Similar presentations:
Liquidity of the enterprise
1.
LiquidityCompleted student 4th year
Philippov Kirill
2.
Liquidity is the ability to turn all existing assets into money. The faster youcan sell property with the least loss in market price, the greater the liquidity.
If problems arise, a liquid company can pay off its debts faster by selling
some property and stay afloat. A company is considered liquid if it has more
assets (money, property) than liabilities (debts).
3.
A liquidity assessment is needed if you haveintentions to cooperate with a specific enterprise.
Thanks to calculations, you can understand how many
assets a company has, how solvent it is and whether it
can pay off its creditors.
A company that has money in its account and a stock
of products in its warehouse is considered liquid. If
necessary, it quickly sells products and pays off debts.
Such a company will arrange delivery of goods without
prepayment or quickly issue a loan.
4.
Liquidity of the enterpriseThe liquidity of an enterprise is calculated from the ratio of debt obligations to liquid
assets. This information is publicly available; all company assets can be seen on the
balance sheet.
The assets of an enterprise can be current or non-current:
Current assets are property that brings dividends to the company for no more than
one year. These include: deposits for up to 1 year, raw materials, money for
settlements with partners, short-term receivables.
Non-current assets are property and money that generate profit for more than 1
year: long-term deposits, equipment, buildings, patents and projects.
Current assets are considered more liquid.
5.
Bank liquidityThe term “bank liquidity” refers to the ability of a bank to pay money to all customers
who have invested in that bank. The bank has current and non-current assets.
The more current assets (cash, shares, bonds) that can be quickly converted into money,
the greater the bank's liquidity. A large number of issued loans reduces the bank's
liquidity. The level of solvency of banks in the Russian Federation is under the control of
the Central Bank of Russia.
Liquidity of securities
This means the ability to be quickly sold at a price close to the market price. Liquidity
also characterizes high supply and demand for a security.
There are two indicators that affect the liquidity of a security. This is the difference
between the highest buy order price and the smallest sell order price (spread) and
trading volume (number of completed trades).
6.
Liquidity of moneyMoney must be equal to its face value. If you can easily pay with them, then they are
liquid. Money in countries with good economies has high liquidity. If the purchasing
power of money falls and its liquidity decreases, this means that prices for services and
goods rise.
Real estate liquidity
If a property can be easily sold, then it is liquid. A transaction can take a long time to
complete, so real estate is less liquid compared to other assets, for example, securities.
7.
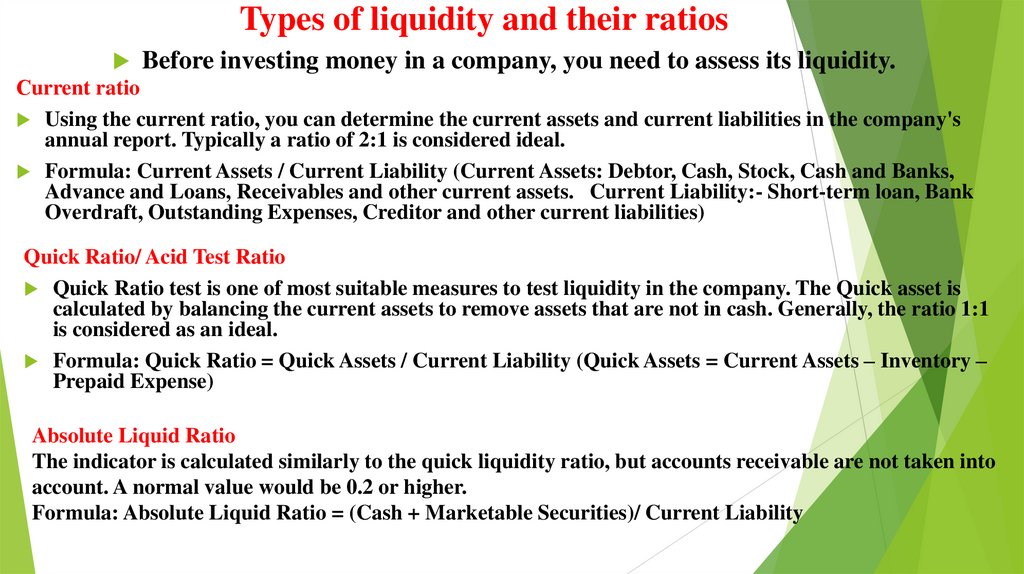
Types of liquidity and their ratiosBefore investing money in a company, you need to assess its liquidity.
Сurrent ratio
Using the current ratio, you can determine the current assets and current liabilities in the company's
annual report. Typically a ratio of 2:1 is considered ideal.
Formula: Current Assets / Current Liability (Current Assets: Debtor, Cash, Stock, Cash and Banks,
Advance and Loans, Receivables and other current assets. Current Liability:- Short-term loan, Bank
Overdraft, Outstanding Expenses, Creditor and other current liabilities)
Quick Ratio/ Acid Test Ratio
Quick Ratio test is one of most suitable measures to test liquidity in the company. The Quick asset is
calculated by balancing the current assets to remove assets that are not in cash. Generally, the ratio 1:1
is considered as an ideal.
Formula: Quick Ratio = Quick Assets / Current Liability (Quick Assets = Current Assets – Inventory –
Prepaid Expense)
Absolute Liquid Ratio
The indicator is calculated similarly to the quick liquidity ratio, but accounts receivable are not taken into
account. A normal value would be 0.2 or higher.
Formula: Absolute Liquid Ratio = (Cash + Marketable Securities)/ Current Liability
8.
Liquidity analysisYou can find out the solvency of a company by looking at its balance sheet. Balance sheet
liquidity is an indicator of the liquidity of the enterprise
The main sign of liquidity is the excess of the value of current assets in relation to short-
term liabilities. The higher this indicator, the better the company's financial condition
and the higher its liquidity.
9.
The company's assets are:The most liquid assets (A1) are funds that can quickly cover debts.
Quickly realizable assets (A2) – this includes current assets that can be converted into money
after a certain time.
Slowly selling assets (A3) are accounts receivable and other inventories, finances for which are
expected in a year or later.
Hard-to-sell assets (A4) are machines and production facilities that cannot be sold quickly.
Current assets are characterized by higher liquidity than company property.
10.
The company's liabilities can also be divided into groups:Current liabilities (P1) are payments for loans and credit, payment of dividends, etc.
Short-term liabilities (P2) are accounts payable that must be repaid within a year.
Long-term liabilities (P3) – long-term accounts payable.
Fixed liabilities (P4) – other liabilities.
A comparison of a company's liabilities and assets is used to determine the liquidity of
the balance sheet.
11.
Conclusion:Liquidity is the ability of an enterprise to pay off its debt obligations at any time.
The more assets a company has (money, equipment, buildings, structures), the greater its
liquidity.
To calculate the liquidity of an enterprise, you can use accounting reports that are
publicly available.
You can increase the company's liquidity by increasing assets and decreasing liabilities,
for example, by eliminating borrowed funds.











 finance
finance








