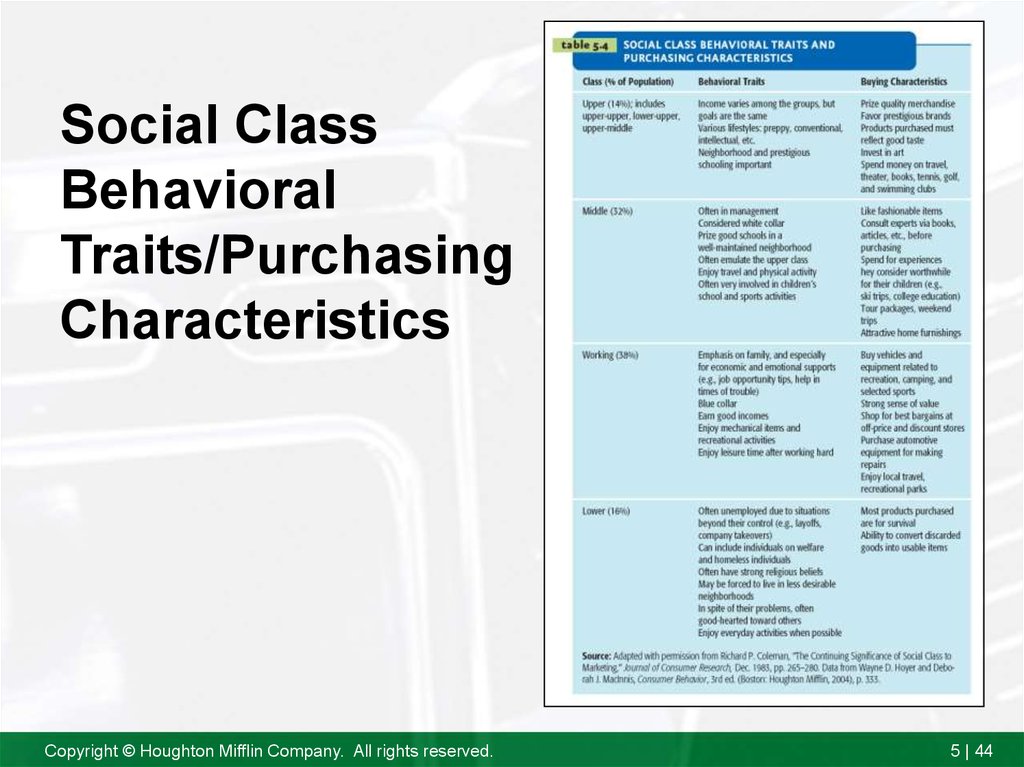
44. Social Class Behavioral Traits/Purchasing Characteristics
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.5 | 44
45. Culture
The accumulation of values, knowledge,beliefs, customs, objects, and concepts
of a society.
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
5 | 45
46. Subcultures
A group of individuals whose characteristicvalues (religion, etc.) and behavior patterns
are similar and different from those of the
surrounding culture.
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
5 | 46
47. U.S. Ethnic Subcultures
African AmericanHispanic
Asian American
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
5 | 47






































 marketing
marketing








