Similar presentations:
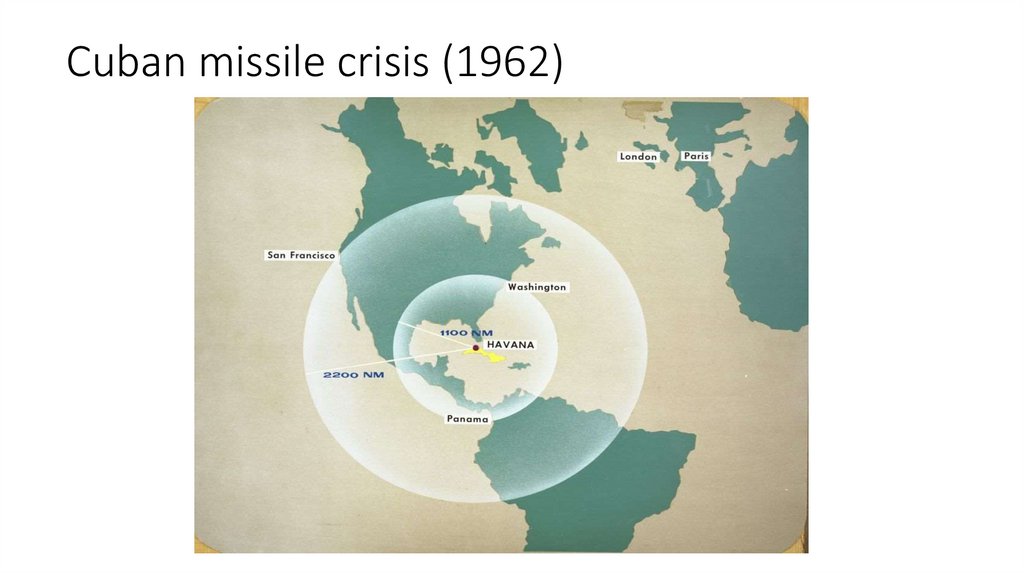
Cuban missile crisis (1962)
1.
Cuban missile crisis (1962)Apotheosis of the Cold War’s arms race
2.
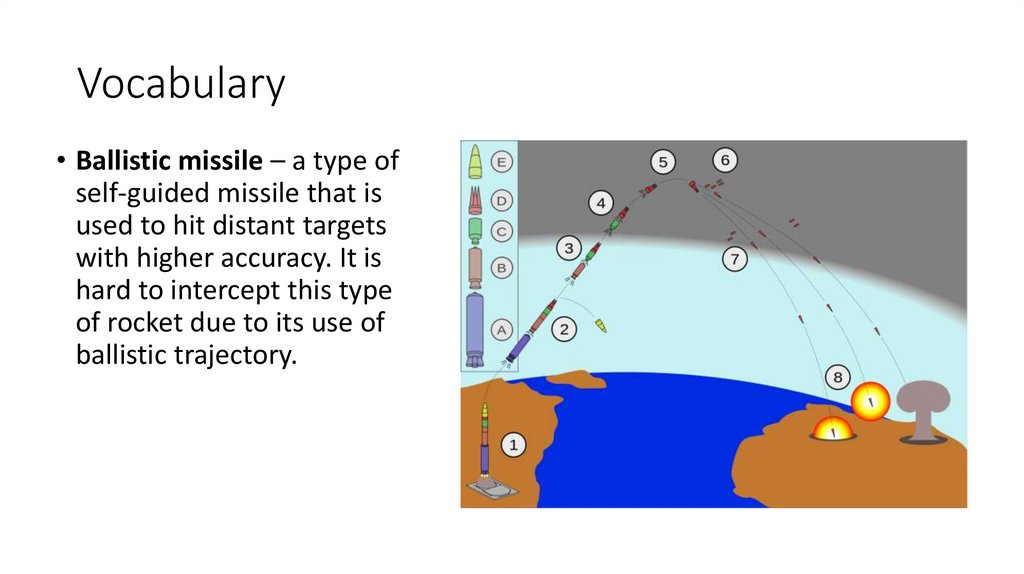
Vocabulary• Ballistic missile – a type of
self-guided missile that is
used to hit distant targets
with higher accuracy. It is
hard to intercept this type
of rocket due to its use of
ballistic trajectory.
3.
Cuban missile crisis (1962)4.
Cuban missile crisis (1962)5.
Cuban missile crisis (1962)John F. Kennedy
US president in 1961-1963
Nikita Sergeyevich Khrushchev
USSR general secretary in 1953-1964
6.
Cuban missile crisis (1962)Ernesto Che Guevara
Cuban communism ideologist
Fidel Castro
Leader of Cuba in 1959-2011
7.
Build-up to the crisis• In 1954-1956
USA and USSR
alternately
invent and test
ballistic missiles
8.
Build-up to the crisis• In 1959 a communist revolution
started in Cuba. It was led by
‘comandante’ Fidel Castro, who
was heavily relying on Soviet
assistance. A brief conflict was
won by the communists. Right
after that Castro met Khrushchev.
Both agreed to enlarge their
cooperation and to take joint
action against the USA.
9.
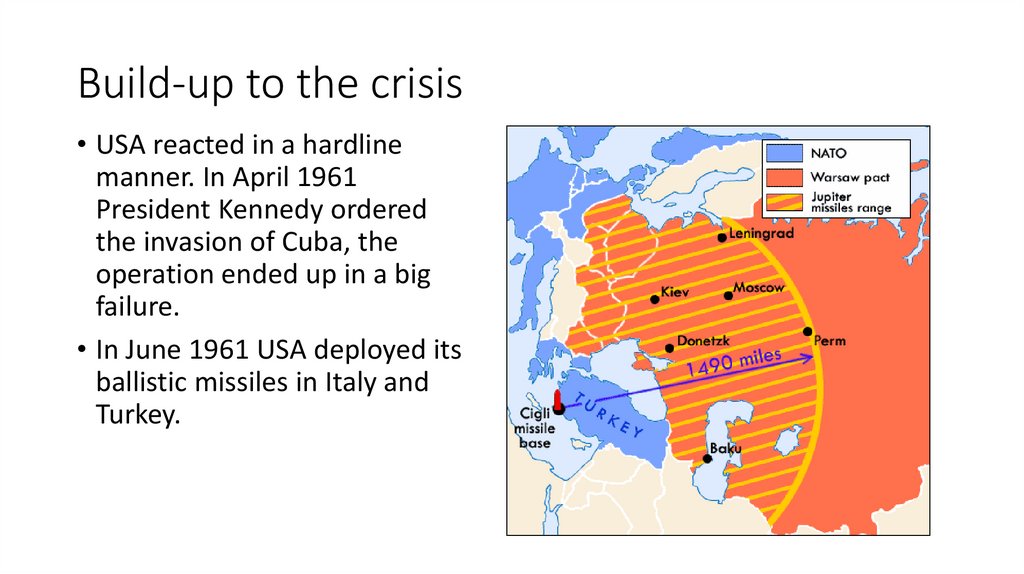
Build-up to the crisis• USA reacted in a hardline
manner. In April 1961
President Kennedy ordered
the invasion of Cuba, the
operation ended up in a big
failure.
• In June 1961 USA deployed its
ballistic missiles in Italy and
Turkey.
10.
Cuban missile crisis (1962)The timeline of events
1962, JulySeptember
USA reconnaissance finds out about Soviet shipments heading to Cuba
1962,
October 22
USA becomes aware of Soviet ballistic missile launchers, stationed in Cuba and targeted
on key American cities. President Kennedy orders naval blockade of Cuba
1962,
October 24
Soviet ships try to break the blockade but pull back at the last moment
1962,
October 28
Khrushchev contacts Kennedy and requests negotiations. Kennedy agrees
1962,
November
Khrushchev guarantees withdrawal of Soviet missiles from Cuba. In exchange, Kennedy
withdrew US missiles from Turkey and committed the US never invading Cuba
11.
Cuban missile crisis results• Both parties complied with the final agreement, showing a good
example of diplomatic work
• Moscow-Washington Hotline established (to let the leaders of US
and USSR have a turf for urgent talks, if needed)
• Negotiations to limit nuclear tests started
• Negotiations to stop nuclear extension program in space started
• More countries became part of Non-Aligned movement (because
they didn’t want to associate themselves neither with USA, nor
with USSR)
12.
Cuban missile crisis results• Mass panic in the USA, food crisis
in some states (Oregon, Ohio,
Florida)
• USSR started improving its civilian
defense infrastructure – air raid
shelters built across the country








 history
history geography
geography








