Similar presentations:
Designing Business Model
1.
DesigningBusiness
Model
NVC-Session 6
By Alisher Ismailov
2.
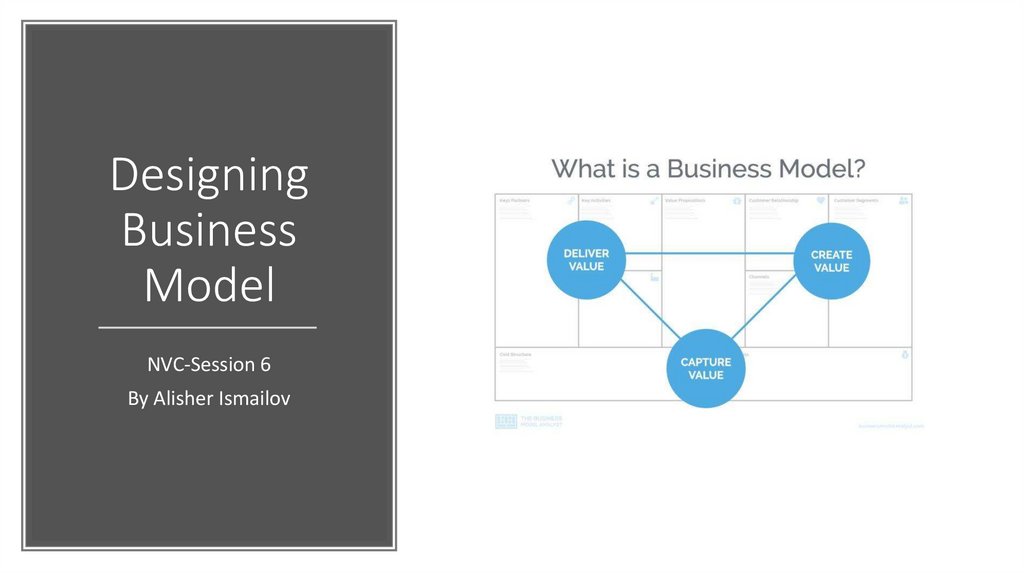
Agenda• What is business model?
• Types of Business Models
• Business Modeling Process
• Business Model Canvas
• Pivots
• Exercise
3.
What is a business Model• The term business model refers
to a company's plan for making
a profit. It identifies the
products or services the
business plans to sell, its
identified target market, and
any anticipated expenses.
4.
Types of Business Models• One-time charge plus (potentially)
ongoing maintenance agreement.
5.
Types of Business Models• Subscription or leasing model:
Now very popular, especially in
the software area with
software as a service (SaaS).
6.
Types of Business Models• Consumables: The classic
razor/razor blade model, where
the initial product purchase is
inexpensive (the razor), but the
consumables needed to
continue using the initial
product (disposable razor
blades) have a high profit
margin.
7.
Types of Business ModelsAdvertising: Selling access to your
user.
8.
Types of Business ModelsTransaction fee: Earning a
commission from a party for a
purchase or action the user
makes concerning that party.
9.
Types of Business ModelsReselling data: Others will pay for
access to information about your
customers, either as a one-time
download or being able to access
a database on a recurring basis.
10.
Types of Business ModelsUsage-based: Customer only pays
when they use the product/
service, but the more they use,
the more they pay.
11.
Types of Business ModelsCell-phone plan: A base plan
allows for a predictable monthly
(or another period) cost, and the
additional ability to use the
product is available at higher
marginal rates.
12.
Types of Business ModelsUpsell high-margin products: A
hybrid variant of consumables
and one-time charge where the
initial sale is for low profit or even
a loss, but money is made when
the customer buys optional highmargin add-on products.
13.
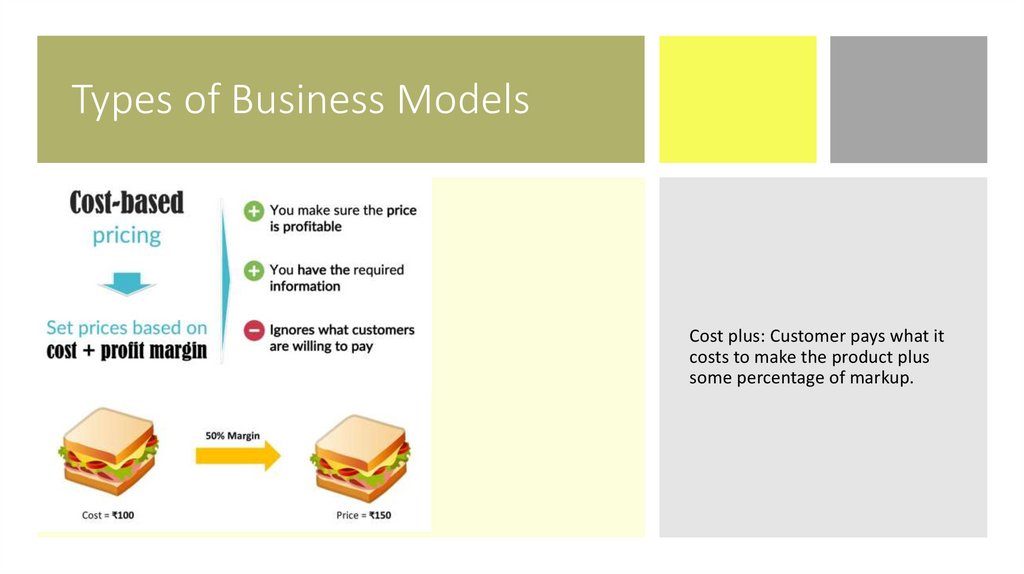
Types of Business ModelsCost plus: Customer pays what it
costs to make the product plus
some percentage of markup.
14.
Types of Business ModelsHourly rates: A consultant or
service provider model not based
on costs but based on human
utilization (variant of usage
model).
15.
Types of Business ModelsPenalty fees: An extreme variant
of the cell phone plan where
there is a small fee for the base
service but there are substantial
charges if you go over a set
condition
16.
Types of Business ModelsFranchise: You create a template
for a business that others pay you
for the right to implement and
use your brand; you also make
money by selling certified
supplies and other
products/services to the
franchisees.
17.
Types of Business Modelshttps://www.youtube.com/watch?v=W4W-Xgbx_mc&ab_channel=KrASIA
Shared savings: Customer pays
only after getting benefit from
the product and pays some
fraction of the benefit they
receive. Conceptually an excellent
model to align customer and
vendor interests, but challenging
to implement
18.
19.
Types of Business ModelsOperating and maintenance: You
are paid to run an operation (e.g.,
plant, IT services) at a fixed price,
with incentives for you to make
more money if you can reduce
costs while maintaining service
levels.
20.
Types of Business ModelsLicensing: Getting paid for your
intellectual property, which
results in high margins
21.
Effect assets have onbusiness model
• A startup does not have much money, nor does it have access to money
through banks, investments, or other means. What models does this
general favor and disfavor for the startup? Can you think of something
creative you can do with a disfavored model to make it more attractive in
this case?
22.
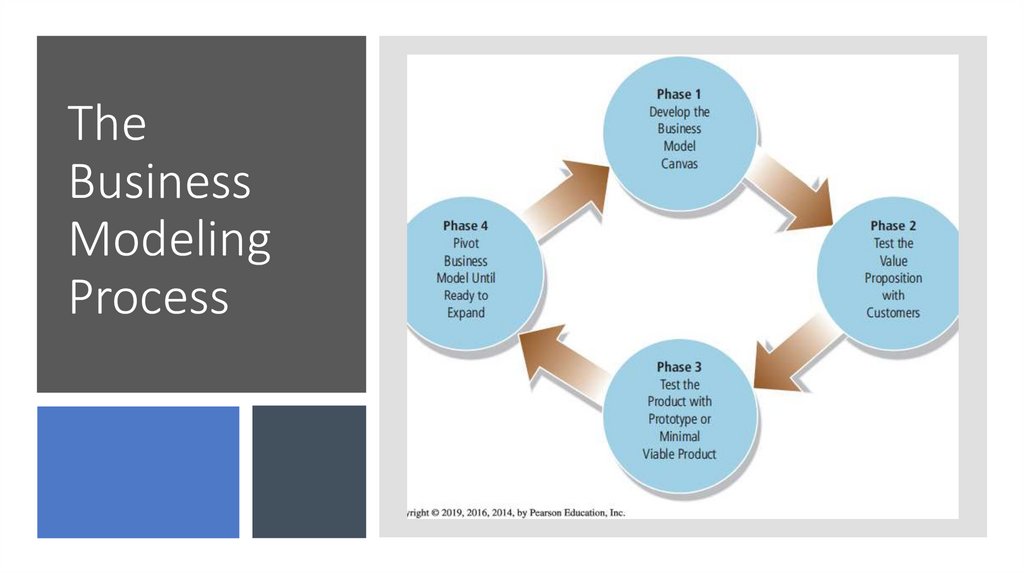
TheBusiness
Modeling
Process
23.
Developingand Testing a
Business
Model
• Key questions to address:
• What value does the business offer
customers?
• Who is my target market?
• What do they expect of me as my customers?
• How do I get information to them, and how
do they want to get the product?
• What are the key activities to make all this
come together, and what will they cost?
• What resources do I need to make this
happen, including money?
• Who are the key partners I will need to
attract to be successful?
24.
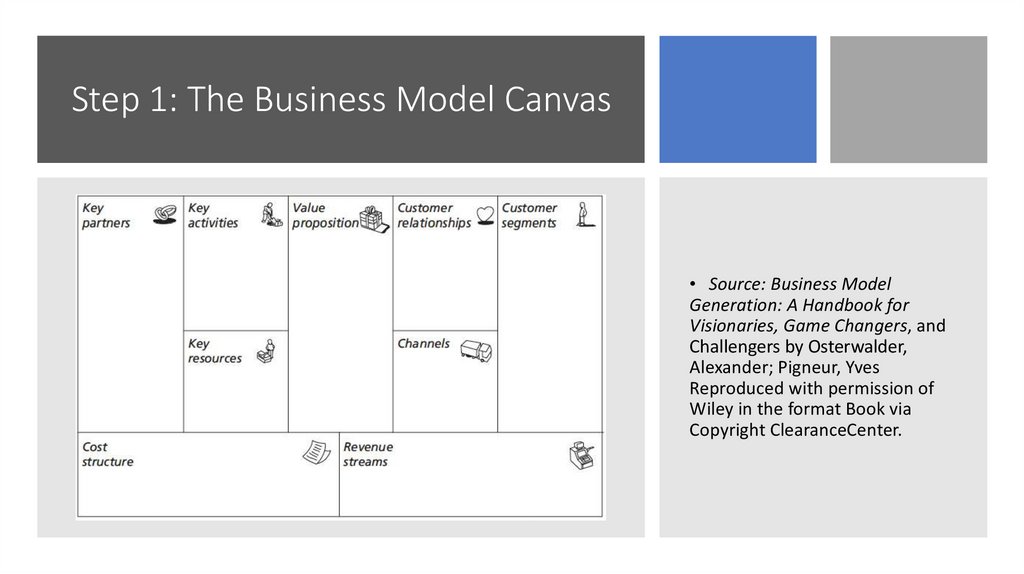
Step 1: The Business Model Canvas• Source: Business Model
Generation: A Handbook for
Visionaries, Game Changers, and
Challengers by Osterwalder,
Alexander; Pigneur, Yves
Reproduced with permission of
Wiley in the format Book via
Copyright ClearanceCenter.
25.
26.
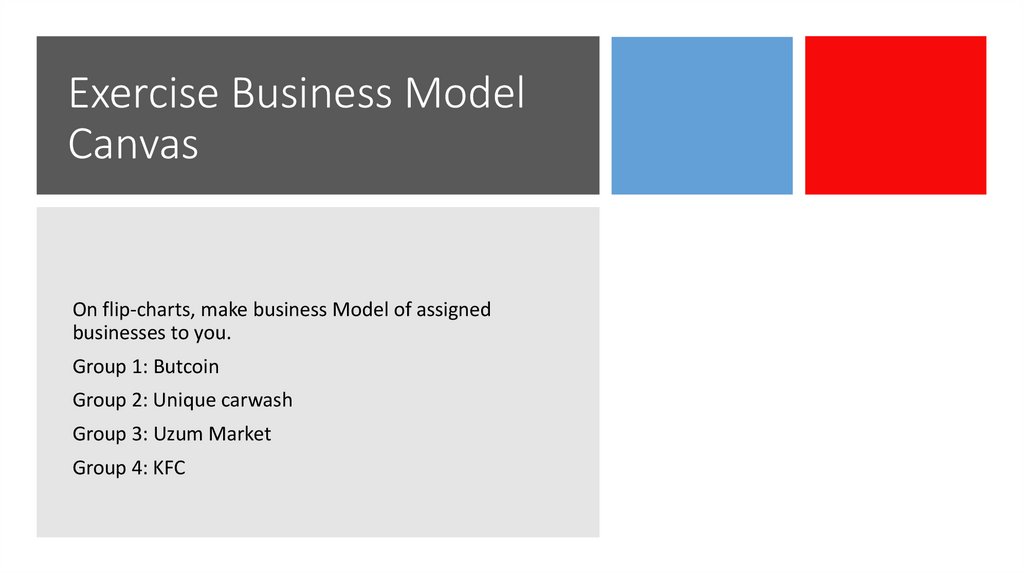
Exercise Business ModelCanvas
On flip-charts, make business Model of assigned
businesses to you.
Group 1: Butcoin
Group 2: Unique carwash
Group 3: Uzum Market
Group 4: KFC
27.
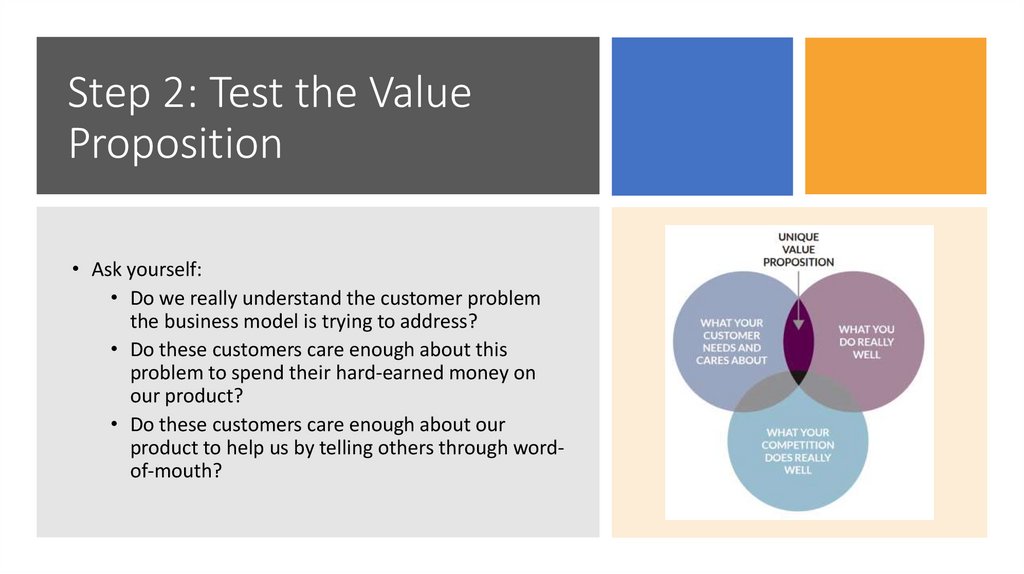
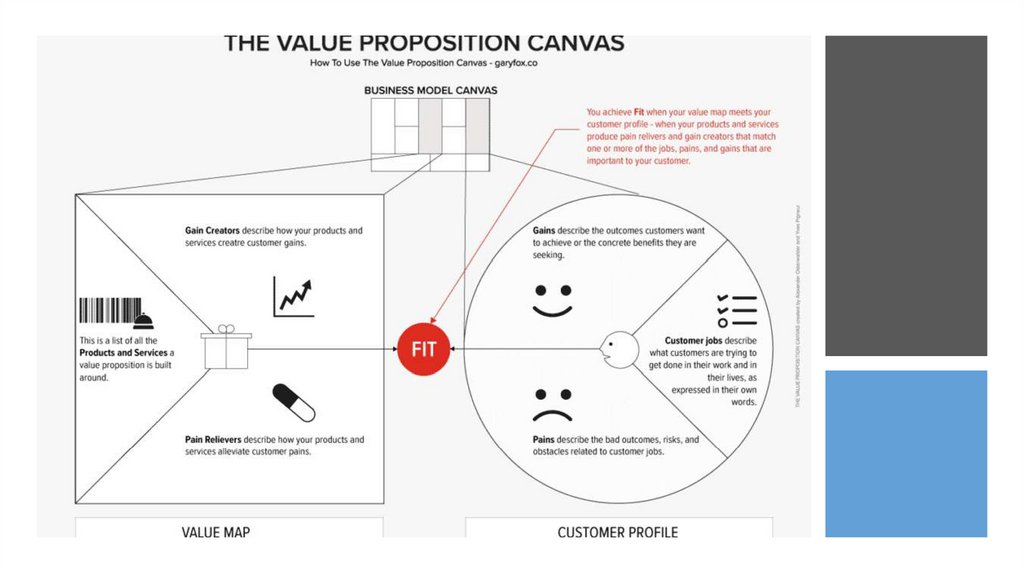
Step 2: Test the ValueProposition
• Ask yourself:
• Do we really understand the customer problem
the business model is trying to address?
• Do these customers care enough about this
problem to spend their hard-earned money on
our product?
• Do these customers care enough about our
product to help us by telling others through wordof-mouth?
28.
29.
Step 3: BusinessPrototyping
• Entrepreneurs test their business models on a small scale
before committing serious resources to launch a business that
might not work.
• Recognizes that a business idea is a hypothesis that needs to be
tested before taking it full scale.
• Test early versions of a product or service using a lean start-up:
a process of rapidly developing simple prototypes to test key
assumptions by engaging real customers
• Begin the lean start-up process using a minimal viable product:
the simplest version of a product or service with which an
entrepreneur can create a sustainable business
30.
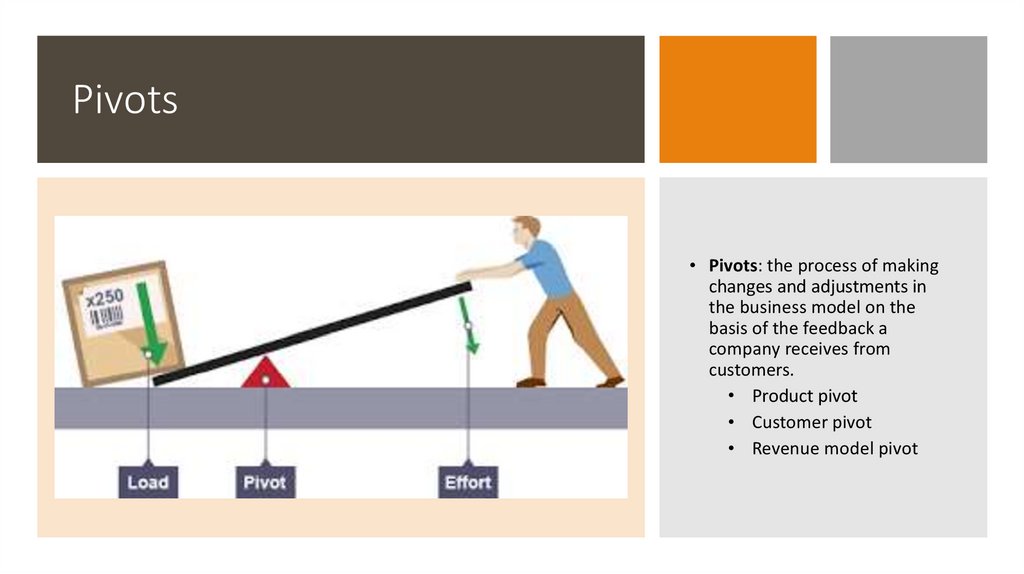
Pivots• Pivots: the process of making
changes and adjustments in
the business model on the
basis of the feedback a
company receives from
customers.
• Product pivot
• Customer pivot
• Revenue model pivot
31.
ConclusionDeveloping a business model helps the entrepreneur
better understand all that will be required to launch
and build a business.
Once the entrepreneur completes the idea assessment,
feasibility study, and business model, he or she is ready
to develop the business plan.




















 business
business








